Struts2学习第3天--OGNL、EL、值栈




JAVA中的OGNL:
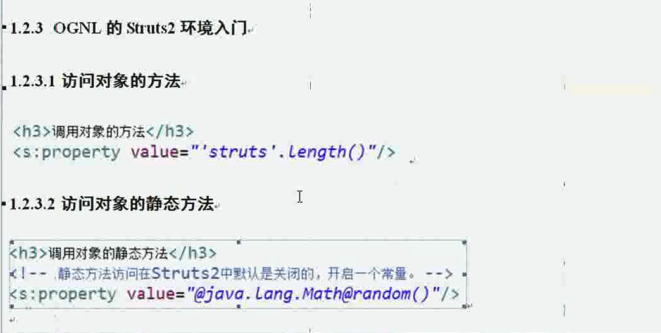
1 调用对象的方法:
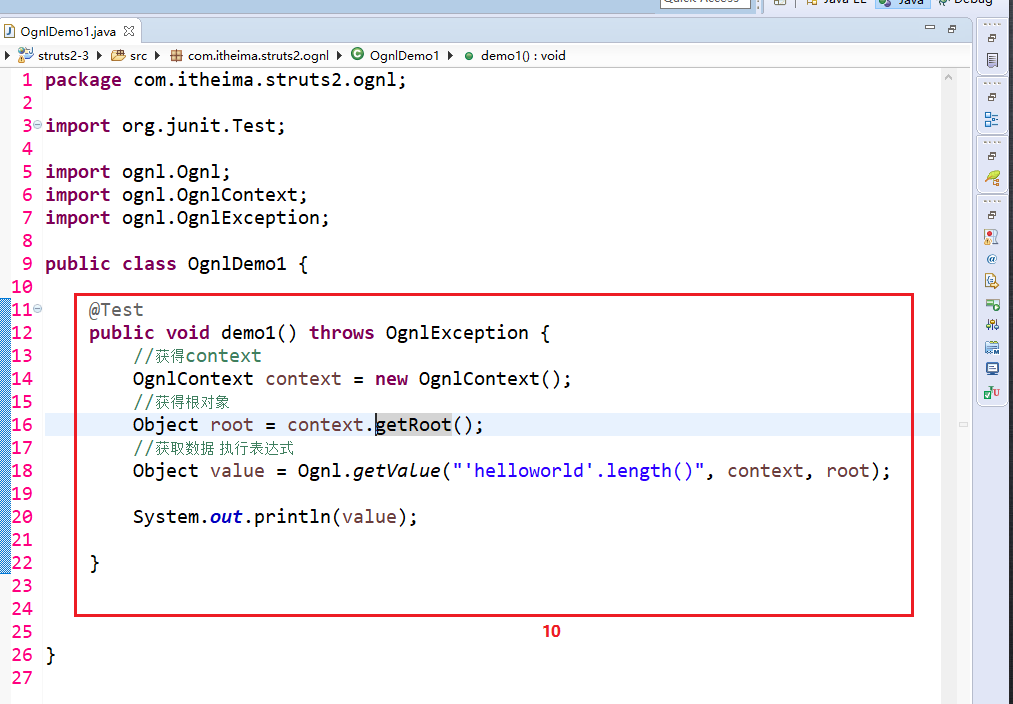
2 访问对象的静态方法:
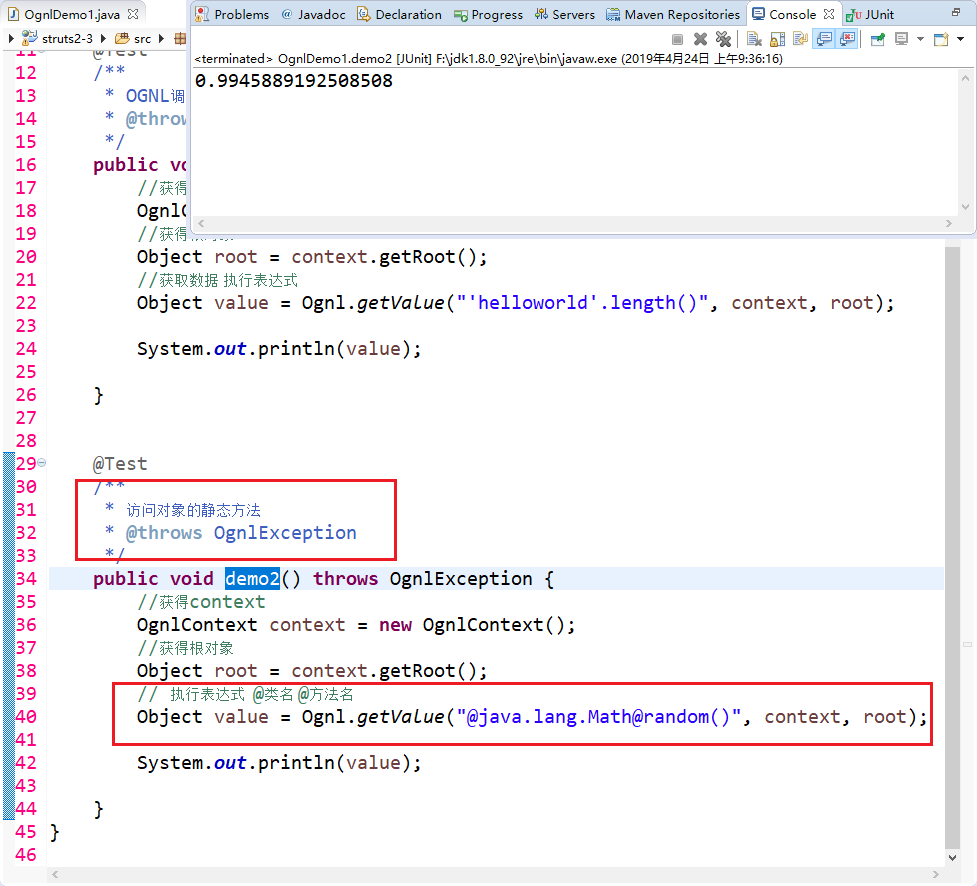
3 获取OGNLContext、Root中的数据。
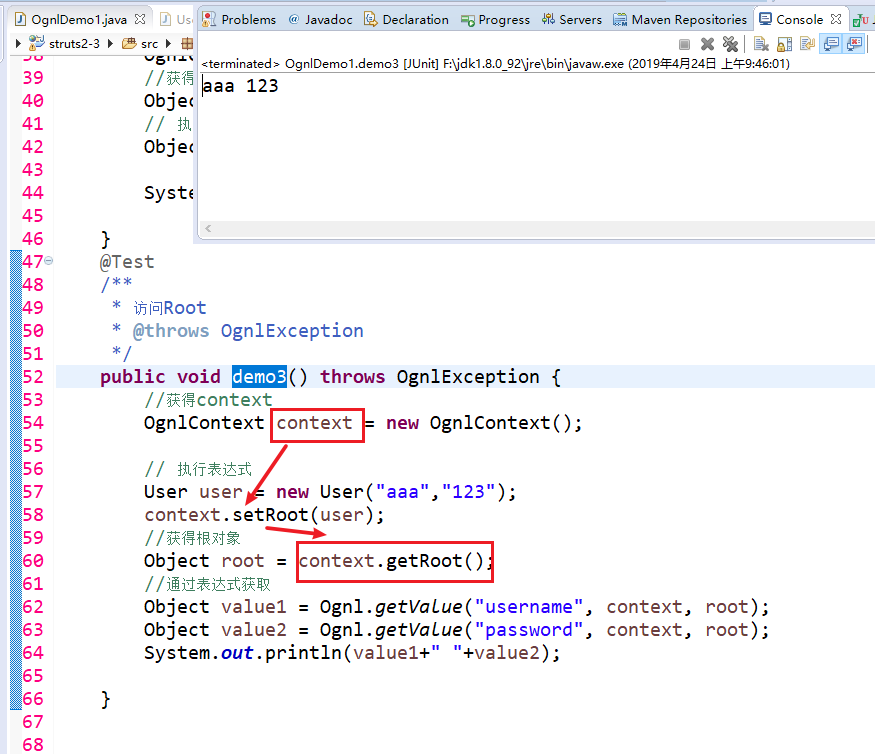
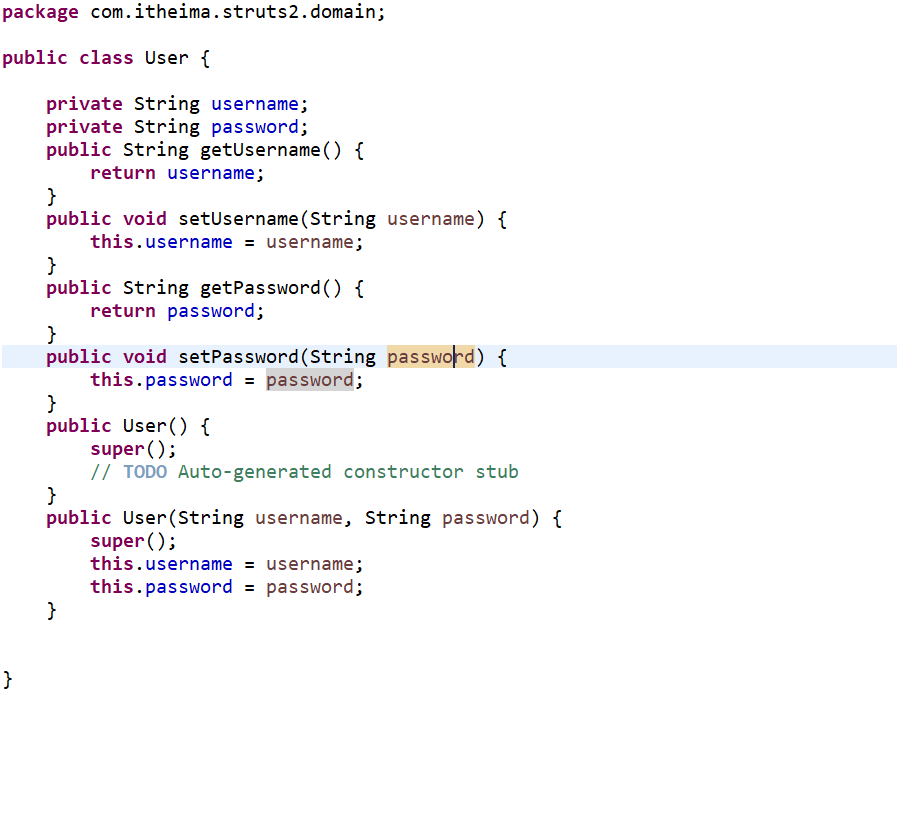
User:
4 访问Context:
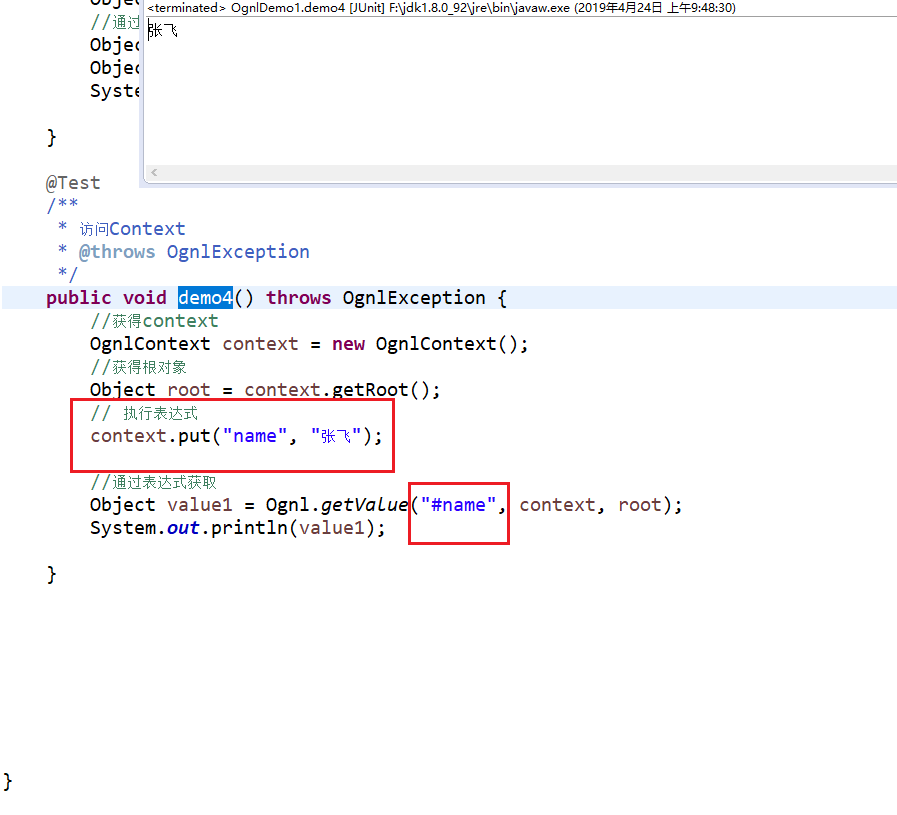
关键还是在Struts2环境中的使用:
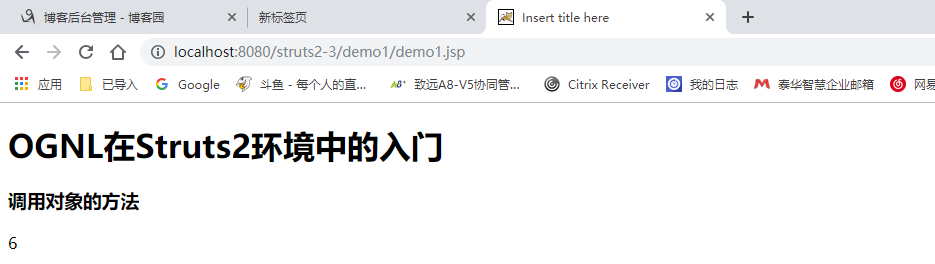
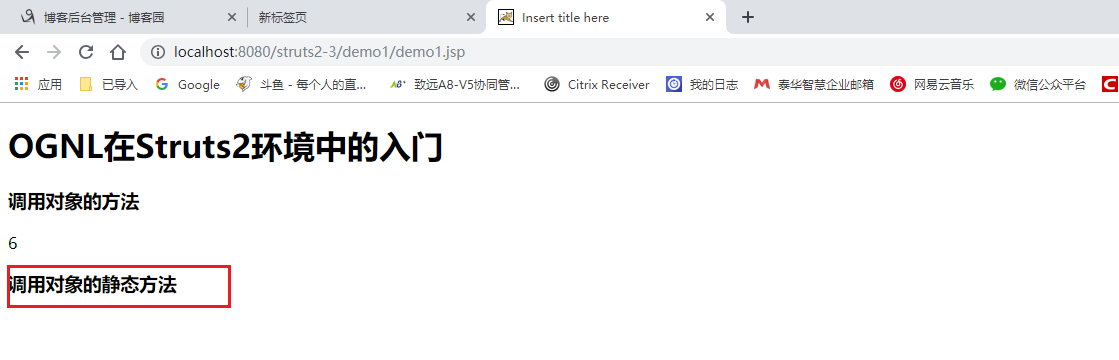
并没有打印 静态方法的值,因为Struts2默认关闭了。

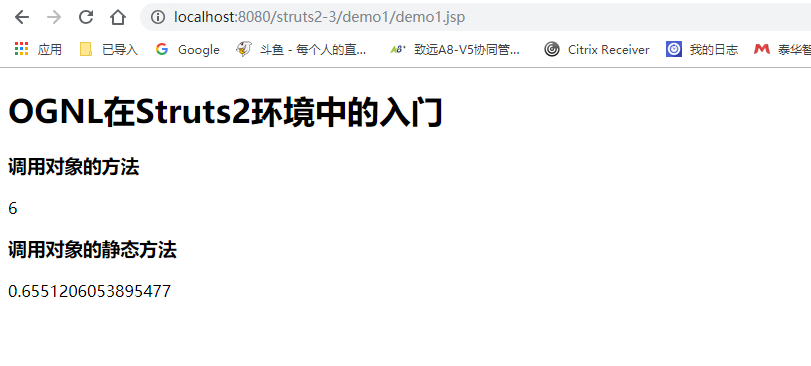
再次刷新后发现有值了。




编写demo

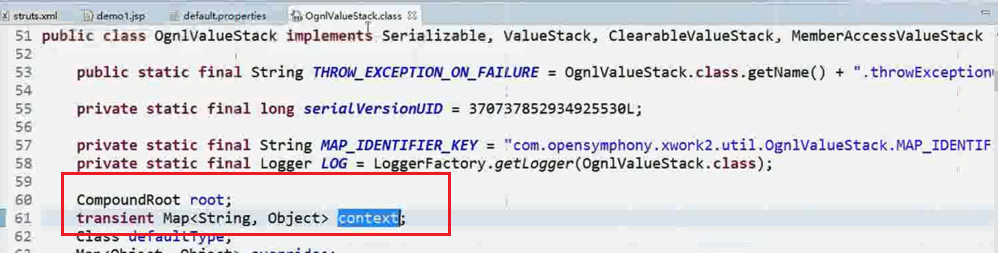
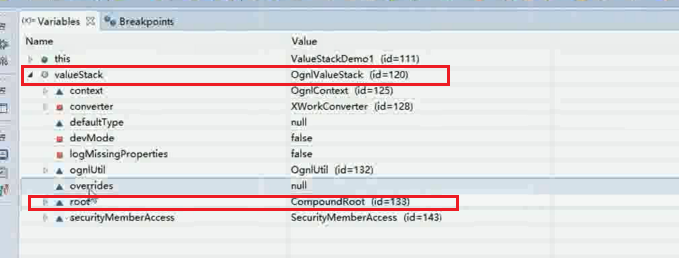
debug启动 打断点发现: root和context均在这里面。



修改demo返回值

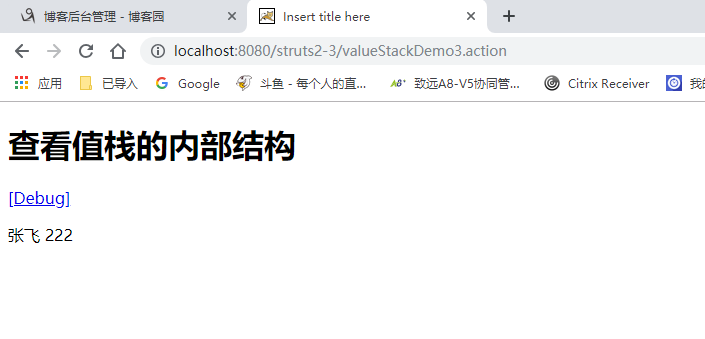
运行:


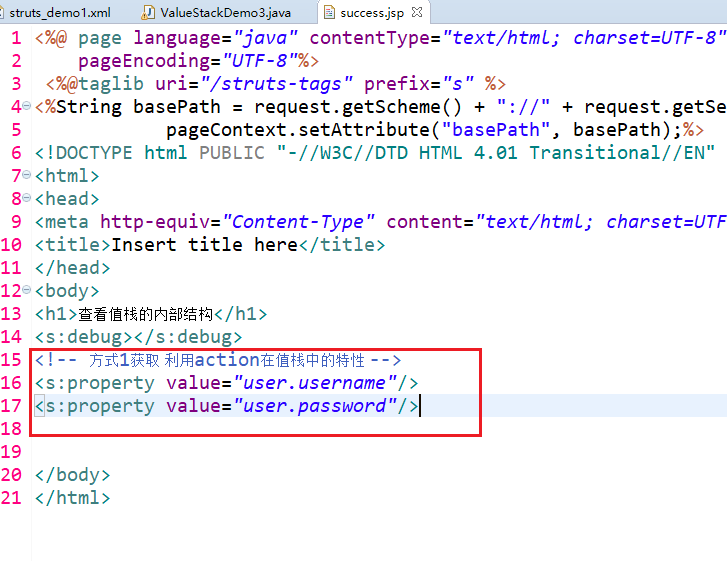
方式1:
方式2:
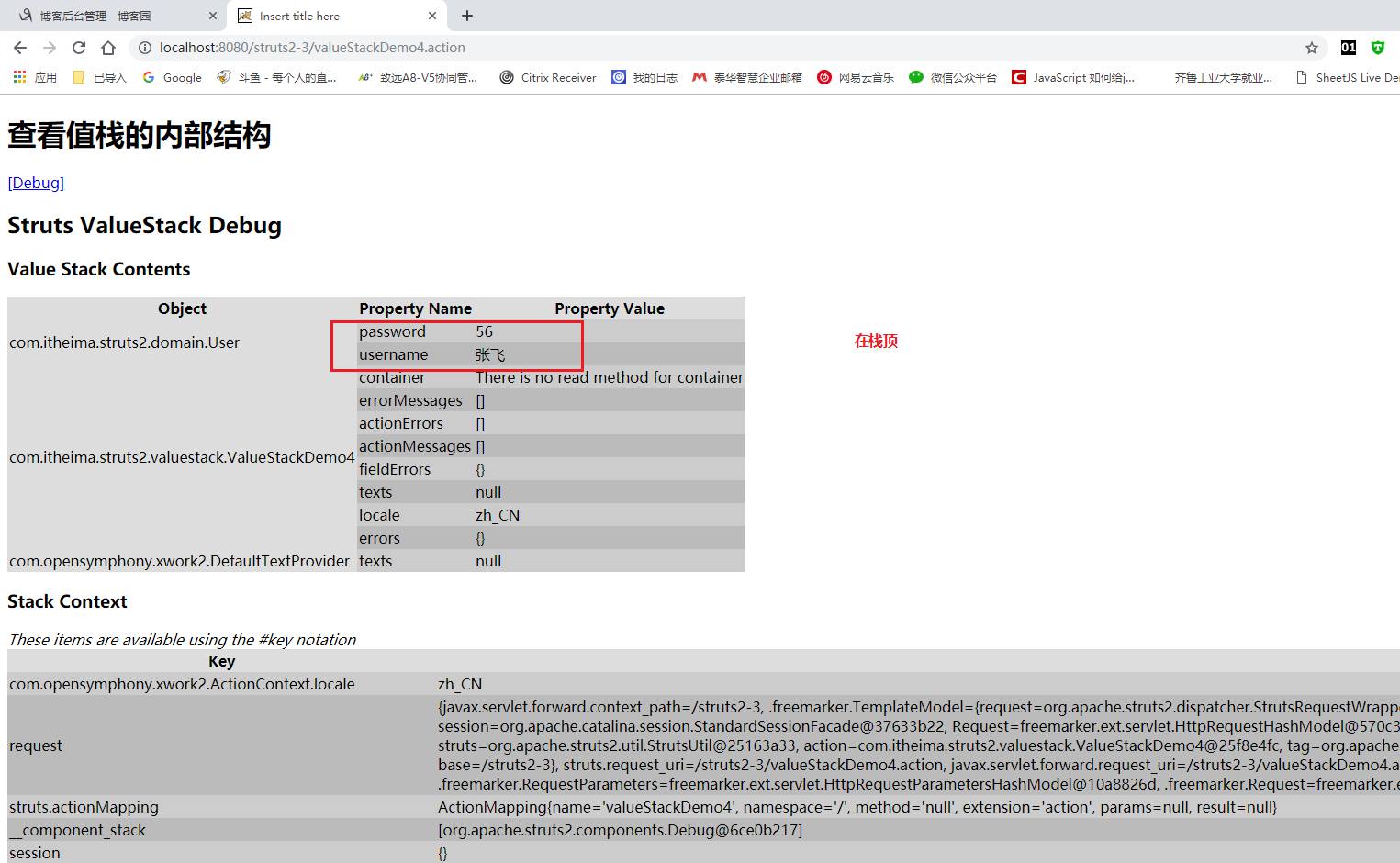

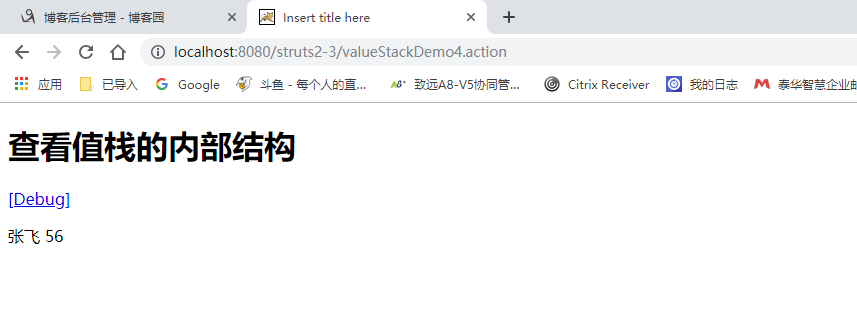
如果有多个user 默认展示栈顶的!!!


没有set get方法 无法查看 但是已经在栈顶了。
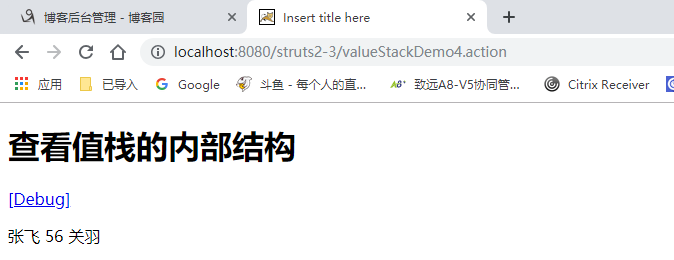
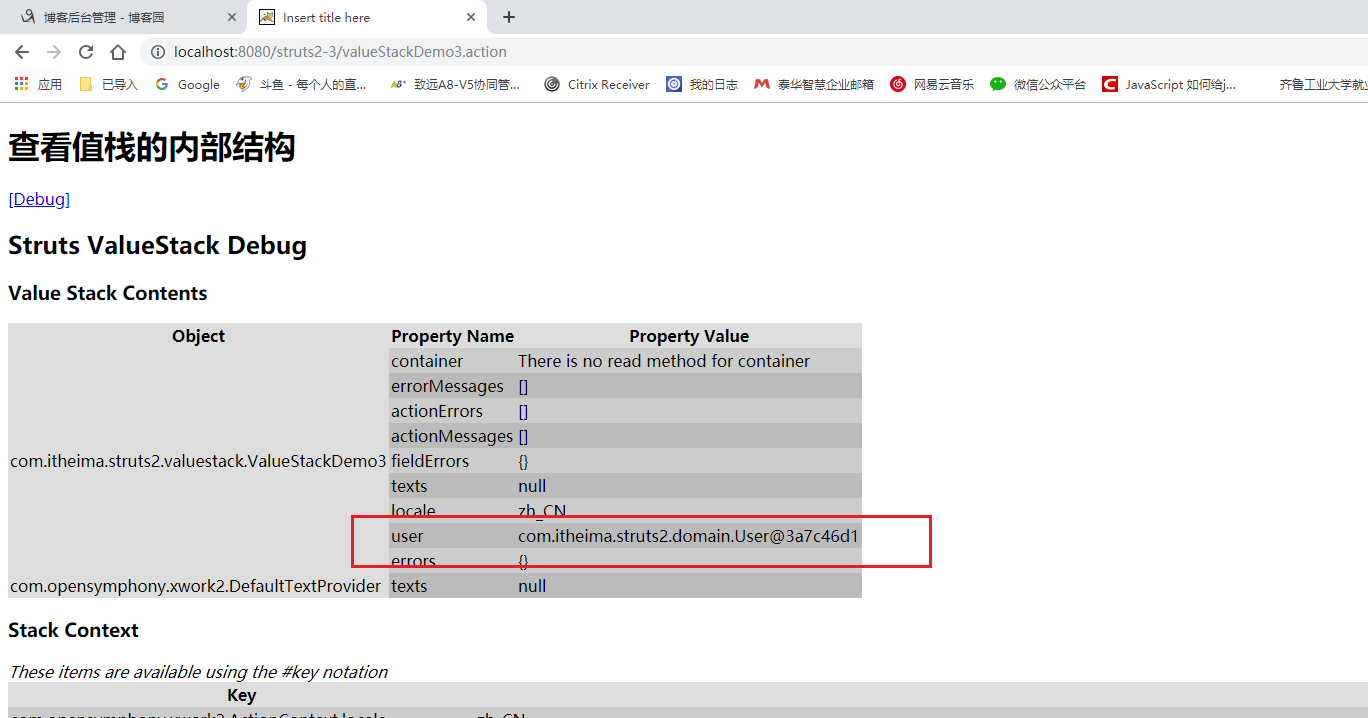
获取值栈的数据:



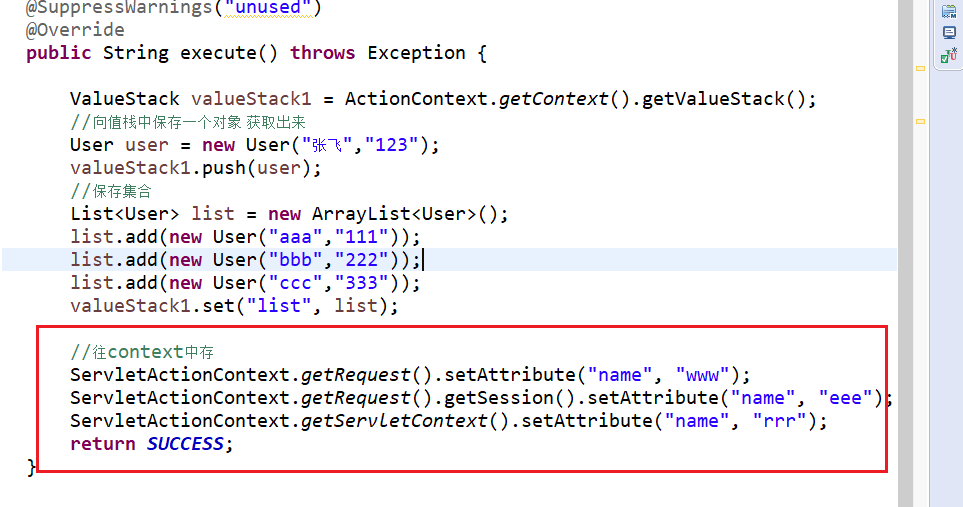

在debug里可以找到:
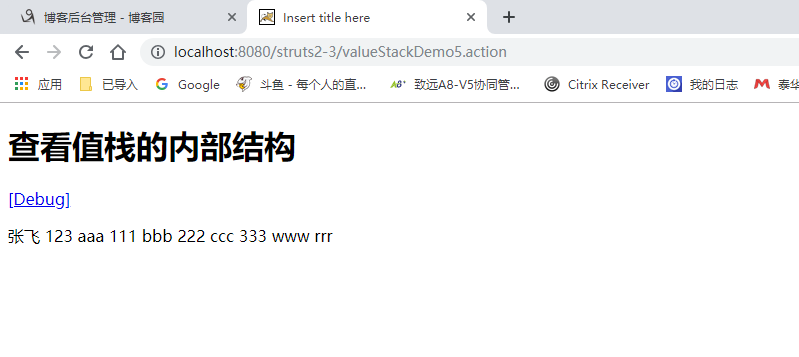
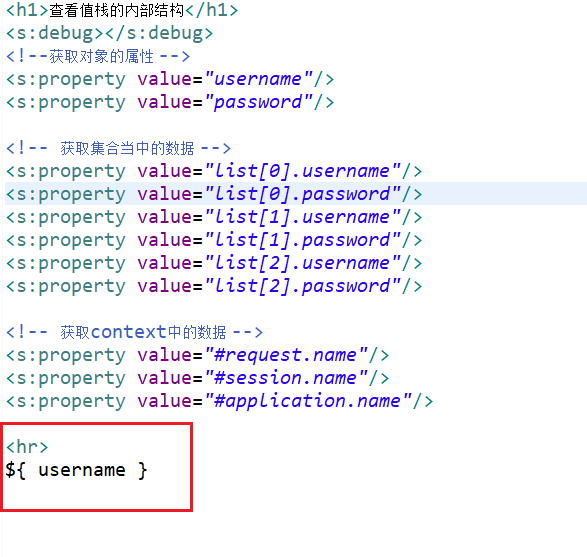
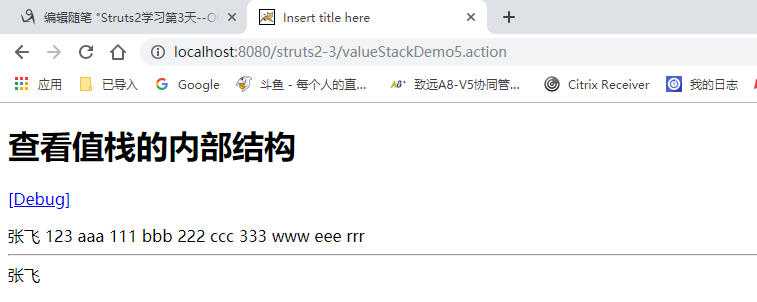

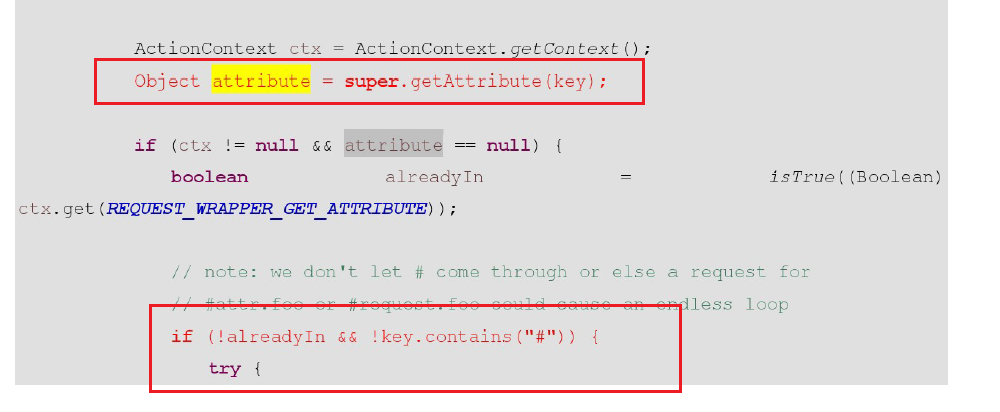
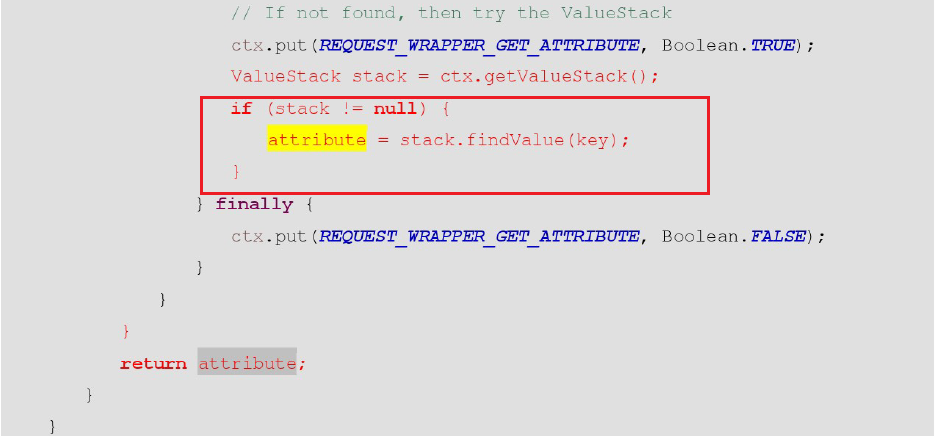
request中找不到 就自动去值栈中寻找。





修改crm
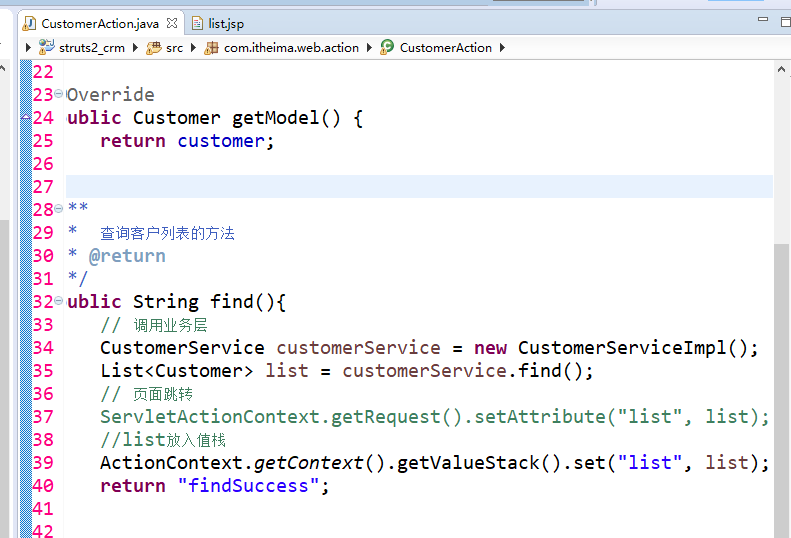
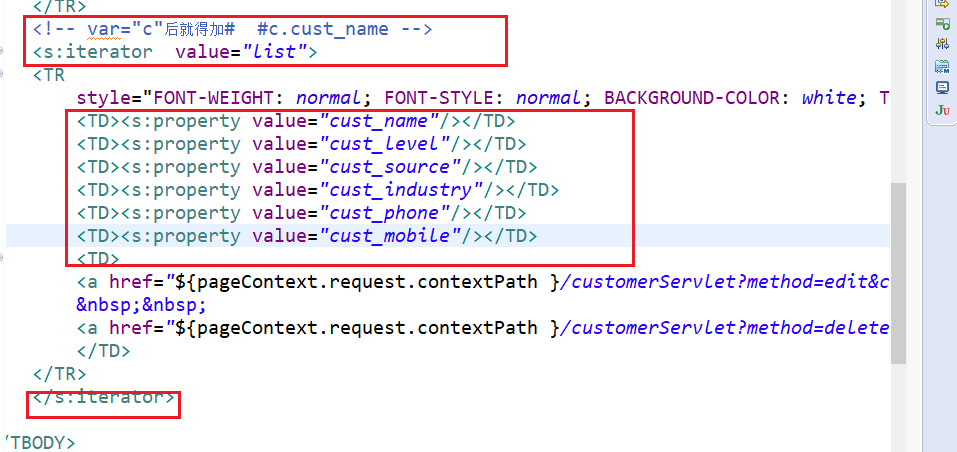
jsp中去掉jstl 引入struts标签库 然后不用foreach循环 改用s标签 。

今日代码:

package com.itheima.struts2.valuestack; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack; /**
* ValueStack内部结构
* @author ZWT
*
*/
public class ValueStackDemo1 extends ActionSupport{ @SuppressWarnings("unused")
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
//获得值栈
ValueStack valueStack = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack(); return SUCCESS;
} }
package com.itheima.struts2.valuestack; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack; /**
* 获得ValueStack对象
* @author ZWT
*
*/
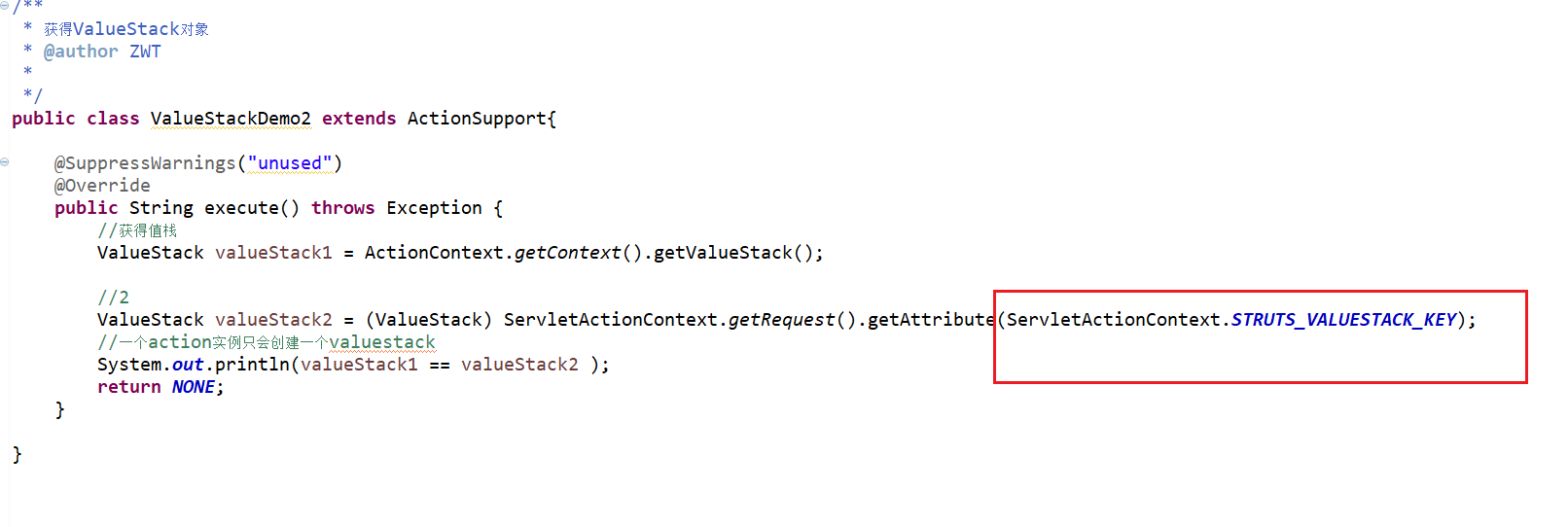
public class ValueStackDemo2 extends ActionSupport{ @SuppressWarnings("unused")
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
//获得值栈
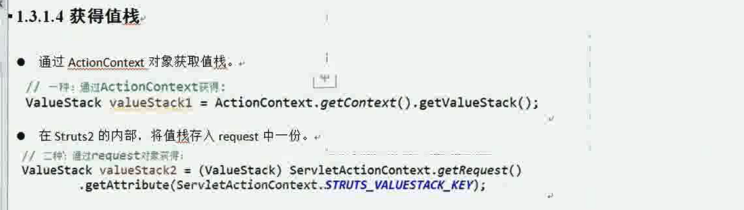
ValueStack valueStack1 = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack(); //2
ValueStack valueStack2 = (ValueStack) ServletActionContext.getRequest().getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
//一个action实例只会创建一个valuestack
System.out.println(valueStack1 == valueStack2 );
return NONE;
} }
package com.itheima.struts2.valuestack; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import com.itheima.struts2.domain.User;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack; /**
* 操作ValueStack
* @author ZWT
*
*/
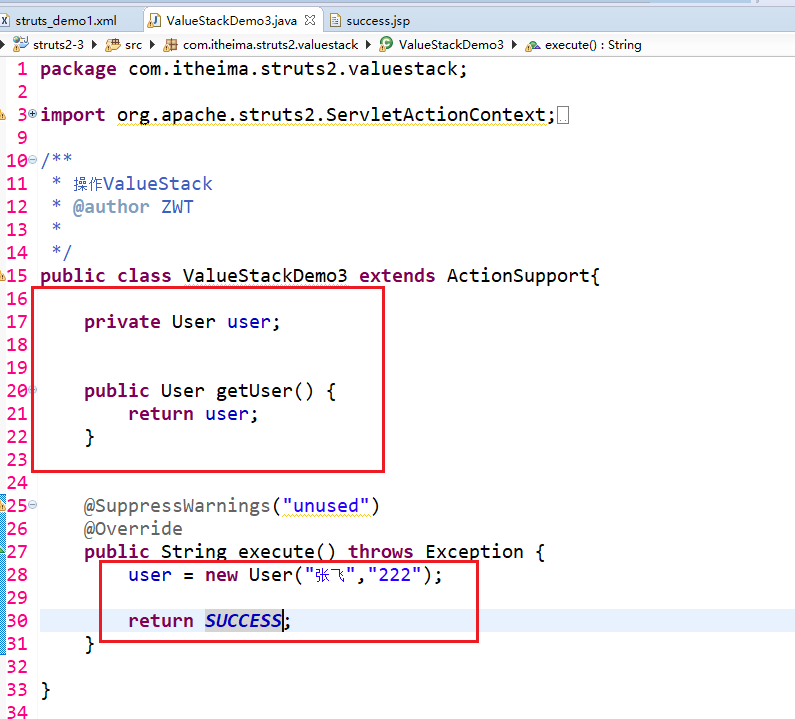
public class ValueStackDemo3 extends ActionSupport{ private User user; public User getUser() {
return user;
} @SuppressWarnings("unused")
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
user = new User("张飞","222"); return SUCCESS;
} }
package com.itheima.struts2.valuestack; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import com.itheima.struts2.domain.User;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack; /**
* 操作ValueStack :方式2 调用值栈中的方法实现
* @author ZWT
*
*/
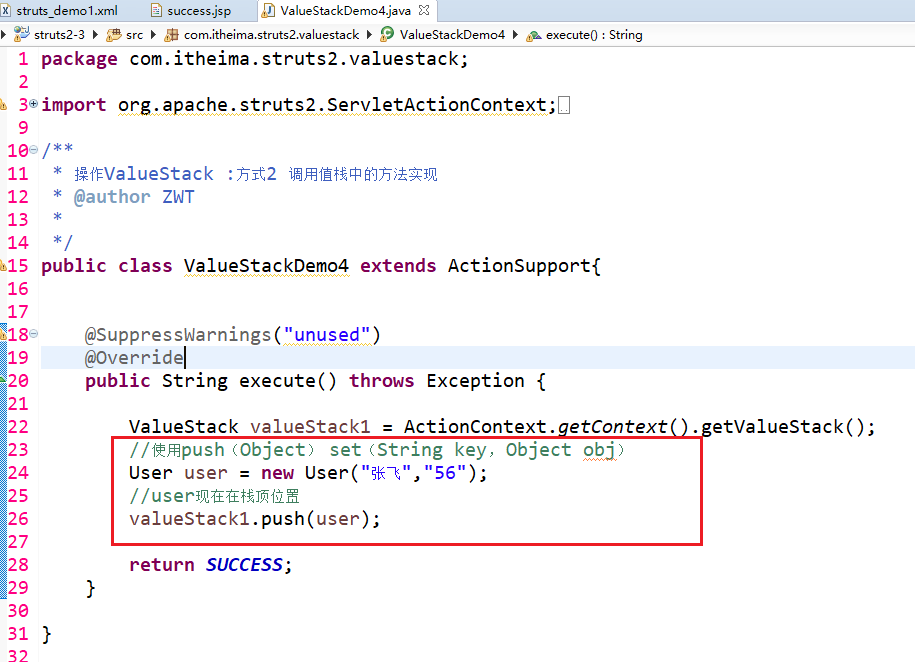
public class ValueStackDemo4 extends ActionSupport{ @SuppressWarnings("unused")
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception { ValueStack valueStack1 = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
//使用push(Object) set(String key, Object obj)
User user = new User("张飞","56");
//user现在在栈顶位置
valueStack1.push(user);
//创建map集合 map压入栈顶
valueStack1.set("name", "关羽");
return SUCCESS;
} }
package com.itheima.struts2.valuestack; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import com.itheima.struts2.domain.User;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack; /**
* 获取值栈的数据
* @author ZWT
*
*/
public class ValueStackDemo5 extends ActionSupport{ @SuppressWarnings("unused")
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception { ValueStack valueStack1 = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
//向值栈中保存一个对象 获取出来
User user = new User("张飞","123");
valueStack1.push(user);
//保存集合
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
list.add(new User("aaa","111"));
list.add(new User("bbb","222"));
list.add(new User("ccc","333"));
valueStack1.set("list", list); //往context中存
ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("name", "www");
ServletActionContext.getRequest().getSession().setAttribute("name", "eee");
ServletActionContext.getServletContext().setAttribute("name", "rrr");
return SUCCESS;
} }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<struts>
<package name="demo1" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="valueStackDemo1" class="com.itheima.struts2.valuestack.ValueStackDemo1">
<result>/demo1/success.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="valueStackDemo2" class="com.itheima.struts2.valuestack.ValueStackDemo2">
</action>
<action name="valueStackDemo3" class="com.itheima.struts2.valuestack.ValueStackDemo3">
<result>/demo1/success.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="valueStackDemo4" class="com.itheima.struts2.valuestack.ValueStackDemo4">
<result>/demo1/success.jsp</result>
</action> <action name="valueStackDemo5" class="com.itheima.struts2.valuestack.ValueStackDemo5">
<result>/demo1/success2.jsp</result>
</action> </package>
</struts>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd">
<struts>
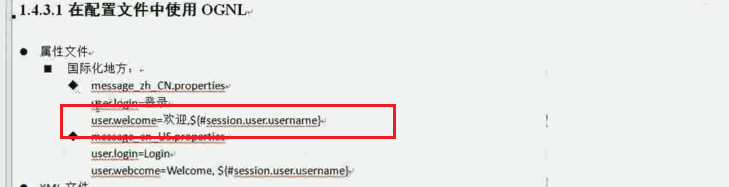
<!-- 配置Struts2的常量 -->
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action"/>
<!--开启静态方法访问 -->
<constant name="struts.ognl.allowStaticMethodAccess" value="true"></constant> <include file="com/itheima/struts2/valuestack/struts_demo1.xml"></include> </struts>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %>
<%String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort()+ request.getContextPath();
pageContext.setAttribute("basePath", basePath);%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
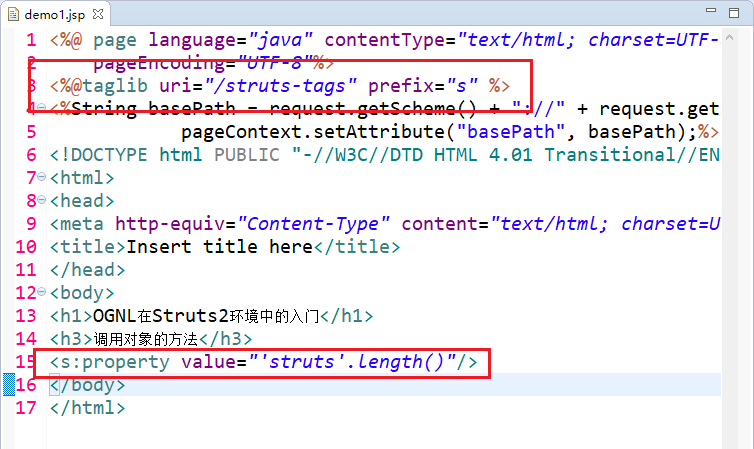
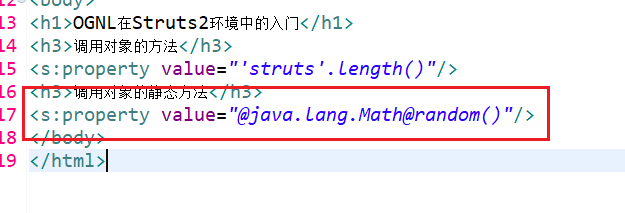
<h1>OGNL在Struts2环境中的入门</h1>
<h3>调用对象的方法</h3>
<s:property value="'struts'.length()"/>
<h3>调用对象的静态方法</h3>
<s:property value="@java.lang.Math@random()"/> </body>
</html>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %>
<%String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort()+ request.getContextPath();
pageContext.setAttribute("basePath", basePath);%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
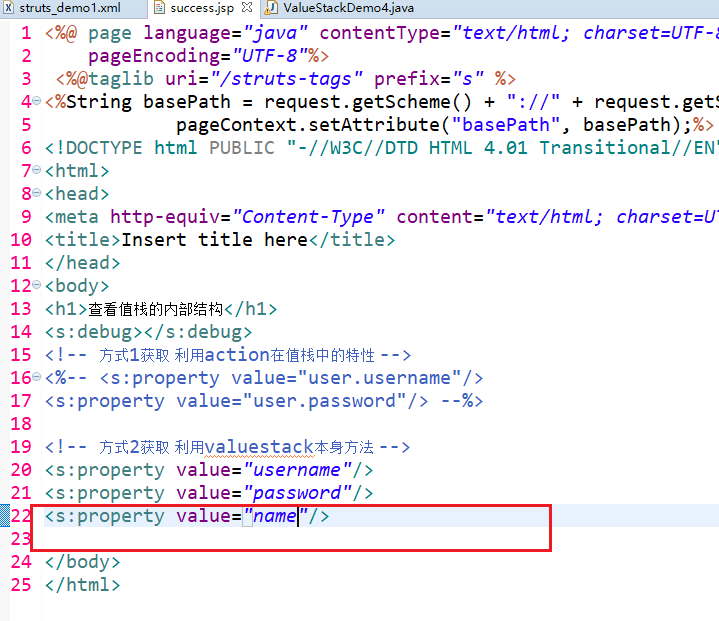
<h1>查看值栈的内部结构</h1>
<s:debug></s:debug>
<!-- 方式1获取 利用action在值栈中的特性 -->
<%-- <s:property value="user.username"/>
<s:property value="user.password"/> --%> <!-- 方式2获取 利用valuestack本身方法 -->
<s:property value="username"/>
<s:property value="password"/>
<s:property value="name"/> </body>
</html>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %>
<%String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort()+ request.getContextPath();
pageContext.setAttribute("basePath", basePath);%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>查看值栈的内部结构</h1>
<s:debug></s:debug>
<!--获取对象的属性 -->
<s:property value="username"/>
<s:property value="password"/> <!-- 获取集合当中的数据 -->
<s:property value="list[0].username"/>
<s:property value="list[0].password"/>
<s:property value="list[1].username"/>
<s:property value="list[1].password"/>
<s:property value="list[2].username"/>
<s:property value="list[2].password"/> <!-- 获取context中的数据 -->
<s:property value="#request.name"/>
<s:property value="#session.name"/>
<s:property value="#application.name"/> <hr>
${ username } </body>
</html>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %>
<%String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort()+ request.getContextPath();
pageContext.setAttribute("basePath", basePath);%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
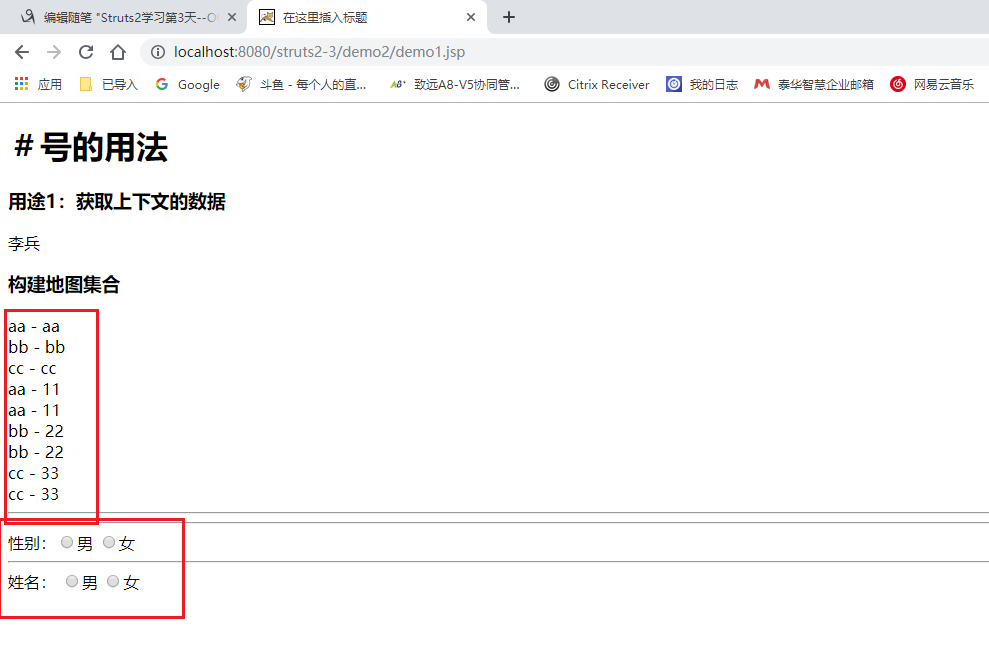
<h1>#号的用法</h1>
<h3>用途1:获取context的数据</h3>
<%
request.setAttribute("name","李兵");
%>
<s:property value="#request.name"/> <h3>构建map集合</h3>
<!-- list i只要定义 context中也有-->
<s:iterator var="i" value="{'aa','bb','cc'}">
<s:property value="i"/>--<s:property value="#i"/><br>
</s:iterator>
<!-- map -->
<s:iterator var="entry" value="#{'aa':'11','bb':'22','cc':'33' }">
<s:property value="key"/>--<s:property value="value"/><br>
<s:property value="#entry.key"/>--<s:property value="#entry.value"/><br>
</s:iterator>
<hr>
<!-- value值 和 外面的‘男’ 一样就用list 不然用map -->
<%-- 性别:<input type="radio" name="sex1" value="男">男
<input type="radio" name="sex1" value="女">女
<hr>
<s:radio list="{'男','女'}" name="sex2" label="姓名" /> --%>
<hr>
性别:<input type="radio" name="sex1" value="1">男
<input type="radio" name="sex1" value="2">女
<hr>
<s:radio list="#{'1':'男','2':'女'}" name="sex2" label="姓名" /> </body>
</html>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %>
<%String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort()+ request.getContextPath();
pageContext.setAttribute("basePath", basePath);%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
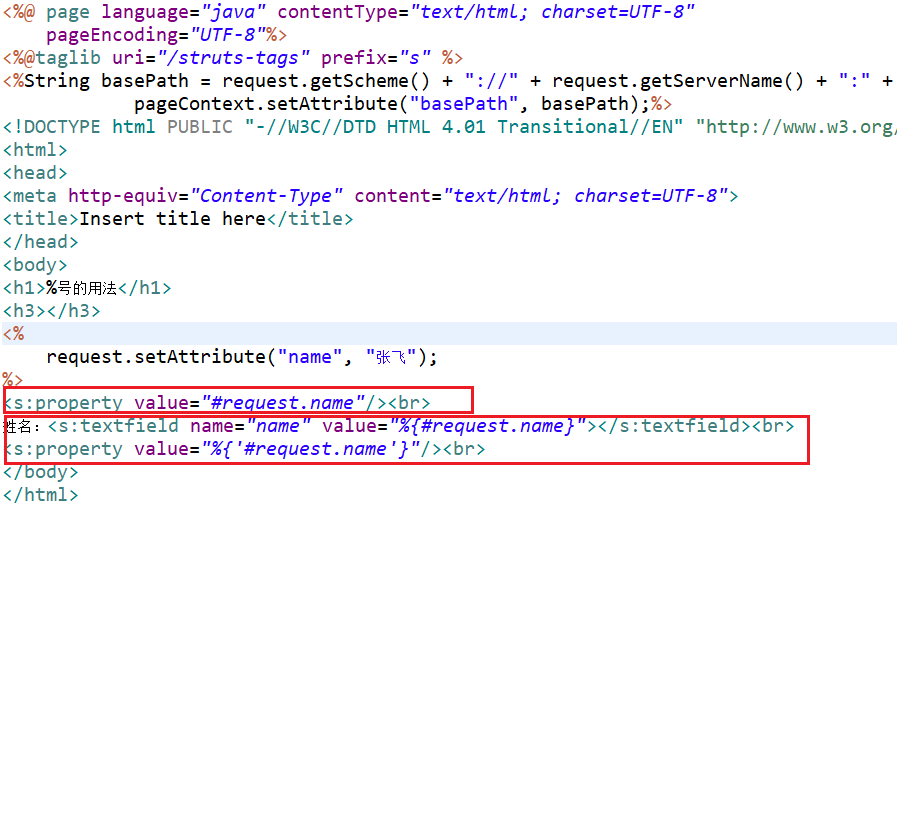
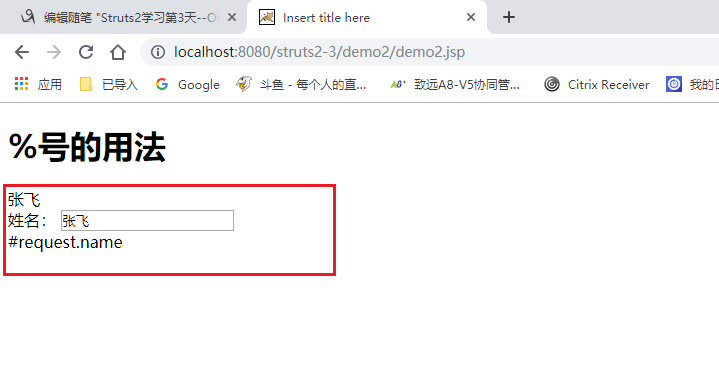
<h1>%号的用法</h1>
<h3></h3>
<%
request.setAttribute("name", "张飞");
%>
<s:property value="#request.name"/><br>
姓名:<s:textfield name="name" value="%{#request.name}"></s:textfield><br>
<s:property value="%{'#request.name'}"/><br>
</body>
</html>
Struts2学习第3天--OGNL、EL、值栈的更多相关文章
- Struts工作机制图+OGNL+EL+值栈(Map,对象栈)
struts 值栈 通过get set方法 方便的获取,设置属性值 比如从jsp页面传来的參数...从Action设置jsp所要回显的内容 注意EL表达式,struts2对request进 ...
- Struts2笔记3--获取ServletAPI和OGNL与值栈
获取ServletAPI: 第一种方式: //在request域中放入属性req,暂且认为getContext()获取的是request域空间,但实际不是 ActionContext.getConte ...
- struts2中,OGNL访问值栈的时候查找的顺序是什么?请排序:模型对象、临时对象、固定名称的对象、Action对象
struts2中,OGNL访问值栈的时候查找的顺序是什么?请排序:模型对象.临时对象.固定名称的对象.Action对象 解答:struts2的值栈排列顺序为:1).临时对象:2).模型对象:3).Ac ...
- (转)OGNL与值栈
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/67709693 OGNL的概述 什么是OGNL 据度娘所说: OGNL是Object-Graph ...
- 框架学习之Struts2(三)---OGNL和值栈
一.OGNL概述 1.1OGNL是对象图导航语言(Object-Graph Navigation Languaged)的缩写,他是一种功能强大的表达式语言,通过简单一致的表达式语法,可以存取Java对 ...
- Struts2学习(四)———— ognl表达式、值栈、actionContext之间的关系
一.什么是Ognl? 通过百度百科查询到的解释,其中详细的说明了OGNL的作用. 下面我们就对OGNL这5个作用进行讲解 1.存取对象的任意属性,简单说就是对javabean进行操作(重要) 2.调用 ...
- Struts2 (三) — OGNL与值栈
一.OGNL表达式 1.概述 1.1什么是OGNL OGNL是Object-Graph Navigation Language的缩写,俗称对象图导航语言. 它是一种功能强大的表达式语言,通过它简单 ...
- EL与OGNL以及值栈的理解
这里先添加下在项目遇到的问题: 这两天在做论坛项目的时候,犯了一个错误:将数据放入值栈中,结果jsp页面获取不到. 困扰了许久: 总结如下: (1)每个action对应相应页面的值栈中值的获取,在属于 ...
- Struts2学习第七课 OGNL
request变成了struts重写的StrutsRequestWrapper 关于值栈: helloWorld时,${productName}读取productName值,实际上该属性并不在requ ...
随机推荐
- 解决在“Resources”参数中指定了项“obj\Debug\KaiShiHID.Form1.resources”多次。“Resources”参数不支持重复项
错误截图: 发生原因描述: 窗体Form1, 有一个分部类; 叫做FormPartial.cs; 双击了FormPartial这个窗体, 然后生成了一个Load事件, 即时就报了编译错误, 然后就删除 ...
- 关于XSS漏洞的简介以及分类
不得不说注入的时代已经过去了,最近xss貌似比较热门.我就去恶补了一下,我表示我只是菜鸟,对xss不了解.所以从最基本的学起. 什么xss漏洞? 一.XSS攻击简介 作为一种HTML注入攻击,XSS攻 ...
- 科学计算工具Numpy简介
Numpy(Numerical Python) Numpy:提供了一个在Python中做科学计算的基础库,重在数值计算,主要用于多维数组(矩阵)处理的库.用来存储和处理大型矩阵,比Python自身的嵌 ...
- Internet Explorer 无法打开该 Internet 站点,请求的站点不可用或无法找到
笔者最近遇见一个神奇的问题,同事在开发时用的谷歌浏览器,实现了一个下载功能,测试也没问题:但测试人员反馈说他那边没法下载,报异常.弹出框 同事跑过来和我商讨这个问题,笔者当时就懵了,于是赶紧查找相关资 ...
- spring中二个重要点
spring核心主要两部分: (1)aop: 面向切面编程,扩展功能不是修改源代码实现 (2)ioc: 控制反转
- Cfree clion windows c语言 socket 网络编程
server.c #include <stdio.h> #include <winsock2.h> #define SERVER_PORT 5208 //侦听端口 int ma ...
- Leetcode:Divide Two Integers分析和实现
题目要求我们用一个32位整数整除另外一个整数,但是不允许我们使用除法,乘法和取模运算. 有趣的问题,下面说一下我的思路: 首先,先给出两个正整数除法运算的过程.假设a为被除数,而b为除数.在计算机中无 ...
- leetcode:Median of Two Sorted Arrays分析和实现
这个问题的大意是提供两个有序的整数数组A与B,A与B并集的中间数.[1,3]与[2]的中间数为2,因为2能将A与B交集均分.而[1,3]与[2,4]的中间数为2.5,取2与3的平均值.故偶数数目的中间 ...
- 在线创建MongoDB免费集群(MangoDB Atlas)
MongoDB Atlas是MongoDB的云服务,构建在亚马逊的AWS上,MongoDB允许用户在上面创建一个免费集群作为学习使用. 1. 注册MongoDB cloud账号: 访问www.mong ...
- 数据预处理 center&scale&box-cox
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/33944129/python-library-for-data-scaling-centering-and-box-cox-tr ...
