Python Numpy-基础教程
1. 为什么要学习numpy?
- numpy可以对整个array进行复杂计算,而不需要像list一样写loop
- 它的
ndarray提供了快速的基于array的数值运算 - memory-efficient container that provides fast numerical operations
- 学习pandas的必备
证明numpy比list优秀:
import numpy as np
my_arr = np.arange(1000000)
my_list = list(range(1000000))
%time for _ in range(10): my_arr2 = my_arr * 2 # Wall time: 25 ms
%time for _ in range(10): my_list2 = [x * 2 for x in my_list] # Wall time: 933 ms
2. Numpy基本用法
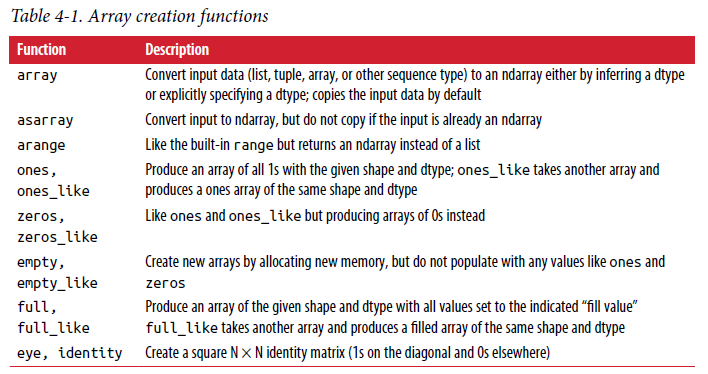
2.1. 创建np.ndarry
注意: numpy只能装同类型的数据
# Method 1: np.array()
## 1-D
a = np.array([1,2,3])
a.shape
a.dtype # int32, boolean, string, float
a.ndim
## 2-D
a = np.array([[0,1,2],[3,4,5]])
# Method 2:使用函数(arange, linspace, ones, zeros, eys, diag,random)创建
a = np.arange(10)
a = np.linspace(0,1,6, endpoint=False)
a = np.ones((3,3))
a = np.zeros((3,3))
a = np.eye(3)
a = np.diag(np.array([1,2,3,4]))
a = np.triu(np.ones((3,3)),1)
# Method 3: Random values
a = np.random.rand(4) # unifomr in [0,1]
a = np.random.randn(4) # Gaussian
np.random.seed(1234)
2.2. Indexing and Slicing
- Slice create a view on the original array(change will affect original array)
# 1-D
a = np.arange(10)
a[5], a[-1] # Index: 4,9
a[5:8] = 12 # Slice: all 5-8 is set as 12
arr[5:8].copy() # Slice without view
# 2-D
a = np.ones((3,3))
a[2] # second row
a[2].copy() # slice without view
a[0][2] # special value
a[:2]
a[:2, 1:] = 0
Boolean Index
names = np.array(['Bob', 'Joe', 'Will', 'Bob', 'Will', 'Joe', 'Joe'])
data = np.random.randn(7, 4)
data[names == 'Bob'] # select a row from data based on the if names equals Bob(boolean value)
data[~(names == 'Bob')] # not equal to Bob
data[(names == 'Bob') | (names == 'Will')] #e qual to Bob and Will
data[data<0] = 0
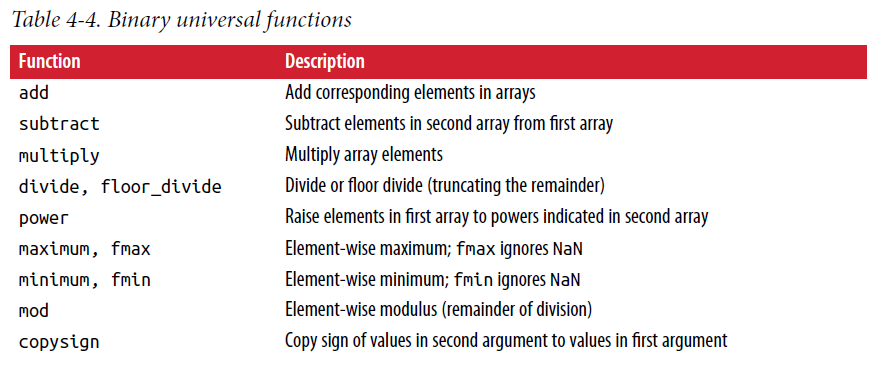
2.3. Universal Functions
a function that performs element-wise operations on data in ndarrays
a = np.arange(10)
b = np.arange(2,12)
# single
a + 1
a*2
np.sqrt(a)
np.exp(a)
np.sin(a)
# binary
a>b # return boolean ndarray
np.array_equal(a,b) # eual?
np.maximum(a, b) # find max value between each pair values
np.logical_or(a,b) # Attentions, a and b must be boolean array

2.4. Array-oriented
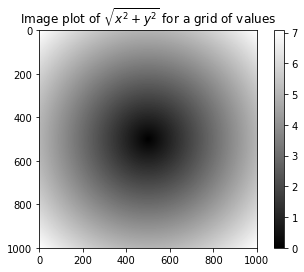
- Probelm 1
we wished to evaluate the function `sqrt(x^2 + y^2)`` across a regular grid of values.
The np.meshgrid function takes two 1D arrays and produces two 2D matrices corresponding to all pairs of (x, y) in the two arrays:
points = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.01) # 1000 equally spaced points
xs, ys = np.meshgrid(points, points)
z = np.sqrt(xs ** 2 + ys ** 2)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
plt.imshow(z, cmap=plt.cm.gray); plt.colorbar()
plt.title("Image plot of $\sqrt{x^2 + y^2}$ for a grid of values")
- Problem 2
we have two array(x,y) and one boolean array, we want select x if boolean=True, while select y if boolean=False->np.where()
xarr = np.array([1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5])
yarr = np.array([2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5])
cond = np.array([True, False, True, True, False])
result = np.where(cond, xarr, yarr) # array([1.1, 2.2, 1.3, 1.4, 2.5])
np.where的后面两个参数可以是array,数字. 是数字的话就可以做替换工作,比如我们将随机生成的array中大于0的替换为2,小于0的替换为-2
arr = np.random.randn(4, 4)
np.where(arr > 0, 2, -2) # 大于0改为2,小于0改为-2
np.where(arr > 0, 2, arr) # 大于0改为2,小于0不变
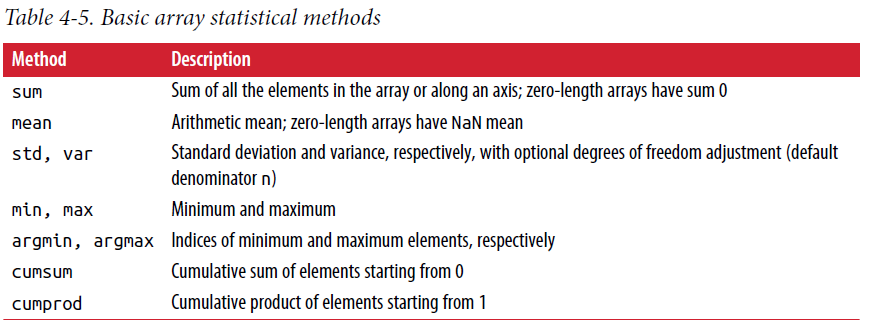
2.5. Mathematical Operations
a = np.random.randn(5, 4)
np.mean(a)
np.mean(a, axis = 1)
np.sum(a)
a.consum()
a.sort()
a.argmax() # index of maxium
names = np.array(['Bob', 'Joe', 'Will', 'Bob', 'Will', 'Joe', 'Joe'])
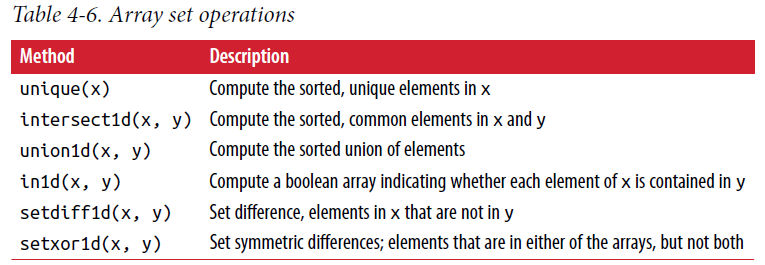
np.unique(names)
sorted(set(names))
Python Numpy-基础教程的更多相关文章
- Python Numpy基础教程
Python Numpy基础教程 本文是一个关于Python numpy的基础学习教程,其中,Python版本为Python 3.x 什么是Numpy Numpy = Numerical + Pyth ...
- Python数据分析基础教程
Python数据分析基础教程(第2版)(高清版)PDF 百度网盘 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1_FsReTBCaL_PzKhM0o6l0g 提取码:nkhw 复制这段内容后 ...
- Python机器学习基础教程-第2章-监督学习之决策树集成
前言 本系列教程基本就是摘抄<Python机器学习基础教程>中的例子内容. 为了便于跟踪和学习,本系列教程在Github上提供了jupyter notebook 版本: Github仓库: ...
- Python机器学习基础教程-第2章-监督学习之决策树
前言 本系列教程基本就是摘抄<Python机器学习基础教程>中的例子内容. 为了便于跟踪和学习,本系列教程在Github上提供了jupyter notebook 版本: Github仓库: ...
- Python机器学习基础教程-第2章-监督学习之线性模型
前言 本系列教程基本就是摘抄<Python机器学习基础教程>中的例子内容. 为了便于跟踪和学习,本系列教程在Github上提供了jupyter notebook 版本: Github仓库: ...
- Python机器学习基础教程-第2章-监督学习之K近邻
前言 本系列教程基本就是摘抄<Python机器学习基础教程>中的例子内容. 为了便于跟踪和学习,本系列教程在Github上提供了jupyter notebook 版本: Github仓库: ...
- Python机器学习基础教程-第1章-鸢尾花的例子KNN
前言 本系列教程基本就是摘抄<Python机器学习基础教程>中的例子内容. 为了便于跟踪和学习,本系列教程在Github上提供了jupyter notebook 版本: Github仓库: ...
- 小白必看Python视频基础教程
Python的排名从去年开始就借助人工智能持续上升,现在它已经成为了第一名.Python的火热,也带动了工程师们的就业热.可能你也想通过学习加入这个炙手可热的行业,可以看看Python视频基础教程,小 ...
- Python机器学习基础教程
介绍 本系列教程基本就是搬运<Python机器学习基础教程>里面的实例. Github仓库 使用 jupyternote book 是一个很好的快速构建代码的选择,本系列教程都能在我的Gi ...
- Python 3基础教程1-环境安装和运行环境
本系列开始介绍Python3的基础教程,为什么要选中Python 3呢?之前呢,学Python 2,看过笨方法学Python,学了不到一个礼拜,就开始用Python写Selenium脚本.最近看到一些 ...
随机推荐
- 实战!基于lamp安装Discuz论坛-技术流ken
简介 我前面的博客已经详细介绍了lamp采用yum安装以及编译安装的方式,这篇博客将基于yum安装的lamp架构来实战安装Discuz论坛,你可以任选其一来完成. 系统环境 centos7.5 服务器 ...
- SpringBoot系列——快速构建项目
前言 springboot官方参考指南:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.1.0.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/ Spri ...
- Linux学习笔记之基本指令
1.ll 注:详细展示当前文件夹下的所有文件及目录 ,与 ls -al 有异曲同工的作用 2.free -m/-h 注:-m:显示当前的内存信息,-m表示以MB为单位显示:-h:以人类能读懂的形式显 ...
- Spring核心——设计模式与IoC
“Spring”——每一个Javaer开发者都绕不开的字眼,从21世纪第一个十年国内异常活跃的SSH框架,到现在以Spring Boot作为入口粘合了各种应用.Spring现在已经完成了从web入口到 ...
- Field 'id' doesn't have a default value错误解决方法
Field 'id' doesn't have a default value 错误提示. 主键类型获取方式为"native"由数据库生成指定. 检查发现数据库中已存在Employ ...
- Dom对象的研究
1.逻辑运算 || && ! 1||2 5&&4 !0 || 遇到第一个为true 的数字就终止并返回 && 遇到第一个为false ...
- [算法总结] 13 道题搞定 BAT 面试——字符串
1. KMP 算法 谈到字符串问题,不得不提的就是 KMP 算法,它是用来解决字符串查找的问题,可以在一个字符串(S)中查找一个子串(W)出现的位置.KMP 算法把字符匹配的时间复杂度缩小到 O(m+ ...
- Java8 Optional类
概述 到目前为止,著名的NullPointerException是导致Java应用程序失败的最常见原因.过去,为了解决空指针异常,Google公司著名的Guava项目引入了Optional类,Guav ...
- 如何处理Express异常?
译者按:根据墨菲定律:“有可能出错的事情,就会出错”.那么,既然代码必然会出错,我们就应该处理好异常. 原文: How to handle errors in Express 译者:Fundebug ...
- vuejs2.0实现分页组件,使用$emit进行事件监听数据传递
上一篇文章介绍了vuejs实现的简单分页,如果我有几个页面都需要有分页效果,不可能每个页面都去复制一下这段代码吧,意思是封装一下,变成通用的组件. 首先使用基础 Vue 构造器,创建一个“子类”,Vu ...
