c++第三次实验
第一题:
先把代码贴上来
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include<conio.h>
#include "canvas.h"
#include "Ball.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Canvas canvas;
char ch; Ball ball1(,);
system("pause"); /*ball1.left(5);
system("pause"); ball1.up(20);
system("pause");*/
while(cin>>ch)
{ cout<<"如果想退出请按q";
switch(ch)
{ case 'w':ball1.up();break;
case 's':ball1.down();break;
case 'a':ball1.left();break;
case 'd':ball1.right();break;
default :break; }
if(ch=='q')break;
} canvas.changeCanvasFg("E"); // 更新画布前景色
system("pause"); canvas.changeCanvasBg("D"); // 更新画布背景色
system("pause"); return ;
}
canvas.h
#ifndef CANVAS_H
#define CANVAS_H #include <string>
using std::string; class Canvas {
public:
Canvas(string bg0="", string fg0="A");
void changeCanvasBg(string bg0);
void changeCanvasFg(string fg0);
void changeCanvasColor(string bg0, string fg0);
private:
string bg; // background color
string fg; // foreground color
}; #endif
ball.h
#ifndef BALL_H
#define BALL_H class Ball {
public:
Ball(int x0=, int y0=); // 在坐标(x,y)处构造一个小球(小球用字符O表示)
void left(int step=); // 左移step
//void left(char step);
void right(int step=); // 右移step
// void right(int step=1);
void up(int step=); // 上移step
//void up(int step=1);
void down(int step=); // 下移step
//void down(int step=1);
private:
int x; // x坐标
int y; // y坐标
}; #endif
ball.cpp
#include "ball.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> // 因为使用了system("cls"); 所以需要包含这个头文件
using std::cout;
using std::endl; const int SIZE_X=; // 小球x轴移动范围0~SIZE_X
const int SIZE_Y=; // 小球y轴移动范围0~SIZE_Y void printline(int n)
{
int i;
for(i=; i <= n-; i ++)
cout << endl;
}
void printspace(int n)
{
int i;
for(int i=; i <= n-; i ++)
cout << " ";
}
Ball::Ball(int x0, int y0):x(x0), y(y0) {
// 打印y0-1行空行
printline( y0);
//for(int line=1; line <= y0-1; line++)
//cout << endl; // 打印x0-1个空格
printspace( x0);
//for(int col=1; col <= x0-1; col++)
//cout << " "; printspace(int y0); // 打印小球
cout << "O" << endl; } void Ball::left(int step) {
x = x-step;
if(x <= )
x=; // 清屏
system("cls"); // 打印y-1行空行
printline( y);
//for(int line=1; line <= y-1; line++)
//cout << endl; // 打印x-1个空格
printspace( x);
//for(int col=1; col <= x-1; col++)
//cout << " "; // 打印小球
cout << "O" << endl; } void Ball::right(int step) {
x = x+step;
if(x >= SIZE_X)
x=SIZE_X; // 清屏
system("cls"); // 打印y-1行空行
printline( y);
//for(int line=1; line <= y-1; line++)
//cout << endl; // 打印x-1个空格
printspace( x);
//for(int col=1; col <= x-1; col++)
//cout << " "; // 打印小球
cout << "O" << endl; } void Ball::up(int step) {
y = y-step;
if(y <= )
y=; // 清屏
system("cls"); // 打印y-1行空行
printline( y);
//for(int line=1; line <= y-1; line++)
//cout << endl; // 打印x-1个空格
printspace( x);
//for(int col=1; col <= x-1; col++)
//cout << " "; // 打印小球
cout << "O" << endl; } void Ball::down(int step) {
y = y+step;
if(y >= SIZE_Y)
y = SIZE_Y; // 清屏
system("cls"); // 打印y-1行空行
printline( y);
//for(int line=1; line <= y-1; line++)
//cout << endl; // 打印x-1个空格
printspace( x);
//for(int col=1; col <= x-1; col++)
//cout << " "; // 打印小球
cout << "O" << endl;
} // 思考:
// Ball类的成员函数实现中,包含大量重复的代码
// 利用所学知识对代码改进优化,使代码更简洁,同时,保持逻辑清晰
canvas.cpp
#include "canvas.h"
#include <cstdlib> Canvas::Canvas(string bg0, string fg0):bg(bg0), fg(fg0) {
string color = "color ";
color += bg0;
color += fg0;
system(color.c_str());
}
void Canvas::changeCanvasBg(string bg0) {
bg = bg0; // 更新画布背景色 string color = "color ";
color += bg;
color += fg;
system(color.c_str()); }
void Canvas::changeCanvasFg(string fg0) {
fg = fg0; // 更新画布前景色 string color = "color ";
color += bg;
color += fg;
system(color.c_str()); }
void Canvas::changeCanvasColor(string bg0, string fg0){
bg = bg0; // 更新画布背景色
fg = fg0; // 更新画布前景色 string color = "color ";
color += bg;
color += fg;
system(color.c_str());
} // 1. 说明
// system("color ××");
// 可以用于改变屏幕的前景色和背景色
// 这里画布类Canvas的默认画布颜色及修改就是利用这个函数实现的 // 由于sysmtem()要求参数必须是const char*类型
// 因此,这里借助string类成员函数c_str完成从string类到const char*类型的转换
// c++标准库中tring类虽然是对char *类的封装,以此实现对字符串更便捷、丰富的操作,但是,仍然是有区别的。 // 2. 思考
// Canvas类成员函数的实现中,有大量重复的代码
// 思考如何进一步优化代码,同时又能保持代码的可读性和简洁、逻辑清晰
我对canvas中的重复代码利用函数简化。
添加了基于WASD控制上下左右的功能。
 图片有点糊 但是还是能看出来。
图片有点糊 但是还是能看出来。
第二题:
还是先贴代码为敬
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <string>
#include "graph.h"
#include "canvas2.h"
using namespace std; int main() {
char ss,ch;
int flag,ll;
string bg0,fg0;
Canvas canvas;
Graph graph1('*',);
graph1.draw(); system("pause");
system("cls"); Graph graph2('$',);
graph2.draw();
system("pause");
system("cls");
while()
{
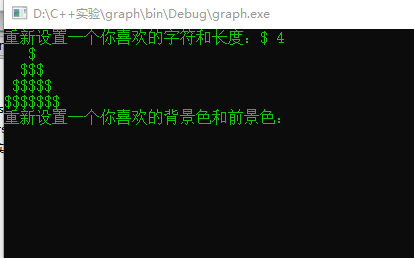
cout<<"重新设置一个你喜欢的字符和长度:";
cin>>ss>>ll;
//cout<<ll;
Graph graph3(ss,ll);
graph3.draw();
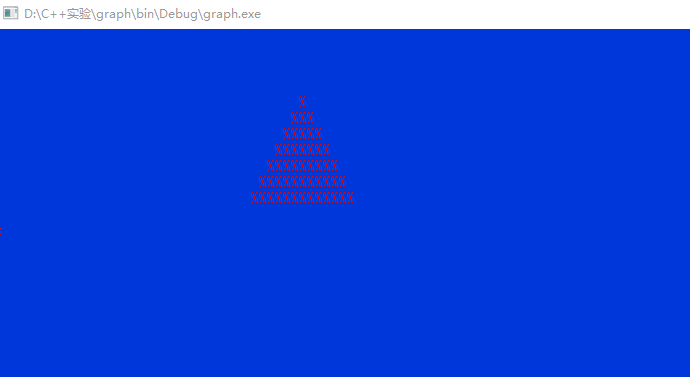
cout<<"重新设置一个你喜欢的背景色和前景色:";
cin>>bg0>>fg0;
canvas.changeCanvasColor(bg0,fg0);
cout<<"如果想退出请按q";
while(cin>>ch)
{ switch(ch)
{ case 'w':graph3.up();break;
case 's':graph3.down();break;
case 'a':graph3.left();break;
case 'd':graph3.right();break;
default :break; }
if(ch=='q')break;
}
system("pause");
system("cls");
cout<<"继续请按1,退出请按2";
cin>>flag;
if(flag==)continue;
else if(flag==)break;
} return ;
}
graph.h
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H // 类Graph的声明
class Graph {
public:
Graph(char ch, int n); // 带有参数的构造函数
void draw(); // 绘制图形
void left(int step=);
void right(int step=);
void up(int step=);
void down(int step=); private:
char symbol;
int size;
int x;
int y;
}; #endif
canvas2.h
#ifndef CANVAS2_H
#define CANVAS2_H #include <string>
using std::string; class Canvas {
public:
Canvas(string bg0="", string fg0="A");
void changeCanvasBg(string bg0);
void changeCanvasFg(string fg0);
void changeCanvasColor(string bg0, string fg0);
private:
string bg; // background color
string fg; // foreground color
}; #endif
graph.cpp
// 类graph的实现 #include "graph.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> // 因为使用了system("cls"); 所以需要包含这个头文件
using namespace std;
const int SIZE_X=; // 小球x轴移动范围0~SIZE_X
const int SIZE_Y=; // 小球y轴移动范围0~SIZE_Y // 带参数的构造函数的实现
Graph::Graph(char ch, int n): symbol(ch), size(n) {
x=;
y=;
} // 成员函数draw()的实现
void Graph::draw()
{
int i,j,k,sum;
sum=*size-; //计算列数
for(i=;i<=size;i++)
{
for(j=;j<=size-i;j++)
cout<<' ';//每一行先打印出(size-行数)个空格
for(k=size-i+;k<=sum-j+;k++)
cout<<symbol;//再打印出剩下的字符
cout<<endl;
}
}
// 功能:绘制size行,显示字符为symbol的指定图形样式 void printline(int n)
{
int i;
for(i=; i <= n-; i ++)
cout << endl;
} void printspace(int n)
{
int i;
for( i=; i <= n-; i ++)
cout << " ";
} void Graph::left(int step)
{
int i,j,k,sum;
x = x-step;
if(x <= )
x=;
system("cls");
printline(y);
sum=*size-;
for(i=;i<=size;i++)
{
printspace(x);
for(j=;j<=size-i;j++)
cout<<' ';
for(k=size-i+;k<=sum-j+;k++)
cout<<symbol;
cout<<endl;
}
}
void Graph::right(int step)
{
int i,j,k,sum;
x = x+step;
if(x >= SIZE_X)
x=SIZE_X;
system("cls");
printline(y);
sum=*size-;
for(i=;i<=size;i++)
{
printspace(x);
for(j=;j<=size-i;j++)
cout<<' ';
for(k=size-i+;k<=sum-j+;k++)
cout<<symbol;
cout<<endl;
}
}
void Graph::up(int step)
{
int i,j,k,sum;
y = y-step;
if(y <= )
y=;
system("cls");
printline(y);
sum=*size-;
for(i=;i<=size;i++)
{
printspace(x);
for(j=;j<=size-i;j++)
cout<<' ';
for(k=size-i+;k<=sum-j+;k++)
cout<<symbol;
cout<<endl;
}
}
void Graph::down(int step)
{
int i,j,k,sum;
y = y+step;
if(y >= SIZE_Y)
y = SIZE_Y;
system("cls");
printline(y);
for(i=;i<=size;i++)
{
printspace(x);
for(j=;j<=size-i;j++)
cout<<' ';
for(k=size-i+;k<=sum-j+;k++)
cout<<symbol;
cout<<endl;
}
}
canvas2.cpp
#include "canvas2.h"
#include <cstdlib> Canvas::Canvas(string bg0, string fg0):bg(bg0), fg(fg0) {
string color = "color ";
color += bg0;
color += fg0;
system(color.c_str());
}
void Canvas::changeCanvasBg(string bg0) {
bg = bg0; // 更新画布背景色 string color = "color ";
color += bg;
color += fg;
system(color.c_str()); }
void Canvas::changeCanvasFg(string fg0) {
fg = fg0; // 更新画布前景色 string color = "color ";
color += bg;
color += fg;
system(color.c_str()); }
void Canvas::changeCanvasColor(string bg0, string fg0){
bg = bg0; // 更新画布背景色
fg = fg0; // 更新画布前景色 string color = "color ";
color += bg;
color += fg;
system(color.c_str());
} // 1. 说明
// system("color ××");
// 可以用于改变屏幕的前景色和背景色
// 这里画布类Canvas的默认画布颜色及修改就是利用这个函数实现的 // 由于sysmtem()要求参数必须是const char*类型
// 因此,这里借助string类成员函数c_str完成从string类到const char*类型的转换
// c++标准库中tring类虽然是对char *类的封装,以此实现对字符串更便捷、丰富的操作,但是,仍然是有区别的。 // 2. 思考
// Canvas类成员函数的实现中,有大量重复的代码
// 思考如何进一步优化代码,同时又能保持代码的可读性和简洁、逻辑清晰
程序运行之后,先显示 Graph graph1('*',5);和Graph graph2('$',7);这两条语句下的图案。按任意键继续后可以输入自定义的字符和行数
然后可以选择前背景色和后背景色。然后想要退出可以按q,不退出就按其他的键进入图形移动界面。
如果想要退出按q即可。如果想再次设置会弹出选择,按1继续,按2退出整个程序。



第三题:
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "fraction.h"
using namespace std; int main ()
{
Fraction a(,);
cout<<"a:";
a.print(a);
Fraction b(,);
cout<<"b:";
b.print(b);
Fraction c();
cout<<"c:";
a.print(c);
Fraction d;
d=d.add(a,b);
cout<<"a+b=";
a.print(d);
a.mytransform(d);
d=d.minus(a,b);
cout<<"a-b=";
a.print(d);
d=d.product(a,b);
cout<<"a*b=";
a.print(d);
d=d.division(a,b);
cout<<"a/b=";
a.print(d); cout<<"当分数分母为0时:";
Fraction e(,);
cout<<"e:";
a.print(e);
cout<<"比较b和c:";
a.compare(b,c);
return ;
}
fraction.h
#ifndef FRACTION_H
#define FRACTION_H class Fraction
{
public:
Fraction(int a=,int b=);
Fraction(Fraction &p);
Fraction add(Fraction p1,Fraction p2);
Fraction minus(Fraction p1,Fraction p2);
Fraction product(Fraction p1,Fraction p2);
Fraction division(Fraction p1,Fraction p2);
void compare(Fraction p1,Fraction p2);
void print(Fraction p);
void standard(int &top,int &bottom);
void mytransform(Fraction p);
int yueshu(int a,int b);
int jueduizhi(int a);
private:
int top;
int bottom;
}; #endif FRACTION_H
fraction.cpp
#include "fraction.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void Fraction::mytransform(Fraction p)
{
cout<<"转换成小数输出:"<<static_cast<double>(p.top)/static_cast<double>(p.bottom)<<endl;
}
int Fraction::yueshu(int a,int b)
{
if(b==)return a;
else
return yueshu(b,a%b);
}
int Fraction::jueduizhi(int a)
{
if(a<)return -a;
else return a;
}
void Fraction::standard(int &top,int &bottom)
{
int gongyueshu;
if(top<&&bottom<)
{
top=-top;
bottom=-bottom;
}
else if(top<||bottom<)
{
if(top>)
{
top=-top;
bottom=-bottom;
}
}
gongyueshu=yueshu(jueduizhi(top),jueduizhi(bottom));
top/=gongyueshu;
bottom/=gongyueshu;
} Fraction::Fraction (int a,int b):top(a),bottom(b)
{
if(b==)
{
cout<<"分母不能为零!分数默认为0/1"<<endl;
top=;
bottom=;
}
}
Fraction::Fraction (Fraction &p)
{
top=p.top;
bottom=p.bottom;
}
Fraction Fraction::add(Fraction p1,Fraction p2)
{
Fraction p3;
p3.bottom=p1.bottom*p2.bottom;
p3.top=p1.top*p2.bottom+p2.top*p1.bottom;
//cout<<p3.top<<p3.bottom<<endl;
standard(p3.top,p3.bottom);
// cout<<p3.top<<p3.bottom<<endl;
return p3;
}
Fraction Fraction::minus(Fraction p1,Fraction p2)
{
Fraction p3;
p3.bottom=p1.bottom*p2.bottom;
p3.top=p1.top*p2.bottom-p2.top*p1.bottom;
standard(p3.top,p3.bottom);
return p3;
}
Fraction Fraction::product(Fraction p1,Fraction p2)
{
Fraction p3;
p3.bottom=p1.bottom*p2.bottom;
p3.top=p1.top*p2.top;
standard(p3.top,p3.bottom);
return p3;
}
Fraction Fraction::division(Fraction p1,Fraction p2)
{
Fraction p3;
p3.bottom=p1.bottom*p2.top;
p3.top=p1.top*p2.bottom;
standard(p3.top,p3.bottom);
return p3;
}
void Fraction::compare(Fraction p1,Fraction p2)
{
int m,n;
m=p1.top*p2.bottom;
n=p1.bottom*p2.top;
if(m/n>)cout<<p1.top<<'/'<<p1.bottom<<'>'<<p2.top<<'/'<<p2.bottom<<endl;
else if(m/n==)cout<<p1.top<<'/'<<p1.bottom<<'='<<p2.top<<'/'<<p2.bottom<<endl;
else cout<<p1.top<<'/'<<p1.bottom<<'<'<<p2.top<<'/'<<p2.bottom<<endl;
}
void Fraction::print(Fraction p)
{
cout<<p.top<<'/'
<<p.bottom<<endl;
}
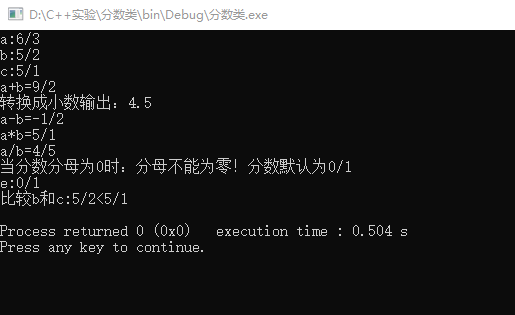
我的程序当创建一个对象没有赋予初值时是0/1,可以进行加减乘除运算,可以将分数转换为小数,当输入的分母为零时提醒错误并改为默认的0/1,可以两个分数进行比较大小。当分数为负数时,负号在分子上。当分子分母不是最简时,进行约分。
实验总结:
1.初步了解了多文件结构的使用方法和运行机制。
2.对类的定义实现和调用加深了理解。
3.了解了简单的用字符控制输出的方法。
c++第三次实验的更多相关文章
- 20145224&20145238 《信息安全系统设计基础》 第三次实验
20145224&20145238 <信息安全系统设计基础>第三次实验 课程:信息安全系统设计基础 班级:1452 姓名:陈颢文 荆玉茗 学号:20145224 20145238 ...
- 20145330Java程序设计第三次实验
20145330<Java程序设计>第三次实验报告 实验三 敏捷开发与XP实践 实验内容 1.使用git上传代码 2.使用git实现代码开发实践 3.实现代码的重载 实验步骤 使用git上 ...
- 20145320《Java程序设计》第三次实验报告
20145320<Java程序设计>第三次实验报告 北京电子科技学院(BESTI)实验报告 课程:Java程序设计 班级:1453 指导教师:娄嘉鹏 实验日期:2016.04.22 15: ...
- Linux第三次实验报告
北京电子科技学院(BESTI) 实 验 报 告 课程:信息安全系统设计基础 班级:201352 姓名:池彬宁 贺邦 学号:20135212 2013520 ...
- 南京邮电大学java第三次实验报告
实 验 报 告 ( 2017 / 2018学年 第2学期) 课程名称 JAVA语言程序设计 实验名称 Java集成开发环境的安装与使用. Java变量.表达式与控制结构 实验时间 2018 年 4 月 ...
- Java第三次实验敏捷开发与XP实验
实验三-1 1.实验要求: 实验三 敏捷开发与XP实践 http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/4795776.html, Eclipse的内容替换成IDEA 参考 http: ...
- java第三次实验报告
北京电子科技学院(BESTI) 实验报告 课程: Java程序设计 班级: 1352 姓名: 池彬宁 学号: 20135212 成绩: 指导教师: 娄嘉鹏 实验日期: 2015.6.3 实验密级: 无 ...
- 20162327WJH第三次实验——查找与排序2
20162327WJH第三次实验--查找与排序2 实 验 报 告 课程:程序设计与数据结构 班级: 1623 姓名: 王旌含 学号:20162327 成绩: 指导教师:娄嘉鹏 王志强 实验日期:11月 ...
- 20155210 潘滢昊 Java第三次实验
Java第三次实验 实验内容 在IDEA中使用工具(Code->Reformate Code)把代码重新格式化 在码云上把自己的学习搭档加入自己的项目中,确认搭档的项目加入自己后,下载搭档实验二 ...
- 20155217 《Java程序设计》第三次实验报告
20155217 <Java程序设计>第三次实验报告 实验内容 XP基础 XP核心实践 相关工具 实验要求 没有Linux基础的同学建议先学习<Linux基础入门(新版)>&l ...
随机推荐
- DCM、PLL、PMCD、MMCM相关
摘自网上 : http://xilinx.eetop.cn/viewnews-1482 The DCM is a Digital Clock Manager - at its heart it is ...
- C++设计模式——模板方法模式
模板方法模式 在GOF的<设计模式:可复用面向对象软件的基础>一书中对模板方法模式是这样说的:定义一个操作中的算法骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中.TemplateMethod使得子类可以不 ...
- C# 最牛逼的Utility工具类
完整代码: using System; using System.Collections.Specialized; using System.IO; using System.Net; using S ...
- python学习之Numpy.genfromtxt
Python 并没有提供数组功能,虽然列表 (list) 可以完成基本的数组功能,但它并不是真正的数组,而且在数据量较大时,使用列表的速度就会慢的让人难受.Numpy 提供了真正的数组功能,以及对数据 ...
- java---- XMLEncoder 和 XMLDecoder 和 xSteam工具使用
XMLEncoder: 将对象写入XML数据中 import org.dom4j.DocumentException; import java.beans.XMLEncoder; import jav ...
- Eclipse连接HBase 报错:org.apache.hadoop.hbase.PleaseHoldException: Master is initializing
在eclipse中连接到HBase报错org.apache.hadoop.hbase.PleaseHoldException: Master is initializing,搜索了好久,网上其它人说的 ...
- python之MySQL MySQLdb 推荐使用姿势,解决中文乱码
0.目录 2.setup(1) 安装步骤,可以顺带安装mysql administrator和mysql query browser(2) 安装完毕,修改 my.ini(3) 重启 mysql 服务: ...
- 02.Numpy
01.array # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Numpy 패키지 특징 - 선형대수(벡터, 행렬) 연산에 효과적인 함수 제공 - lis ...
- Codeforces 1045E. Ancient civilizations 构造 计算几何 凸包
原文链接https://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/CF1045E.html 4K码量构造题,CF血腥残暴! 题解 首先,如果所有点颜色相同,那么直接连个菊花搞定. ...
- Noj - 在线强化训练3
状态 题号 竞赛题号 标题 1091 A 求解逆波兰表达式(Calculate the reverse Polish notation) 1017 B 数列 1323 C 穷举n位二进制数 ...
