The Qt Resource System
The Qt Resource System
The Qt resource system is a platform-independent mechanism for storing binary files in the application's executable. This is useful if your application always needs a certain set of files (icons, translation files, etc.) and you don't want to run the risk of losing the files.
The resource system is based on tight cooperation between qmake, rcc (Qt's resource compiler), and QFile.
Resource Collection Files (.qrc)
The resources associated with an application are specified in a .qrc file, an XML-based file format that lists files on the disk and optionally assigns them a resource name that the application must use to access the resource.
Here's an example .qrc file:
<!DOCTYPE RCC><RCC version="1.0">
<qresource>
<file>images/copy.png</file>
<file>images/cut.png</file>
<file>images/new.png</file>
<file>images/open.png</file>
<file>images/paste.png</file>
<file>images/save.png</file>
</qresource>
</RCC>
The resource files listed in the .qrc file are files that are part of the application's source tree. The specified paths are relative to the directory containing the .qrc file. Note that the listed resource files must be located in the same directory as the .qrc file, or one of its subdirectories.
Resource data can either be compiled into the binary and thus accessed immediately in application code, or a binary resource can be created and at a later point in application code registered with the resource system.
By default, resources are accessible in the application under the same file name as they have in the source tree, with a :/ prefix, or by a URLwith a qrc scheme.
For example, the file path :/images/cut.png or the URL qrc:///images/cut.png would give access to the cut.png file, whose location in the application's source tree is images/cut.png. This can be changed using the file tag's alias attribute:
<file alias="cut-img.png">images/cut.png</file>
The file is then accessible as :/cut-img.png from the application. It is also possible to specify a path prefix for all files in the .qrc file using the qresource tag's prefix attribute:
<qresource prefix="/myresources">
<file alias="cut-img.png">images/cut.png</file>
</qresource>
In this case, the file is accessible as :/myresources/cut-img.png.
Some resources need to change based on the user's locale, such as translation files or icons. This is done by adding a lang attribute to the qresource tag, specifying a suitable locale string. For example:
<qresource>
<file>cut.jpg</file>
</qresource>
<qresource lang="fr">
<file alias="cut.jpg">cut_fr.jpg</file>
</qresource>
If the user's locale is French (i.e., QLocale::system().name() returns "fr_FR"), :/cut.jpg becomes a reference to the cut_fr.jpg image. For other locales, cut.jpg is used.
See the QLocale documentation for a description of the format to use for locale strings.
External Binary Resources
For an external binary resource to be created you must create the resource data (commonly given the .rcc extension) by passing the -binary switch to rcc. Once the binary resource is created you can register the resource with the QResource API.
For example, a set of resource data specified in a .qrc file can be compiled in the following way:
rcc -binary myresource.qrc -o myresource.rcc
In the application, this resource would be registered with code like this:
QResource::registerResource("/path/to/myresource.rcc");
Compiled-In Resources
For a resource to be compiled into the binary the .qrc file must be mentioned in the application's .pro file so that qmake knows about it. For example:
RESOURCES = application.qrc
qmake will produce make rules to generate a file called qrc_application.cpp that is linked into the application. This file contains all the data for the images and other resources as static C++ arrays of compressed binary data. The qrc_application.cpp file is automatically regenerated whenever the .qrc file changes or one of the files that it refers to changes. If you don't use .pro files, you can either invoke rccmanually or add build rules to your build system.
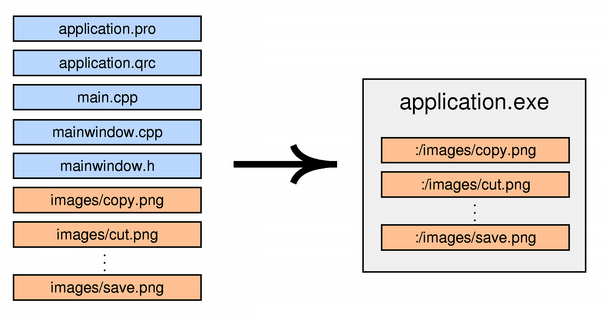
Currently, Qt always stores the data directly in the executable, even on Windows, macOS, and iOS, where the operating system provides native support for resources. This might change in a future Qt release.
Compression
Resources are compressed by default (in the ZIP format). It is possible to turn off compression. This can be useful if your resources already contain a compressed format, such as .png files. You do this by giving the -no-compress command line argument.
rcc -no-compress myresources.qrc
rcc also gives you some control over the compression. You can specify the compression level and the threshold level to consider while compressing files, for example:
rcc -compress 2 -threshold 3 myresources.qrc
Using Resources in the Application
In the application, resource paths can be used in most places instead of ordinary file system paths. In particular, you can pass a resource path instead of a file name to the QIcon, QImage, or QPixmap constructor:
cutAct = new QAction(QIcon(":/images/cut.png"), tr("Cu&t"), this);
See the Application example for an actual application that uses Qt's resource system to store its icons.
In memory, resources are represented by a tree of resource objects. The tree is automatically built at startup and used by QFile for resolving paths to resources. You can use a QDir initialized with ":/" to navigate through the resource tree from the root.
Qt's resources support the concept of a search path list. If you then refer to a resource with : instead of :/ as the prefix, the resource will be looked up using the search path list. The search path list is empty at startup; call QDir::addSearchPath() to add paths to it.
Using Resources in a Library
If you have resources in a library, you need to force initialization of your resources by calling Q_INIT_RESOURCE() with the base name of the .qrc file. For example:
MyClass::MyClass() : BaseClass()
{
Q_INIT_RESOURCE(resources); QFile file(":/myfile.dat");
...
}
This ensures that the resources are linked into the final application binary in the case of static linking. You should put the initialization code close to where the resources are used in your library, so that clients of your library will only link in the resources if they use the feature of the library that depends on them.
Note: As the resource initializers generated by rcc are declared in the global namespace, your calls to Q_INIT_RESOURCE() also need to be done outside of any namespace.
If the library includes resources that are not used internally, but instead exposed to clients of the library, the initialization needs to happen in the application code. For example:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
Q_INIT_RESOURCE(graphlib); QFile file(":/graph.png");
...
return app.exec();
}
As before, this ensures that the resources are linked into the final application binary in the case of static linking, but also triggers loading of the library in the case of dynamic linking, such as plugins.
Similarly, if you must unload a set of resources explicitly (because a plugin is being unloaded or the resources are not valid any longer), you can force removal of your resources by calling Q_CLEANUP_RESOURCE() with the same base name as above.
Note: The use of Q_INIT_RESOURCE() and Q_CLEANUP_RESOURCE() is not necessary when the resource is built as part of the application.
The Qt Resource System的更多相关文章
- Qt Resource System Qt资源体系(qrc rcc)
Qt资源体系采用平台独立机制来存储应用程序执行时的二进制文件.这种机制在应用程序需要一些确定的文件(图标.翻译文件等等)而且又不想冒丢失文件的风险时是有用的. 资源体系依赖于 qmake, rcc ( ...
- 7、Qt MetaObject System详解
网上的资源比较乱,该文章整理自地址:http://www.xuebuyuan.com/735789.html Qt meta-object系统基于三个方面: 1.QObject提供一个基类,方便派生类 ...
- Qt MetaObject System详解
网上的资源比较乱,该文章整理自地址:http://www.xuebuyuan.com/735789.html Qt meta-object系统基于三个方面: 1.QObject提供一个基类,方便派生类 ...
- Qt Resource系统概说(资源压缩不压缩都可以)
什么是Qt Resource系统?简单的说,就是在可执行程序中存储binary文件,而且还是与平台无关的. 与Qt Resource系统密切相关的有三个法宝,分别是qmake.rcc.QFile. q ...
- Qt属性系统(Qt Property System)
Qt提供了巧妙的属性系统,它与某些编译器支持的属性系统相似.然而,作为平台和编译器无关的库,Qt不能够依赖于那些非标准的编译器特性,比如__property 或者 [property].Qt的解决方案 ...
- Qt之资源系统
简述 Qt 的资源系统用于存储应用程序的可执行二进制文件,它采用平台无关的机制.当你的程序总需要这样的一系列文件(图标.翻译文件等)并且不想冒丢失某些文件的风险时,这就显得十分有用. 资源系统基于 q ...
- 如何在Qt资源文件中包含和释放exe等各种类型文件?
操作系统:Windows 10 X64 企业版 Qt: 5.8.0 QtCreater: 4.2.1 刚刚开始学习Qt,不断遇到困难和挑战,前几天在各个QQ群里询问如何在Qt的资源文件中包含和释放ex ...
- 【Qt官方例程学习笔记】Application Example(构成界面/QAction/退出时询问保存/用户偏好载入和保存/文本文件的载入和保存/QCommandLineParser解析运行参数)
The Application example shows how to implement a standard GUI application with menus, toolbars, and ...
- [Qt Creator 快速入门] 第5章 应用程序主窗口
对于日常见到的应用程序而言,许多都是基于主窗口的,主窗口中包含了菜单栏.工具栏.状态栏和中心区域等.这一章会详细介绍主窗口的每一个部分,还会涉及资源管理.富文本处理.拖放操作和文档打印等相关内容.重点 ...
随机推荐
- iOS 9 适配中出现的坑
整理 iOS 9 适配中出现的坑(图文) 2015-10-22 iOS开发 库克表示:“现在在中国有150多万的开发者在iOS当中开发应用程序,我们鼓励更多的人开发应用程序,也鼓励更多的创业加入.” ...
- oracle11g本地可以访问但局域网无法访问
问题描述,现在有两台电脑 A 和 B : 1)电脑 A 上有 Oracle11G服务端: ip地址 192.168.1.198; 端口1521: 2)电脑 A 本机连接数据库正常,可以登录及操作等: ...
- Interface_GL通过gl_interface导入日记账(案例)
2014-06-17 BaoXinjian
- unity, 人物与移动跳台的交互
----更新(2015-7-1): 也可以用itween来移动跳台. ---- 例如人物跳到往复运动的移动跳台上后应随跳台运动. 要实现这个效果有两个思路,一是用运动学一是用动力学. 用动力学实现就是 ...
- JavaScript中的陷阱(关于变量声明,函数)
查看:http://www.css88.com/archives/5347#more-5347
- Android Gradle 引用本地 AAR 的几种方式
折衷方案: 1.方式2 - 不完美解决办法2 2.再使用"自定义Gradle代码"来减轻重复设置的问题. 自定义Gradle代码如下: repositories { flatDir ...
- 笔记本上安装centos7
1.下载centos的dvd镜像就够了.地址: 2.制作u盘镜像. 1)下载安装UltraIOS,(百度云->软件文件夹有,for me). 2)打开镜像,选择“启动”-->“写入硬盘镜像 ...
- xapp1052之dma_test.v
dma_test是针对dma硬件设计的仿真测试文件,文件包括DMA写数据测试,DMA读数据测试以及DMA读写数据测试.这个测试文件其实就是模拟pc的应用程序对fpga设备进行DMA读写. DMA写测试 ...
- IAsyncResult 接口
IAsyncResult 接口由包含可异步操作的方法的类实现.它是启动异步操作的方法的返回类型,如 FileStream.BeginRead,也是结束异步操作的方法的第三个参数的类型,如 FileSt ...
- linux命令(30):tail
linux ---tail命令 linux中tail命令---用于查看文件内容 最基本的是cat.more和less. 1. 如果你只想看文件的前5行,可以使用head命令,如: head -5 /e ...
