http代理阅读4 响应缓存处理
if (c->read->ready) {
ngx_http_upstream_process_header(r, u); //读事件触发 准备处理http头部信息
return;
}
向上游服务器发送数据完毕后就会检测是否收到上游服务器的响应:
static void
ngx_http_upstream_process_header(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_upstream_t *u)
{//读取FCGI头部数据,或者proxy头部数据。ngx_http_upstream_send_request发送完数据后,
//会调用这里,或者有可写事件的时候会调用这里。
//ngx_http_upstream_connect函数连接fastcgi后,会设置这个回调函数为fcgi连接的可读事件回调。
ssize_t n;
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_connection_t *c; c = u->peer.connection; ngx_log_debug2(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_HTTP, c->log, 0,
"http upstream process header, fd:%d, buffer_size:%uz", c->fd, u->conf->buffer_size); c->log->action = "reading response header from upstream"; if (c->read->timedout) {//读超时了,轮询下一个。 ngx_event_expire_timers超时后走到这里
//该定时器添加地方在ngx_http_upstream_send_request
ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_TIMEOUT);
return;
} if (!u->request_sent && ngx_http_upstream_test_connect(c) != NGX_OK) {
////请求未发送到上游服务器 同时连接测试不通过 转移到下一个server
ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_ERROR);
return;
} if (u->buffer.start == NULL) { //分配一块缓存,用来存放接受回来的数据。
u->buffer.start = ngx_palloc(r->pool, u->conf->buffer_size);
//头部行部分(也就是第一个fastcgi data标识信息,里面也会携带一部分网页数据)的fastcgi标识信息开辟的空间用buffer_size配置指定
if (u->buffer.start == NULL) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u,
NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
return;
} u->buffer.pos = u->buffer.start;
u->buffer.last = u->buffer.start;
u->buffer.end = u->buffer.start + u->conf->buffer_size;
u->buffer.temporary = 1;
u->buffer.tag = u->output.tag; //初始化headers_in存放头部信息,后端FCGI,proxy解析后的HTTP头部将放入这里
if (ngx_list_init(&u->headers_in.headers, r->pool, 8,
sizeof(ngx_table_elt_t))
!= NGX_OK)
{
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u,
NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
return;
} #if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
/*
pVpVZ"
KEY: /test.php //下面是后端实际返回的内容,上面的是预留的头部
IX-Powered-By: PHP/5.2.13
Content-type: text/html <Html>
<Head>
<title>Your page Subject and domain name</title>
*/
if (r->cache) { //注意这里跳过了预留的头部内存,用于存储cache写入文件时候的头部部分,见
u->buffer.pos += r->cache->header_start;
u->buffer.last = u->buffer.pos;
}
#endif
} for ( ;; ) {
//recv 为 ngx_unix_recv,读取数据放在u->buffer.last的位置,返回读到的大小u->peer.connection->read->ready == 1 (size==n) 时;
//也就是 u->buffer.end-u->buffer.last == size == n; 也就是size 大小的缓存去读数据时, 返回的n == szie;也就是内核还有数据没有读出来,
//此时 u->perr.connection->read->ready 不为0 标示还有数据没有读
n = c->recv(c, u->buffer.last, u->buffer.end - u->buffer.last);
if (n == NGX_AGAIN) { //内核缓冲区已经没数据了
#if 0
ngx_add_timer(rev, u->read_timeout);
#endif
if (ngx_handle_read_event(c->read, 0, NGX_FUNC_LINE) != NGX_OK) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u,
NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
return;
}
return;
}
if (n == 0) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ERR, c->log, 0,
"upstream prematurely closed connection");
}
if (n == NGX_ERROR || n == 0) {
ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_ERROR);
return;
}
u->buffer.last += n;
//ngx_http_xxx_process_header ngx_http_proxy_process_header ngx_http_proxy_process_status_line
rc = u->process_header(r);//ngx_http_fastcgi_process_header等,进行数据处理,比如后端返回的数据头部解析,body读取等。
if (rc == NGX_AGAIN) {
ngx_log_debugall(c->log, 0, " ngx_http_upstream_process_header u->process_header() return NGX_AGAIN");
if (u->buffer.last == u->buffer.end) { //分配的用来存储fastcgi STDOUT头部行包体的buf已经用完了头部行都还没有解析完成,
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ERR, c->log, 0,
"upstream sent too big header");
ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u,
NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_INVALID_HEADER);
return;
}
continue;
}
break;
}
if (rc == NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_INVALID_HEADER) {
ngx_http_upstream_next(r, u, NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_FT_INVALID_HEADER);
return;
}
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
return;
}
/* rc == NGX_OK */
u->state->header_time = ngx_current_msec - u->state->response_time;
if (u->headers_in.status_n >= NGX_HTTP_SPECIAL_RESPONSE) {
if (ngx_http_upstream_test_next(r, u) == NGX_OK) {
return;
}
if (ngx_http_upstream_intercept_errors(r, u) == NGX_OK) {
return;
}
}
//到这里,FCGI等格式的数据已经解析为标准HTTP的表示形式了(除了BODY),所以可以进行upstream的process_headers。
//上面的 u->process_header(r)已经进行FCGI等格式的解析了。下面将头部数据拷贝到headers_out.headers数组中。
if (ngx_http_upstream_process_headers(r, u) != NGX_OK) {
return;
}
if (!r->subrequest_in_memory) {//如果没有子请求了,那就直接发送响应给客户端吧。
当请求的ngx_http_request_t结构体中subrequest_in_memory标志位为1时,将采用第1种方式,即upstream不转发响应包体到下游,
由HTTP模块实现的input_filter方法处理包体;当subrequest_in_memory为0时,upstream会转发响应包体。
当ngx_http_upstream_conf_t配置结构体中的buffering标志位为1时,将开启更多的内存和磁盘文件用于缓存上游的响应包体,这意味上游网速更快;
当buffering为0时,将使用固定大小的缓冲区(就是上面介绍的buffer缓冲区)来转发响应包体
//buffering方式和非buffering方式在函数ngx_http_upstream_send_response分惜
ngx_http_upstream_send_response(r, u);//给客户端发送响应,里面会处理header,body分开发送的情况
return;
}
/* subrequest content in memory */
//子请求,并且后端数据需要保存到内存在
//注意下面只是把后端数据存到buf中,但是没有发送到客户端,实际发送一般是由ngx_http_finalize_request->ngx_http_set_write_handler实现 if (u->input_filter == NULL) {
u->input_filter_init = ngx_http_upstream_non_buffered_filter_init;
u->input_filter = ngx_http_upstream_non_buffered_filter;
u->input_filter_ctx = r;
} if (u->input_filter_init(u->input_filter_ctx) == NGX_ERROR) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
}
n = u->buffer.last - u->buffer.pos;
if (n) {
u->buffer.last = u->buffer.pos;
u->state->response_length += n;
if (u->input_filter(u->input_filter_ctx, n) == NGX_ERROR) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
}
}
if (u->length == 0) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, 0);
return;
}
u->read_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_process_body_in_memory;//设置body部分的读事件回调。
ngx_http_upstream_process_body_in_memory(r, u);
}
http request 结构体


/*
对于每个ngx_http_request_t请求来说,只能访问一个上游服务器,但对于一个客户端请求来说,可以派生出许多子请求,任何一个子请求都
可以访问一个上游服务器,这些子请求的结果组合起来就可以使来自客户端的请求处理复杂的业务。
*/
//ngx_http_parse_request_line解析请求行, ngx_http_process_request_headers解析头部行(请求头部)
//请求的所有信息都可以都可以在ngx_http_request_s结构获取到
struct ngx_http_request_s { //当接收到客户端请求数据后,调用ngx_http_create_request中创建并赋值
uint32_t signature; /* "HTTP" */ /*
在接收到客户端数据后,会创建一个ngx_http_request_s,其connection成员指向对应的accept成功后获取到的连接信息
ngx_connection_t,见ngx_http_create_request
这个请求对应的客户端连接 如果该r是子请求,其connection成员指向顶层root父请求的ngx_connection_t,因为它们都是对应的同一个客户端连接,见ngx_http_subrequest
*/
ngx_connection_t *connection; /*
ctx与ngx_http_conf_ctxt结构的3个数组成员非常相似,它们都
表示指向void指针的数组。HTTP框架就是在ctx数组中保存所有HTTP模块上下文结构体的指针的,所有模块的请求上下文空间在
ngx_http_create_request中创建。获取和设置分别在ngx_http_get_module_ctx和ngx_http_set_ctx,为每个请求创建ngx_http_request_s的时候
都会为该请求的ctx[]为所有的模块创建一个指针,也就是每个模块在ngx_http_request_s中有一个ctx
*/ //在应答完后,在ngx_http_filter_finalize_request会把ctx指向的空间全部清0 参考4.5节
void **ctx; //指向存放所有HTTP模块的上下文结构体的指针数组,实际上发送给客户端的应答完成后,会把ctx全部置0
/*
当客户端建立连接后,并发送请求数据过来后,在ngx_http_create_request中从ngx_http_connection_t->conf_ctx获取这三个值,也就是根据客户端连接
本端所处IP:port所对应的默认server{}块上下文,如果是以下情况:ip:port相同,单在不同的server{}块中,那么有可能客户端请求过来的时候携带的host
头部项的server_name不在默认的server{}中,而在另外的server{}中,所以需要通过ngx_http_set_virtual_server重新获取server{}和location{}上下文配置
例如:
server { #1
listen 1.1.1.1:80;
server_name aaa
} server { #2
listen 1.1.1.1:80;
server_name bbb
}
这个配置在ngx_http_init_connection中把ngx_http_connection_t->conf_ctx指向ngx_http_addr_conf_s->default_server,也就是指向#1,然后
ngx_http_create_request中把main_conf srv_conf loc_conf 指向#1,
但如果请求行的头部的host:bbb,那么需要重新获取对应的server{} #2,见ngx_http_set_virtual_server
*/ //ngx_http_create_request和ngx_http_set_virtual_server 已经rewrite过程中(例如ngx_http_core_find_location
//ngx_http_core_post_rewrite_phase ngx_http_internal_redirect ngx_http_internal_redirect 子请求ngx_http_subrequest)都可能对他们赋值
void **main_conf; //指向请求对应的存放main级别配置结构体的指针数组
void **srv_conf; //指向请求对应的存放srv级别配置结构体的指针数组 赋值见ngx_http_set_virtual_server
void **loc_conf; //指向请求对应的存放loc级别配置结构体的指针数组 赋值见ngx_http_set_virtual_server /*
在接收完HTTP头部,第一次在业务上处理HTTP请求时,HTTP框架提供的处理方法是ngx_http_process_request。但如果该方法无法一次处
理完该请求的全部业务,在归还控制权到epoll事件模块后,该请求再次被回调时,将通过ngx_http_request_handler方法来处理,而这个
方法中对于可读事件的处理就是调用read_event_handler处理请求。也就是说,HTTP模块希望在底层处理请求的读事件时,重新实现read_event_handler方法 //在读取客户端来的包体时,赋值为ngx_http_read_client_request_body_handler
丢弃客户端的包体时,赋值为ngx_http_discarded_request_body_handler
*/ //注意ngx_http_upstream_t和ngx_http_request_t都有该成员 分别在ngx_http_request_handler和ngx_http_upstream_handler中执行
ngx_http_event_handler_pt read_event_handler; /* 与read_event_handler回调方法类似,如果ngx_http_request_handler方法判断当前事件是可写事件,则调用write_event_handler处理请求 */
/*请求行和请求头部解析完成后,会在ngx_http_handler中赋值为ngx_http_core_run_phases 子请求的的handler为ngx_http_handler
当发送响应的时候,如果一次没有发送完,则设在为ngx_http_writer
*/ //注意ngx_http_upstream_t和ngx_http_request_t都有该成员 分别在ngx_http_request_handler和ngx_http_upstream_handler中执行
//如果采用buffer方式缓存后端包体,则在发送包体给客户端浏览器的时候,会把客户端连接的write_e_hand置为ngx_http_upstream_process_downstream
//在触发epoll_in的同时也会触发epoll_out,从而会执行该函数
ngx_http_event_handler_pt write_event_handler;//父请求重新激活后的回调方法 #if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
//通过ngx_http_upstream_cache_get获取
ngx_http_cache_t *cache;//在客户端请求过来后,在ngx_http_upstream_cache->ngx_http_file_cache_new中赋值r->caceh = ngx_http_cache_t
#endif /*
如果没有使用upstream机制,那么ngx_http_request_t中的upstream成员是NULL空指针,在ngx_http_upstream_create中创建空间
*/
ngx_http_upstream_t *upstream; //upstream机制用到的结构体
ngx_array_t *upstream_states; //创建空间和赋值见ngx_http_upstream_init_request
/* of ngx_http_upstream_state_t */ /*
表示这个请求的内存池,在ngx_http_free_request方法中销毁。它与ngx_connection-t中的内存池意义不同,当请求释放时,TCP连接可能并
没有关闭,这时请求的内存池会销毁,但ngx_connection_t的内存池并不会销毁
*/
ngx_pool_t *pool;
//其中,header_in指向Nginx收到的未经解析的HTTP头部,这里暂不关注它(header_in就是接收HTTP头部的缓冲区)。 header_in存放请求行,headers_in存放头部行
//请求行和请求头部内容都在该buffer中
ngx_buf_t *header_in;//用于接收HTTP请求内容的缓冲区,主要用于接收HTTP头部,该指针指向ngx_connection_t->buffer //类型的headers_in则存储已经解析过的HTTP头部。
/*常用的HTTP头部信息可以通过r->headers_in获取,不常用的HTTP头部则需要遍历r->headers_in.headers来遍历获取*/
/*
ngx_http_process_request_headers方法在接收、解析完HTTP请求的头部后,会把解析完的每一个HTTP头部加入到headers_in的headers链表中,同时会构造headers_in中的其他成员
*/ //参考ngx_http_headers_in,通过该数组中的回调hander来存储解析到的请求行name:value中的value到headers_in的响应成员中,见ngx_http_process_request_headers
//注意:在需要把客户端请求头发送到后端的话,在请求头后面可能添加有HTTP_相关变量,例如fastcgi,见ngx_http_fastcgi_create_request
ngx_http_headers_in_t headers_in; //http头部行解析后的内容都由该成员存储 header_in存放请求行,headers_in存放头部行
//只要指定headers_out中的成员,就可以在调用ngx_http_send_header时正确地把HTTP头部发出
//HTTP模块会把想要发送的HTTP响应信息放到headers_out中,期望HTTP框架将headers_out中的成员序列化为HTTP响应包发送给用户
ngx_http_headers_out_t headers_out;
//如果是upstream赋值的来源是后端服务器会有的头部行中拷贝,参考ngx_http_upstream_headers_in中的copy_handler /*
接收完请求的包体后,可以在r->request_body->temp_file->file中获取临时文件(假定将r->request_body_in_file_only标志位设为1,那就一定可以
在这个变量获取到包体。)。file是一个ngx_file_t类型。这里,我们可以从
r->request_body->temp_file->file.name中获取Nginx接收到的请求包体所在文件的名称(包括路径)。
*/ //在ngx_http_read_client_request_body中分配存储空间 读取的客户端包体存储在r->request_body->bufs链表和临时文件r->request_body->temp_file中 ngx_http_read_client_request_body
//读取客户包体即使是存入临时文件中,当所有包体读取完毕后(见ngx_http_do_read_client_request_body),还是会让r->request_body->bufs指向文件中的相关偏移内存地址
//向上游发送包体u->request_bufs(ngx_http_fastcgi_create_request),接收客户端的包体在r->request_body
ngx_http_request_body_t *request_body; //接收HTTP请求中包体的数据结构,为NULL表示还没有分配空间
//min(lingering_time,lingering_timeout)这段时间内可以继续读取数据,如果客户端有发送数据过来,见ngx_http_set_lingering_close
time_t lingering_time; //延迟关闭连接的时间
//ngx_http_request_t结构体中有两个成员表示这个请求的开始处理时间:start sec成员和start msec成员
/*
当前请求初始化时的时间。start sec是格林威治时间1970年1月1日凌晨0点0分0秒到当前时间的秒数。如果这个请求是子请求,则该时间
是子请求的生成时间;如果这个请求是用户发来的请求,则是在建立起TCP连接后,第一次接收到可读事件时的时间
*/
time_t start_sec;
ngx_msec_t start_msec;//与start_sec配合使用,表示相对于start_set秒的毫秒偏移量 //以下9个成员都是ngx_http_proces s_request_line方法在接收、解析HTTP请求行时解析出的信息
/*
注意 Nginx中对内存的控制相当严格,为了避免不必要的内存开销,许多需要用到的成员都不是重新分配内存后存储的,而是直接指向用户请求中的相应地址。
例如,method_name.data、request_start这两个指针实际指向的都是同一个地址。而且,因为它们是简单的内存指针,不是指向字符串的指针,所以,在大部分情况下,都不能将这些u_char*指针当做字符串使用。
*/ //NGX_HTTP_GET | NGX_HTTP_HEAD等,为NGX_HTTP_HEAD表示只需要发送HTTP头部字段
/* HTTP2的method赋值见ngx_http_v2_parse_method */
ngx_uint_t method; //对应客户端请求中请求行的请求方法GET、POS等,取值见NGX_HTTP_GET,也可以用下面的method_name进行字符串比较
/*
http_protocol指向用户请求中HTTP的起始地址。
http_version是Nginx解析过的协议版本,它的取值范围如下:
#define NGX_HTTP_VERSION_9 9
#define NGX_HTTP_VERSION_10 1000
#define NGX_HTTP_VERSION_11 1001
建议使用http_version分析HTTP的协议版本。
最后,使用request_start和request_end可以获取原始的用户请求行。
*/
ngx_uint_t http_version;//http_version是Nginx解析过的协议版本,它的取值范围如下:
/* 如果是HTTP2,则赋值见ngx_http_v2_construct_request_line */
ngx_str_t request_line; //请求行内容 //ngx_str_t类型的uri成员指向用户请求中的URI。同理,u_char*类型的uri_start和uri_end也与request_start、method_end的用法相似,唯一不
//同的是,method_end指向方法名的最后一个字符,而uri_end指向URI结束后的下一个地址,也就是最后一个字符的下一个字符地址(HTTP框架的行为),
//这是大部分u_char*类型指针对“xxx_start”和“xxx_end”变量的用法。
//http://10.135.10.167/mytest中的/mytest http://10.135.10.167/mytest?abc?ttt中的/mytest
//同时"GET /mytest?abc?ttt HTTP/1.1"中的mytest和uri中的一样
ngx_str_t uri;
//arg指向用户请求中的URL参数。 http://10.135.10.167/mytest?abc?ttt中的abc?ttt
//同时"GET /mytest?abc?ttt HTTP/1.1"中的mytest?abc?ttt和uri中的一样 /*把请求中GET /download/nginx-1.9.2.rar?st=xhWL03HbtjrojpEAfiD6Mw&e=1452139931 HTTP/1.1的st和e形成变量$arg_st #arg_e,value分别
为xhWL03HbtjrojpEAfiD6Mw 1452139931即$arg_st=xhWL03HbtjrojpEAfiD6Mw,#arg_e=1452139931,见ngx_http_arg */
ngx_str_t args;
/*
ngx_str_t类型的extern成员指向用户请求的文件扩展名。例如,在访问“GET /a.txt HTTP/1.1”时,extern的值是{len = 3, data = "txt"},
而在访问“GET /a HTTP/1.1”时,extern的值为空,也就是{len = 0, data = 0x0}。
uri_ext指针指向的地址与extern.data相同。
*/
ngx_str_t exten; //http://10.135.10.167/mytest/ac.txt中的txt
/*
url参数中出现+、空格、=、%、&、#等字符的解决办法
url出现了有+,空格,/,?,%,#,&,=等特殊符号的时候,可能在服务器端无法获得正确的参数值,如何是好?
解决办法
将这些字符转化成服务器可以识别的字符,对应关系如下:
URL字符转义 用其它字符替代吧,或用全角的。 + URL 中+号表示空格 %2B
空格 URL中的空格可以用+号或者编码 %20
/ 分隔目录和子目录 %2F
? 分隔实际的URL和参数 %3F
% 指定特殊字符 %25
# 表示书签 %23
& URL 中指定的参数间的分隔符 %26
= URL 中指定参数的值 %3D
*/
//unparsed_uri表示没有进行URL解码的原始请求。例如,当uri为“/a b”时,unparsed_uri是“/a%20b”(空格字符做完编码后是%20)。
ngx_str_t unparsed_uri;//参考:为什么要对URI进行编码:
/* HTTP2的method赋值见ngx_http_v2_parse_method,在组新的HTTP2头部行后,赋值见ngx_http_v2_construct_request_line */
ngx_str_t method_name;//见method GET POST等
ngx_str_t http_protocol;//GET /sample.jsp HTTP/1.1 中的HTTP/1.1 /* 当ngx_http_header_filter方法无法一次性发送HTTP头部时,将会有以下两个现象同时发生:请求的out成员中将会保存剩余的响应头部,见ngx_http_header_filter */
/* 表示需要发送给客户端的HTTP响应。out中保存着由headers_out中序列化后的表示HTTP头部的TCP流。在调用ngx_http_output_filter方法后,
out中还会保存待发送的HTTP包体,它是实现异步发送HTTP响应的关键 */
ngx_chain_t *out;//ngx_http_write_filter把in中的数据拼接到out后面,然后调用writev发送,没有发送完 /* 当前请求既可能是用户发来的请求,也可能是派生出的子请求,而main则标识一系列相关的派生子请
求的原始请求,我们一般可通过main和当前请求的地址是否相等来判断当前请求是否为用户发来的原始请求 */ //main成员始终指向一系列有亲缘关系的请求中的唯一的那个原始请求,初始赋值见ngx_http_create_request
//客户端的建立连接的时候r->main =r(ngx_http_create_request),如果是创建子请求,sr->main = r->main(ngx_http_subrequest)子请求->main=最上层的r
/* 主请求保存在main字段中,这里其实就是最上层跟请求,例如当前是四层子请求,则main始终指向第一层父请求,
而不是第三次父请求,parent指向第三层父请求 */
ngx_http_request_t *main; //赋值见ngx_http_subrequest
ngx_http_request_t *parent;//当前请求的父请求。注意,父请求未必是原始请求 赋值见ngx_http_subrequest //ngx_http_subrequest中赋值,表示对应的子请求r,该结构可以表示子请求信息
//postponed删除在ngx_http_finalize_request
//当客户端请求需要通过多个subrequest访问后端的时候,就需要对这多个后端的应答进行合适的顺序整理才能发往客户端
ngx_http_postponed_request_t *postponed; //与subrequest子请求相关的功能 postponed中数据依次发送参考ngx_http_postpone_filter方法
ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *post_subrequest;/* 保存回调handler及数据,在子请求执行完,将会调用 */ /* 所有的子请求都是通过posted_requests这个单链表来链接起来的,执行post子请求时调用的
ngx_http_run_posted_requests方法就是通过遍历该单链表来执行子请求的 */
//ngx_http_post_request中创建ngx_http_posted_request_t空间
//ngx_http_post_request将该子请求挂载在主请求的posted_requests链表队尾,在ngx_http_run_posted_requests中执行
ngx_http_posted_request_t *posted_requests; //通过posted_requests就把各个子请求以单向链表的数据结构形式组织起来 /*
全局的ngx_http_phase_engine_t结构体中定义了一个ngx_http_phase_handler_t回调方法组成的数组,而phase_handler成员则与该数组配合使用,
表示请求下次应当执行以phase_handler作为序号指定的数组中的回调方法。HTTP框架正是以这种方式把各个HTTP摸块集成起来处理请求的
*///phase_handler实际上是该阶段的处理方法函数在ngx_http_phase_engine_t->handlers数组中的位置
ngx_int_t phase_handler;
//表示NGX HTTP CONTENT PHASE阶段提供给HTTP模块处理请求的一种方式,content handler指向HTTP模块实现的请求处理方法,在ngx_http_core_content_phase中执行
//ngx_http_proxy_handler ngx_http_redis2_handler ngx_http_fastcgi_handler等
ngx_http_handler_pt content_handler; ////在ngx_http_update_location_config中赋值给r->content_handler = clcf->handler;
/*
在NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE阶段需要判断请求是否具有访问权限时,通过access_code来传递HTTP模块的handler回调方法的返回值,如果access_code为0,
则表示请求具备访问权限,反之则说明请求不具备访问权限 NGXHTTPPREACCESSPHASE、NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE、NGX HTTPPOST_ACCESS_PHASE,很好理解,做访问权限检查的前期、中期、后期工作,
其中后期工作是固定的,判断前面访问权限检查的结果(状态码存故在字段r->access_code内),如果当前请求没有访问权限,那么直接返回状
态403错误,所以这个阶段也无法去挂载额外的回调函数。
*/
ngx_uint_t access_code; //赋值见ngx_http_core_access_phase
/*
ngx_http_core_main_conf_t->variables数组成员的结构式ngx_http_variable_s, ngx_http_request_s->variables数组成员结构是ngx_variable_value_t,
这两个结构的关系很密切,一个所谓变量,一个所谓变量值 r->variables这个变量和cmcf->variables是一一对应的,形成var_ name与var_value对,所以两个数组里的同一个下标位置元素刚好就是
相互对应的变量名和变量值,而我们在使用某个变量时总会先通过函数ngx_http_get_variable_index获得它在变量名数组里的index下标,也就是变
量名里的index字段值,然后利用这个index下标进而去变量值数组里取对应的值
*/ //分配的节点数见ngx_http_create_request,和ngx_http_core_main_conf_t->variables一一对应
//变量ngx_http_script_var_code_t->index表示Nginx变量$file在ngx_http_core_main_conf_t->variables数组内的下标,对应每个请求的变量值存储空间就为r->variables[code->index],参考ngx_http_script_set_var_code
ngx_http_variable_value_t *variables; //注意和ngx_http_core_main_conf_t->variables的区别 #if (NGX_PCRE)
/*
例如正则表达式语句re.name= ^(/download/.*)/media/(.*)/tt/(.*)$, s=/download/aa/media/bdb/tt/ad,则他们会匹配,同时匹配的
变量数有3个,则返回值为3+1=4,如果不匹配则返回-1 这里*2是因为获取前面例子中的3个变量对应的值需要成对使用r->captures,参考ngx_http_script_copy_capture_code等
*/
ngx_uint_t ncaptures; //赋值见ngx_http_regex_exec //最大的$n*2
int *captures; //每个不同的正则解析之后的结果,存放在这里。$1,$2等
u_char *captures_data; //进行正则表达式匹配的原字符串,例如http://10.135.2.1/download/aaa/media/bbb.com中的/download/aaa/media/bbb.com
#endif /* limit_rate成员表示发送响应的最大速率,当它大于0时,表示需要限速。limit rate表示每秒可以发送的字节数,超过这个数字就需要限速;
然而,限速这个动作必须是在发送了limit_rate_after字节的响应后才能生效(对于小响应包的优化设计) */
//实际最后通过ngx_writev_chain发送数据的时候,还会限制一次
size_t limit_rate; //限速的相关计算方法参考ngx_http_write_filter
size_t limit_rate_after; /* used to learn the Apache compatible response length without a header */
size_t header_size; //所有头部行内容之和,可以参考ngx_http_header_filter off_t request_length; //HTTP请求的全部长度,包括HTTP包体 ngx_uint_t err_status; //错误码,取值为NGX_HTTP_BAD_REQUEST等 //当连接建立成功后,当收到客户端的第一个请求的时候会通过ngx_http_wait_request_handler->ngx_http_create_request创建ngx_http_request_t
//同时把r->http_connection指向accept客户端连接成功时候创建的ngx_http_connection_t,这里面有存储server{}上下文ctx和server_name等信息
//该ngx_http_request_t会一直有效,除非关闭连接。因此该函数只会调用一次,也就是第一个客户端请求报文过来的时候创建,一直持续到连接关闭
//该结构存储了服务器端接收客户端连接时,服务器端所在的server{]上下文ctx server_name等配置信息
ngx_http_connection_t *http_connection; //存储ngx_connection_t->data指向的ngx_http_connection_t,见ngx_http_create_request #if (NGX_HTTP_SPDY)
ngx_http_spdy_stream_t *spdy_stream;
#endif #if (NGX_HTTP_V2)
/* 赋值见ngx_http_v2_create_stream */
ngx_http_v2_stream_t *stream;
#endif ngx_http_log_handler_pt log_handler;
//在这个请求中如果打开了某些资源,并需要在请求结束时释放,那么都需要在把定义的释放资源方法添加到cleanup成员中
/*
如果没有需要清理的资源,则cleanup为空指针,否则HTTP模块可以向cleanup中以单链表的形式无限制地添加ngx_http_cleanup_t结构体,
用以在请求结束时释放资源 */
ngx_http_cleanup_t *cleanup;
//默认值r->subrequests = NGX_HTTP_MAX_SUBREQUESTS + 1;见ngx_http_create_request
unsigned subrequests:8; //该r最多还可以处理多少个子请求 /*
在阅读HTTP反向代理模块(ngx_http_proxy_module)源代码时,会发现它并没有调用r->main->count++,其中proxy模块是这样启动upstream机制的:
ngx_http_read_client_request_body(r,ngx_http_upstream_init);,这表示读取完用户请求的HTTP包体后才会调用ngx_http_upstream_init方法
启动upstream机制。由于ngx_http_read_client_request_body的第一行有效语句是r->maln->count++,所以HTTP反向代理模块不能
再次在其代码中执行r->main->count++。 这个过程看起来似乎让人困惑。为什么有时需要把引用计数加1,有时却不需要呢?因为ngx_http_read- client_request_body读取请求包体是
一个异步操作(需要epoll多次调度方能完成的可称其为异步操作),ngx_http_upstream_init方法启用upstream机制也是一个异步操作,因此,
从理论上来说,每执行一次异步操作应该把引用计数加1,而异步操作结束时应该调用ngx_http_finalize_request方法把引用计数减1。另外,
ngx_http_read_client_request_body方法内是加过引用计数的,而ngx_http_upstream_init方法内却没有加过引用计数(或许Nginx将来会修改
这个问题)。在HTTP反向代理模块中,它的ngx_http_proxy_handler方法中用“ngx_http_read- client_request_body(r,ngx_http_upstream_init);”
语句同时启动了两个异步操作,注意,这行语句中只加了一次引用计数。执行这行语句的ngx_http_proxy_handler方法返回时只调用
ngx_http_finalize_request方法一次,这是正确的。对于mytest模块也一样,务必要保证对引用计数的增加和减少是配对进行的。
*/
/*
表示当前请求的引用次数。例如,在使用subrequest功能时,依附在这个请求上的子请求数目会返回到count上,每增加一个子请求,count数就要加1。
其中任何一个子请求派生出新的子请求时,对应的原始请求(main指针指向的请求)的count值都要加1。又如,当我们接收HTTP包体时,由于这也是
一个异步调用,所以count上也需要加1,这样在结束请求时,就不会在count引用计数未清零时销毁请求
*/
unsigned count:8; //应用计数 ngx_http_close_request中-1
/* 如果AIO上下文中还在处理这个请求,blocked必然是大于0的,这时ngx_http_close_request方法不能结束请求
ngx_http_copy_aio_handler会自增,当内核把数据发送出去后会在ngx_http_copy_aio_event_handler自剪
*/
unsigned blocked:8; //阻塞标志位,目前仅由aio使用 为0,表示没有HTTP模块还需要处理请求
//ngx_http_copy_aio_handler handler ngx_http_copy_aio_event_handler执行后,会置回到0
//ngx_http_copy_thread_handler ngx_http_copy_thread_event_handler置0
//ngx_http_cache_thread_handler置1, ngx_http_cache_thread_event_handler置0
//ngx_http_file_cache_aio_read中置1,
unsigned aio:1; //标志位,为1时表示当前请求正在使用异步文件IO unsigned http_state:4; //赋值见ngx_http_state_e中的成员 /* URI with "/." and on Win32 with "//" */
unsigned complex_uri:1; /* URI with "%" */
unsigned quoted_uri:1; /* URI with "+" */
unsigned plus_in_uri:1; /* URI with " " */
unsigned space_in_uri:1; //uri中是否带有空格
//头部帧内容部分header合法性检查,见ngx_http_v2_validate_header
unsigned invalid_header:1; //头部行解析不正确,见ngx_http_parse_header_line unsigned add_uri_to_alias:1;
unsigned valid_location:1; //ngx_http_handler中置1
//如果有rewrite 内部重定向 uri带有args等会直接置0,否则如果uri中有空格会置1
unsigned valid_unparsed_uri:1;//r->valid_unparsed_uri = r->space_in_uri ? 0 : 1; /*
将uri_changed设置为0后,也就标志说URL没有变化,那么,在ngx_http_core_post_rewrite_phase中就不会执行里面的if语句,也就不会
再次走到find config的过程了,而是继续处理后面的。不然正常情况,rewrite成功后是会重新来一次的,相当于一个全新的请求。
*/ // 例如rewrite ^.*$ www.galaxywind.com last;就会多次执行rewrite ngx_http_script_regex_start_code中置1
unsigned uri_changed:1; //标志位,为1时表示URL发生过rewrite重写 只要不是rewrite xxx bbb sss;aaa不是break结束都会置1
//表示使用rewrite重写URL的次数。因为目前最多可以更改10次,所以uri_changes初始化为11,而每重写URL -次就把uri_changes减1,
//一旦uri_changes等于0,则向用户返回失败
unsigned uri_changes:4; //NGX_HTTP_MAX_URI_CHANGES + 1; unsigned request_body_in_single_buf:1;//client_body_in_single_buffer on | off;设置
//置1包体需要存入临时文件中 如果request_body_no_buffering为1表示不用缓存包体,那么request_body_in_file_only也为0,因为不用缓存包体,那么就不用写到临时文件中
/*注意:如果每次开辟的client_body_buffer_size空间都存储满了还没有读取到完整的包体,则还是会把之前读满了的buf中的内容拷贝到临时文件,参考
ngx_http_do_read_client_request_body -> ngx_http_request_body_filter和ngx_http_read_client_request_body -> ngx_http_request_body_filter
*/
unsigned request_body_in_file_only:1; //"client_body_in_file_only on |clean"设置 和request_body_no_buffering是互斥的
unsigned request_body_in_persistent_file:1; //"client_body_in_file_only on"设置
unsigned request_body_in_clean_file:1;//"client_body_in_file_only clean"设置
unsigned request_body_file_group_access:1; //是否有组权限,如果有一般为0600
unsigned request_body_file_log_level:3;
//默认是为0的表示需要缓存客户端包体,决定是否需要转发客户端包体到后端,如果request_body_no_buffering为1表示不用缓存包体,那么request_body_in_file_only也为0,因为不用缓存包体,那么就不用写到临时文件中
unsigned request_body_no_buffering:1; //是否缓存HTTP包体,如果不缓存包体,和request_body_in_file_only是互斥的,见ngx_http_read_client_request_body /*
upstream有3种处理上游响应包体的方式,但HTTP模块如何告诉upstream使用哪一种方式处理上游的响应包体呢?
当请求的ngx_http_request_t结构体中subrequest_in_memory标志位为1时,将采用第1种方式,即upstream不转发响应包体
到下游,由HTTP模块实现的input_filter方法处理包体;当subrequest_in_memory为0时,upstream会转发响应包体。当ngx_http_upstream_conf_t
配置结构体中的buffering标志位为1时,将开启更多的内存和磁盘文件用于缓存上游的响应包体,这意味上游网速更快;当buffering
为0时,将使用固定大小的缓冲区(就是上面介绍的buffer缓冲区)来转发响应包体。
*/
unsigned subrequest_in_memory:1; //ngx_http_subrequest中赋值 NGX_HTTP_SUBREQUEST_IN_MEMORY
unsigned waited:1; //ngx_http_subrequest中赋值 NGX_HTTP_SUBREQUEST_WAITED #if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
unsigned cached:1;//如果客户端请求过来有读到缓存文件,则置1,见ngx_http_file_cache_read ngx_http_upstream_cache_send
#endif #if (NGX_HTTP_GZIP)
unsigned gzip_tested:1;
unsigned gzip_ok:1;
unsigned gzip_vary:1;
#endif unsigned proxy:1;
unsigned bypass_cache:1;
unsigned no_cache:1; /*
* instead of using the request context data in
* ngx_http_limit_conn_module and ngx_http_limit_req_module
* we use the single bits in the request structure
*/
unsigned limit_conn_set:1;
unsigned limit_req_set:1; #if 0
unsigned cacheable:1;
#endif unsigned pipeline:1;
//如果后端发送过来的头部行中不带有Content-length:xxx 这种情况1.1版本HTTP直接设置chunked为1, 见ngx_http_chunked_header_filter
//如果后端带有Transfer-Encoding: chunked会置1
unsigned chunked:1; //chunk编码方式组包实际组包过程参考ngx_http_chunked_body_filter
//当下游的r->method == NGX_HTTP_HEAD请求方法只请求头部行,则会在ngx_http_header_filter中置1
//HTTP2头部帧发送在ngx_http_v2_header_filter中置1
unsigned header_only:1; //表示是否只有行、头部,没有包体 ngx_http_header_filter中置1
//在1.0以上版本默认是长连接,1.0以上版本默认置1,如果在请求头里面没有设置连接方式,见ngx_http_handler
//标志位,为1时表示当前请求是keepalive请求 1长连接 0短连接 长连接时间通过请求头部的Keep-Alive:设置,参考ngx_http_headers_in_t
unsigned keepalive:1; //赋值见ngx_http_handler
//延迟关闭标志位,为1时表示需要延迟关闭。例如,在接收完HTTP头部时如果发现包体存在,该标志位会设为1,而放弃接收包体时则会设为o
unsigned lingering_close:1;
//如果discard_body为1,则证明曾经执行过丢弃包体的方法,现在包体正在被丢弃中,见ngx_http_read_client_request_body
unsigned discard_body:1;//标志住,为1时表示正在丢弃HTTP请求中的包体
unsigned reading_body:1; //标记包体还没有读完,需要继续读取包体,见 ngx_http_read_client_request_body /* 在这一步骤中,把phase_handler序号设为server_rewrite_index,这意味着无论之前执行到哪一个阶段,马上都要重新从NGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE
阶段开始再次执行,这是Nginx的请求可以反复rewrite重定向的基础。见ngx_http_handler */
//ngx_http_internal_redirect置1 创建子请求的时候,子请求也要置1,见ngx_http_subrequest,所有子请求需要做重定向
//内部重定向是从NGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE处继续执行(ngx_http_internal_redirect),而重新rewrite是从NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE处执行(ngx_http_core_post_rewrite_phase)
unsigned internal:1;//t标志位,为1时表示请求的当前状态是在做内部跳转,
unsigned error_page:1; //默认0,在ngx_http_special_response_handler中可能置1
unsigned filter_finalize:1;
unsigned post_action:1;//ngx_http_post_action中置1 默认为0,除非post_action XXX配置
unsigned request_complete:1;
unsigned request_output:1;//表示有数据需要往客户端发送,ngx_http_copy_filter中置1
//为I时表示发送给客户端的HTTP响应头部已经发送。在调用ngx_http_send_header方法后,若已经成功地启动响应头部发送流程,
//该标志位就会置为1,用来防止反复地发送头部
unsigned header_sent:1;
unsigned expect_tested:1;
unsigned root_tested:1;
unsigned done:1;
unsigned logged:1;
/* ngx_http_copy_filter中赋值 */
unsigned buffered:4;//表示缓冲中是否有待发送内容的标志位,参考ngx_http_copy_filter unsigned main_filter_need_in_memory:1;
unsigned filter_need_in_memory:1;
unsigned filter_need_temporary:1;
unsigned allow_ranges:1; //支持断点续传 参考3.8.3节
unsigned single_range:1;
//
unsigned disable_not_modified:1; //r->disable_not_modified = !u->cacheable;因此默认为0 #if (NGX_STAT_STUB)
unsigned stat_reading:1;
unsigned stat_writing:1;
#endif /* used to parse HTTP headers */ //状态机解析HTTP时使用state来表示当前的解析状态
ngx_uint_t state; //解析状态,见ngx_http_parse_header_line
//header_hash为Accept-Language:zh-cn中Accept-Language所有字符串做hash运算的结果
ngx_uint_t header_hash; //头部行中一行所有内容计算ngx_hash的结构,参考ngx_http_parse_header_line
//lowcase_index为Accept-Language:zh-cn中Accept-Language字符数,也就是15个字节
ngx_uint_t lowcase_index; // 参考ngx_http_parse_header_line
//存储Accept-Language:zh-cn中的Accept-Language字符串到lowcase_header。如果是AAA_BBB:CCC,则该数组存储的是_BBB
u_char lowcase_header[NGX_HTTP_LC_HEADER_LEN]; //http头部内容,不包括应答行或者请求行,参考ngx_http_parse_header_line /*
例如:Accept:image/gif.image/jpeg,**
Accept对应于key,header_name_start header_name_end分别指向这个Accept字符串的头和尾
image/gif.image/jpeg,** 为value部分,header_start header_end分别对应value的头和尾,可以参考mytest_upstream_process_header
*/
//header_name_start指向Accept-Language:zh-cn中的A处
u_char *header_name_start; //解析到的一行http头部行中的一行的name开始处 //赋值见ngx_http_parse_header_line
//header_name_start指向Accept-Language:zh-cn中的:处
u_char *header_name_end; //解析到的一行http头部行中的一行的name的尾部 //赋值见ngx_http_parse_header_line
u_char *header_start;//header_start指向Accept-Language:zh-cn中的z字符处
u_char *header_end;//header_end指向Accept-Language:zh-cn中的末尾换行处 /*
* a memory that can be reused after parsing a request line
* via ngx_http_ephemeral_t
*/ //ngx_str_t类型的uri成员指向用户请求中的URI。同理,u_char*类型的uri_start和uri_end也与request_start、request_end的用法相似,唯一不
//同的是,method_end指向方法名的最后一个字符,而uri_end指向URI结束后的下一个地址,也就是最后一个字符的下一个字符地址(HTTP框架的行为),
//这是大部分u_char*类型指针对“xxx_start”和“xxx_end”变量的用法。
u_char *uri_start;//HTTP2的赋值见ngx_http_v2_parse_path
u_char *uri_end;//HTTP2的赋值见ngx_http_v2_parse_path /*
ngx_str_t类型的extern成员指向用户请求的文件扩展名。例如,在访问“GET /a.txt HTTP/1.1”时,extern的值是{len = 3, data = "txt"},
而在访问“GET /a HTTP/1.1”时,extern的值为空,也就是{len = 0, data = 0x0}。
uri_ext指针指向的地址与extern.data相同。
*/ //GET /sample.jsp HTTP/1.1 后面的文件如果有.字符,则指向该.后面的jsp字符串,表示文件扩展名
u_char *uri_ext;
//"GET /aaaaaaaa?bbbb.txt HTTP/1.1"中的bbb.txt字符串头位置处
u_char *args_start;//args_start指向URL参数的起始地址,配合uri_end使用也可以获得URL参数。 /* 通过request_start和request_end可以获得用户完整的请求行 */
u_char *request_start; //请求行开始处
u_char *request_end; //请求行结尾处
u_char *method_end; //GET POST字符串结尾处 //HTTP2的赋值见ngx_http_v2_parse_scheme
u_char *schema_start;
u_char *schema_end;
u_char *host_start;
u_char *host_end;
u_char *port_start;
u_char *port_end; // HTTP/1.1前面的1代表major,后面的1代表minor
unsigned http_minor:16;
unsigned http_major:16;
};
http server发送响应到请求端处理
//发送后端返回回来的数据给客户端。里面会处理header,body分开发送的情况的
static void
ngx_http_upstream_send_response(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_upstream_t *u)
{
int tcp_nodelay;
ssize_t n;
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_event_pipe_t *p;
ngx_connection_t *c;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
int flag;
time_t now, valid; rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);//先发header,再发body //调用每一个filter过滤,处理头部数据。最后将数据发送给客户端。调用ngx_http_top_header_filter if (rc == NGX_ERROR || rc > NGX_OK || r->post_action) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, rc);
return;
} u->header_sent = 1;//标记已经发送了头部字段,至少是已经挂载出去,经过了filter了。 if (u->upgrade) {
ngx_http_upstream_upgrade(r, u);
return;
}
c = r->connection;
if (r->header_only) {//如果只需要发送头部数据,比如客户端用curl -I 访问的。返回204状态码即可。
if (!u->buffering) { //配置不需要缓存包体,或者后端要求不配置缓存包体,直接结束
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, rc);
return;
}
if (!u->cacheable && !u->store) { //如果定义了#if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)则可能置1
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, rc);
return;
}
u->pipe->downstream_error = 1; //命名客户端只请求头部行,但是上游雀配置或者要求缓存或者存储包体
}
if (r->request_body && r->request_body->temp_file) { //客户端发送过来的包体存储在临时文件中,则需要把存储临时文件删除
ngx_pool_run_cleanup_file(r->pool, r->request_body->temp_file->file.fd);
//之前临时文件内容已经不需要了,因为在ngx_http_fastcgi_create_request(ngx_http_xxx_create_request)中已经把临时文件中的内容
//赋值给u->request_bufs并通过发送到了后端服务器,现在需要发往客户端的内容为上游应答回来的包体,因此此临时文件内容已经没用了
r->request_body->temp_file->file.fd = NGX_INVALID_FILE;
}
clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module);
/*
如果开启缓冲,那么Nginx将尽可能多地读取后端服务器的响应数据,等达到一定量(比如buffer满)再传送给最终客户端。如果关闭,
那么Nginx对数据的中转就是一个同步的过程,即从后端服务器接收到响应数据就立即将其发送给客户端。
*/
flag = u->buffering;
ngx_log_debug1(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_HTTP, c->log, 0, "ngx_http_upstream_send_response, buffering flag:%d", flag);
if (!u->buffering) {
//buffering为1,表示上游来的包体先缓存上游发送来的包体,然后在发送到下游,如果该值为0,则接收多少上游包体就向下游转发多少包体 if (u->input_filter == NULL) { //如果input_filter为空,则设置默认的filter,然后准备发送数据到客户端。然后试着读读FCGI
u->input_filter_init = ngx_http_upstream_non_buffered_filter_init;
//ngx_http_upstream_non_buffered_filter将u->buffer.last - u->buffer.pos之间的数据放到u->out_bufs发送缓冲去链表里面。
//根据具体的到上游转发的方式,选择使用fastcgi memcached等,ngx_http_xxx_filter
u->input_filter = ngx_http_upstream_non_buffered_filter; //一般就设置为这个默认的,memcache为ngx_http_memcached_filter
u->input_filter_ctx = r;
}
//设置upstream的读事件回调,设置客户端连接的写事件回调。
u->read_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_process_non_buffered_upstream;
r->write_event_handler =
ngx_http_upstream_process_non_buffered_downstream;//调用过滤模块一个个过滤body,最终发送出去。
r->limit_rate = 0;
//ngx_http_XXX_input_filter_init(如ngx_http_fastcgi_input_filter_init ngx_http_proxy_input_filter_init ngx_http_proxy_input_filter_init)
//只有memcached会执行ngx_http_memcached_filter_init,其他方式什么也没做
if (u->input_filter_init(u->input_filter_ctx) == NGX_ERROR) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
}
if (clcf->tcp_nodelay && c->tcp_nodelay == NGX_TCP_NODELAY_UNSET) {
ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_HTTP, c->log, 0, "tcp_nodelay");
tcp_nodelay = 1;
if (setsockopt(c->fd, IPPROTO_TCP, TCP_NODELAY,
(const void *) &tcp_nodelay, sizeof(int)) == -1)
{
ngx_connection_error(c, ngx_socket_errno,
"setsockopt(TCP_NODELAY) failed");
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
}
c->tcp_nodelay = NGX_TCP_NODELAY_SET;
}
n = u->buffer.last - u->buffer.pos; /*
不是还没接收包体嘛,为什么就开始发送了呢? 这是因为在前面的ngx_http_upstream_process_header接收fastcgi头部行标识包体处理的时候,有可能会把一部分fastcgi包体标识也收过了,
因此需要处理
*/
if (n) {//得到将要发送的数据的大小,每次有多少就发送多少。不等待upstream了 因为这是不缓存方式发送包体到客户端
u->buffer.last = u->buffer.pos;
u->state->response_length += n;//统计请求的返回包体数据(不包括请求行)长度。
//下面input_filter只是简单的拷贝buffer上面的数据总共n长度的,到u->out_bufs里面去,以待发送。
//ngx_http_xxx_non_buffered_filter(如ngx_http_fastcgi_non_buffered_filter)
if (u->input_filter(u->input_filter_ctx, n) == NGX_ERROR) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
}
ngx_http_upstream_process_non_buffered_downstream(r);
} else {
u->buffer.pos = u->buffer.start;
u->buffer.last = u->buffer.start;
if (ngx_http_send_special(r, NGX_HTTP_FLUSH) == NGX_ERROR) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
}
/------------/u->peer.connection->read->ready == 1 (size==n)
if (u->peer.connection->read->ready || u->length == 0) {
ngx_http_upstream_process_non_buffered_upstream(r, u);
}
} return; //这里会返回回去
}
/* TODO: preallocate event_pipe bufs, look "Content-Length" */ ----------------------------
----------------------------
p->preread_bufs = ngx_alloc_chain_link(r->pool);
if (p->preread_bufs == NULL) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
}
p->preread_bufs->buf = &u->buffer; //把包体部分的pos和last存储到p->preread_bufs->buf
p->preread_bufs->next = NULL;
u->buffer.recycled = 1;
//之前读取后端头部行信息的时候的buf还有剩余数据,这部分数据就是包体数据,也就是读取头部行fastcgi标识信息的时候把部分包体数据读取了
p->preread_size = u->buffer.last - u->buffer.pos;
if (u->cacheable) { //注意走到这里的时候,前面已经把后端头部行信息解析出来了,u->buffer.pos指向的是实际数据部分
p->buf_to_file = ngx_calloc_buf(r->pool);
if (p->buf_to_file == NULL) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
}
//指向的是为获取后端头部行的时候分配的第一个缓冲区,buf大小由xxx_buffer_size(fastcgi_buffer_size proxy_buffer_size memcached_buffer_size)指定
/*
这里面只存储了头部行buffer中头部行的内容部分,因为后面写临时文件的时候,需要把后端头部行也写进来,由于前面读取头部行后指针已经指向了数据部分
因此需要临时用buf_to_file->start指向头部行部分开始,pos指向数据部分开始,也就是头部行部分结尾
*/
p->buf_to_file->start = u->buffer.start;
p->buf_to_file->pos = u->buffer.start;
p->buf_to_file->last = u->buffer.pos;
p->buf_to_file->temporary = 1;
}
-----------------------------------
//buffering方式,后端头部信息已经读取完毕了,如果后端还有包体需要发送,则本端通过该方式读取
u->read_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_process_upstream;
r->write_event_handler = ngx_http_upstream_process_downstream; //当可写事件促发的时候,通过该函数继续写数据
ngx_http_upstream_process_upstream(r, u);
}
处理响应包体转发
/*
ngx_http_upstream_send_response发送完HERDER后,如果是非缓冲模式,会调用这里将数据发送出去的。
这个函数实际上判断一下超时后,就调用ngx_http_upstream_process_non_buffered_request了。nginx老方法。
*/
static void
//buffring模式通过ngx_http_upstream_process_upstream该函数处理,非buffring模式通过ngx_http_upstream_process_non_buffered_downstream处理
ngx_http_upstream_process_non_buffered_downstream(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
ngx_event_t *wev;
ngx_connection_t *c;
ngx_http_upstream_t *u; c = r->connection;
u = r->upstream;
wev = c->write; ngx_log_debug0(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_HTTP, c->log, 0,
"http upstream process non buffered downstream"); c->log->action = "sending to client"; if (wev->timedout) {
c->timedout = 1;
ngx_connection_error(c, NGX_ETIMEDOUT, "client timed out");
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_HTTP_REQUEST_TIME_OUT);
return;
} //下面开始将out_bufs里面的数据发送出去,然后读取数据,然后发送,如此循环。
ngx_http_upstream_process_non_buffered_request(r, 1);
}
/*
调用过滤模块,将数据发送出去,do_write为是否要给客户端发送数据。
1.如果要发送,就调用ngx_http_output_filter将数据发送出去。
2.然后ngx_unix_recv读取数据,放入out_bufs里面去。如此循环
*/
static void
ngx_http_upstream_process_non_buffered_request(ngx_http_request_t *r,
ngx_uint_t do_write)
{
size_t size;
ssize_t n;
ngx_buf_t *b;
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_connection_t *downstream, *upstream;
ngx_http_upstream_t *u;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
u = r->upstream;
downstream = r->connection;//找到这个请求的客户端连接
upstream = u->peer.connection;//找到上游的连接
b = &u->buffer; //找到这坨要发送的数据,不过大部分都被input filter放到out_bufs里面去了。 do_write = do_write || u->length == 0; //do_write为1时表示要立即发送给客户端。 for ( ;; ) { if (do_write) { //要立即发送。
//out_bufs中的数据是从ngx_http_fastcgi_non_buffered_filter获取
if (u->out_bufs || u->busy_bufs) {
//如果u->out_bufs不为NULL则说明有需要发送的数据,这是u->input_filter_init(u->input_filter_ctx)(ngx_http_upstream_non_buffered_filter)拷贝到这里的。
//u->busy_bufs代表是在读取fastcgi请求头的时候,可能里面会带有包体数据,就是通过这里发送
rc = ngx_http_output_filter(r, u->out_bufs); if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
} //就是把ngx_http_output_filter调用后未发送完毕的数据buf添加到busy_bufs中,如果下次再次调用ngx_http_output_filter后把busy_bufs中上一次没有发送完的发送出去了,则把对应的buf移除添加到free中
//下面将out_bufs的元素移动到busy_bufs的后面;将已经发送完毕的busy_bufs链表元素移动到free_bufs里面
ngx_chain_update_chains(r->pool, &u->free_bufs, &u->busy_bufs,
&u->out_bufs, u->output.tag);
} if (u->busy_bufs == NULL) {//busy_bufs没有了,都发完了。想要发送的数据都已经发送完毕 if (u->length == 0
|| (upstream->read->eof && u->length == -1)) //包体数据已经读完了
{
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, 0);
return;
}
if (upstream->read->eof) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ERR, upstream->log, 0,
"upstream prematurely closed connection"); ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u,
NGX_HTTP_BAD_GATEWAY);
return;
} if (upstream->read->error) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u,
NGX_HTTP_BAD_GATEWAY);
return;
}
b->pos = b->start;//重置u->buffer,以便与下次使用,从开始起。b指向的空间可以继续读数据了
b->last = b->start;
}
}
size = b->end - b->last;//得到当前buf的剩余空间
if (size && upstream->read->ready) {
//为什么可能走到这里?因为在 ngx_http_upstream_process_header 中读取后端数据的时候,buf大小默认为页面大小ngx_pagesize
//单有可能后端发送过来的数据比ngx_pagesize大,因此就没有读完,也就是recv中不会吧ready置0,所以这里可以继续读
ngx_http_upstream_process_header
n = upstream->recv(upstream, b->last, size);
if (n == NGX_AGAIN) { //说明已经内核缓冲区数据已经读完,退出循环,然后根据epoll事件来继续触发读取后端数据
break;
}
if (n > 0) {
u->state->response_length += n; if (u->input_filter(u->input_filter_ctx, n) == NGX_ERROR) {
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
}
}
do_write = 1;//因为刚刚无论如何n大于0,所以读取了数据,那么下一个循环会将out_bufs的数据发送出去的。
continue;
} break;
} clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module); if (downstream->data == r) {
if (ngx_handle_write_event(downstream->write, clcf->send_lowat, NGX_FUNC_LINE)
!= NGX_OK)
{
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
}
} if (downstream->write->active && !downstream->write->ready) {
//例如我把数据把数据写到内核协议栈到写满协议栈缓存,但是对端一直不读取的时候,数据一直发不出去了,也不会触发epoll_wait写事件,
//这里加个定时器就是为了避免这种情况发生
ngx_add_timer(downstream->write, clcf->send_timeout, NGX_FUNC_LINE);
} else if (downstream->write->timer_set) {
ngx_del_timer(downstream->write, NGX_FUNC_LINE);
} if (ngx_handle_read_event(upstream->read, 0, NGX_FUNC_LINE) != NGX_OK) { //epoll在accept的时候读写已经加入epoll中,因此对epoll来说没用
ngx_http_upstream_finalize_request(r, u, NGX_ERROR);
return;
} if (upstream->read->active && !upstream->read->ready) {
ngx_add_timer(upstream->read, u->conf->read_timeout, NGX_FUNC_LINE);
} else if (upstream->read->timer_set) {
ngx_del_timer(upstream->read, NGX_FUNC_LINE);
}
}
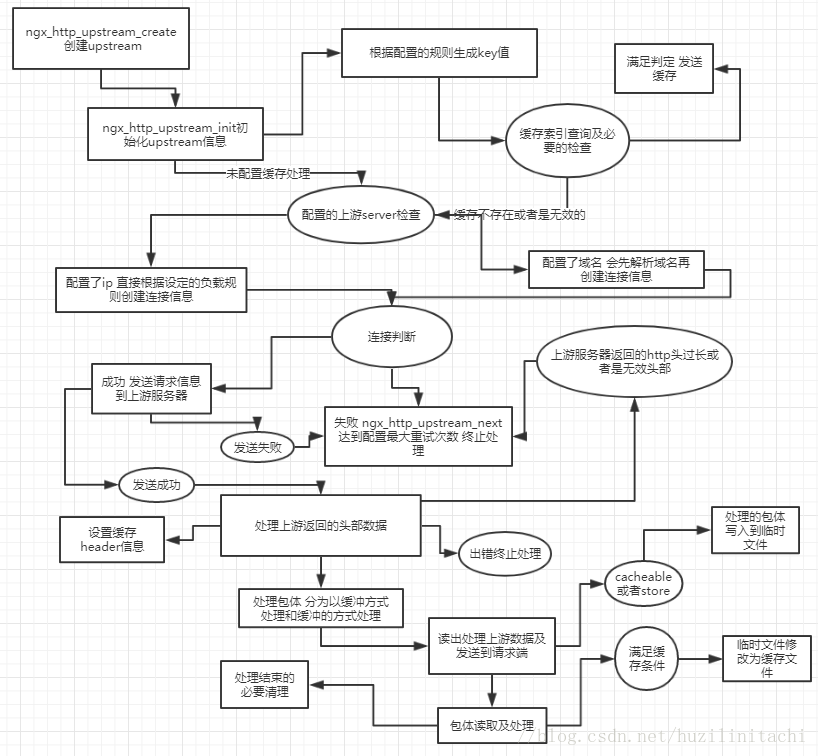
http代理阅读4 响应缓存处理的更多相关文章
- Asp.Net Core 2.1+的视图缓存(响应缓存)
响应缓存Razor 页与 ASP.NET 核心 2.0 中不支持. 此功能将支持ASP.NET 核心 2.1 版本. 在老的版本的MVC里面,有一种可以缓存视图的特性(OutputCache),可以保 ...
- 详解Asp.Net Core 2.1+的视图缓存(响应缓存)
响应缓存Razor 页与 ASP.NET 核心 2.0 中不支持. 此功能将支持ASP.NET 核心 2.1 版本. 在老的版本的MVC里面,有一种可以缓存视图的特性(OutputCache),可以保 ...
- http 代理阅读1
代理模式数据流处理: //配置proxy_pass后,在 ngx_http_core_content_phase 里面指向该函数 /* 那么,当有请求访问到特定的location的时候(假设这个loc ...
- http代理阅读3 发送mem处理
每次客户端有可读数据触发时,优先检测是否还有数据没有发送,如果有则发送数据,然后在读取client数据 //向后端发送请求的调用过程 //ngx_http_upstream_send_request_ ...
- Nginx反向代理 负载均衡 页面缓存 URL重写及读写分离
大纲 一.前言 二.环境准备 三.安装与配置Nginx 四.Nginx之反向代理 五.Nginx之负载均衡 六.Nginx之页面缓存 七.Nginx之URL重写 八.Nginx之读写分离 注,操作系统 ...
- Nginx特性验证-反向代理/负载均衡/页面缓存/URL重定向
原文发表于cu:2016-08-25 参考文档: Nginx 反向代理.负载均衡.页面缓存.URL重写等:http://freeloda.blog.51cto.com/2033581/1288553 ...
- .net core响应缓存
按照官网资料操作无效,这里使用https://github.com/speige/AspNetCore.ResponseCaching.Extensions的扩展包 安装AspNetCore.Resp ...
- http代理阅读2
向上游服务器发送请求处理 static void ngx_http_upstream_send_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_upstream_t * ...
- 巧用Fiddler代理来禁止资源缓存,从而达到每次都是从服务器加载最新的资源
Fiddler -> Rules -> Performance -> Disable Caching 直接设置禁用缓存,再在没有清除缓存功能的APP 中重新加载最新的页面, 每 ...
随机推荐
- Dubbo部分知识点总结
Dubbo部分 Dubbo工作原理 dubbo工作原理第一层:service层,接口层,给服务提供者和消费者来实现的第二层:config层,配置层,主要是对dubbo进行各种配置的第三层:proxy层 ...
- 实验二 HTML中图片和超链接的应用
实验二 HTML中图片和超链接的应用 [实验目的] 1.通过本例要求掌握常见的图像格式及图像的插入方法. 2.能够修改图像属性,利用外部图像处理软件编辑图像. 3.掌握设置各类超级连接的方法. 4.灵 ...
- 多测师讲解接口测试 _windows中搭建环境cms_高级讲师肖sir
eclipse集成开发环境 搭建开发环境需要安装的工具如下 jdk-8u60-windows-x64.exe jdk eclipse.rar 集成开发框架 mysql-inst ...
- 多测师讲解html _无序列表006_高级讲师肖sir
<!DOCTYPE html><html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>无 ...
- Redis的介绍以及安装
redis 是一个开源(BSD许可)的,内存中的数据结构存储系统,它可以用作数据库,缓存和消息中间件 高速缓存介绍 高速缓存利用内存保存数据,读写速度远超硬盘 高速缓存可以减少 I/O 操作,降 ...
- iNeuOS工业互联平台,设备容器(物联网)改版,并且实现设备数据点的实时计算和预警。发布3.2版本
目 录 1. 概述... 2 2. 平台演示... 2 3. 设备容器新版本介绍... 2 4. 全局数据计算及预警平台... 3 5. ...
- 并查集算法Union-Find的思想、实现以及应用
并查集算法,也叫Union-Find算法,主要用于解决图论中的动态连通性问题. Union-Find算法类 这里直接给出并查集算法类UnionFind.class,如下: /** * Union-Fi ...
- selenium---输入内容后搜索
from time import sleep from selenium import webdriver br = webdriver.Chrome() url = "https://ww ...
- django环境安装与项目创建方式
1.安装django pip install django2.检查django版本 : python -m django --version 3.创建项目 django-admin startproj ...
- Vue踩坑日记-This dependency was not found:element-ui.js
该问题为在Vue启动项目时候报错找不到element-ui模块 解决办法:打开CMD 控制台 CD到项目根目录 我的目录(C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\cms-heli ...
