B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed
5 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
The main road in Bytecity is a straight line from south to north. Conveniently, there are coordinates measured in meters from the southernmost building in north direction.
At some points on the road there are n friends, and i-th of them is standing at the point xi meters and can move with any speed no greater than vi meters per second in any of the two directions along the road: south or north.
You are to compute the minimum time needed to gather all the n friends at some point on the road. Note that the point they meet at doesn't need to have integer coordinate.
The first line contains single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 60 000) — the number of friends.
The second line contains n integers x1, x2, ..., xn (1 ≤ xi ≤ 109) — the current coordinates of the friends, in meters.
The third line contains n integers v1, v2, ..., vn (1 ≤ vi ≤ 109) — the maximum speeds of the friends, in meters per second.
Print the minimum time (in seconds) needed for all the n friends to meet at some point on the road.
Your answer will be considered correct, if its absolute or relative error isn't greater than 10 - 6. Formally, let your answer be a, while jury's answer be b. Your answer will be considered correct if 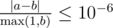 holds.
holds.
3
7 1 3
1 2 1
2.000000000000
4
5 10 3 2
2 3 2 4
1.400000000000
In the first sample, all friends can gather at the point 5 within 2 seconds. In order to achieve this, the first friend should go south all the time at his maximum speed, while the second and the third friends should go north at their maximum speeds.
思路:二分;
二分时间,然后每次检查时求出每个点所能到达的左右的距离,然后求线段的最大重叠。复杂度(n*log^2(n))
或者二分每次检查时求出每个点所能到达的左右的距离,然后维护最小的右端r,和最大的左端l,如果r > l成立复杂度n*log(n);
1 #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
2 #include<stdio.h>
3 #include<algorithm>
4 #include<iostream>
5 #include<string.h>
6 #include<stdlib.h>
7 #include<queue>
8 #include<map>
9 #include<math.h>
10 #include<vector>
11 const int N = 1e6+6;
12 using namespace std;
13 typedef long long LL;
14 double x[70000];
15 double v[70000];
16 typedef struct node
17 {
18 double val;
19 int k;
20 } ss;
21 bool cmp(node p,node q)
22 {
23 if(p.val == q.val)
24 return p.k > q.k;
25 else return p.val < q.val;
26 }
27 ss ask[70000*2];
28 bool check(double c,int n);
29 int main(void)
30 {
31 int n;
32 scanf("%d",&n);
33 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
34 scanf("%lf",&x[i]);
35 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
36 scanf("%lf",&v[i]);
37 int t = 100;
38 double ll = 0,rr = 1e10;
39 double acc = -1;
40 while(t)
41 {
42 double mid = (ll+rr)/2;
43 if(check(mid,n))
44 {
45 acc = mid;
46 rr = mid;
47 //printf("%lf\n",mid);
48 }
49 else ll = mid;
50 t--;
51 }
52 printf("%.10f\n",acc);
53 return 0;
54 }
55 bool check(double c,int n)
56 {
57 int cn = 0;
58 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
59 {
60 ask[cn].val = max((double)0,x[i] - c*v[i]);
61 ask[cn].k = 1;
62 cn++;
63 ask[cn].val = x[i] + c*v[i];
64 ask[cn].k = -1;
65 cn++;
66 }
67 int sum = 0;
68 sort(ask,ask+cn,cmp);
69 for(int i = 0; i < cn; i++)
70 {
71 sum += ask[i].k;
72 if(sum == n)
73 return true;
74 }
75 return false;
76 }
1 #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
2 #include<stdio.h>
3 #include<algorithm>
4 #include<iostream>
5 #include<string.h>
6 #include<stdlib.h>
7 #include<queue>
8 #include<map>
9 #include<math.h>
10 #include<vector>
11 const int N = 1e6+6;
12 using namespace std;
13 typedef long long LL;
14 double x[70000];
15 double v[70000];
16 typedef struct node
17 {
18 double val;
19 int k;
20 } ss;
21 bool cmp(node p,node q)
22 {
23 if(p.val == q.val)
24 return p.k > q.k;
25 else return p.val < q.val;
26 }
27 ss ask[70000*2];
28 bool check(double c,int n);
29 int main(void)
30 {
31 int n;
32 scanf("%d",&n);
33 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
34 scanf("%lf",&x[i]);
35 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
36 scanf("%lf",&v[i]);
37 int t = 100;
38 double ll = 0,rr = 1e10;
39 double acc = -1;
40 while(t)
41 {
42 double mid = (ll+rr)/2;
43 if(check(mid,n))
44 {
45 acc = mid;
46 rr = mid;
47 //printf("%lf\n",mid);
48 }
49 else ll = mid;
50 t--;
51 }
52 printf("%.10f\n",acc);
53 return 0;
54 }
55 bool check(double c,int n)
56 {
57 int cn = 0;
58 double maxx = 1e10;
59 double minn = 0;
60 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
61 {
62 minn = max(minn,x[i] - c*v[i]);
63 maxx = min(maxx,x[i] + c*v[i]);
64 }
65 if(maxx >= minn)return true;
66 return false;
67 }
n*log(n)
B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed的更多相关文章
- codeforces 782B The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed (三分)
The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed Problem Description The main road in Bytecity is a straight line ...
- code force 403B.B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed
B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed time limit per test 5 seconds memory limit per test 256 megab ...
- Cf Round #403 B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed(二分答案)
The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed 我发现我最近越来越zz了,md 连调程序都不会了,首先要有想法,之后输出如果和期望的不一样就从输入开始一步一步地调啊,tmd现在 ...
- Codeforces Round #403 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2017 Finals) B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed
地址:http://codeforces.com/contest/782/problem/B 题目: B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed time limit ...
- AC日记——The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed codeforces 780b
780B - The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed 思路: 二分答案: 代码: #include <cstdio> #include <cstrin ...
- Codeforces 782B The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed(二分答案)
题目链接 The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed 二分答案即可. check的时候先算出每个点可到达的范围的区间,然后求并集.判断一下是否满足l <= r就好了. ...
- codeforces 782B The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed+hdu 4355+hdu 2438 (三分)
B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Change ...
- CodeForce-782B The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed(高精度二分)
https://vjudge.net/problem/CodeForces-782B B. The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed time limit per tes ...
- codeforces 782B - The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed
time limit per test 5 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output standa ...
随机推荐
- 汽车C2M模式综述
- 监督学习&非监督学习
监督学习 1 - 3 - Supervised Learning 在监督学习中,数据集中的每个例子,算法将预测得到例子的""正确答案"",像房子的价格,或者溜 ...
- GraphScope 集群部署
GraphScope 集群部署 1 k8s集群搭建 大致步骤如下: 安装docker.在ubuntu上,可以简单的通过命令sudo apt install docker.io来安装. 安装kubele ...
- Android 高级UI组件(三)
一.popupWindow 1.AlertDialog和PopupWindow最关键的区别是AlertDialog不能指定显示位置,只能默认显示在屏幕最中间(当然也可以通过设置WindowManage ...
- my37_MGR流控对数据库性能的影响以及MGR与主从的性能对比
mysql> show variables like 'group_replication_flow_control_applier_threshold'; +----------------- ...
- 【Linux】【Services】【SaaS】Docker+kubernetes(9. 安装consul实现服务注册发现)
1. 简介 1.1. 官方网站: https://www.consul.io 1.2. Consul的功能: 服务发现:通过DNS或HTTP接口使得消费者发现服务,应用程序可以轻松找到所依赖的服务. ...
- VueAPI 2 (生命周期钩子函数)
所有的生命周期钩子自动绑定 this 上下文到实例中,因此你可以访问数据,对属性和方法进行运算.这意味着你不能使用箭头函数来定义一个生命周期方法. beforeCreate 在实例初始化之后,此时还不 ...
- Project Reactor工厂方法和错误处理
工厂方法创建流 Backpressure : the ability for the consumer to signal the producer that the rate of emission ...
- 使用OPC与PLC通讯 一
总结自己在opc与自控开发的经验.首先介绍OPC DA模式下的OPC各种操作. 在使用opc时需要引用到 OPCDAAuto.dll 这个类库. 在项目引用后需要注册这个类库,否则程序跑起来会报错,& ...
- DevOps和SRE的区别
目录 一.误区 二.DevOps 和 SRE 定义 三.两者产生背景和历史 四.两者的职能不同 五.工作内容不同 六.DevOps 和 SRE 关系 七.附录:技能点 DevOps SRE 一.误区 ...
