Codeforces Round #318(Div 1) 573A, 573B,573C
转载请注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/fraud/ ——by fraud
这场的前两题完全是手速题。。。A题写了7分钟,交的时候已经500+了,好在B题出的速度勉强凑活吧,and C题也没有FST
Limak is an old brown bear. He often plays poker with his friends. Today they went to a casino. There are n players (including Limak himself) and right now all of them have bids on the table. i-th of them has bid with size ai dollars.
Each player can double his bid any number of times and triple his bid any number of times. The casino has a great jackpot for making all bids equal. Is it possible that Limak and his friends will win a jackpot?
First line of input contains an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 105), the number of players.
The second line contains n integer numbers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the bids of players.
Print "Yes" (without the quotes) if players can make their bids become equal, or "No" otherwise.
4
75 150 75 50
Yes
3
100 150 250
No
In the first sample test first and third players should double their bids twice, second player should double his bid once and fourth player should both double and triple his bid.
It can be shown that in the second sample test there is no way to make all bids equal.
A题没啥好说的,把因为可以乘2或乘三,那只要看看除了2和3之外,其他的因子是否相同即可
//#####################
//Author:fraud
//Blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/fraud/
//#####################
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <ios>
#include <iomanip>
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
#define XINF INT_MAX
#define INF 0x3FFFFFFF
#define mp(X,Y) make_pair(X,Y)
#define pb(X) push_back(X)
#define rep(X,N) for(int X=0;X<N;X++)
#define rep2(X,L,R) for(int X=L;X<=R;X++)
#define dep(X,R,L) for(int X=R;X>=L;X--)
#define clr(A,X) memset(A,X,sizeof(A))
#define IT iterator
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef vector<PII> VII;
typedef vector<int> VI;
int a[];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
cin>>n;
rep(i,n){
cin>>a[i];
while(a[i]%==)a[i]/=;
while(a[i]%==)a[i]/=;
}
int ff = ;
rep(i,n-)if(a[i]!=a[i+])ff = ;
if(ff)cout<<"No"<<endl;
else cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
return ;
}
代码君
Limak is a little bear who loves to play. Today he is playing by destroying block towers. He built n towers in a row. The i-th tower is made of hi identical blocks. For clarification see picture for the first sample.
Limak will repeat the following operation till everything is destroyed.
Block is called internal if it has all four neighbors, i.e. it has each side (top, left, down and right) adjacent to other block or to the floor. Otherwise, block is boundary. In one operation Limak destroys all boundary blocks. His paws are very fast and he destroys all those blocks at the same time.
Limak is ready to start. You task is to count how many operations will it take him to destroy all towers.
The first line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105).
The second line contains n space-separated integers h1, h2, ..., hn (1 ≤ hi ≤ 109) — sizes of towers.
Print the number of operations needed to destroy all towers.
6
2 1 4 6 2 2
3
7
3 3 3 1 3 3 3
2
The picture below shows all three operations for the first sample test. Each time boundary blocks are marked with red color.
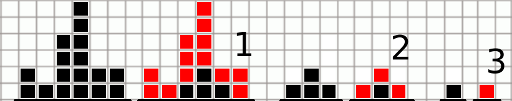 After first operation there are four blocks left and only one remains after second operation. This last block is destroyed in third operation.
After first operation there are four blocks left and only one remains after second operation. This last block is destroyed in third operation.
同样很水,从左到右以及从右到左各扫一遍即可
//#####################
//Author:fraud
//Blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/fraud/
//#####################
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <ios>
#include <iomanip>
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
#define XINF INT_MAX
#define INF 0x3FFFFFFF
#define mp(X,Y) make_pair(X,Y)
#define pb(X) push_back(X)
#define rep(X,N) for(int X=0;X<N;X++)
#define rep2(X,L,R) for(int X=L;X<=R;X++)
#define dep(X,R,L) for(int X=R;X>=L;X--)
#define clr(A,X) memset(A,X,sizeof(A))
#define IT iterator
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef vector<PII> VII;
typedef vector<int> VI;
int h[];
int dp[];
int dp2[];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
cin>>n;
rep(i,n)cin>>h[i];
int maxx = ;
dp[] = dp2[n-] = ;
rep2(i,,n-)dp[i] = min(h[i],dp[i-]+);
dep(i,n-,)dp2[i] = min(h[i],dp2[i+]+);
rep(i,n)dp[i] = min(dp[i],dp2[i]);
rep(i,n)maxx = max(dp[i],maxx);
cout<<maxx<<endl;
return ;
}
代码君
Limak is a little bear who learns to draw. People usually start with houses, fences and flowers but why would bears do it? Limak lives in the forest and he decides to draw a tree.
Recall that tree is a connected graph consisting of n vertices and n - 1 edges.
Limak chose a tree with n vertices. He has infinite strip of paper with two parallel rows of dots. Little bear wants to assign vertices of a tree to some n distinct dots on a paper so that edges would intersect only at their endpoints — drawn tree must be planar. Below you can see one of correct drawings for the first sample test.

Is it possible for Limak to draw chosen tree?
The first line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105).
Next n - 1 lines contain description of a tree. i-th of them contains two space-separated integers ai and bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n, ai ≠ bi) denoting an edge between vertices ai and bi. It's guaranteed that given description forms a tree.
Print "Yes" (without the quotes) if Limak can draw chosen tree. Otherwise, print "No" (without the quotes).
8
1 2
1 3
1 6
6 4
6 7
6 5
7 8
Yes
13
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 5
2 6
2 7
3 8
3 9
3 10
4 11
4 12
4 13
No
一开始少考虑了一些,然后只是判断儿子不符合的情况,然后还有一些漏考虑的细节。
统计有多少个一定要占一半边的子树,如果超过两个,那就是不符合的。
树形dp,第一次dfs统计好所有子树,第二遍,把根的信息传下来一起考虑就ok了。
//#####################
//Author:fraud
//Blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/fraud/
//#####################
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <ios>
#include <iomanip>
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
#define XINF INT_MAX
#define INF 0x3FFFFFFF
#define mp(X,Y) make_pair(X,Y)
#define pb(X) push_back(X)
#define rep(X,N) for(int X=0;X<N;X++)
#define rep2(X,L,R) for(int X=L;X<=R;X++)
#define dep(X,R,L) for(int X=R;X>=L;X--)
#define clr(A,X) memset(A,X,sizeof(A))
#define IT iterator
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef vector<PII> VII;
typedef vector<int> VI;
vector<int>G[];
int dp[];
int ff = ;
void dfs(int u,int fa){
int num = ;
int sz = G[u].size();
rep(i,sz){
int v = G[u][i];
if(v == fa)continue;
dfs(v,u);
dp[u] += dp[v];
num++;
}
if(!dp[u])dp[u] = ;
if(dp[u] == && num == )dp[u]++;
}
void dfs2(int u,int fa,int num){
int sz = G[u].size();
int n = ;
if(num>)n++;
rep(i,sz){
int v = G[u][i];
if(v == fa)continue;
int tmp = ;
tmp = max(num+dp[u]-dp[v],tmp);
if(tmp == && num == )tmp = ;
dfs2(v,u,tmp);
if(dp[v]>)n++;
}
if(n>)ff = ;
} int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
cin>>n;
int u,v;
rep(i,n-){
cin>>u>>v;
u--;v--;
G[u].pb(v);
G[v].pb(u);
}
dfs(,-);
dfs2(,-,); if(ff)cout<<"No"<<endl;
else cout<<"Yes"<<endl; return ;
}
Codeforces Round #318(Div 1) 573A, 573B,573C的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #318 (Div. 2) D Bear and Blocks (数学)
不难发现在一次操作以后,hi=min(hi-1,hi-1,hi+1),迭代这个式子得到k次操作以后hi=min(hi-j-(k-j),hi-k,hi+j-(k-j)),j = 1,2,3... 当k ...
- Codeforces Round #318 (Div. 2) B Bear and Three Musketeers (暴力)
算一下复杂度.发现可以直接暴.对于u枚举a和b,判断一下是否连边,更新答案. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int n,m; ; ...
- Codeforces Round #318 (Div. 2) A Bear and Elections (优先队列模拟,水题)
优先队列模拟一下就好. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; priority_queue<int>q; int main( ...
- Codeforces Round #318 (Div. 2) C Bear and Poker (数学)
简单题,求一下所有数的2和3的幂是任意调整的,把2和3的因子除掉以后必须相等. 求lcm,爆了long long.我得好好反省一下,对连乘不敏感 #include<bits/stdc++.h&g ...
- Codeforces Round #366 (Div. 2) ABC
Codeforces Round #366 (Div. 2) A I hate that I love that I hate it水题 #I hate that I love that I hate ...
- Codeforces Round #354 (Div. 2) ABCD
Codeforces Round #354 (Div. 2) Problems # Name A Nicholas and Permutation standard input/out ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)
直达–>Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) A Brain’s Photos 给你一个NxM的矩阵,一个字母代表一种颜色,如果有”C”,”M”,”Y”三种中任意一种就输 ...
- cf之路,1,Codeforces Round #345 (Div. 2)
cf之路,1,Codeforces Round #345 (Div. 2) ps:昨天第一次参加cf比赛,比赛之前为了熟悉下cf比赛题目的难度.所以做了round#345连试试水的深浅..... ...
- Codeforces Round #279 (Div. 2) ABCDE
Codeforces Round #279 (Div. 2) 做得我都变绿了! Problems # Name A Team Olympiad standard input/outpu ...
随机推荐
- phplib template说明
phplib template phplib有五大功能:将数据库驱动和对数据库操作完全分离:支持session:权限许可:模板:购物 车 说明:1.第一个简单的模板页first.html模板中的{ma ...
- macbook air 安装win7系统时,到最后一步要进入win7,需要给PC设置一个用户名,键盘没反应
从 bootcamp安装:1.一定要同时选中第一项 制作usb安装盘和第二项 从网上下载最新的windows支持软件,2.然后再选第三项 安装winDows,3.当进入安装界面时选择你要安装的boot ...
- Docker for Windows
Docker for Windows使用简介 在上一篇文章中,通过演练指导的方式,介绍了在Docker中运行ASP.NET Core Web API应用程序的过程.本文将介绍Docker for Wi ...
- i++ 与 ++i 的从字节码层面看二者的区别
/** * javap命令可以对class反汇编得到其字节码文件(此命令并不是jdk8开始的,只不过jdk8中对工具进行加强,增加了一些参数,可通过 javap -help了解) * * 注意: * ...
- 周末献礼 MyVoix2.0.js 麦克风波形绘制(一)
最近更新了之前发布的语音识别框架MyVoix,加入了麦克风的波形分析效果.没有看过MyVoix介绍的同学请猛戳(传送门) Github地址 在新的更新中,波形分析可以绑定麦克风源,也可以单独配合别的音 ...
- git操作的各种命令整理
1.常用的Git命令 命令 简要说明 git add 添加至暂存区 git add–interactive 交互式添加 git apply 应用补丁 git am 应用邮件格式补丁 git ann ...
- Android 用户登录
1:服务端代码如下 <?php /** *登录成功就返回 1,否则返回 0 */ $REQUEST_METHOD=$_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD']; if($REQUEST_ ...
- android ftp案例分析
使用方法: FTPClient client = new FTPClient(); client.connect("ftp.host.com", 8021); client.log ...
- P0口上拉电阻选择
如果是驱动led,那么用1K左右的就行了.如果希望亮度大一些,电阻可减小,最小不要小于200欧姆,否则电流太大:如果希望亮度小一些,电阻可增大,增加到多少呢,主要看亮度情况,以亮度合适为准,一般来说超 ...
- COJ 0260 HDNOIP201204四个国王
HDNOIP201204四个国王 难度级别:A: 运行时间限制:1000ms: 运行空间限制:51200KB: 代码长度限制:2000000B 试题描述 在N*M的棋盘上摆国际象棋中的“国王”.如果两 ...
