sklearn机器学习-特征提取1
scikit-learn机器学习的特征提取部分较多nlp内容,故学到一半学不下去,看完nltk再来补上
scikit-learn机器学习的特征提取这一章感觉讲的不是特别好,所以会结合着来看
首先是Dictvectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
onehot_encoder = DictVectorizer()
X = [{'city':'New York'},{'city':'San Francisco'},{'city':'Chapel Hill'}]
print(onehot_encoder.fit_transform(X).toarray())
[[0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]
[1. 0. 0.]]
这里的toarray方法,在很多one-hot方法中都有,需要注意一下
然后这里必须传入字典形式
measurements = [{'city':'Beijing','country':'CN','temperature':33.},{'city':'London','country':'UK','temperature':12.},{'city':'San Fransisco','country':'USA','temperature':18.}]
#从sklearn.feature_extraction导入DictVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
vec = DictVectorizer()
#输出转化后的特征矩阵
print(vec.fit_transform(measurements).toarray())
#输出各个维度的特征含义
print(vec.get_feature_names_out())
[[ 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 33.]
[ 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 12.]
[ 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 18.]]
['city=Beijing' 'city=London' 'city=San Fransisco' 'country=CN'
'country=UK' 'country=USA' 'temperature']
StandardScalar:
$X = \frac{x-\mu}{\sigma}$
MinMaxScalar:
$X = \frac{x-x_{min}(axis=0)}{x_{max}(axis=0)-x_{min}(axis=0)}$
scale:
$X = \frac{x-x_{mean}}{\sigma}$
或者还可以使用RoubustScalar
from sklearn import preprocessing
import numpy as np
X = np.array([[0,0,5,13,9,1],[0,0,13,15,10,15],[0,3,15,2,0,11]])
print(preprocessing.scale(X))
[[ 0. -0.70710678 -1.38873015 0.52489066 0.59299945 -1.35873244]
[ 0. -0.70710678 0.46291005 0.87481777 0.81537425 1.01904933]
[ 0. 1.41421356 0.9258201 -1.39970842 -1.4083737 0.33968311]]
或者也可以直接写
from sklearn.preprocessing import scale
import numpy as np
X = np.array([[0,0,5,13,9,1],[0,0,13,15,10,15],[0,3,15,2,0,11]])
sc = scale(X)
print(sc)
词袋模型
希望我能用一段中文描述,多记一下这个CountVectorizer
CountVectorizer是属于常见的特征数值计算类,是一个文本特征提取方法,对于每一个训练文本,只考虑每种词汇在该训练文本中出现的频率,也即ConutVectorizer会将文本中的词语转换为词频矩阵
corpus = ['UNC played Duke in basketball','duke lost the basketball game']
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
vectorizer = CountVectorizer()
print(vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus).todense())
print(vectorizer.vocabulary_)
注意,这里有Duke,还有duke
[[1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1]
[1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0]]
{'unc': 7, 'played': 5, 'duke': 1, 'in': 3, 'basketball': 0, 'lost': 4, 'the': 6, 'game': 2}
corpus.append("I ate a sandwich")
print(vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus).todense())
print(vectorizer.vocabulary_)
[[0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1]
[0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0]
[1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0]]
{'unc': 9, 'played': 6, 'duke': 2, 'in': 4, 'basketball': 1, 'lost': 5, 'the': 8, 'game': 3, 'ate': 0, 'sandwich': 7}
上述文档中,第一行应该是和第二行比较接近,在sklearn中,用eculidean_distances来计算向量间的距离
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import euclidean_distances
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
corpus = ['UNC played Duke in basketball','Duke lost the basketball game','I ate a sandwich']# 文集
vectorizer =CountVectorizer()#
counts = vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus).todense() #得到文集corpus的特征向量,并将其转为密集矩阵
print(counts)
for x,y in [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2]]:
dist = euclidean_distances(counts[x],counts[y])
print('文档{}与文档{}的距离{}'.format(x,y,dist))
[[0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1]
[0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0]
[1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0]]
文档0与文档1的距离[[2.44948974]]
文档0与文档2的距离[[2.64575131]]
文档1与文档2的距离[[2.64575131]]
维度太高的话,复杂度会比较大,一般需要用到降维的方法
方法一在上述中用到了,就是所有大写都变成了小写
方法二,停用词过滤,即加上stop_words
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(stop_words='english')
print(vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus).todense())
print(vectorizer.vocabulary_)
[[0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1]
[0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0]
[1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0]]
{'unc': 7, 'played': 5, 'duke': 2, 'basketball': 1, 'lost': 4, 'game': 3, 'ate': 0, 'sandwich': 6}
方法三,还是CountVectorizer,这次是词干提取和词形还原
词干提取:去后缀

词形还原:将单词的复杂形态转变成最基础的形态
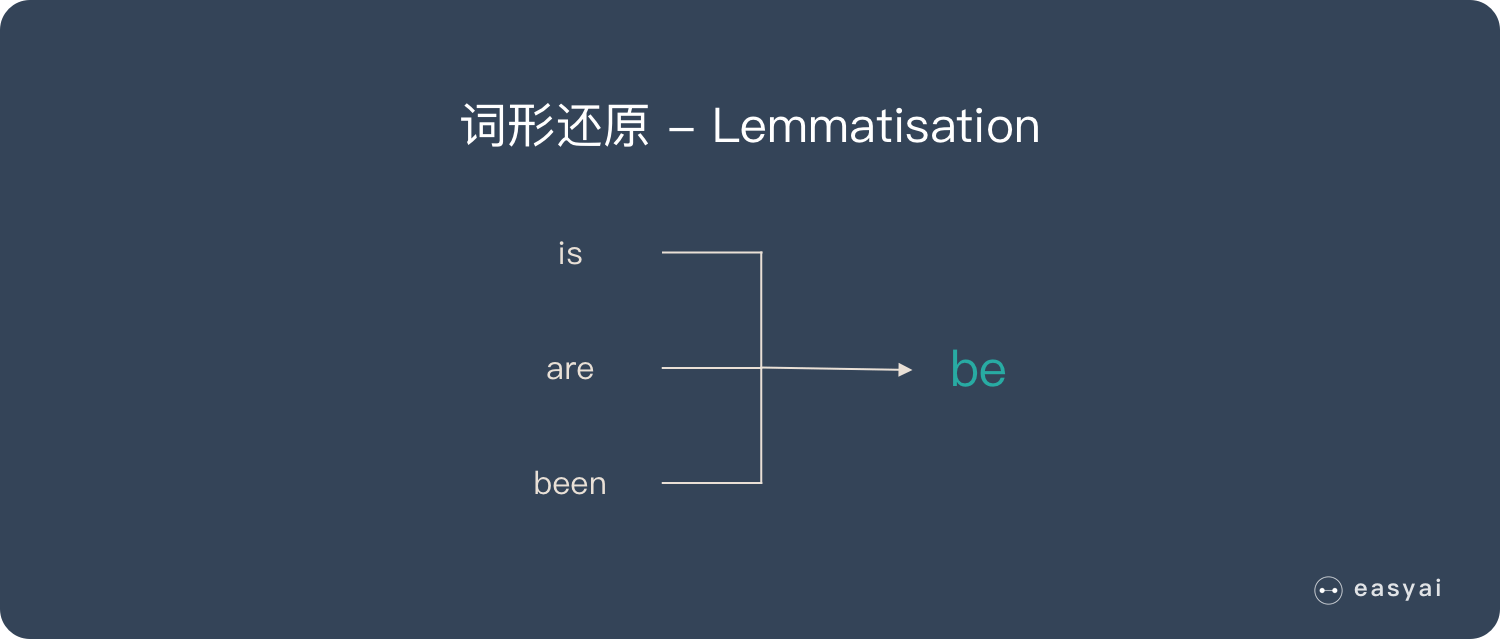
词干提取主要方法:Porter、Snowball、Lancaster
词形还原主要方法:使用NLTK库,再加上WordNet方法
在实际的代码中,注意一下一下内容的输出
corpus = ['he ate the sandwiches ','Every sandwich was eaten by him']
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(binary=True,stop_words='english')
print(vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus).todense())
print(vectorizer.vocabulary_)
[[1 0 0 1]
[0 1 1 0]]
{'ate': 0, 'sandwiches': 3, 'sandwich': 2, 'eaten': 1}
corpus = ['he ate the sandwiches every day','Every sandwich was eaten by him']
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(binary=True,stop_words='english')
print(vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus).todense())
print(vectorizer.vocabulary_)
[[1 1 0 0 1]
[0 0 1 1 0]]
{'ate': 0, 'sandwiches': 4, 'day': 1, 'sandwich': 3, 'eaten': 2}
corpus = ['jack ate the sandwiches every day','Every sandwich was eaten by him']
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(binary=True,stop_words='english')
print(vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus).todense())
print(vectorizer.vocabulary_)
[[1 1 0 1 0 1]
[0 0 1 0 1 0]]
{'jack': 3, 'ate': 0, 'sandwiches': 5, 'day': 1, 'sandwich': 4, 'eaten': 2}
可以看出,上述的词干提取,并不是简答剔除重复的,而是将无用的信息页剔除掉了,这一点需要注意。同时也反映了CountVectorizer的好用
接下来使用nltk
corpus = ['I am gathering ingredients for the sandwich.','There were many wizards at the gathering.']
from nltk.stem.wordnet import WordNetLemmatizer
lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize('gathering','v'))
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize('gathering','n'))
gather
gathering
sklearn机器学习-特征提取1的更多相关文章
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 19.7 和 sklearn机器学习模型 实现人脸微笑检测
0.引言 利用机器学习的方法训练微笑检测模型,给一张人脸照片,判断是否微笑: 使用的数据集中69张没笑脸,65张有笑脸,训练结果识别精度在95%附近: 效果: 图1 示例效果 工程利用pytho ...
- 使用sklearn机器学习库实现线性回归
import numpy as np # 导入科学技术框架import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 导入画图工具from sklearn.linear_model imp ...
- Python线性回归算法【解析解,sklearn机器学习库】
一.概述 参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/yszd/p/8529704.html 二.代码实现[解析解] import numpy as np import matplotl ...
- 用python+sklearn(机器学习)实现天气预报数据 模型和使用
用python+sklearn机器学习实现天气预报 模型和使用 项目地址 系列教程 0.前言 1.建立模型 a.准备 引入所需要的头文件 选择模型 选择评估方法 获取数据集 b.建立模型 c.获取模型 ...
- 用python+sklearn(机器学习)实现天气预报数据 数据
用python+sklearn机器学习实现天气预报 数据 项目地址 系列教程 勘误表 0.前言 1.爬虫 a.确认要被爬取的网页网址 b.爬虫部分 c.网页内容匹配取出部分 d.写入csv文件格式化 ...
- 用python+sklearn(机器学习)实现天气预报 准备
用python+sklearn机器学习实现天气预报 准备 项目地址 系列教程 0.流程介绍 1. 环境搭建 a.python b.涉及到的机器学习相关库 sklearn panda seaborn j ...
- 5分钟教你玩转 sklearn 机器学习(上)
假期结束,你的状态有没有回归?那么,放空脑袋后,先来学习学习,欢迎大家继续关注腾讯云技术社区. 作者:赵成龙 这是一篇很难写的文章,因为我希望这篇文章能对大家有所帮助.我不会给大家介绍机器学习,数据挖 ...
- sklearn文本特征提取
http://cloga.info/2014/01/19/sklearn_text_feature_extraction/ 文本特征提取 词袋(Bag of Words)表征 文本分析是机器学习算法的 ...
- Feature extraction - sklearn文本特征提取
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/41957763 文本特征提取 词袋(Bag of Words)表征 文本分析是机器学习算法的主要应用领域 ...
随机推荐
- Spring根据路径前缀获取不同Resource
相关文章:https://www.jianshu.com/p/5bab9e03ab92 官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-f ...
- AQS 支持两种同步方式?
1.独占式 2.共享式 这样方便使用者实现不同类型的同步组件,独占式如 ReentrantLock,共享式如 Semaphore,CountDownLatch,组合式的如 ReentrantReadW ...
- 学习zabbix(七)
zabbix自定义监控项 1.创建主机组,可以根据redis.mysql.web等创建对于的主机组 2.创建主机 3.创建Screens 4.自定义监控项 zabbix_agentd.conf配置文件 ...
- 【freertos】006-任务切换实现细节
前言 任务调度实现的两个核心: 调度器实现:(上一章节已描述调度基础) 任务切换实现. 接口层实现. 原文:李柱明博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/lizhuming/p/1608 ...
- 攻防世界baby_web
baby_web 题目提示想想初始页,但我们一访问就会跳转到1.php我们使用bp抓包分析,我们发送到repeater模块修改请求访问1.php内容看看 发现flag隐藏了我们去hex中看看 这样我们 ...
- 微信小程序黑客马拉松即将开始,来做最酷的 Mini Program Creators!
微信小程序黑客马拉松正式启动 近日,小程序斩获一项世界级殊荣--作为一项全新的技术和应用创新,小程序首次获选世界互联网领先科技成果.目前小程序应用数量已超过 100 万,覆盖了 200 多个细分行业, ...
- vue和mint-ui loadMore 实现上拉加载和下拉刷新
首先安装mint-ui组件库 npm install mint-ui 在main.js中引入mint-ui和样式 import 'mint-ui/lib/style.css' import MintU ...
- 各种类型的Dialog
下面是几种对话框的效果 图一: 图二: 图三: 图四: 图五: 图六: 图七: 图1效果:该效果是当按返回按钮时弹出一个提示,来确保无误操作,采用常见的对话框样式. 代码: 创建对话框方法dialog ...
- js手机号隐藏中间四位
var tel = "13122223333"; var reg = /^(\d{3})\d{4}(\d{4})$/; tel = tel.replace(reg, "$ ...
- Water 2.5.8 发布,一站式服务治理平台
Water(水孕育万物...) Water 为项目开发.服务治理,提供一站式解决方案(可以理解为微服务架构支持套件).基于 Solon 框架开发,并支持完整的 Solon Cloud 规范:已在生产环 ...
