spring源码解析--上
本文是作者原创,版权归作者所有.若要转载,请注明出处.
首先是配置类
package com.lusai.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.lusai.service")
public class SpringConfig { }
然后是IndexService
package com.lusai.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service
public class IndexService { public void hello(){
System.out.println("IndexService");
} }
然后是测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);//从这里开始看
IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
indexService.hello();
}
看结果
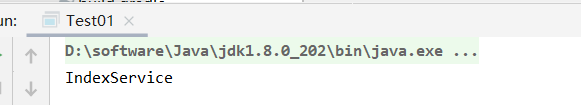
可以看到,IndexService 已经交给spring管理了,我们就开始学习源码吧
/**
* 这个构造方法需要传入一个配置类
* 然后会把这个被注解了的类通过注解读取器读取,继而解析
* Create a new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext, deriving bean definitions
* from the given annotated classes and automatically refreshing the context.
* @param annotatedClasses one or more annotated classes,
* e.g. {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes
*/
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
//annotatedClasses ---> 配置类的class对象
//这里由于他有父类,故而会先调用父类的构造方法,然后才会调用自己的构造方法
//在自己构造方法中初始一个读取器和扫描器
this();//进这里看
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();
}
继续看this()
/**
* 初始化一个bean的读取器和扫描器
* 何谓读取器和扫描器参考上面的属性注释
* 默认构造函数,如果直接调用这个默认构造方法,需要在稍后通过调用其register()
* 去注册配置类(javaconfig),并调用refresh()方法刷新容器,
* 触发容器对注解Bean的载入、解析和注册过程
* Create a new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext that needs to be populated
* through {@link #register} calls and then manually {@linkplain #refresh refreshed}.
*/
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
/**
* 父类的构造方法
* 创建一个读取注解的Bean定义读取器
* 什么是BeanDefinition
*/
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
//可以用来扫描包或者类,继而转换成BeanDefinition
//但是实际上我们扫描包工作不是scanner这个对象来完成的
//是spring自己new的一个ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
//这里的scanner仅仅是为了程序员能够在外部调用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象的scan方法
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
我们看一下this.reader
/**
* 这个类顾名思义是一个reader,一个读取器
* 读取什么呢?还是顾名思义:AnnotatedBeanDefinition意思是读取一个被加了注解的BeanDefinition
* 这个类在构造方法中实例化的
*/
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
我们再看一下AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 的定义
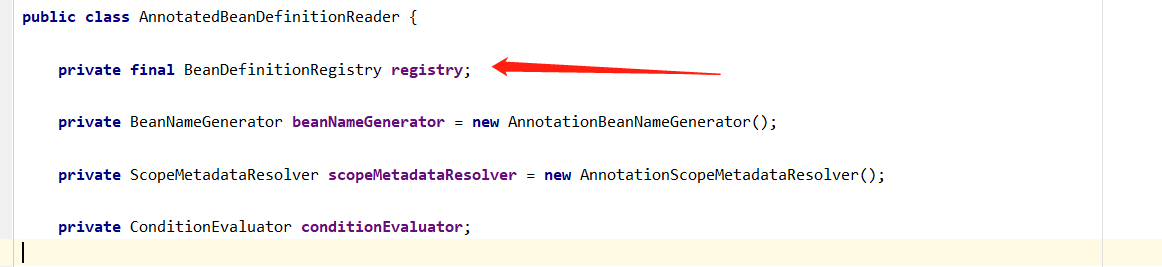
可以看出有个BeanDefinitionRegistry,看这个名字应该是BeanDefinition的注册器,那么BeanDefinition是什么呢,看一下
/**
* BeanDefinition描述了一个bean实例
* A BeanDefinition describes a bean instance, which has property values,
* constructor argument values, and further information supplied by
* concrete implementations.
*
* <p>This is just a minimal interface: The main intention is to allow a
* {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} such as {@link PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer}
* to introspect and modify property values and other bean metadata.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @since 19.03.2004
* @see ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#getBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ChildBeanDefinition
*/
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement { /**
* 单例作用域的作用域标识符:“singleton”。
* Scope identifier for the standard singleton scope: "singleton".
* <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
* @see #setScope
*/
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON; /**
* 非单例作用域的作用域标识符:“prototype”。
* Scope identifier for the standard prototype scope: "prototype".
* <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
* @see #setScope
*/
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE; /**
* 还没搞懂 权限的值
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a major part
* of the application. Typically corresponds to a user-defined bean.
*/
int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0; /**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a supporting
* part of some larger configuration, typically an outer
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
* {@code SUPPORT} beans are considered important enough to be aware
* of when looking more closely at a particular
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition},
* but not when looking at the overall configuration of an application.
*/
int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1; /**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is providing an
* entirely background role and has no relevance to the end-user. This hint is
* used when registering beans that are completely part of the internal workings
* of a {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
* 就是我这Bean是Spring自己的,和你用户没有一毛钱关系
*/
int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2; // Modifiable attributes /**
* 设置父BeanDefinition的名字
* Set the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
void setParentName(@Nullable String parentName); /**
* 获得父BeanDefinition的名字
* Return the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getParentName(); /**
* 指定此BeanDefinition的bean类名
* Specify the bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>The class name can be modified during bean factory post-processing,
* typically replacing the original class name with a parsed variant of it.
* @see #setParentName
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName); /**
* 获取此BeanDefinition的bean类名
* Return the current bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>Note that this does not have to be the actual class name used at runtime, in
* case of a child definition overriding/inheriting the class name from its parent.
* Also, this may just be the class that a factory method is called on, or it may
* even be empty in case of a factory bean reference that a method is called on.
* Hence, do <i>not</i> consider this to be the definitive bean type at runtime but
* rather only use it for parsing purposes at the individual bean definition level.
* @see #getParentName()
* @see #getFactoryBeanName()
* @see #getFactoryMethodName()
*/
@Nullable
String getBeanClassName(); /**
*设置此BeanDefinition的scope的类型
* Override the target scope of this bean, specifying a new scope name.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
void setScope(@Nullable String scope); /**
* 获取此BeanDefinition的scope的类型
* Return the name of the current target scope for this bean,
* or {@code null} if not known yet.
*/
@Nullable
String getScope(); /**
* 设置懒加载
* Set whether this bean should be lazily initialized.
* <p>If {@code false}, the bean will get instantiated on startup by bean
* factories that perform eager initialization of singletons.
*/
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit); /**
* 获取是否懒加载
* Return whether this bean should be lazily initialized, i.e. not
* eagerly instantiated on startup. Only applicable to a singleton bean.
*/
boolean isLazyInit(); /**
* 设置dependsOn,将首先初始化这些bean
* Set the names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized.
* The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first.
*/
void setDependsOn(@Nullable String... dependsOn); /**
* 获取被dependsOn的beans的名字
* Return the bean names that this bean depends on.
*/
@Nullable
String[] getDependsOn(); /**
* 设置是否参与自动装配的候选,与autowire-candidate有关
* Set whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
* <p>Note that this flag is designed to only affect type-based autowiring.
* It does not affect explicit references by name, which will get resolved even
* if the specified bean is not marked as an autowire candidate. As a consequence,
* autowiring by name will nevertheless inject a bean if the name matches.
*/
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate); /**
* 获取是否参与自动装配的候选
* Return whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
*/
boolean isAutowireCandidate(); /**
* 设置@Primay注解
* Set whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
* <p>If this value is {@code true} for exactly one bean among multiple
* matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker.
*/
void setPrimary(boolean primary); /**
* 获取该bean是否被@Primay注解
* Return whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
*/
boolean isPrimary(); /**
* Specify the factory bean to use, if any.
* This the name of the bean to call the specified factory method on.
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setFactoryBeanName(@Nullable String factoryBeanName); /**
* Return the factory bean name, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getFactoryBeanName(); /**
* 与bean标签的factory-method有关
* Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with
* constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified.
* The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any,
* or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class.
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setBeanClassName
*/
void setFactoryMethodName(@Nullable String factoryMethodName); /**
* Return a factory method, if any.
*/
@Nullable
String getFactoryMethodName(); /**
* 存放构造方法的参数和顺序等 constructor-arg标签的index和name等属性
* Return the constructor argument values for this bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* @return the ConstructorArgumentValues object (never {@code null})
*/
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues(); /**
* 判断构造方法有没有参数值
* Return if there are constructor argument values defined for this bean.
* @since 5.0.2
*/
default boolean hasConstructorArgumentValues() {
return !getConstructorArgumentValues().isEmpty();
} /**
* bean标签的property属性
* Return the property values to be applied to a new instance of the bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* @return the MutablePropertyValues object (never {@code null})
*/
MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues(); /**
* Return if there are property values values defined for this bean.
* @since 5.0.2
*/
default boolean hasPropertyValues() {
return !getPropertyValues().isEmpty();
} /**
* Set the name of the initializer method.
* @since 5.1
*/
void setInitMethodName(@Nullable String initMethodName); /**
* Return the name of the initializer method.
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
String getInitMethodName(); /**
* Set the name of the destroy method.
* @since 5.1
*/
void setDestroyMethodName(@Nullable String destroyMethodName); /**
* Return the name of the destroy method.
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
String getDestroyMethodName(); /**
* Set the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides the frameworks as well as tools with an indication of
* the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}.
* @since 5.1
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
*/
void setRole(int role); /**
* Get the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides the frameworks as well as tools with an indication of
* the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}.
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
*/
int getRole(); /**
* @Description注解,描述,无太大意义
* Set a human-readable description of this bean definition.
* @since 5.1
*/
void setDescription(@Nullable String description); /**
* Return a human-readable description of this bean definition.
*/
@Nullable
String getDescription(); // Read-only attributes /**
* Return whether this a <b>Singleton</b>, with a single, shared instance
* returned on all calls.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
*/
boolean isSingleton(); /**
* Return whether this a <b>Prototype</b>, with an independent instance
* returned for each call.
* @since 3.0
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
boolean isPrototype(); /**
* 判断是否是抽象类,为什么可以是抽象类
* Return whether this bean is "abstract", that is, not meant to be instantiated.
*/
boolean isAbstract(); /**
* 对文件的描述
* Return a description of the resource that this bean definition
* came from (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors).
*/
@Nullable
String getResourceDescription(); /**
* Return the originating BeanDefinition, or {@code null} if none.
* Allows for retrieving the decorated bean definition, if any.
* <p>Note that this method returns the immediate originator. Iterate through the
* originator chain to find the original BeanDefinition as defined by the user.
*/
@Nullable
BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition(); }
BeanDefinition描述了一个bean实例,可以理解为:我们定义的对象交给spring管理以后会变成一个个BeanDefinition
好了,看看下一个
//可以用来扫描包或者类,继而转换成BeanDefinition
//但是实际上我们扫描包工作不是scanner这个对象来完成的
//是spring自己new的一个ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
//这里的scanner仅仅是为了程序员能够在外部调用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象的scan方法
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
这里的scanner 我们也不深究,姑且认为是一个扫描器
继续看构造方法
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
//annotatedClasses ---> 配置类的class对象
//这里由于他有父类,故而会先调用父类的构造方法,然后才会调用自己的构造方法
//在自己构造方法中初始一个读取器和扫描器
this();
register(annotatedClasses);//进这里看
refresh();
}
看register方法
/**
* 注册单个bean给容器
* 比如有新加的类可以用这个方法
* 但是注册注册之后需要手动调用refresh方法去触发容器解析注解
*
* 有两个意思
* 他可以注册一个配置类
* 他还可以单独注册一个bean
* Register one or more annotated classes to be processed.
* <p>Note that {@link #refresh()} must be called in order for the context
* to fully process the new classes.
* @param annotatedClasses one or more annotated classes,
* e.g. {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes
* @see #scan(String...)
* @see #refresh()
*/
public void register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
Assert.notEmpty(annotatedClasses, "At least one annotated class must be specified");
this.reader.register(annotatedClasses);//被注解的类
}
我们把配置类的扫描注释掉看下
@Configuration
//@ComponentScan("com.lusai.service")
public class SpringConfig { }
运行测试类,看下结果
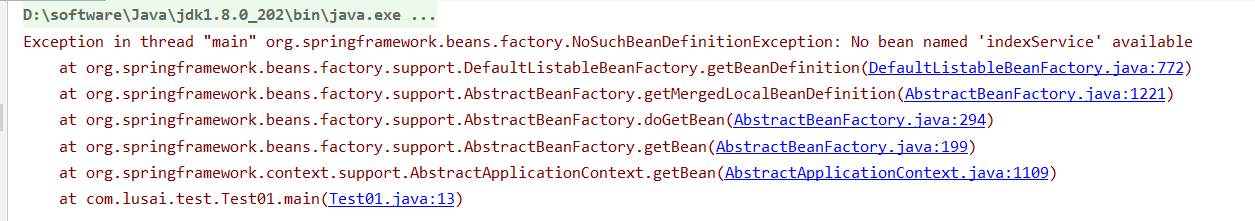
扫描不到报错,我们改成如下形式再试一下
public static void main(String[] args) {
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IndexService.class);
IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
indexService.hello();
}
看结果
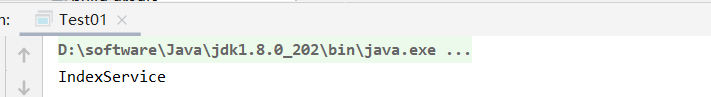
ok,可以看出register方法有两个意思:1.他可以注册一个配置类2.他还可以单独注册一个bean
好了,继续点进去看源码
/**
* Register one or more annotated classes to be processed.
* <p>Calls to {@code register} are idempotent; adding the same
* annotated class more than once has no additional effect.
* @param annotatedClasses one or more annotated classes,
* e.g. {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes
*/
public void register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
for (Class<?> annotatedClass : annotatedClasses) {
registerBean(annotatedClass);
}
}
继续看registerBean
/**
* Register a bean from the given bean class, deriving its metadata from
* class-declared annotations.
* @param annotatedClass the class of the bean
*/
public void registerBean(Class<?> annotatedClass) {
doRegisterBean(annotatedClass, null, null, null);
}
继续看doRegisterBean
/**
* Register a bean from the given bean class, deriving its metadata from
* class-declared annotations.
* @param annotatedClass the class of the bean
* @param instanceSupplier a callback for creating an instance of the bean
* (may be {@code null})
* @param name an explicit name for the bean
* @param qualifiers specific qualifier annotations to consider, if any,
* in addition to qualifiers at the bean class level
* @param definitionCustomizers one or more callbacks for customizing the
* factory's {@link BeanDefinition}, e.g. setting a lazy-init or primary flag
* @since 5.0
*/
<T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> annotatedClass, @Nullable Supplier<T> instanceSupplier, @Nullable String name,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers, BeanDefinitionCustomizer... definitionCustomizers) { /**
* 根据指定的bean创建一个AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
* 这个AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition可以理解为一个数据结构
* AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition包含了类的其他信息,比如一些元信息
* scope,lazy等等.
* 此时因为传入的注解,所以new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition
*/
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(annotatedClass);
/**
* 判断这个类是否需要跳过解析
* 通过代码可以知道spring判断是否跳过解析,主要判断类有没有加注解
*/
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
} abd.setInstanceSupplier(instanceSupplier);
/**
* 得到类的作用域 singleton
*/
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
/**
* 把类的作用域添加到数据结构结构中
*/
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
/**
* 生成类的名字通过beanNameGenerator
*/
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
/**
* 处理类当中的通用注解
* 分析源码可以知道他主要处理
* Lazy DependsOn Primary Role等等注解
* 处理完成之后processCommonDefinitionAnnotations中依然是把他添加到数据结构当中
*/
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {//qualifiers总是为null
for (Class<? extends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) {
//如果配置了@Primary注解,如果加了则作为首选
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
//懒加载,前面加过
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
//如果使用了除@Primary和@Lazy以外的其他注解,则为该Bean添加一个根据名字自动装配的限定符
//这里难以理解,后面会详细介绍
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
//自定义注解
for (BeanDefinitionCustomizer customizer : definitionCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(abd);
} /**
* 这个BeanDefinitionHolder也是一个数据结构,这个对象放入了BeanDefinition和beanName,可以理解为一个map
*/
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
/**
* ScopedProxyMode 这个知识点比较复杂,需要结合web去理解
* 可以暂时放一下,等说道springmvc的时候再说
* 或者看情况现在说也是一样的
*/
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
/**
* 把上述的这个数据结构注册给registry
* registy就是AnnotatonConfigApplicationContext
* AnnotatonConfigApplicationContext在初始化的時候通過調用父類的構造方法
* 實例化了一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
* *registerBeanDefinition里面就是把definitionHolder这个数据结构包含的信息注册到
* DefaultListableBeanFactory这个工厂
*/
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
看下这行的源码
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
继续
public static void processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(AnnotatedBeanDefinition abd) {
processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd, abd.getMetadata());
}
继续
/**
* 检查常用的注解
* @param abd
* @param metadata
*/
static void processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(AnnotatedBeanDefinition abd, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
//检查Lazy注解,如果有将它放入AnnotatedBeanDefinition
AnnotationAttributes lazy = attributesFor(metadata, Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null) {
abd.setLazyInit(lazy.getBoolean("value"));
}
else if (abd.getMetadata() != metadata) {
lazy = attributesFor(abd.getMetadata(), Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null) {
abd.setLazyInit(lazy.getBoolean("value"));
}
}
//检查Primary注解,如果有将它放入AnnotatedBeanDefinition
if (metadata.isAnnotated(Primary.class.getName())) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
//检查DependsOn注解,如果有将它放入AnnotatedBeanDefinition
AnnotationAttributes dependsOn = attributesFor(metadata, DependsOn.class);
if (dependsOn != null) {
abd.setDependsOn(dependsOn.getStringArray("value"));
}
//检查Role注解,如果有将它放入AnnotatedBeanDefinition
AnnotationAttributes role = attributesFor(metadata, Role.class);
if (role != null) {
abd.setRole(role.getNumber("value").intValue());
}
//检查Description注解,如果有将它放入AnnotatedBeanDefinition
AnnotationAttributes description = attributesFor(metadata, Description.class);
if (description != null) {
abd.setDescription(description.getString("value"));
}
}
分析源码可以知道他主要处理Lazy DependsOn Primary Role等等注解
处理完成之后是把他添加到AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition数据结构当中
继续看下面
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
看下BeanDefinitionHolder 的定义
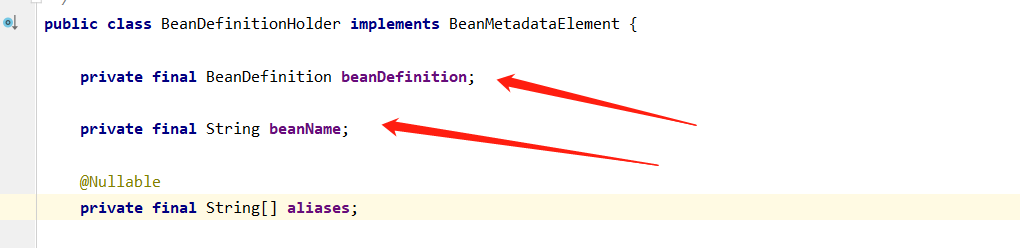
这个BeanDefinitionHolder也是一个对象,这个对象放入了BeanDefinition和beanName
好了,我们看最后一行关键代码:
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
点进去
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { // Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();//获取beanName
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());//关键代码 //别名,先不看
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
看那行关键代码
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { //DefaultListableBeanFactory
this.beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
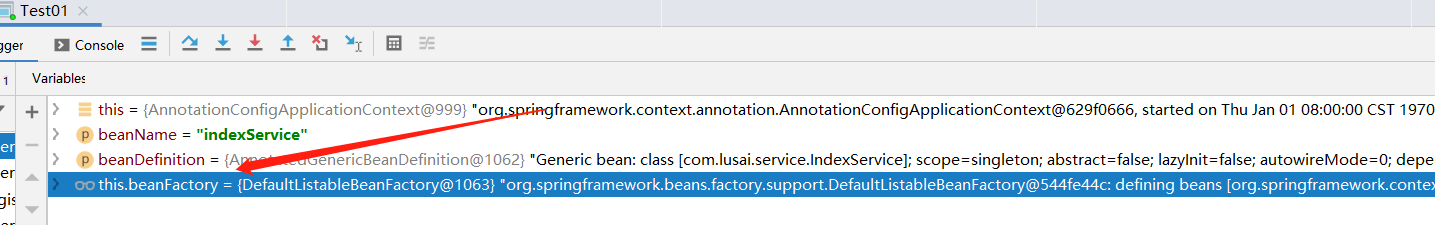
这里的this.beanFactory是DefaultListableBeanFactory,这个是默认的bean工厂
再点进去看
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null"); if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {//验证
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
} BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {//关键代码
// Still in startup registration phase
//这里的beanDefinitionMap是一个map,存放beanName,beanDefinition
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
//这里的beanDefinitionNames是一个list,存放beanName
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
} if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}
看我注释的地方,那里就是关键代码
这里的this.beanDefinitionMap看一下
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name. */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
这里我们debug一下
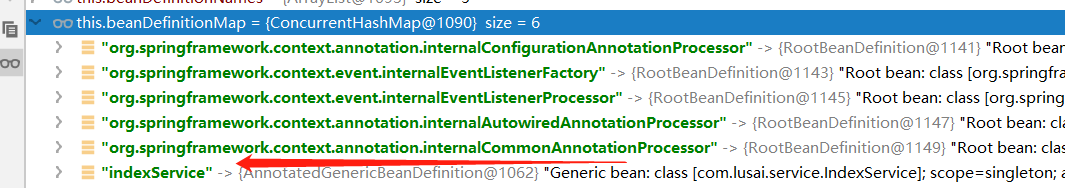
可以看到除了indexService之外很多内置的bean,那么这些类是什么时候注册的,都有什么用呢?我们后面再研究
我们register看完了,现在看refresh方法
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
//annotatedClasses ---> 配置类的class对象
//这里由于他有父类,故而会先调用父类的构造方法,然后才会调用自己的构造方法
//在自己构造方法中初始一个读取器和扫描器
this();
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();//进这里看
}
点进去
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
////准备工作包括设置启动时间,是否激活标识位,
// 初始化属性源(property source)配置
prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//返回一个factory 为什么需要返回一个工厂
//因为要对工厂进行初始化
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
//准备工厂
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. //这个方法在当前版本的spring是没用任何代码的
//可能spring期待在后面的版本中去扩展吧
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//在spring的环境中去执行已经被注册的 factory processors
//设置执行自定义的ProcessBeanFactory 和spring内部自己定义的
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//注册beanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context.
//初始化应用事件广播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
} // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
看看下面这行
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
点进去
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}
继续看getBeanFactory()方法
@Override
public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
return this.beanFactory;
}
这里的this.beanFactory就是上文提到的DefaultListableBeanFactory
private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
好,下面我们看这行
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
点进去
/**
*
* 配置其标准的特征,比如上下文的加载器ClassLoader和post-processors回调
* Configure the factory's standard context characteristics,
* such as the context's ClassLoader and post-processors.
* @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure
* 此处的beanFactory参数等于DefaultListableFactory
*/
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
//bean表达式解释器,后面说 能够获取bean当中的属性在前台页面
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
//对象与string类型的转换 <property red="dao">
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment())); // Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
//添加一个后置管理器
//ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
// 能够在bean中获得到各种*Aware(*Aware都有其作用)
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));//核心代码 beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class); // BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this); // Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this)); // Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
} //意思是如果自定义的Bean中没有名为"systemProperties"和"systemEnvironment"的Bean,
// 则注册两个Bena,Key为"systemProperties"和"systemEnvironment",Value为Map,
// 这两个Bean就是一些系统配置和系统环境信息
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
我们看一下核心的那行代码
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));//核心代码
打断点
@Override
public void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) {
Assert.notNull(beanPostProcessor, "BeanPostProcessor must not be null");
// Remove from old position, if any
this.beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor);
// Track whether it is instantiation/destruction aware
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
this.hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
this.hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
// Add to end of list
this.beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor);//核心代码
}
我们看一下this.beanPostProcessors是什么
/** BeanPostProcessors to apply in createBean. */ private final List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
BeanPostProcessor就是传说中的后置处理器,通过实现BeanPostProcessor接口,程序员就可插手bean实例化的过程
我们试一下
@Service
public class IndexService { public IndexService(){
System.out.println("IndexService 构造方法");
} @PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("IndexService init方法");
} public void hello(){
System.out.println("IndexService");
} }
配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.lusai")
public class SpringConfig { }
实现BeanPostProcessor接口的类
@Component
public class TestBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { /**
* 在bean初始化之前执行
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("indexService")){
System.out.println("indexService postProcessBeforeInitialization");
}
//这里也可以产生代理对象 Proxy.newProxyInstance()
return bean;
} /**
* 初始化之后
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("indexService")){
System.out.println("indexService postProcessAfterInitialization");
}
return bean;
}
}
测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IndexService.class);
IndexService indexService = (IndexService) applicationContext.getBean("indexService");
indexService.hello();
}
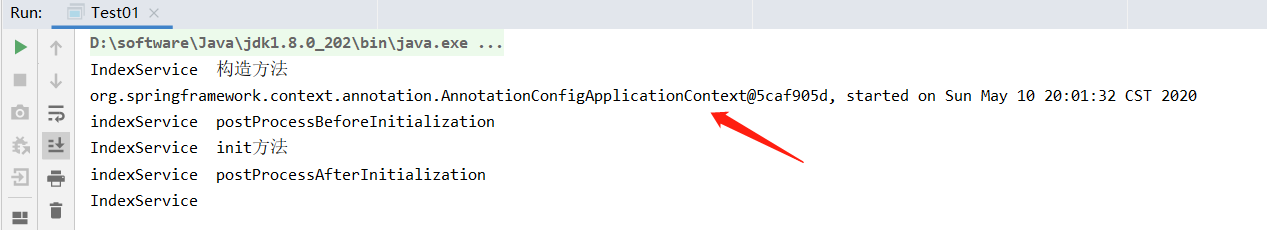
看下结果
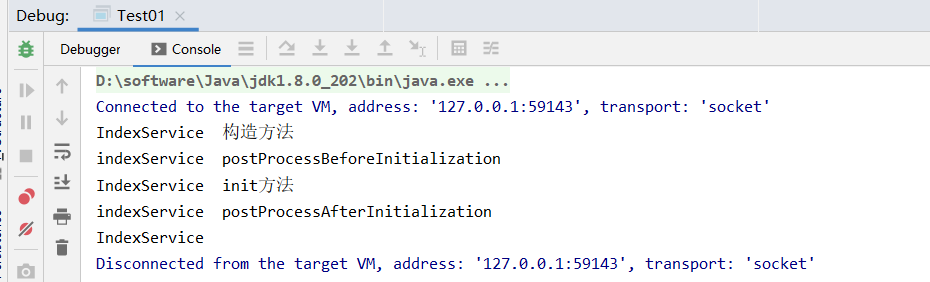
插手成功
好了,我们继续这行代码
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));//核心代码
我们看下此处的ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,这个类实现了BeanPostProcessor 接口,重写了postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
AccessControlContext acc = null;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null &&
(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)) {
acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext();
}
if (acc != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return null;
}, acc);
}
else {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);//看这行
}
return bean;
}
}
看下那行代码
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {//EnvironmentAware用于获取配置文件
//比如this.applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("url")
//ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.applicationContext.getEnvironment();
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {//实现ApplicationContextAware接口,可以在spring管理的单例bean中中使用原型依赖bean
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
我们测试一下ApplicationContextAware接口
@Service
public class IndexService implements ApplicationContextAware { private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public IndexService(){
System.out.println("IndexService 构造方法");
} @PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("IndexService init方法");
} public void hello(){
System.out.println("IndexService");
} @Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext=applicationContext;
System.out.println(applicationContext);
}
}
运行测试类,看下结果
好了,我们继续看源码
//目前是空方法,留给后续扩展
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); //完成扫描和解析(类--->beanDefinition) beanDefinitionMap
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
第一个是空方法,看第二行
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//先看下getBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
先看下getBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法
public List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() {
return this.beanFactoryPostProcessors;
}
这里的this.beanFactoryPostProcessors就是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的集合,如下
private final List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
那么BeanFactoryPostProcessor是什么?有什么用呢?
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是spring的扩展点之一
* 实现该接口,可以在spring的bean创建之前修改bean的定义属性。
* spring允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何其它bean之前读取配置元数据,
* 并可以根据需要进行修改,例如可以把bean的scope从singleton改为prototype,也可以把property的值给修改掉。
* 可以同时配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并通过设置'order'属性来控制各个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行次序。
* BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件之后,在bean实例化之前执行的
来测试一下这个功能
@Component
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
BeanDefinition indexService = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("indexService");
String scope = indexService.getScope();
System.out.println(scope);
indexService.setScope("prototype");
System.out.println(scope);
}
}
这篇就先到这里吧
spring源码解析--上的更多相关文章
- Spring源码解析 - AbstractBeanFactory 实现接口与父类分析
我们先来看类图吧: 除了BeanFactory这一支的接口,AbstractBeanFactory主要实现了AliasRegistry和SingletonBeanRegistry接口. 这边主要提供了 ...
- spring 源码解析
1. [文件] spring源码.txt ~ 15B 下载(167) ? 1 springн┤┬вио╬Ш: 2. [文件] spring源码分析之AOP.txt ~ 15KB 下载( ...
- Spring源码解析-ioc容器的设计
Spring源码解析-ioc容器的设计 1 IoC容器系列的设计:BeanFactory和ApplicatioContext 在Spring容器中,主要分为两个主要的容器系列,一个是实现BeanFac ...
- Spring源码解析系列汇总
相信我,你会收藏这篇文章的 本篇文章是这段时间撸出来的Spring源码解析系列文章的汇总,总共包含以下专题.喜欢的同学可以收藏起来以备不时之需 SpringIOC源码解析(上) 本篇文章搭建了IOC源 ...
- Spring源码解析之BeanFactoryPostProcessor(三)
在上一章中笔者介绍了refresh()的<1>处是如何获取beanFactory对象,下面我们要来学习refresh()方法的<2>处是如何调用invokeBeanFactor ...
- Spring源码解析之ConfigurationClassPostProcessor(二)
上一个章节,笔者向大家介绍了spring是如何来过滤配置类的,下面我们来看看在过滤出配置类后,spring是如何来解析配置类的.首先过滤出来的配置类会存放在configCandidates列表, 在代 ...
- Spring源码解析之八finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法即初始化单例bean
Spring源码解析之八finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法即初始化单例bean 七千字长文深刻解读,Spirng中是如何初始化单例bean的,和面试中最常问的Sprin ...
- Spring源码解析——循环依赖的解决方案
一.前言 承接<Spring源码解析--创建bean>.<Spring源码解析--创建bean的实例>,我们今天接着聊聊,循环依赖的解决方案,即创建bean的ObjectFac ...
- Spring源码解析之PropertyPlaceholderHelper(占位符解析器)
Spring源码解析之PropertyPlaceholderHelper(占位符解析器) https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39471249/article/details/7 ...
随机推荐
- 最后の冲刺 for Alpha release 12/15/2015
好开心啊,又吃成长快乐了~ 据说release前一天,团队的工作效率会达到顶峰.亲证无效!!! release当天才是团队智力效力能力的巅峰好不好?!因为,今天,plan B:福昕pdf reader ...
- stand up meeting 12/8/2015
part 组员 今日工作 工作耗时/h 明日计划 工作耗时/h UI 冯晓云 -------------- -- ----------- -- PDF Reader 朱玉影 ...
- C - Mind Control CodeForces - 1291C
菜到家了,题意都读不懂. 题目大意: 总共有n个人和n个数字 n个人拍成一队,n个数字也是有顺序的 你排在第m个位置 按照顺序的每个人可以拿走这个序列中的第一个数字或者最后一个数字 你可以在所有人操作 ...
- ATcoder--D - Summer Vacation
这个题目的题意有点难搞 题目连接: https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc137/tasks/abc137_d 题目大意:输入n和m 指的是一共有n个输入在m天前一共能赚到的钱 ...
- Linux下nginx自启动配置
1.在linux系统的/etc/init.d/目录下创建nginx文件 vim /etc/init.d/nginx 在脚本中添加一下命令(内容主要参考官方文档) #!/bin/sh # # nginx ...
- python3+selenium3自动化1——元素定位
1.selenium的webdriver提供了八种基本的元素定位方法 打开浏览器 driver = webdriver.Chrome() driver.get('https://www.baidu.c ...
- Jmeter 使用正则表达式提取响应结果中的值
正则表达式提取的界面如下图: apply to: Main sample and sub-samples:作用于父节点取样器及对应子节点取样器Main sample only:仅作用于父节点取样器Su ...
- idea中哪些好用到飞起的插件,偷懒神器
idea中开发人员的偷懒神器-插件 本期推荐一些开发人员常用的一些idea插件.偷懒神器在此,不再秃头! 1. idea安装插件的方法. file->setting->plugins ...
- php时间:获取上一个月,本月天数,下一个月
时间戳转日期 date() 日期转时间戳 strtotime() 当前时间戳time() 获取当前月的天数: $i=; $y=; echo date("t",strtotime(& ...
- Qt 用户通过对话框选择文件
void class::on_pushButton_clicked() { fileFullPath = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("Sel ...
