201772020113李清华《面向对象程序设计(java)》第九周学习总结
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握java异常处理技术;
(2) 了解断言的用法;
(3) 了解日志的用途;
(4) 掌握程序基础调试技巧;
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:用命令行与IDE两种环境下编辑调试运行源程序ExceptionDemo1、ExceptionDemo2,结合程序运行结果理解程序,掌握未检查异常和已检查异常的区别。
|
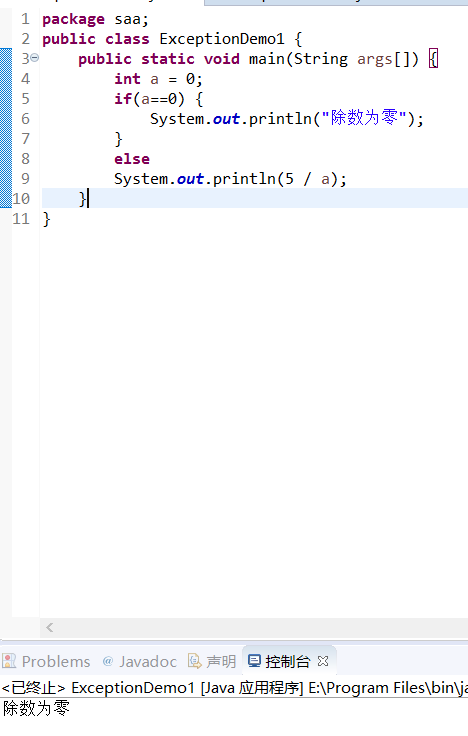
//异常示例1 public class ExceptionDemo1 { public static void main(String args[]) { int a = 0; System.out.println(5 / a); } } |
|
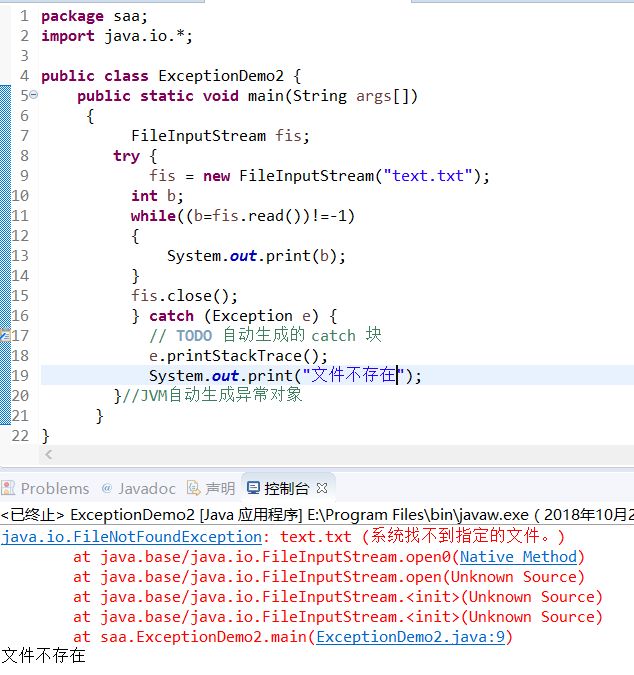
//异常示例2 import java.io.*; public class ExceptionDemo2 { public static void main(String args[]) { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt");//JVM自动生成异常对象 int b; while((b=fis.read())!=-1) { System.out.print(b); } fis.close(); } } |
实验结果:未检查异常:


修改后:
实验2: 导入以下示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 在elipse IDE中编辑、编译、调试运行教材281页7-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
l 掌握Throwable类的堆栈跟踪方法;
package stackTrace; import java.util.*; /**
* A program that displays a trace feature of a recursive method call.
* @version 1.01 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class StackTraceTest
{
/**
* Computes the factorial of a number
* @param n a non-negative integer
* @return n! = 1 * 2 * . . . * n
*/
public static int factorial(int n)
{
System.out.println("factorial(" + n + "):");
Throwable t = new Throwable();
StackTraceElement[] frames = t.getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement f : frames)
System.out.println(f);
int r;
if (n <= 1) r = 1;
else r = n * factorial(n - 1);
System.out.println("return " + r);
return r;
} public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter n: ");
int n = in.nextInt();
factorial(n);
}
}
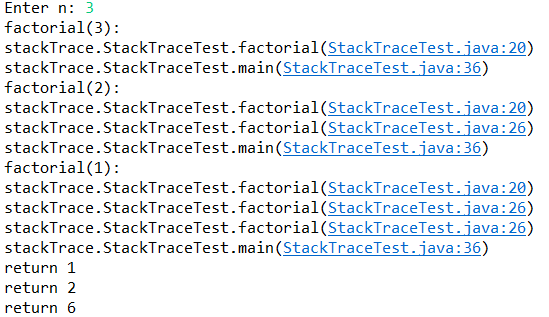
测试程序2:
l Java语言的异常处理有积极处理方法和消极处理两种方式;
l 下列两个简答程序范例给出了两种异常处理的代码格式。在elipse IDE中编辑、调试运行源程序ExceptionalTest.java,将程序中的text文件更换为身份证号.txt,要求将文件内容读入内容,并在控制台显示;
掌握两种异常处理技术的特点。
|
//积极处理方式 import java.io.*; class ExceptionTest { public static void main (string args[]) { try{ FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt"); } catch(FileNotFoundExcption e) { …… } …… } } |
|
//消极处理方式 import java.io.*; class ExceptionTest { public static void main (string args[]) throws FileNotFoundExcption { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt"); } } |
//积极处理方式
package aaa;
import java.io.*;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String args[])
{
FileInputStream fis;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("text.txt");
int b;
while((b=fis.read())!=-1)
{
System.out.print(b);
}
fis.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}//JVM自动生成异常对象
}
}
//消极处理方式
package aaa;
import java.io.*;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
FileInputStream fis;
fis = new FileInputStream("text.txt");
int b;
while((b=fis.read())!=-1)
{
System.out.print(b);
}
fis.close();
}
}


实验3: 编程练习
练习1:
l 编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
l 按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
l 查询最大年龄的人员信息;
l 查询最小年龄人员信息;
l 输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
l 查询人员中是否有你的同乡;
l 在以上程序适当位置加入异常捕获代码。
package test1; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{
private static ArrayList<Student> studentlist;
public static void main(String[] args) {
studentlist = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("F:\\身份证号.txt");
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String number = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String province =linescanner.nextLine();
Student student = new Student();
student.setName(name);
student.setnumber(number);
student.setsex(sex);
int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
student.setage(a);
student.setprovince(province);
studentlist.add(student); }
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("学生信息文件找不到");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean isTrue = true;
while (isTrue) {
System.out.println("选择你的操作,输入正确格式的选项");
System.out.println("A.按姓名字典排序");
System.out.println("B.输出年龄最大和年龄最小的人");
System.out.println("C.寻找老乡");
System.out.println("D.寻找年龄相近的人");
System.out.println("F.退出");
String m = scanner.next();
switch (m) {
case "A":
Collections.sort(studentlist);
System.out.println(studentlist.toString());
break;
case "B":
int max=0,min=100;
int j,k1 = 0,k2=0;
for(int i=1;i<studentlist.size();i++)
{
j=studentlist.get(i).getage();
if(j>max)
{
max=j;
k1=i;
}
if(j<min)
{
min=j;
k2=i;
} }
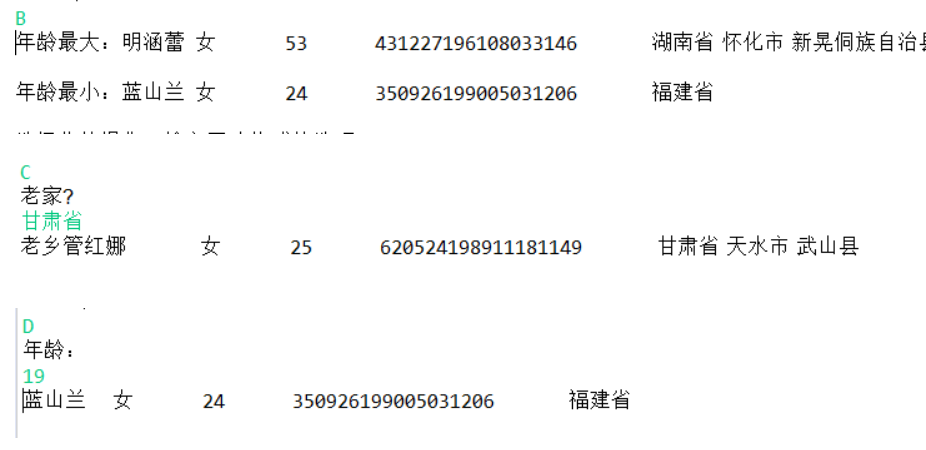
System.out.println("年龄最大:"+studentlist.get(k1));
System.out.println("年龄最小:"+studentlist.get(k2));
break;
case "C":
System.out.println("老家?");
String find = scanner.next();
String place=find.substring(0,3);
for (int i = 0; i <studentlist.size(); i++)
{
if(studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1,4).equals(place))
System.out.println("老乡"+studentlist.get(i));
}
break; case "D":
System.out.println("年龄:");
int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
int near=agenear(yourage);
int value=yourage-studentlist.get(near).getage();
System.out.println(""+studentlist.get(near));
break;
case "F":
isTrue = false;
System.out.println("退出程序!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误"); }
}
}
public static int agenear(int age) {
int j=0,min=53,value=0,k=0;
for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++)
{
value=studentlist.get(i).getage()-age;
if(value<0) value=-value;
if (value<min)
{
min=value;
k=i;
}
}
return k;
} }
package test1;
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private String number ;
private String sex ;
private int age;
private String province;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getnumber() {
return number;
}
public void setnumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getsex() {
return sex ;
}
public void setsex(String sex ) {
this.sex =sex ;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
// int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
this.age= age;
}
public String getprovince() {
return province;
}
public void setprovince(String province) {
this.province=province ;
}
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
}
public String toString() {
return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n";
}
}

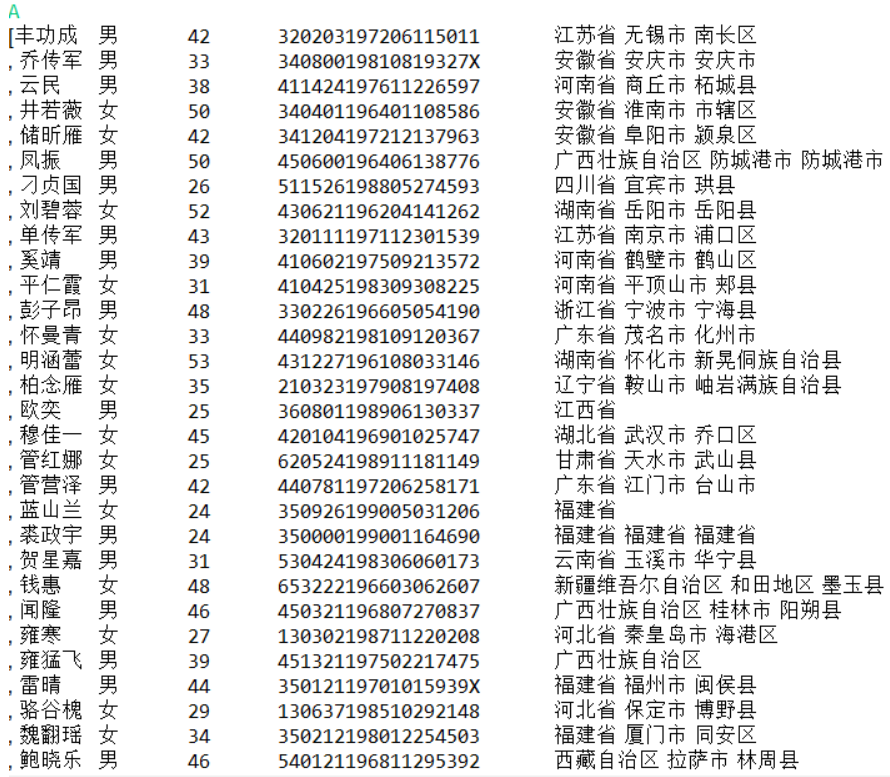
注:以下实验课后完成
练习2:
l 编写一个计算器类,可以完成加、减、乘、除的操作;
l 利用计算机类,设计一个小学生100以内数的四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
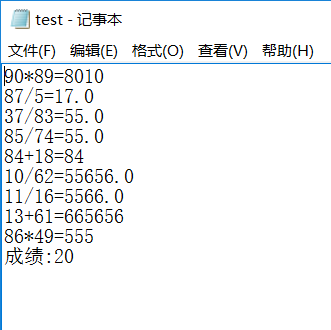
l 将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt;
l 在以上程序适当位置加入异常捕获代码。
实验4:断言、日志、程序调试技巧验证实验。
实验程序1:
|
//断言程序示例 public class AssertDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { test1(-5); test2(-3); }
private static void test1(int a){ assert a > 0; System.out.println(a); } private static void test2(int a){ assert a > 0 : "something goes wrong here, a cannot be less than 0"; System.out.println(a); } } |
l 在elipse下调试程序AssertDemo,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 注释语句test1(-5);后重新运行程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握断言的使用特点及用法。
package shiyan;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.PrintWriter; public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
PrintWriter output=new PrintWriter("E:/test.txt");
int sum=0;
jisuanji js=new jisuanji();
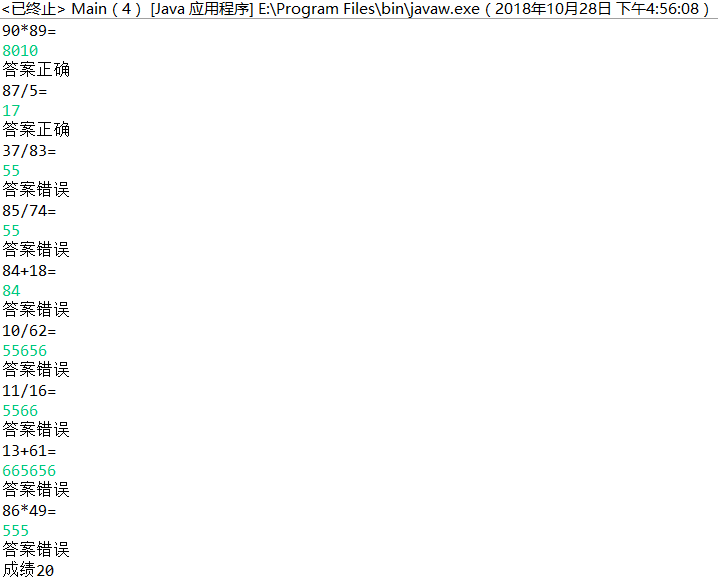
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int n = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3); switch(n)
{
case 1:
System.out.println(a+"/"+b+"=");
while(b==0){
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
double c = in.nextDouble();
output.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c);
if (c == js.chu(a,b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("答案错误");
} break; case 2:
System.out.println(a+"*"+b+"=");
int c1 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c1);
if (c1 == js.chen(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("答案错误");
}
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(a+"+"+b+"=");
int c2 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c2);
if (c2 == js.jia(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("答案错误");
} break ;
case 4:
System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"=");
int c3 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c3);
if (c3 == js.jian(a,b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("答案正确");
}
else {
System.out.println("答案错误");
}
break ; } }
System.out.println("成绩"+sum);
output.println("成绩:"+sum);
output.close();
}
}
package shiyan;
public class jisuanji {
private int a;
private int b;
public int jia(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
public int jian(int a,int b)
{
return a-b;
}
public int chen(int a,int b)
{
return a*b;
}
public int chu(int a,int b)
{
if(b==0)
{
return 0;
}
else
return a/b;
}
}
201772020113李清华《面向对象程序设计(java)》第九周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 20155312 2016-2017-2 《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
20155312 2016-2017-2 <Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 课堂内容总结 两个类有公用的东西放在父类里. 面向对象的三要素 封装 继承 多态:用父类声明引用,子类生成对象 ...
- 20155303 2016-2017-2 《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
20155303 2016-2017-2 <Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 目录 学习内容总结(Linux命令) 教材学习中的问题和解决过程 代码调试中的问题和解决过程 代码托管 上周考 ...
- 20155321 2016-2017-2 《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
20155321 2016-2017-2 <Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 JDBC简介 厂商在实现JDBC驱动程序时,依方式可将驱动程序分为四种类型: JDBC-OD ...
- 20145302张薇《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
20145302 <Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 第十六周 JDBC简介 撰写应用程序是利用通信协议对数据库进行指令交换,以进行数据的增删查找 JDBC目的:让Jav ...
- 20145213《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
20145213<Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 教材学习总结 "五一"假期过得太快,就像龙卷风.没有一点点防备,就与Java博客撞个满怀.在这个普天同庆的节日里,根 ...
- 21045308刘昊阳 《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
21045308刘昊阳 <Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 第16章 整合数据库 16.1 JDBC入门 16.1.1 JDBC简介 数据库本身是个独立运行的应用程序 撰 ...
- 20145337 《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
20145337 <Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 数据库本身是个独立运行的应用程序 撰写应用程序是利用通信协议对数据库进行指令交换,以进行数据的增删查找 JDBC可以 ...
- 《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
20145224 <Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 第十六章 整合数据库 JDBC入门 ·数据库本身是个独立运行的应用程序 ·撰写应用程序是利用通信协议对数据库进行指令交换,以进行数据的 ...
- 20145236 《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
20145236 <Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 第十六章 整合数据库 JDBC简介 1.JDBC是java联机数据库的标准规范.它定义了一组标准类与接口,标准API ...
- 201521123061 《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
201521123061 <Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 1. 本周学习总结 2. 书面作业 本次PTA作业题集异常 1.常用异常 题目5-1 1.1 截图你的提交结果(出现学号) 1 ...
随机推荐
- 学习笔记CB003:分块、标记、关系抽取、文法特征结构
分块,根据句子的词和词性,按照规则组织合分块,分块代表实体.常见实体,组织.人员.地点.日期.时间.名词短语分块(NP-chunking),通过词性标记.规则识别,通过机器学习方法识别.介词短语(PP ...
- layui layui.open弹窗后按enter键不停弹窗问题的解决
问题描述:layui.open弹窗后,点击enter键会不停弹窗,背景颜色变得越来越深 解决办法:1.使用回调函数让按钮失去焦点 var info = layer.open({ type: 2 , t ...
- Windows7 Autoconfiguration IPv4 Address 导致无法上网
Windows7 Autoconfiguration IPv4 Address 导致无法上 (2010-03-30 16:44:57) 转载▼ 标签: 杂谈 分类: 电脑软件问题 Windows7 A ...
- UnicodeEncodeError: 'ascii' codec can't encode characters in position 1-5: ordinal not in range(128)
原因是pip安装python包会加载我的用户目录,我的用户目录恰好是中文的,ascii不能编码.解决办法是: python目录 Python27\Lib\site-packages 建一个文件site ...
- 用于模拟百度分享的errno错误代码
0:成功;-1:由于您分享了违反相关法律法规的文件,分享功能已被禁用,之前分享出去的文件不受影响.;-2:用户不存在;请刷新页面后重试;-3:文件不存在;请刷新页面后重试;-4:登录信息有误,请重新登 ...
- Linux基础入门-基本概念及操作
桌面环境: KDE.GNOME.XFCE.LXDE 实验楼使用的是XFCE 终端: gnome-terminal, kconsole, xterm, rxvt, kvt, nxterm, eterm ...
- docker:构建nginx+php-fpm镜像(一):构建nginx自启动镜像
步骤一:手动安装nginx环境,并记录全过程: #使用yum更新系统 yum -y update #下面编译安装tengine,查看有哪些包需要安装 #安装wget包,用于获取安装软件包 yum ...
- python判断平台
网上找到的判断平台的方法,特此记录 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import platform osName = platform.system() if(osName == 'W ...
- HTML 理解标签 - 帧
帧 : frame(已弃用) 是一个HTML元素,它定义了可以显示另一个HTML文档的特定区域.一个框架应该用在一个框架内 <frameset> iframe 表示嵌套的浏览上下文,有效地 ...
- 你云我云•兄弟夜谈会 第三季 企业IT架构
你云我云•兄弟夜谈会 第三季 企业IT架构 你云我云•兄弟夜谈会 第二季 5G 你云我云•兄弟夜谈会 第一季 企业云 0. 概况 时间:2019年2月23日 22:00~23:30 主题:企业IT架构 ...
