Spring笔记(8) - @EventListener注解探究
在上文中讲了Spring的事件监听机制,流程是:定义事件、监听器,发布事件,控制台输出监听到的事件内容。
在上文的扩展中 使用 @EventListener 注解来自定义监听器,监听指定的事件,比如下面的案例:
@Component
public class UserManagerListener {
//ApplicationEvent能监听到所有的事件,如果为EmailEvent.class则只能监听到关于邮件的事件
//EventListener有两个参数(可以不写,直接在方法参数里面写上要监听的事件即可):
// classes:表示哪一个事件类
// condition:当满足什么条件是会调用该方法
@EventListener(classes = ApplicationEvent.class)
public void listen(ApplicationEvent event){
System.out.println("用户管理功能监听到的事件。。。。"+event);
}
}
通过上面的案例发现代码比实现 ApplicationListener 接口更简洁,那这个注解为什么功能这么强大呢,接下来我们来分析它的源码:
/**
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 4.2
* @see EventListenerMethodProcessor
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface EventListener {
.......
}
通过源码发现是通过使用 EventListenerMethodProcessor 处理器来解析该注解,将标注了 @EventListener 的方法进行解析, 获取拦截方法,对拦截方法进行转换,变成 ApplicationListener 然
后放入到 IOC 容器中,在publishEvent 时,通过 getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(a
pplicationEvent, eventType)方法,获取到 ApplicationListener 对象,通过反射调用方法。下面是 EventListenerMethodProcessor 处理器的类图关系:
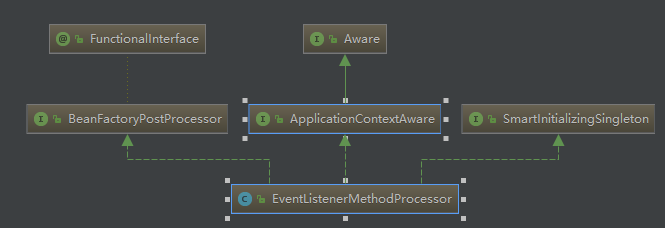
可以看到 EventListenerMethodProcessor 是实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 和 SmartInitializingSingleton 这两个接口。在前文 Spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor探究 中讲述了
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的执行时机,在 refresh 容器的时候, 调用 invokeBeanFactoryPostProce
ssors() 方法时, 会执行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory() 方法设置一个默认的监听器工厂 :DefaultEventListenerFactory。
/**
* Registers {@link EventListener} methods as individual {@link ApplicationListener} instances.
* Implements {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} (as of 5.1) primarily for early retrieval,
* avoiding AOP checks for this processor bean and its {@link EventListenerFactory} delegates.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 4.2
* @see EventListenerFactory
* @see DefaultEventListenerFactory
*/
public class EventListenerMethodProcessor
implements SmartInitializingSingleton, ApplicationContextAware, BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
......
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory; Map<String, EventListenerFactory> beans = beanFactory.getBeansOfType(EventListenerFactory.class, false, false);
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = new ArrayList<>(beans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(factories);
//DefaultEventListenerFactory
this.eventListenerFactories = factories;
}
.......
}
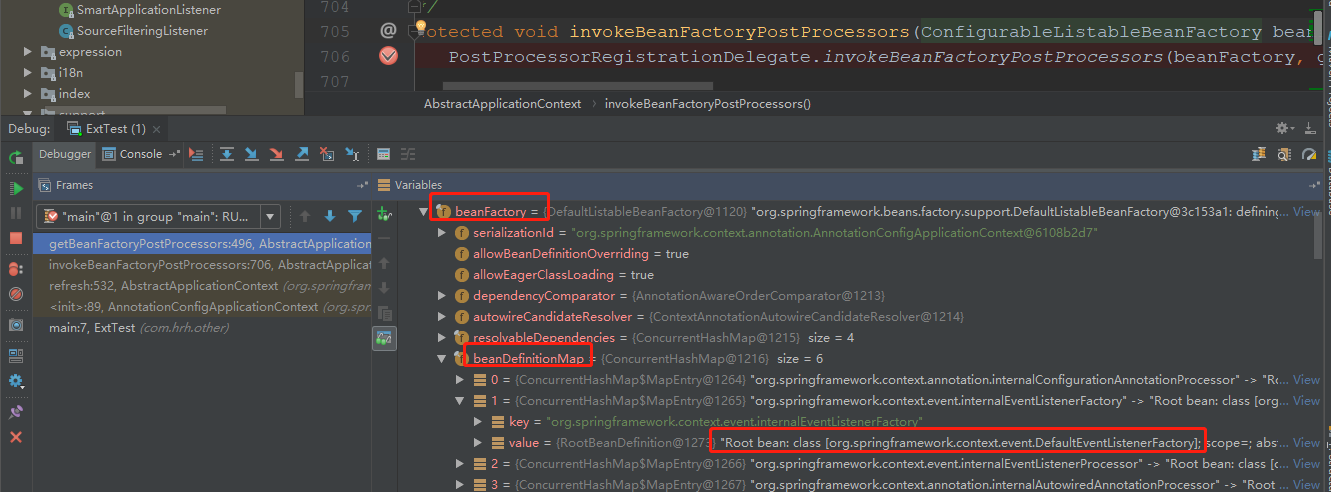
而SmartInitializingSingleton 这个接口只有一个方法 afterSingletonsInstantiated(),这个方法在全部单实例创建完成之后执行,接下来对这个方法进行深入探讨,我们对 EventListenerMethodProcessor里面的实现方法 afterSingletonsInstantiated 打一个断点 debug 运行下:
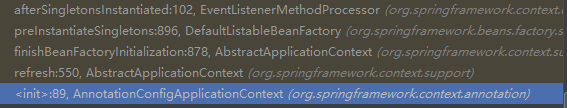
从中我们可以看到,流程是: IOC容器创建对象 --> refresh() --> finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)(初始化剩下的所有单实例bean) --> beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons()(初始化剩下的所有单实例bean)--> smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated()
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
} // Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
//获取所有的注册bean名称
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames); // Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
//先创建所有的单实例bean
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);//创建bean实例
}
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);//创建bean实例
}
}
} // Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
//创建完成后进行遍历,如果bean是SmartInitializingSingleton类型,执行afterSingletonsInstantiated方法
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
从上面可以看出其调用时机是,遍历容器中注册的 BeanDefinition, 调用所有 getBean() 方法创建实例之后, 才会开始遍历执行 afterSingletonsInstantiated() 方法。
接下来详细解析下 EventListenerMethodProcessor 的 afterSingletonsInstantiated 方法,重点看 processBean 方法:
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.beanFactory;
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "No ConfigurableListableBeanFactory set");
String[] beanNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!ScopedProxyUtils.isScopedTarget(beanName)) {
Class<?> type = null;
try {
type = AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass(beanFactory, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (type != null) {
if (ScopedObject.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) {
try {
Class<?> targetClass = AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass(
beanFactory, ScopedProxyUtils.getTargetBeanName(beanName));
if (targetClass != null) {
type = targetClass;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An invalid scoped proxy arrangement - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target bean for scoped proxy '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
try {
processBean(beanName, type);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Failed to process @EventListener " +
"annotation on bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
}
}
private void processBean(final String beanName, final Class<?> targetType) {
//不包含没有注解的class,注解是EventListener的类型,是Spring容器的类型
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetType) &&
AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetType, EventListener.class) &&
!isSpringContainerClass(targetType)) { Map<Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null;
try {
//获取标注了 @EventListener 注解的监听方法
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>) method ->
AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable type in a method signature, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve methods for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
//监听方法添加到没有注解的集合
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(annotatedMethods)) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetType);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @EventListener annotations found on bean class: " + targetType.getName());
}
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = this.applicationContext;
Assert.state(context != null, "No ApplicationContext set");
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = this.eventListenerFactories;
Assert.state(factories != null, "EventListenerFactory List not initialized");
for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) {
for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {
// 判断是否支持该方法 在DefaultEventListenerFactory中写死的返回true
if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) {
//选择方法 beanName 这里是AddDataEventListener的beanName 默认是addDataEventListener
Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, context.getType(beanName));
//将监听方法转换为ApplicationListener(ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter)对象
ApplicationListener<?> applicationListener =
factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);
// 如果是ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter对象 就把context和evaluator传进去
if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) {
((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener).init(context, this.evaluator);
}
//将创建的 ApplicationListener 加入到容器中
context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
break;
}
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(annotatedMethods.size() + " @EventListener methods processed on bean '" +
beanName + "': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
}
//class是在org.springframework包下,注解类型不是组件
private static boolean isSpringContainerClass(Class<?> clazz) {
return (clazz.getName().startsWith("org.springframework.") &&
!AnnotatedElementUtils.isAnnotated(ClassUtils.getUserClass(clazz), Component.class));
}
后面就是添加listener到Context中:
1)如果有applicationEventMulticaster,添加到ApplicationContext.applicationEventMulticas
ter中;
2)如果没有applicationEventMulticaster,添加到ApplicationContext.applicationListeners中;
最后是触发事件监听了 AbstractApplicationContext.publishEvent --> SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent --> invokeListener --> doInvokeListener --> ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter.onApplicationEvent
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
processEvent(event);
}
ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter#processEvent
public void processEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
Object[] args = resolveArguments(event);
if (shouldHandle(event, args)) {
// 反射执行真正的方法
Object result = doInvoke(args);
if (result != null) {
handleResult(result);
}
else {
logger.trace("No result object given - no result to handle");
}
}
}
在ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter.doInvoke中会反射执行真正的方法:
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) {
//获取目标对象
Object bean = getTargetBean();
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.method);
try {
//反射执行监听方法
return this.method.invoke(bean, args);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
assertTargetBean(this.method, bean, args);
throw new IllegalStateException(getInvocationErrorMessage(bean, ex.getMessage(), args), ex);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getInvocationErrorMessage(bean, ex.getMessage(), args), ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
// Throw underlying exception
Throwable targetException = ex.getTargetException();
if (targetException instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) targetException;
}
else {
String msg = getInvocationErrorMessage(bean, "Failed to invoke event listener method", args);
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(targetException, msg);
}
}
}
Spring笔记(8) - @EventListener注解探究的更多相关文章
- Spring笔记02_注解_IOC
目录 Spring笔记02 1. Spring整合连接池 1.1 Spring整合C3P0 1.2 Spring整合DBCP 1.3 最终版 2. 基于注解的IOC配置 2.1 导包 2.2 配置文件 ...
- Spring笔记(6) - Spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor探究
一.背景 在说BeanFactoryPostProcessor之前,先来说下BeanPostProcessor,在前文Spring笔记(2) - 生命周期/属性赋值/自动装配及部分源码解析中讲解了Be ...
- Spring笔记04_AOP注解开发_模板_事务
目录 1. Spring基于AspectJ的注解的AOP开发 1. 1 SpringAOP的注解入门 1.2 Spring的AOP的注解通知类型 1.2.1 @Before:前置通知 1.2.2 @A ...
- Spring笔记(7) - Spring的事件和监听机制
一.背景 事件机制作为一种编程机制,在很多开发语言中都提供了支持,同时许多开源框架的设计中都使用了事件机制,比如SpringFramework. 在 Java 语言中,Java 的事件机制参与者有3种 ...
- Spring笔记01_下载_概述_监听器
目录 Spring笔记01 1.Spring介绍 1.1 Spring概述 1.2 Spring好处 1.3 Spring结构体系 1.4 在项目中的架构 1.5 程序的耦合和解耦 2. Spring ...
- Spring笔记:IOC基础
Spring笔记:IOC基础 引入IOC 在Java基础中,我们往往使用常见关键字来完成服务对象的创建.举个例子我们有很多U盘,有金士顿的(KingstonUSBDisk)的.闪迪的(SanUSBDi ...
- Spring笔记(3) - debug源码AOP原理解析
案例 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy//开启基于注解的aop模式 @Configuration public class AOPConfig { //业务逻辑类加入容器中 @Bean ...
- Spring系列20:注解详解和Spring注解增强(基础内功)
有部分小伙伴反馈说前面基于注解的Spring中大量使用注解,由于对Java的注解不熟悉,有点难受.建议总结一篇的Java注解的基础知识,那么,它来了! 本文内容 什么是注解? 如何定义注解 如何使用注 ...
- [Spring框架]Spring开发实例: XML+注解.
前言: 本文为自己学习Spring记录所用, 文章内容包括Spring的概述已经简单开发, 主要涉及IOC相关知识, 希望能够对新入门Spring的同学有帮助, 也希望大家一起讨论相关的知识. 一. ...
随机推荐
- vue项目打包-2-九五小庞
vue项目打包 一.终端运行命令 npm run build 二.打包成功的标志与项目的改变,如下图: 3.点击index.html,通过浏览器运行,出现以下报错,如图: 四.那么应该如何修改呢?具体 ...
- Request对象基础应用实例代码一
输入用户名:<br><input type="text" name="yhm"><br><br>输入密码:< ...
- 用Docker容器安装Jenkins
先安装Docker 可以参考我的上一篇文章 链接 拉取Jenkins最新镜像,可跟版本号 不跟默认拉取最新镜像 docker pull jenkins/jenkins 创建JenKins的工作目录 m ...
- pytest文档57-计算单元测试代码覆盖率(pytest-cov)
前言 我们在做测试的时候,经常遇到领导的灵魂拷问:你的测试用例覆盖率是多少,达到100%了么?你如何保证你的测试质量? 测试用例的覆盖率如何统计呢,如何知道开发的代码,我们都测到了,不会存在漏测的情况 ...
- linux安装jdk-centos7系统:
1 官网下载 http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151.html
- laravel重写
laravel location / { try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string; } ci location / { try_files $uri ...
- thinkpad怎么设置u盘启动
1.按下笔记本的开机键,当屏幕出现"Press F1 for ThinkPad BIOS Setup Utility"提示时,迅速按下f1键,此时系统就自动进入到ThinkPad的 ...
- 第七章 TCP和UDP原理
一.引入 1.TCP/IP协议族的传输层协议主要包括TCP和UDP 2.TCP是面向连接的可靠的传输层协议.它支持在并不可靠的网络上实现面向连接的可靠的数据传输 3.UDP是无连接的传输协议,主要用于 ...
- poj1654 -- Area (任意多边形面积)
Area Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 20444 Accepted: 5567 Description ...
- 解析SparkStreaming和Kafka集成的两种方式
spark streaming是基于微批处理的流式计算引擎,通常是利用spark core或者spark core与spark sql一起来处理数据.在企业实时处理架构中,通常将spark strea ...
