LeetCode707:设计链表 Design Linked List
爱写bug (ID:iCodeBugs)
设计链表的实现。您可以选择使用单链表或双链表。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0-index 的。
在链表类中实现这些功能:
- get(index):获取链表中第
index个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。 - addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为
val的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。 - addAtTail(val):将值为
val的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。 - addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第
index个节点之前添加值为val的节点。如果index等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果index大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。 - deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引
index有效,则删除链表中的第index个节点。
Design your implementation of the linked list. You can choose to use the singly linked list or the doubly linked list. A node in a singly linked list should have two attributes: val and next. val is the value of the current node, and next is a pointer/reference to the next node. If you want to use the doubly linked list, you will need one more attribute prev to indicate the previous node in the linked list. Assume all nodes in the linked list are 0-indexed.
Implement these functions in your linked list class:
- get(index) : Get the value of the
index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return-1. - addAtHead(val) : Add a node of value
valbefore the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. - addAtTail(val) : Append a node of value
valto the last element of the linked list. - addAtIndex(index, val) : Add a node of value
valbefore theindex-th node in the linked list. Ifindexequals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. - deleteAtIndex(index) : Delete the
index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid.
示例:
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();
linkedList.addAtHead(1);
linkedList.addAtTail(3);
linkedList.addAtIndex(1,2); //链表变为1-> 2-> 3
linkedList.get(1); //返回2
linkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); //现在链表是1-> 3
linkedList.get(1); //返回3
提示:
- 所有值都在
[1, 1000]之内。 - 操作次数将在
[1, 1000]之内。 - 请不要使用内置的 LinkedList 库。
解题思路:
先看图解:
- 单链表添加操作
如果我们想在给定的结点 prev 之后添加新值,我们应该:
- 使用给定值初始化新结点
cur;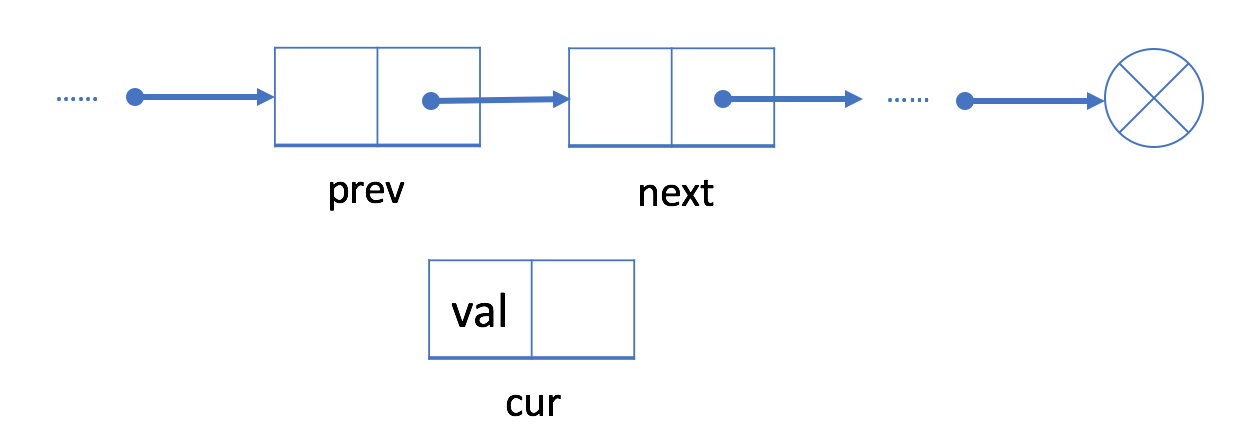
- 将
cur的“next”字段链接到 prev 的下一个结点next;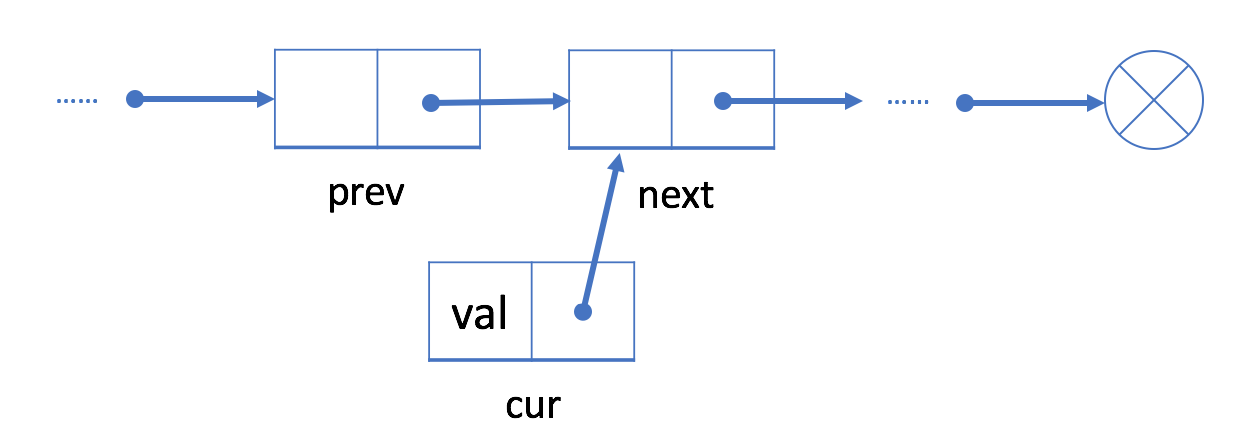
- 将
prev中的“next”字段链接到cur。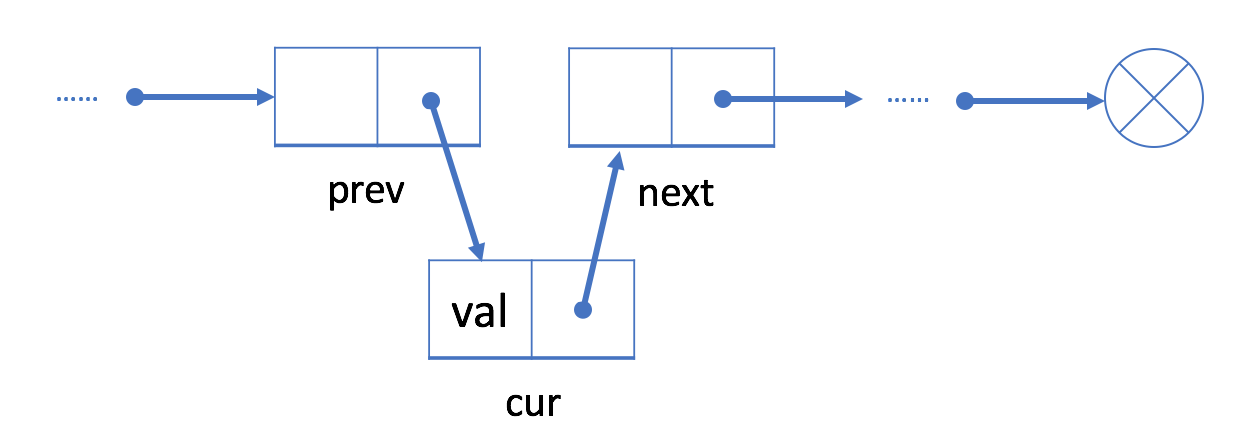
- 删除第一个结点
如果我们想删除第一个结点,策略会有所不同。
正如之前所提到的,我们使用头结点 head 来表示链表。我们的头是下面示例中的黑色结点 23。
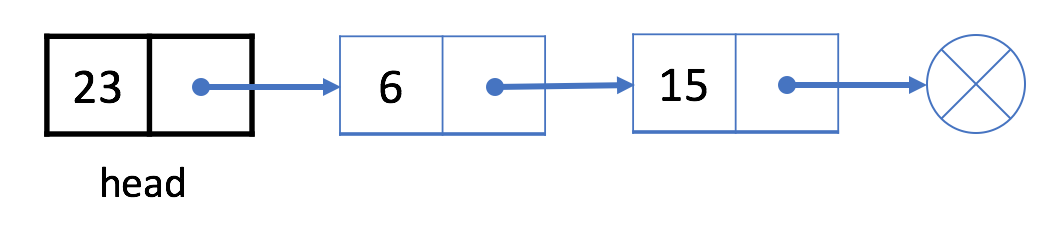
如果想要删除第一个结点,我们可以简单地将下一个结点分配给 head。也就是说,删除之后我们的头将会是结点 6。
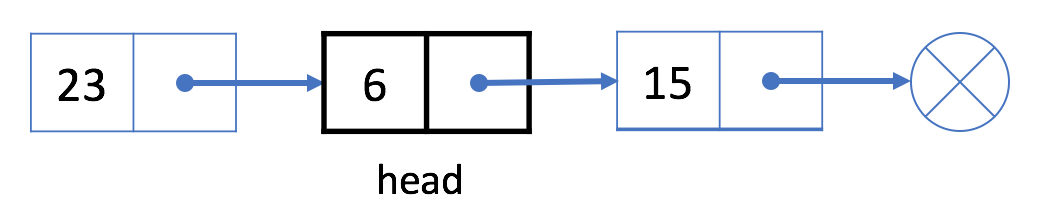
链表从头结点开始,因此结点 23 不再在我们的链表中。
图片来源于LeetCode中国官网
高级程序设计语言中一般都有内置链表,这道题就是让复现链表,看到有很多是用ArrayList、List等数据结构解的,很搞笑,题目说不能使用 LinkedList 库,但 LinkedList 是继承的ArrayList、List,,直接用这两个库一点意义都没有。其实理解一下链表原理就好,高级语言都封装好了链表,如果项目真的到了需要改写链表底层结构来优化性能的那一步,那时候在实践中基本已经摸清了这些东西。
Java:
class Node {//定义Node
int val;
Node next;
Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
Node head;//头
Node tail;//尾
int size = 0;//链表长度
public MyLinkedList() {//初始化数据
head = new Node(0);//为了方便初始化一个本不存在的head,值为0
tail = head;//初始下尾也指向和头同一个对象
size = 0;
}
public int get(int index) {
if (index >= size || index < 0) {//index不在查找区间返回-1
return -1;
}
Node cur = head;
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) {//从head一个一个向下遍历,到index
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.val;//返回值
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
Node temp = head.next;//temp对象是真实链表的第一个节点(因为head一直是初始化的 0 )
head.next = new Node(val);//构造的虚拟节点head的下一个节点指向新插入的节点
head.next.next = temp;//新插入节点指向原本第一个真实节点
size++;//计数
if (size == 1) {
tail = head.next;//如果只有一个节点此时尾节点也指向新加入的节点
}
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {//添加尾节点
tail.next = new Node(val);//把尾节点下一个对象指向新加入节点即可
tail = tail.next;//刷新尾节点为新加入的节点
size++;
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if (index > size) {//插入值不在范围直接返回。
return;
}
Node cur = head;//当前节点从头节点开始
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {//遍历到 插入位置的前一个节点 因为要求是插入到index的前面
cur = cur.next;
}
Node temp = cur.next;//暂存当前节点的下一个节点
cur.next = new Node(val);//把当前节点下一个对象指向新节点
if (index == size) {
tail = cur.next;//如果插入位置刚好是最后一个则把尾节点指向新加入节点
}
cur.next.next = temp;//新节点的下一个节点指向暂存节点位置
size++;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index >= size || index < 0) {
return;
}
Node cur = head;//从头节点遍历到index目标节点的前一个节点 因为要删除目标节点
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;//目标节点前一个节点的下一个节点指向目标节点的下一个节点
size--;//刷新节点数量
if (cur.next == null) {
tail = cur;
}
}
}
Python3:
class Node:
def __init__(self, val, _next=None):
self.next = _next
self.val = val
class MyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
self.size = 0
def get(self, index: int) -> int:
if index > self.size - 1 or index < 0:
return -1
node = self.head
for i in range(index):
node = node.next
return node.val
def addAtHead(self, val: int) -> None:
node = Node(val, self.head)
self.head = node
if self.size == 0:
self.tail = node
self.size = self.size + 1
def addAtTail(self, val: int) -> None:
node = Node(val)
if self.size == 0:
self.head = self.tail = node # 原链表为空时,添加新节点后,更新链表的头指针和尾指针为新增节点。
else:
self.tail.next = node # 原链表不为空时,使原尾指针指向新节点,即可将新节点添加至原链表尾部
self.tail = node # 更新尾指针
self.size = self.size + 1 # 更新此时链表的长度
def addAtIndex(self, index: int, val: int) -> None:
node = Node(val)
if index > self.size:
return
if index <= 0:
return self.addAtHead(val) # index 小于等于0都默认为头指针后添加节点
if index == self.size: # 如果index等于链表的长度添加尾指针后添加节点
return self.addAtTail(val)
prev = self.head # 第一个节点对象开始遍历
for i in range(index - 1):
prev = prev.next
temp = prev.next
prev.next = node
node.next = temp
self.size = self.size + 1
def deleteAtIndex(self, index: int) -> None:
if index < 0 or index >= self.size:
return
prev = self.head
if index == 0:
self.head = self.head.next
self.size = self.size - 1
return
for i in range(index - 1):
prev = prev.next
if index == self.size - 1:
self.tail = prev
prev.next = prev.next.next
self.size = self.size - 1
公众号:爱写bug (ID:iCodeBugs)

LeetCode707:设计链表 Design Linked List的更多相关文章
- [Swift]LeetCode707. 设计链表 | Design Linked List
Design your implementation of the linked list. You can choose to use the singly linked list or the d ...
- LeetCode707 设计链表
设计链表的实现.您可以选择使用单链表或双链表.单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next.val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用.如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 ...
- Leetcode707.Design Linked List设计链表
设计链表的实现.您可以选择使用单链表或双链表.单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next.val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用.如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 ...
- 【LeetCode】Design Linked List(设计链表)
这道题是LeetCode里的第707到题.这是在学习链表时碰见的. 题目要求: 设计链表的实现.您可以选择使用单链表或双链表.单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next.val 是当前节点的 ...
- C#LeetCode刷题之#707-设计链表(Design Linked List)
问题 该文章的最新版本已迁移至个人博客[比特飞],单击链接 https://www.byteflying.com/archives/4118 访问. 设计链表的实现.您可以选择使用单链表或双链表.单链 ...
- 707. Design Linked List
1. 原始题目 Design your implementation of the linked list. You can choose to use the singly linked list ...
- 【LeetCode】设计题 design(共38题)
链接:https://leetcode.com/tag/design/ [146]LRU Cache [155]Min Stack [170]Two Sum III - Data structure ...
- LeetCode | 707. 设计链表
设计链表的实现.您可以选择使用单链表或双链表.单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next.val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用.如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 ...
- 异或链表(XOR linked list)
异或链表(Xor Linked List)也是一种链式存储结构,它可以降低空间复杂度达到和双向链表一样目的,任何一个节点可以方便的访问它的前驱节点和后继结点.可以参阅wiki 普通的双向链表 clas ...
随机推荐
- 《细说PHP》第四版 样章 第23章 自定义PHP接口规范 6
23.4 API的设计原则和规范 API是服务提供方和使用方之间对接的通道,前面我们设计的一些简单API的例子,基本上比较随意,没有使用任何规范.设想一下,每个平台都可能存在大量的API,如果API ...
- Bag of Tricks for Image Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks
这篇文章来自李沐大神团队,使用各种CNN tricks,将原始的resnet在imagenet上提升了四个点.记录一下,可以用到自己的网络上.如果图片显示不了,点击链接观看 baseline mode ...
- oracle多表关联update
日常的开发中一般都是写的单表update语句,很少写多表关联的update. 不同于SQL Server,在Oracle中,update的多表连接更新和select的多表连接查询在使用的方法上存在较大 ...
- Dubbo+Zookeeper实现简单的远程方法调用示例
1. Dubbo介绍 示例代码:Github 1.1 RPC Remote Procedure Call:远程过程调用 1.2 Dubbo架构 Subscribe 订阅:签署:赞成 Monitor 监 ...
- IT从业者不可不知的三条定律
信息技术行业,也就是我们所说的IT行业,有着传统行业所未有的发展速度和模式,当然也有着它独特的发展定律.如果你是从事相关行业,下面讲到的三条定律,不可不知. 摩尔定律 比尔·盖茨曾跟通用公司老板说:如 ...
- Web前端—— JQuery迷你版实现以及使用
JQuery迷你版实现以及使用 tiny_jquery.js var $ = function (selector) { var ele = document.querySelector(select ...
- SpringMVC详解------参数绑定
SpringMVC详解------参数绑定 转载于:https://blog.csdn.net/swebin/article/details/92795422 目录 1.SpringMVC 参数绑定 ...
- sharepointOnline的外接应用创建
#CODE STARTS HERE $programFiles = [environment]::getfolderpath("programfiles") add-type -P ...
- java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: java.util.zip.ZipException: invalid LOC header (bad signature)异常解决方法
java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: org.apache.catalina.LifecycleException: Failed to start com ...
- linux环境下安装selenium+chrom+chromdriver.exe
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/yoyocat915/article/details/80580066 原文:https://blog.csdn.net/hanxue6898/art ...
