HashMap集合遍历随机性问题分析
一、原因分析
1.1 HashMap对象的遍历
HashMap的遍历是通过此类中字段table数组进行顺序遍历,原因如下所示:


1 #HashMap 迭代遍历源码
2 public final boolean hasNext() {
3 return next != null;
4 }
5
6 final Node<K,V> nextNode() {
7 Node<K,V>[] t;
8 Node<K,V> e = next;
9 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
10 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
11 if (e == null)
12 throw new NoSuchElementException();
13 //遍历完此索引位置的所有冲突的Node(链表或者是红黑树结构)
14 if ((next = (current = e).next) == null && (t = table) != null) {
15 //索引位置遍历完成,继续顺着table数组遍历下一个索引位置
16 do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
17 }
18 return e;
19 }
而具体每个对象落到table数组的哪个索引位置,是通过hashCode值和HashMap的容量求余得到,所以其遍历顺序完全依赖hashCode值,所以我们分析下集合的对象的hashCode值是否是动态变化的,如果是变化的,其在table数组中的位置就是动态可变的,那遍历顺序也是动态可变的,从而导致相同产品的不同版本是随机相互覆盖的。分析过程如下所示:
我们自定义存储在HashMap集合中的元素类对象,如下所示:


1 public class Personal {
2 private String name;
3 private String age;
4 private CityEnum city;
5
6 public Personal(String name, String age, CityEnum city) {
7 this.name = name;
8 this.age = age;
9 this.city = city;
10 }
11
12 public String getName() {
13 return name;
14 }
15
16 public void setName(String name) {
17 this.name = name;
18 }
19
20 public String getAge() {
21 return age;
22 }
23
24 public void setAge(String age) {
25 this.age = age;
26 }
27
28 public CityEnum getCity() {
29 return city;
30 }
31
32 public void setCity(CityEnum city) {
33 this.city = city;
34 }
35
36 @Override
37 public boolean equals(Object o) {
38 if (this == o) return true;
39 if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
40 Personal personal = (Personal) o;
41 return Objects.equals(name, personal.name) && Objects.equals(age, personal.age) && city == personal.city;
42 }
43
44 @Override
45 public int hashCode() {
46 CityEnum city = this.getCity();
47 int hashCode = 0;
48 hashCode += this.getCity().hashCode()+this.getName().hashCode()+this.getAge().hashCode();
49 return hashCode;
50 }
51 }
以及其依赖的枚举字段city:


1 public enum CityEnum {
2 BEIJING,
3 SHANGHAI,
4 HENAN,
5 TIANJIN
6 }
由于Personal此类重写了hashCode()方法:


1 public int hashCode() {
2 int h = hash;
3 if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
4 char val[] = value;
5
6 for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
7 h = 31 * h + val[i];
8 }
9 hash = h;
10 }
11 return h;
12 }
其上生成hashCode使用的字段包括两种数据类型(String和CityEnum),他们各自的hashCode的实现如下所示:
1. String类重写的hashCode方法如下所示:


1 public int hashCode() {
2 int h = hash;
3 if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
4 char val[] = value;
5
6 for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
7 h = 31 * h + val[i];
8 }
9 hash = h;
10 }
11 return h;
12 }
对于String的hashCode方法,从源码可以看出,只和其值有关系,所以相同的字符串在不同的进程之间永远是相同的,不存在变化的情况。
2. CityEnum类没有实现hashCode方法,使用的是Object类的本地hashCode方法,如下所示:
public native int hashCode();
而对于CityEnum类来说,由于使用的是其父类Object的native方法hashCode(),对于相同ServiceName枚举值,此方法的返回值在不同进程之间是不同的。
opjdk的实现源码方法可追溯到方法FastHashCode:https://github.com/bpupadhyaya/openjdk-8/blob/master/hotspot/src/share/vm/runtime/synchronizer.cpp(native源码查询方式可参考我的另一篇文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/chenmingming0225/p/17797117.html),具体生成hashCode的方法如下所示:


1 static inline intptr_t get_next_hash(Thread * Self, oop obj) {
2 intptr_t value = 0 ;
3 if (hashCode == 0) {
4 // This form uses an unguarded global Park-Miller RNG,
5 // so it's possible for two threads to race and generate the same RNG.
6 // On MP system we'll have lots of RW access to a global, so the
7 // mechanism induces lots of coherency traffic.
8 value = os::random() ;
9 } else
10 if (hashCode == 1) {
11 // This variation has the property of being stable (idempotent)
12 // between STW operations. This can be useful in some of the 1-0
13 // synchronization schemes.
14 intptr_t addrBits = cast_from_oop<intptr_t>(obj) >> 3 ;
15 value = addrBits ^ (addrBits >> 5) ^ GVars.stwRandom ;
16 } else
17 if (hashCode == 2) {
18 value = 1 ; // for sensitivity testing
19 } else
20 if (hashCode == 3) {
21 value = ++GVars.hcSequence ;
22 } else
23 if (hashCode == 4) {
24 #cast_from_oop将obj对象的地址(引用)转换为整数类型
25 value = cast_from_oop<intptr_t>(obj) ;
26 } else {
27 // Marsaglia's xor-shift scheme with thread-specific state
28 // This is probably the best overall implementation -- we'll
29 // likely make this the default in future releases.
30 unsigned t = Self->_hashStateX ;
31 t ^= (t << 11) ;
32 Self->_hashStateX = Self->_hashStateY ;
33 Self->_hashStateY = Self->_hashStateZ ;
34 Self->_hashStateZ = Self->_hashStateW ;
35 unsigned v = Self->_hashStateW ;
36 v = (v ^ (v >> 19)) ^ (t ^ (t >> 8)) ;
37 Self->_hashStateW = v ;
38 value = v ;
39 }
40
41 value &= markOopDesc::hash_mask;
42 if (value == 0) value = 0xBAD ;
43 assert (value != markOopDesc::no_hash, "invariant") ;
44 TEVENT (hashCode: GENERATE) ;
45 return value;
46 }
默认hashCode值是多少?

hashCode=5时,将走else中的逻辑,此逻辑使用Marsaglia's xor-shift 算法,这个算法的核心思想是通过位操作和状态变量的混合,生成看似随机的哈希码。这样的哈希 码通常用于散列表等数据结构中,以平均分散数据,降低哈希冲突的概率。由于哈希码的生成是基于对象地址和线程状状态,因此对于相同对象和相同线程状态,生成的 哈希码是一致的,但不同对象和不同线程可能会生成不同的哈希码。
也可在启动java进程中加入-XX:hashCode=2指定使用哪种hashCode生成算法,如下所示:
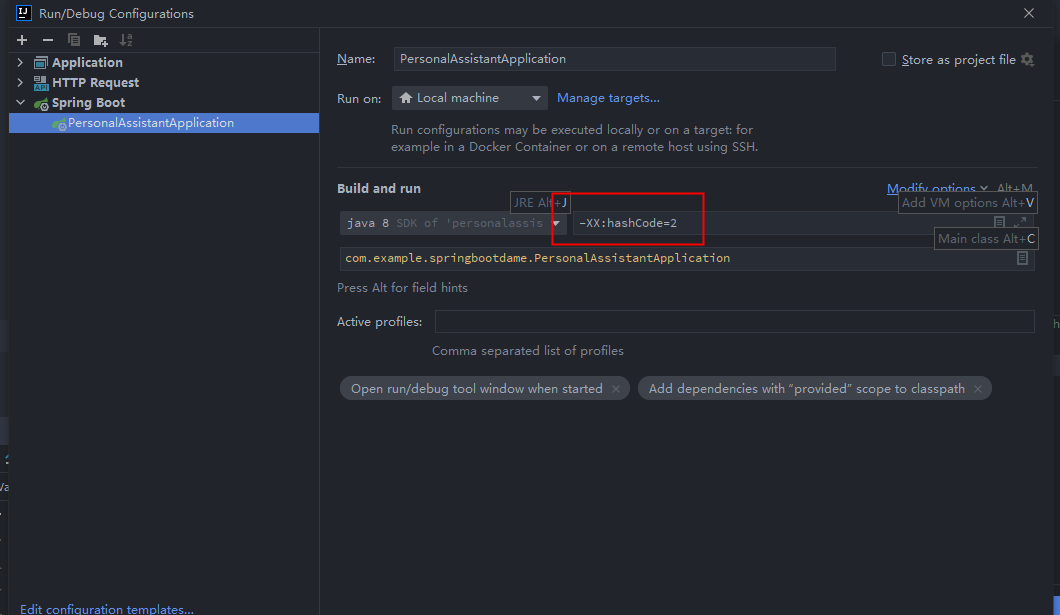
也可参考这篇文章去理解:https://juejin.cn/post/6873019885597753357
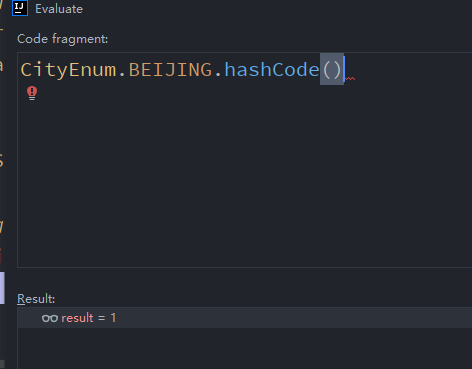
验证1,2两部分的分析,举例如下:


1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 System.out.println("1".hashCode());
3 System.out.println("12".hashCode());
4 System.out.println(CityEnum.BEIJING.hashCode());
5 }
本地在两个项目下执行以上main函数,输出结果如下所示:
#进程1
49
1569
1313953385
#进程2
49
1569
2081191879
1.2 HashMap对象的扩容
实际上HashMap对象扩容之后,也可能导致两个元素的遍历先后顺序发生变化,映射到业务上就是,当打包的产品的数量达到扩容的阈值时,也会发生不同版本的相同产品的遍历顺序发生变化,扩容方法源码如下所示,可通过其中注释理解其含义:


1 final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
2 Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
3 int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
4 int oldThr = threshold;
5 int newCap, newThr = 0;
6 if (oldCap > 0) {
7 if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
8 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
9 return oldTab;
10 }
11 else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
12 oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
13 newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
14 }
15 else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
16 newCap = oldThr;
17 else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
18 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
19 newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
20 }
21 if (newThr == 0) {
22 float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
23 newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
24 (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
25 }
26 threshold = newThr;
27 @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
28 Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
29 table = newTab;
30 if (oldTab != null) {
31 for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
32 Node<K,V> e;
33 if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
34 oldTab[j] = null;
35 //此索引位置无hash冲突
36 if (e.next == null)
37 newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
38 //此索引位置有hash冲突,且是红黑树数据结构
39 else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
40 ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
41 //此索引位置有hash冲突,且是链表数据结构
42 else { // preserve order
43 //保持索引位置不变的链表的头尾
44 Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
45 //索引位置迁移到高位(当前索引位置+oldCap)的链表的头尾
46 Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
47 Node<K,V> next;
48 do {
49 next = e.next;
50 //(e.hash & oldCap) == 0时,e.hash &(oldCap-1)=e.hash &(2oldCap-1)
51 if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
52 if (loTail == null)
53 loHead = e;
54 else
55 loTail.next = e;
56 loTail = e;
57 }
58 //(e.hash & oldCap) != 0时,e.hash &(oldCap-1) + oldCap = e.hash &(2oldCap-1)
59 else {
60 if (hiTail == null)
61 hiHead = e;
62 else
63 hiTail.next = e;
64 hiTail = e;
65 }
66 } while ((e = next) != null);
67 if (loTail != null) {
68 loTail.next = null;
69 newTab[j] = loHead;
70 }
71 if (hiTail != null) {
72 hiTail.next = null;
73 newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
74 }
75 }
76 }
77 }
78 }
79 return newTab;
80 }


1 #treeNode遍历
2 final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) {
3 TreeNode<K,V> b = this;
4 // Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving order
5 TreeNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
6 TreeNode<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
7 int lc = 0, hc = 0;
8 for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) {
9 //从这里可以看出jdk1.8,当链表数据量大于8时转换为红黑树,但是还保留了其链表结构(感兴趣的可以从push方法中发现),此部分遍历用的就是链表的结构
10 next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next;
11 e.next = null;
12 if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) {
13 if ((e.prev = loTail) == null)
14 loHead = e;
15 else
16 loTail.next = e;
17 loTail = e;
18 ++lc;
19 }
20 else {
21 if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null)
22 hiHead = e;
23 else
24 hiTail.next = e;
25 hiTail = e;
26 ++hc;
27 }
28 }
29
30 if (loHead != null) {
31 if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
32 tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map);
33 else {
34 tab[index] = loHead;
35 if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified)
36 loHead.treeify(tab);
37 }
38 }
39 if (hiHead != null) {
40 if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
41 tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map);
42 else {
43 tab[index + bit] = hiHead;
44 if (loHead != null)
45 hiHead.treeify(tab);
46 }
47 }
48 }
1.2.1 基本知识点
哈希值对链表数组的长度取模,得到值所在的索引位置,里面使用位运算(&)代替普通的(%)运算。
1. 为什么[用位运算(&)代替普通的(%)运算?
位运算(&)效率要比取模运算(%)高很多,主要原因是位运算直接对内存数据进行操作,不需要转成十进制,因此处理速度非常快。
2. 位运算(&)为什么能代(%)运算?
从2进制角度来看,X / 2^n相当于 X >> n,即把X右移n位,此时得到了X / 2^n的商,而被移掉的部分(后n位),则是X % 2^n,也就是余数,想获取后n位的值只需要与2^n-1求与即可获得,所以,X % 2^n = X & (2^n - 1),也就是说, 一个数对 2^n 取模相当于一个数和 (2^n - 1) 做按位与 运算。
1.2.2 扩容导致遍历顺序变化
定义personal1和Personal2两个对象,如下所示:
Personal personal1=new Personal("张三","20",CityEnum.BEIJING);
Personal personal2=new Personal("李四","21",CityEnum.SHANGHAI);
假设personal1和Personal2的hashCode分别为9和4,HashSet<Personal> 对象的初始容量为8
1. 假设某次请求中,map中的元素个数小于8*0.75=6,迭代器遍历map时,由于9%8=1,4%8=4,那么两个产品的遍历先后顺序是Personal1,Personal2;
2. 假设某次请求中,map中的元素个数大于8*0.75=6,达到扩容阈值,则会执行resize() 方法,map的容量变成16,迭代器遍历map时,由于9%16=9,4%16=4,那么两个产品的遍历先后顺序是Personal2,Personal1;
由上可知,当发生扩容是,两个相同的对象放入扩容前后的集合中的索引位置发生变换,迭代遍历先后顺序可能变换;
二、结论
由第二部分分析过程可知,由于HashSet<Personal>中的Personal对象,由于有个字段是枚举类没有实现父类Object的hashCode方法而使用父类的native hashCode()方法获取hash值,同一个元素对象其hash值在不同进程间是不同的,所以导致存储相同个数(大于1)的Personal的集合对象HashSet<Personal>,在不同进程间对其进行迭代遍历的顺序不同。如果像保证集合中自定义元素的遍历顺序在任何进程间不变,需要重写hashCode方法,是得其值只与其.toString值有关,而与地址等动态变量无关即可。
HashMap集合遍历随机性问题分析的更多相关文章
- HashMap集合-遍历方法
# HashMap集合-遍历方法 先定义好集合: public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> onemap=ne ...
- HashMap 集合的遍历
HashMap 集合的遍历: 两种方式遍历HashMap: //集合hashMap的遍历: //方式一: @Test public void testMethod1(){ HashMap<Str ...
- java集合遍历删除指定元素异常分析总结
在使用集合的过程中,我们经常会有遍历集合元素,删除指定的元素的需求,而对于这种需求我们往往使用会犯些小错误,导致程序抛异常或者与预期结果不对,本人很早之前就遇到过这个坑,当时没注意总结,结果前段时间又 ...
- 如何遍历HashMap集合?
在Java中,HashMap是一种常用的数据结构,它提供了快速的查找.插入和删除操作.当我们需要遍历HashMap中的所有元素时,可以利用三种不同的方法实现. 方法一:使用键值对遍历 HashMap中 ...
- Map集合遍历的方式(以HashMap为例)
环境:jdk1.8 HashMap的遍历方式有多种,下面将会一一列出. 首先我们先在HashMap中添加几个键值对. HashMap<Integer, String> map = new ...
- Java 之 HashMap 集合
一.HashMap 概述 java.util.HashMap<k,v> 集合 implements Map<k,v> 接口 HashMap 集合的特点: 1.HashMap 集 ...
- HashMap循环遍历方式及其性能对比(zhuan)
http://www.trinea.cn/android/hashmap-loop-performance/ ********************************************* ...
- HashMap循环遍历方式及其性能对比
主要介绍HashMap的四种循环遍历方式,各种方式的性能测试对比,根据HashMap的源码实现分析性能结果,总结结论. 1. Map的四种遍历方式 下面只是简单介绍各种遍历示例(以HashMap为 ...
- [集合]Collection集合框架源码分析
Collection接口 在java的集合类库中,基本接口是Collection,该接口的在集合中的源码定义如下(将源码中的注释删掉了): public interface Collection< ...
- 并发-HashMap和HashTable源码分析
HashMap和HashTable源码分析 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/luanlouis/article/details/41576373 http://www.cnblog ...
随机推荐
- 使用pip或者手动安装第三方库出现“由于目标计算机积极拒绝,无法连接”错误的解决办法
网上找了很多地方,都没找到怎么解决,之前用pip安装成功过,但是翻过墙后,pip安装第三方库的时候发现错误,如图:
- 【Python微信机器人】第六篇:优化使用方式,可pip安装
优化内容 这篇不聊技术点,说一下优化后的Python机器人代码怎么使用,优化内容如下: 将hook库独立成一个库,发布到pypi,可使用pip安装 将微信相关的代码发布成另一个库,也可以pip安装 g ...
- 安装了华企盾DSC防泄密,所有进程的加密文件都无法打开
用pchunter等工具查看系统回调中是否有文件厂商不存在的(system目录的除外),在恢复模式删除掉,或者用360系统急救箱查杀一下
- shopify主题模板速度优化
前两天一位新客户说他的shopify店铺加载速度很慢,首页完全加载需要 5~6 秒甚至更高,问ytkah有没办法帮忙优化一下.shopify网站速度优化要看具体用了什么模板,有什么功能,哪些可以改哪些 ...
- 设计模式Java实战,彻底学会
这是全网最强的Java设计模式实战教程.此教程用实际项目场景,结合SpringBoot,让你真正掌握设计模式. 网址是:Java设计模式实战专栏介绍 - 自学精灵(也可以百度搜索"自学 ...
- mysql 数据库 定时 备份到阿里云盘
仓库地址: gitee:db_backup_script: mysql 数据库 定时/实时 备份数据库到阿里云盘,备份成功后消息可通知到钉钉群.企业微信群.wxpusher (gitee.com gi ...
- 提取 PE文件 / 目标程序 的各种信息
前段时间项目需要实现对 Windows PE 文件版本信息的提取,如文件说明.文件版本.产品名称.版权.原始文件名等信息.获取这些信息在 Windows 下当然有一系列的 API 函数供调用,简单方便 ...
- C++通过文件指针获取文件大小
目录 1. 叙述 2. 结论 1. 叙述 对于读取本地文件,很多时候需要预先知道本地文件的大小在进行读取.网上给出的方案是移动文件指针,计算文件头和文件尾的偏移,计算出文件的大小.但是我总觉得这样做可 ...
- C++篇:第十章_命名空间_知识点大全
C++篇为本人学C++时所做笔记(特别是疑难杂点),全是硬货,虽然看着枯燥但会让你收益颇丰,可用作学习C++的一大利器 十.命名空间 命名空间可以在全局作用域或其他命名空间内部定义,但不能在函数.结构 ...
- MindSpore!这款刚刚开源的深度学习框架我爱了!
[摘要] 本文主要通过两个实际应用案例:一是基于本地 Jupyter Notebook 的 MNIST 手写数据识别:二是基于华为云服务器的 CIFAR-10 图像分类,对开源框架 MindSpore ...
