TypeScript 源码详细解读(2)词法1-字符处理
本节文章研究的代码位于 tsc/src/compiler/scanner.ts
字符
任何源码都是由很多字符组成的,这些字符可以是字母、数字、空格、符号、汉字等……
每一个字符都有一个编码值,比如字符“a”的编码值是97,字符“林”的编码值是26519。
每个字符对应的编码值是多少是由编码表决定的,上面所示的编码值是全球统一的编码表 Unicode 中的编码值,如果没有特别声明,所有编码值都是以 Unicode 为准的。
一般地,字符的编码值都是有序的,比如字符“a”的编码值是97,字符“b”的编码值是98,字符“c”的编码值是99,汉字则是按照笔划顺序排序的。在给字符串排序时,也是根据每个字符的编码值大小进行排序的。
如果想要判断一个字符是不是英文字母,只需要判断这个字符的编码值是否位于字符“a”的编码值和字符“z”的编码值之间即可。
在 JavaScript 中,可以通过 "a".charCodeAt(0) 获取字符“a”的编码值;通过 String.fromCharCode(97) 获取指定编码值对应的字符。
CharacterCodes 枚举
在代码中如果直接写 99,你可能不清楚这个数字的含义,但如果写成 CharacterCodes.c,你就可以很快明白。通过枚举给每个编码值定义一个名称,方便读者理解,同时我们也不需要去记忆每个字符的实际编码值。CharacterCodes 枚举位于 tsc/src/compiler/types.ts,源码如下:
/* @internal */
export const enum CharacterCodes {
_0 = 0x30,
_1 = 0x31,
// ...(略)
_9 = 0x39, a = 0x61,
b = 0x62,// ...(略)
z = 0x7A, A = 0x41,// ...(略)
Z = 0x5a, ampersand = 0x26, // &
asterisk = 0x2A, // *
// ...(略)
}
字符判断
要判断一个字符是不是数字字符,只需确认它的字符编码是不是在“0”和“9”的编码值之间:
function isDigit(ch: number): boolean { // 参数 ch 表示一个编码值
return ch >= CharacterCodes._0 && ch <= CharacterCodes._9;
}
同理,还可以判断其它字符,比如判断是不是换行符:
export function isLineBreak(ch: number): boolean {
// ES5 7.3:
// The ECMAScript line terminator characters are listed in Table 3.
// Table 3: Line Terminator Characters
// Code Unit Value Name Formal Name
// \u000A Line Feed <LF>
// \u000D Carriage Return <CR>
// \u2028 Line separator <LS>
// \u2029 Paragraph separator <PS>
// Only the characters in Table 3 are treated as line terminators. Other new line or line
// breaking characters are treated as white space but not as line terminators.
return ch === CharacterCodes.lineFeed ||
ch === CharacterCodes.carriageReturn ||
ch === CharacterCodes.lineSeparator ||
ch === CharacterCodes.paragraphSeparator;
}
根据 ES 规范,换行符一共有 4 个,虽然平常我们只实用前两个,但对有些语言来说,后两个也是需要的。
判断是不是空格:
export function isWhiteSpaceLike(ch: number): boolean {
return isWhiteSpaceSingleLine(ch) || isLineBreak(ch);
}
/** Does not include line breaks. For that, see isWhiteSpaceLike. */
export function isWhiteSpaceSingleLine(ch: number): boolean {
// Note: nextLine is in the Zs space, and should be considered to be a whitespace.
// It is explicitly not a line-break as it isn't in the exact set specified by EcmaScript.
return ch === CharacterCodes.space ||
ch === CharacterCodes.tab ||
ch === CharacterCodes.verticalTab ||
ch === CharacterCodes.formFeed ||
ch === CharacterCodes.nonBreakingSpace ||
ch === CharacterCodes.nextLine ||
ch === CharacterCodes.ogham ||
ch >= CharacterCodes.enQuad && ch <= CharacterCodes.zeroWidthSpace ||
ch === CharacterCodes.narrowNoBreakSpace ||
ch === CharacterCodes.mathematicalSpace ||
ch === CharacterCodes.ideographicSpace ||
ch === CharacterCodes.byteOrderMark;
}
有的地方需要把换行当空格处理,有的地方不需要,所以 TypeScript 拆成两个函数,一个包括换行符,一个不包括。
判断标识符(Identifier)
标识符即俗称的变量名,我们都知道 JS 中变量名是不能随便取的,是有规则的,比如开头不能是数字。
在 ES 规范中,明确地点名了:哪些字符可以做标识符;哪些字符可以做标识符但不能以它开头。TypeScript 实现了 isUnicodeIdentifierStart 和 isUnicodeIdentifierPart 来分别判断。
哪些字符可以做标识符,其实是没有简单的规律的,这些都是在 ES 规范一个个手动指定的,规范中这个列表很长,最简单的实现就是:手动记录每个字符是否允许作标识符,然后查表。
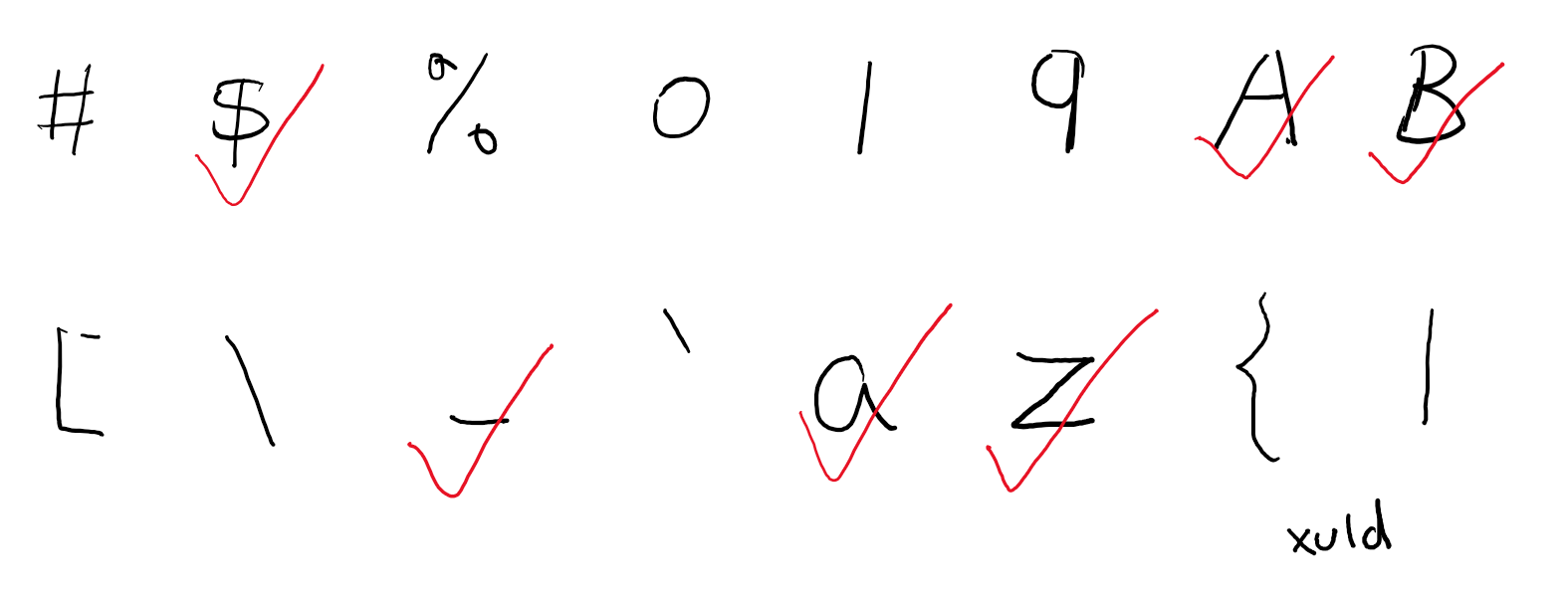
不过字符很多,每个字符单独记录要占用很大空间,所以 TypeScript 设计了一个小算法来压缩内存,算法基于这么一个事实:一般地,允许作为标识符的字符都是连续的一段(比如“a”到“z”)。
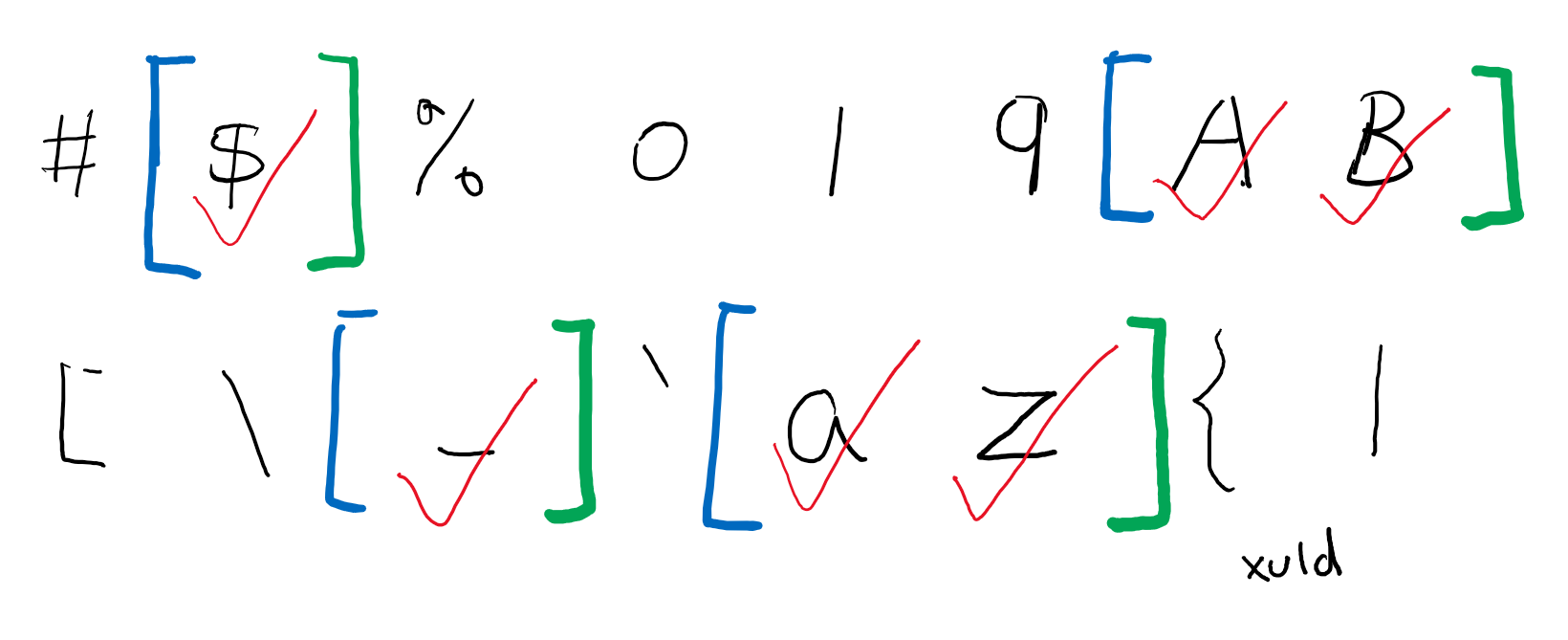
只要记录每段的开头和结尾部分,就可以比原先的记录该段的所有字符,要更节约内存。
将所有开始位置和结束位置放在同一个数组,数组的奇数位即图中的蓝色段,表示每段开头,偶数位即绿色段,表示每段结尾。
当需要查找一个字符是不是标识符时,采用二分搜索算法,快速定位确认它是否在包含的段中。
const unicodeESNextIdentifierStart = [65, 90, 97, 122, 170, /*...(略) */, 194560, 195101]
const unicodeESNextIdentifierPart = [48, 57, 65, /*...(略) */, 917999] function lookupInUnicodeMap(code: number, map: readonly number[]): boolean {
// 由于代码中多数字符还是英文字符,如果是就不查表直接判断
// Bail out quickly if it couldn't possibly be in the map.
if (code < map[0]) {
return false;
} // 以下是标准二分搜索算法,不懂的同学请自己补课
// Perform binary search in one of the Unicode range maps
let lo = 0;
let hi: number = map.length;
let mid: number; while (lo + 1 < hi) {
mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
// mid has to be even to catch a range's beginning
mid -= mid % 2;
if (map[mid] <= code && code <= map[mid + 1]) {
return true;
}
if (code < map[mid]) {
hi = mid;
} else {
lo = mid + 2;
}
} return false;
}
接下来就可以看明白 isUnicodeIdentifierStart 和 isUnicodeIdentifierPart 这两个函数了:
/* @internal */ export function isUnicodeIdentifierStart(code: number, languageVersion: ScriptTarget | undefined) {
return languageVersion! >= ScriptTarget.ES2015 ?
lookupInUnicodeMap(code, unicodeESNextIdentifierStart) :
languageVersion! === ScriptTarget.ES5 ? lookupInUnicodeMap(code, unicodeES5IdentifierStart) :
lookupInUnicodeMap(code, unicodeES3IdentifierStart);
}
function isUnicodeIdentifierPart(code: number, languageVersion: ScriptTarget | undefined) {
return languageVersion! >= ScriptTarget.ES2015 ?
lookupInUnicodeMap(code, unicodeESNextIdentifierPart) :
languageVersion! === ScriptTarget.ES5 ? lookupInUnicodeMap(code, unicodeES5IdentifierPart) :
lookupInUnicodeMap(code, unicodeES3IdentifierPart);
}
由于 TypeScript 支持不同版本的 ES 代码,且不同版本的 ES 规范对标识符的定义有细微查表,所以 TypeScript 内部准备了不同版本的表。
通过以上俩函数的结合,也就可以判断一个字符串是不是合法的标识符了:
/* @internal */
export function isIdentifierText(name: string, languageVersion: ScriptTarget | undefined): boolean {
let ch = codePointAt(name, 0);
if (!isIdentifierStart(ch, languageVersion)) {
return false;
} for (let i = charSize(ch); i < name.length; i += charSize(ch)) {
if (!isIdentifierPart(ch = codePointAt(name, i), languageVersion)) {
return false;
}
} return true;
}
行列号和索引
如果将源码看成字符串,每个字符都有一个字符串的下标索引,同时这个字符又可以理解为源码中的第几行第几列。
给定一个字符串的索引,可以通过扫描这个索引之前有几个换行符确定这个索引属于第几行第几列,反过来,通过行列号也可以确认这个位置对应的字符串索引。
在源码中如果发现一个错误,编译器需要向用户报告错误,并明确指出位置,一般地,编译器需要将错误的行列报出来(如果报的是索引那你自己慢慢数……),为了能够在报错时知道这些位置,编译器在词法扫描阶段就需要保存一切源码位置了,那编译器存的是行列号还是索引呢?
有的编译器选择了存行列号,因为行列号才是用户最后需要的,但行列号意味着需要两个字段存储这个信息,如果将它们分别处理,每次处理行列号的地方都需要两行代码,如果将它们合并为一个对象,这在 JavaScript 引擎中会造成大量的引用对象,影响性能。因此 TypeScript 选择:存储索引。出错的时候,再将索引换算成行列号显示出来。
TypeScript 用 Position(位置)这个术语表示索引,用 LineAndCharacter(行和字符)这个术语表示行列号。这三者都是从 0 开始计数的,即 line = 0 表示第一行。
为什么是 LineAndCharacter 而不是 LineAndColumn(行列),主要为了和 VSCode 中的 LineColumn 区分,多数情况,LineAndCharacter 和 LineAndColumn 是一样的,除非碰到制表符(TAB)缩进,一个 TAB 始终是一个字符,但它可能跨越 2 列、4 列、8列等(具体根据用户配置)。TypeScript 并不在意 TAB 这个字符,统一将它当一个字符处理可以简单许多,所以为了避免和 VSCode 的行列混淆,改用了别的称呼。
基于索引计算行列号需要遍历这个索引之前的所有字符,为了加速计算,TypeScript 作了一个小优化:缓存每行第一个字符的索引,然后通过二分搜索查找对应的行列(又是二分?)
首先计算每行第一个字符的索引表:
/* @internal */
export function computeLineStarts(text: string): number[] {
const result: number[] = new Array();
let pos = 0;
let lineStart = 0;
while (pos < text.length) {
const ch = text.charCodeAt(pos);
pos++;
switch (ch) {
case CharacterCodes.carriageReturn:
if (text.charCodeAt(pos) === CharacterCodes.lineFeed) {
pos++;
}
// falls through
case CharacterCodes.lineFeed:
result.push(lineStart);
lineStart = pos;
break;
default:
if (ch > CharacterCodes.maxAsciiCharacter && isLineBreak(ch)) {
result.push(lineStart);
lineStart = pos;
}
break;
}
}
result.push(lineStart);
return result;
}
然后检索索引表查询行列号:
/* @internal */
/**
* We assume the first line starts at position 0 and 'position' is non-negative.
*/
export function computeLineAndCharacterOfPosition(lineStarts: readonly number[], position: number): LineAndCharacter {
let lineNumber = binarySearch(lineStarts, position, identity, compareValues);
if (lineNumber < 0) {
// If the actual position was not found,
// the binary search returns the 2's-complement of the next line start
// e.g. if the line starts at [5, 10, 23, 80] and the position requested was 20
// then the search will return -2.
//
// We want the index of the previous line start, so we subtract 1.
// Review 2's-complement if this is confusing.
lineNumber = ~lineNumber - 1;
Debug.assert(lineNumber !== -1, "position cannot precede the beginning of the file");
}
return {
line: lineNumber,
character: position - lineStarts[lineNumber]
};
}
同时使用索引表也可以实现从行列号查询索引:
/* @internal */
export function computePositionOfLineAndCharacter(lineStarts: readonly number[], line: number, character: number, debugText?: string, allowEdits?: true): number {
if (line < 0 || line >= lineStarts.length) {
if (allowEdits) {
// Clamp line to nearest allowable value
line = line < 0 ? 0 : line >= lineStarts.length ? lineStarts.length - 1 : line;
}
else {
Debug.fail(`Bad line number. Line: ${line}, lineStarts.length: ${lineStarts.length} , line map is correct? ${debugText !== undefined ? arraysEqual(lineStarts, computeLineStarts(debugText)) : "unknown"}`);
}
} const res = lineStarts[line] + character;
if (allowEdits) {
// Clamp to nearest allowable values to allow the underlying to be edited without crashing (accuracy is lost, instead)
// TODO: Somehow track edits between file as it was during the creation of sourcemap we have and the current file and
// apply them to the computed position to improve accuracy
return res > lineStarts[line + 1] ? lineStarts[line + 1] : typeof debugText === "string" && res > debugText.length ? debugText.length : res;
}
if (line < lineStarts.length - 1) {
Debug.assert(res < lineStarts[line + 1]);
}
else if (debugText !== undefined) {
Debug.assert(res <= debugText.length); // Allow single character overflow for trailing newline
}
return res;
}
小结
本节介绍了 scanner 中的一些独立函数,这些函数都将被词法扫描程序中调用。先独立理解了这些概念,对完全理解词法扫描会有重大帮助。
下节将介绍:词法扫描的实现(即 scanner.ts 中剩余的其它函数)【更新于 2020-1-18】
#如果你有问题可以在评论区提问#
TypeScript 源码详细解读(2)词法1-字符处理的更多相关文章
- TypeScript 源码详细解读(3)词法2-标记解析
在上一节主要介绍了单个字符的处理,现在我们已经有了对单个字符分析的能力,比如: 判断字符是否是换行符:isLineBreak 判断字符是否是空格:isWhiteSpaceSingleLine 判断字符 ...
- TypeScript 源码详细解读(1)总览
TypeScript 由微软在 2012 年 10 月首发,经过几年的发展,已经成为国内外很多前端团队的首选编程语言.前端三大框架中的 Angular 和 Vue 3 也都改用了 TypeScript ...
- TypeScript 源码详细解读(4)语法1-语法树
在上一节介绍了标记的解析,就相当于识别了一句话里有哪些词语,接下来就是把这些词语组成完整的句子,即拼装标记为语法树. 树(tree) 树是计算机数据结构里的专业术语.就像一个学校有很多年级,每个年级下 ...
- AQS源码详细解读
AQS源码详细解读 目录 AQS源码详细解读 基础 CAS相关知识 通过标识位进行线程挂起的并发编程范式 MPSC队列的实现技巧 代码讲解 独占模式 独占模式下请求资源 独占模式下的释放资源 共享模式 ...
- 基于LNMP的Zabbbix之Zabbix Agent源码详细安装,但不给图
基于LNMP的Zabbbix之Zabbix Server源码详细安装:http://www.cnblogs.com/losbyday/p/5828547.html wget http://jaist. ...
- LinkedHashMap 源码详细分析(JDK1.8)
1. 概述 LinkedHashMap 继承自 HashMap,在 HashMap 基础上,通过维护一条双向链表,解决了 HashMap 不能随时保持遍历顺序和插入顺序一致的问题.除此之外,Linke ...
- SpringMVC+Maven开发项目源码详细介绍
代码地址如下:http://www.demodashi.com/demo/11638.html Spring MVC概述 Spring MVC框架是一个开源的Java平台,为开发强大的基于Java的W ...
- Thrift之代码生成器Compiler原理及源码详细解析1
我的新浪微博:http://weibo.com/freshairbrucewoo. 欢迎大家相互交流,共同提高技术. 又很久没有写博客了,最近忙着研究GlusterFS,本来周末打算写几篇博客的,但是 ...
- 集合-LinkedHashMap 源码详细分析(JDK1.8)
1. 概述 LinkedHashMap 继承自 HashMap,在 HashMap 基础上,通过维护一条双向链表,解决了 HashMap 不能随时保持遍历顺序和插入顺序一致的问题.除此之外,Linke ...
- 一文读懂Spring动态配置多数据源---源码详细分析
Spring动态多数据源源码分析及解读 一.为什么要研究Spring动态多数据源 期初,最开始的原因是:想将答题服务中发送主观题答题数据给批改中间件这块抽象出来, 但这块主要使用的是mq消息的方式 ...
随机推荐
- MYSQL存储过程-练习5 游标
MYSQL存储过程-练习5 游标 1 DELIMITER $ 2 CREATE PROCEDURE sp_cur() 3 BEGIN 4 DECLARE bkname VARCHAR(200); 5 ...
- 19 Transformer 解码器的两个为什么(为什么做掩码、为什么用编码器-解码器注意力)
博客配套视频链接: https://space.bilibili.com/383551518?spm_id_from=333.1007.0.0 b 站直接看 配套 github 链接:https:// ...
- CDQ&整体二分-三维偏序(陌上花开)
题面 本文讲cdq,整体二分的思路与做法.=分治VS数据结构 其实维度这一方面,空间几何可以是维度,像时间这样有规定顺序的词语也可能是维度. cdq 三维偏序,一般可以用一维一维的消.可以用cdq嵌套 ...
- KubeSphere 社区双周报| 2024.08.16-08.29
KubeSphere 社区双周报主要整理展示新增的贡献者名单和证书.新增的讲师证书以及两周内提交过 commit 的贡献者,并对近期重要的 PR 进行解析,同时还包含了线上/线下活动和布道推广等一系列 ...
- 云原生周刊:一条 Kubernetes 命令引发的悲剧
开源项目 KSail 用于在 Docker 中配置支持 GitOps 的 K8s 集群的 CLI 工具. nginx-gateway-fabric NGINX Gateway Fabric 是一个开源 ...
- python多进程完成模拟支付
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- '''@auther :mr.qin @IDE:pycharm''' from tool.Common import ...
- IPV6改造 华为云如此简单
现在很多企业都在搞这个IPV6改造,说实话这个IPV6改造我这边也不是特别精通,也是通过查阅各种资料来了解IPV6这个东西,下面是我查的一些资料大家可以借鉴一下. IPv6改造三步曲--Vecloud ...
- LLM应用实战: OpenAI多代理新作-Swarm
1.背景 本qiang~关注到OpenAI两周前发布的轻量级多代理框架Swarm,因此想要深入了解了一下,运行了官方提供的例子,整理并总结一些心得体会~ 源码非常简单,各位看官们可以小读一下,本文采用 ...
- Rust编程与项目实战-结构体
<Rust编程与项目实战>(朱文伟,李建英)[摘要 书评 试读]- 京东图书 (jd.com) 在Rust中,结构体(Struct)是一种自定义数据类型,它允许我们将多个相关的值组合在一起 ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 380 (A~E)题解
A - 123233 遍历字符串统计出现次数即可. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define int long long c ...
