yarn_action
https://maprdocs.mapr.com/home/AdministratorGuide/ResourceAllocation-YARNContainer.html
yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb
yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb
A YARN application can be a MapReduce v2 application or a non-MapReduce application. The Warden on each node calculates the resources that can be allocated to process YARN applications. Each application has an Application Master that negotiates YARN container resources. For MapReduce applications, YARN processes each map or reduce task in a container. The Application Master requests resources from the Resource Manager based on memory, CPU, and disk requirements for the YARN containers. For YARN containers that process MapReduce v2 tasks, there are additional considerations. See YARN Container Resource Allocation for MapReduce v2 Applications for details.
https://maprdocs.mapr.com/home/AdministratorGuide/ResourceAllocation-MRv2Apps.html#ResourceAllocationforJobs_26983357-d3e431
YARN Container Resources for MapReduce v2 Applications
In addition to the YARN container resource allocation parameters, the MapReduce ApplicationMaster also considers the following container requirements when it sends requests to the ResourceManager for containers to run MapReduce jobs:
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
1024 | Defines the container size for map tasks in MB. |
mapreduce.reduce.memory.mb |
3072 |
Defines the container size for reduce tasks in MB. |
mapreduce.reduce.java.opts |
-Xmx2560m | Java options for reduce tasks. |
mapreduce.map.java.opts |
-Xmx900m | Java options for map tasks. |
|
|
0.5 |
Defines the number of disks a map task requires. For example, a node with 4 disks can run 8 map tasks at a time. Note: If I/O intensive tasks do not run on the node, you may want to change this value. |
|
|
1.33 |
Defines the number of disks that a reduce task requires. For example, a node with 4 disks can run 3 reduce tasks at a time. Note: If I/O intensive tasks do not run on the node, you might want to change this value. |
You can use one of the following methods to change the default configuration:
- Provide updated values in the
mapred-site.xmlfile on the node that runs the job. You can use central configuration to change this value on each node that runs the NodeManager in the cluster. Then, restart NodeManager on each node in the cluster. Themapred-site.xmlfile for MapReduce ve applications is located in the following directory:opt/mapr/hadoop/hadoop-2.x.x/etc/hadoop
- Override the default values from the command line for each application that requires a non-default value.
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/FairScheduler.html
【默认仅分配内存】
Fair scheduling is a method of assigning resources to applications such that all apps get, on average, an equal share of resources over time. Hadoop NextGen is capable of scheduling multiple resource types. By default, the Fair Scheduler bases scheduling fairness decisions only on memory. It can be configured to schedule with both memory and CPU, using the notion of Dominant Resource Fairness developed by Ghodsi et al. When there is a single app running, that app uses the entire cluster. When other apps are submitted, resources that free up are assigned to the new apps, so that each app eventually on gets roughly the same amount of resources. Unlike the default Hadoop scheduler, which forms a queue of apps, this lets short apps finish in reasonable time while not starving long-lived apps. It is also a reasonable way to share a cluster between a number of users. Finally, fair sharing can also work with app priorities - the priorities are used as weights to determine the fraction of total resources that each app should get.
【单一队列】
The scheduler organizes apps further into “queues”, and shares resources fairly between these queues. By default, all users share a single queue, named “default”. If an app specifically lists a queue in a container resource request, the request is submitted to that queue. It is also possible to assign queues based on the user name included with the request through configuration. Within each queue, a scheduling policy is used to share resources between the running apps. The default is memory-based fair sharing, but FIFO and multi-resource with Dominant Resource Fairness can also be configured. Queues can be arranged in a hierarchy to divide resources and configured with weights to share the cluster in specific proportions.
In addition to providing fair sharing, the Fair Scheduler allows assigning guaranteed minimum shares to queues, which is useful for ensuring that certain users, groups or production applications always get sufficient resources. When a queue contains apps, it gets at least its minimum share, but when the queue does not need its full guaranteed share, the excess is split between other running apps. This lets the scheduler guarantee capacity for queues while utilizing resources efficiently when these queues don’t contain applications.
【限制单用户单队列的应用数】
The Fair Scheduler lets all apps run by default, but it is also possible to limit the number of running apps per user and per queue through the config file. This can be useful when a user must submit hundreds of apps at once, or in general to improve performance if running too many apps at once would cause too much intermediate data to be created or too much context-switching. Limiting the apps does not cause any subsequently submitted apps to fail, only to wait in the scheduler’s queue until some of the user’s earlier apps finish.
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YARN.html
The ResourceManager has two main components: Scheduler and ApplicationsManager.
【仅调度,不监控和追踪应用状态,不处理应用故障和硬件故障】
The Scheduler is responsible for allocating resources to the various running applications subject to familiar constraints of capacities, queues etc. The Scheduler is pure scheduler in the sense that it performs no monitoring or tracking of status for the application. Also, it offers no guarantees about restarting failed tasks either due to application failure or hardware failures. The Scheduler performs its scheduling function based on the resource requirements of the applications; it does so based on the abstract notion of a resource Container which incorporates elements such as memory, cpu, disk, network etc.
The Scheduler has a pluggable policy which is responsible for partitioning the cluster resources among the various queues, applications etc. The current schedulers such as the CapacityScheduler and the FairScheduler would be some examples of plug-ins.
【应用管理者重启容器】
The ApplicationsManager is responsible for accepting job-submissions, negotiating the first container for executing the application specific ApplicationMaster and provides the service for restarting the ApplicationMaster container on failure. The per-application ApplicationMaster has the responsibility of negotiating appropriate resource containers from the Scheduler, tracking their status and monitoring for progress.
【支持资源预留】
MapReduce in hadoop-2.x maintains API compatibility with previous stable release (hadoop-1.x). This means that all MapReduce jobs should still run unchanged on top of YARN with just a recompile.
YARN supports the notion of resource reservation via the ReservationSystem, a component that allows users to specify a profile of resources over-time and temporal constraints (e.g., deadlines), and reserve resources to ensure the predictable execution of important jobs.The ReservationSystem tracks resources over-time, performs admission control for reservations, and dynamically instruct the underlying scheduler to ensure that the reservation is fullfilled.
In order to scale YARN beyond few thousands nodes, YARN supports the notion of Federation via the YARN Federation feature. Federation allows to transparently wire together multiple yarn (sub-)clusters, and make them appear as a single massive cluster. This can be used to achieve larger scale, and/or to allow multiple independent clusters to be used together for very large jobs, or for tenants who have capacity across all of them.
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YARN.html
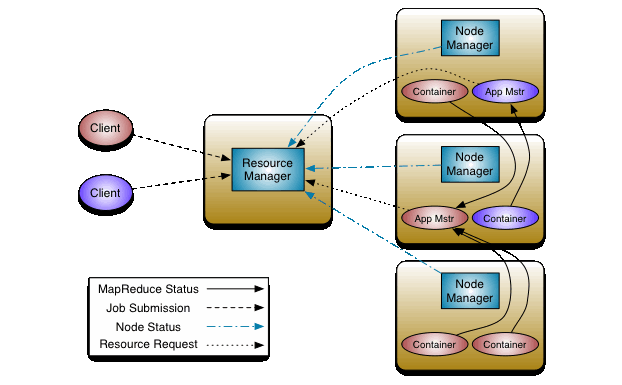
The fundamental idea of YARN is to split up the functionalities of resource management and job scheduling/monitoring into separate daemons. The idea is to have a global ResourceManager (RM) and per-application ApplicationMaster (AM). An application is either a single job or a DAG of jobs.
The ResourceManager and the NodeManager form the data-computation framework. The ResourceManager is the ultimate authority that arbitrates resources among all the applications in the system. The NodeManager is the per-machine framework agent who is responsible for containers, monitoring their resource usage (cpu, memory, disk, network) and reporting the same to the ResourceManager/Scheduler.
The per-application ApplicationMaster is, in effect, a framework specific library and is tasked with negotiating resources from the ResourceManager and working with the NodeManager(s) to execute and monitor the tasks.
yarn_action的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- Codeforces 734C [水][暴力][贪心]
题意: 要生产n个物品,每个花费时间为x. 有两种魔法,每种最多使用1个. 其中第一种魔法可以使每个物品生产的花费时间变为ai,相应的花费是bi;第二种魔法可以减少ci个物品,相应的花费是di,并且保 ...
- mysql事物隔离级别
mysql实现了四种隔离级别 Read Uncommitted(未提交读) 在该隔离级别,所有事务都可以看到其他未提交事务的执行结果.本隔离级别很少用于实际应用,因为它的性能也不比其他级别好多少.读取 ...
- 开源日历TimesSquare在iOS7下诡异渲染的解决办法
因为没有时间自己写一个日历,所以暂时使用了一个三方的日历https://github.com/square/objc-TimesSquare 但是在iOS7下.突然产生了一个诡异的BUG..如下图: ...
- JAVAWEB开发之JSP、EL、及会话技术(Cookie和Session)的使用详解
Servlet的缺点 开发人员要十分熟悉JAVA 不利于页面调试和维护(修改,重新编译) 很难利用网页设计工具进行页面设计(HTML内容导入到servlet中,用PrintWriter的对象进行输出) ...
- Oracle中group by 的扩展函数rollup、cube、grouping sets
Oracle的group by除了基本使用方法以外,还有3种扩展使用方法,各自是rollup.cube.grouping sets.分别介绍例如以下: 1.rollup 对数据库表emp.如果当中两个 ...
- hdu-5015-233 Matrix-矩阵
非常显然矩阵的第一列为: 0 a[1] a[2] a[3] a[4] 我们转化一下,转化为 23 a[1] a[2] a[3] a[4] 3 那么由第一列转移到第二列则为 23*10+3 a[1]+2 ...
- XML基础知识学习
概念: XML 指可扩展标记语言 XML 是一种标记语言,非常类似 HTML ,文本文件. XML 的设计宗旨是数据传输,而非显示数据 .存储和传输复杂的关系模型数据 XML 标签没有被提前定义 使用 ...
- 使用Hadoop自己的类操作HDFS
package hdfs; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.I ...
- 阿里云服务器教程–SSH 登录时出现如下错误:Host key verification failed
注意:本文相关 Linux 配置及说明已在 CentOS 6.5 64 位操作系统中进行过测试.其它类型及版本操作系统配置可能有所差异,具体情况请参阅相应操作系统官方文档. 问题描述 使用 SSH 登 ...
- 强大易用的日期和时间库 Joda Time
Joda-Time提供了一组Java类包用于处理包括ISO8601标准在内的date和time.可以利用它把JDK Date和Calendar类完全替换掉,而且仍然能够提供很好的集成,并且它是线程安全 ...
