论文解读(SAGPool)《Self-Attention Graph Pooling》
论文信息
论文标题:Self-Attention Graph Pooling
论文作者:Junhyun Lee, Inyeop Lee, Jaewoo Kang
论文来源:2019, ICML
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
1 Introduction
图池化三种类型:
- Topology based pooling;
- Hierarchical pooling;(使用所有从 GNN 获得的节点表示)
- Hierarchical pooling;
关于 Hierarchical pooling 聚类分配矩阵:
$\begin{array}{j}S^{(l)}=\operatorname{softmax}\left(\mathrm{GNN}_{l}\left(A^{(l)}, X^{(l)}\right)\right) \\A^{(l+1)}=S^{(l) \top} A^{(l)} S^{(l)}\end{array} \quad\quad\quad\quad(1)$
gPool 取得了与 DiffPool 相当的性能,gPool 需要的存储复杂度为 $\mathcal{O}(|V|+|E|)$,而 DiffPool 需要 $\mathcal{O}\left(k|V|^{2}\right)$,其中 $V$、$E$ 和 $k$ 分别表示顶点、边和池化率。gPool 使用一个可学习的向量 $p$ 来计算投影分数,然后使用这些分数来选择排名靠前的节点。投影得分由 $p$ 与所有节点的特征之间的点积得到。这些分数表示可以保留的节点的信息量。下面的公式大致描述了 gPool 中的池化过程:
$\begin{array}{l} y=X^{(l)} \mathbf{p}^{(l)} /\left\|\mathbf{p}^{(l)}\right\|\\ \mathrm{idx}=\operatorname{top}-\operatorname{rank}(y,\lceil k N\rceil)\\A^{(l+1)}=A_{\mathrm{idx}, \mathrm{idx}}^{(l)}\end{array} \quad\quad\quad\quad(2)$
2 Method
框架如下:
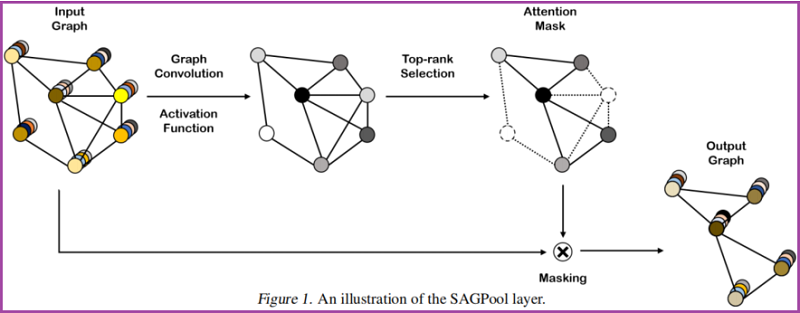
2.1. Self-Attention Graph Pooling
Self-attention mask
本文使用图卷积来获得自注意分数:
$Z=\sigma\left(\tilde{D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} \tilde{A} \tilde{D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} X \Theta_{a t t}\right) \quad\quad\quad\quad(3)$
其中,自注意得分 $Z \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times 1}$、邻接矩阵 $\tilde{A} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times N}$、注意力参数矩阵 $\Theta_{a t t} \in \mathbb{R}^{F \times 1}$、特征矩阵 $X \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times F}$、度矩阵 $\tilde{D} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times N}$。
这里考虑节点选择方法,即使输入不同大小和结构的图,也会保留输入图的部分节点。
$\begin{array}{l} \mathrm{idx}=\operatorname{top}-\operatorname{rank}(Z,\lceil k N\rceil)\\Z_{\text {mask }}=Z_{\mathrm{idx}}\end{array} \quad\quad\quad\quad(4)$
基于自注意得分 $Z$ ,选择保留前 $ \lceil k N\rceil$ 个节点,其中 $k \in(0,1]$ 代表着池化率(pooling ratio),$Z_{\text{mask}}$ 是 feature attention mask。。
Graph pooling
接着获得新特征矩阵和邻接矩阵:
$\begin{array}{l} X^{\prime}=X_{\mathrm{idx},:}\\X_{\text {out }}=X^{\prime} \odot Z_{\text {mask }}\\A_{\text {out }}=A_{\mathrm{idx}, \mathrm{idx}}\end{array} \quad\quad\quad\quad(5)$
其中,$\odot$ is the broadcasted elementwise product。
Variation of SAGPool
$Z=\sigma(\operatorname{GNN}(X, A)) \quad\quad\quad\quad(6)$
$Z=\sigma\left(\operatorname{GNN}\left(X, A+A^{2}\right)\right) \quad\quad\quad\quad(7)$
$Z=\sigma\left(\mathrm{GNN}_{2}\left(\sigma\left(\mathrm{GNN}_{1}(X, A)\right), A\right)\right) \quad\quad\quad\quad(8)$
$Z=\frac{1}{M} \sum_{m} \sigma\left(\mathrm{GNN}_{m}(X, A)\right) \quad\quad\quad\quad(9)$
2.2 Model Architecture
本节用来验证模块的有效性。
Convolution layer
图卷积 GCN:
$h^{(l+1)}=\sigma\left(\tilde{D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} \tilde{A} \tilde{D}^{-\frac{1}{2}} h^{(l)} \Theta\right) \quad\quad\quad\quad(10)$
与 $\text{Eq.3}$ 不同的是,$\Theta \in \mathbb{R}^{F \times F^{\prime}}$ 。
Readout layer
根据 JK-net architecture 的思想:
$s=\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} x_{i} \| \max _{i=1}^{N} x_{i} \quad\quad\quad\quad(11)$
其中:
- $N$ 代表着节点的个数;
- $x_{i}$ 代表着第 $i$ 个节点的特征向量;
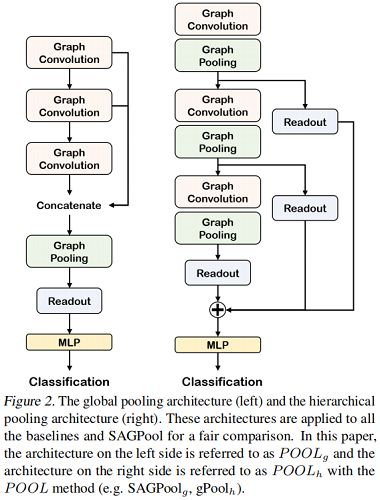
Global pooling architecture & Hierarchical pooling architecture
对比如下:
3 Experiments
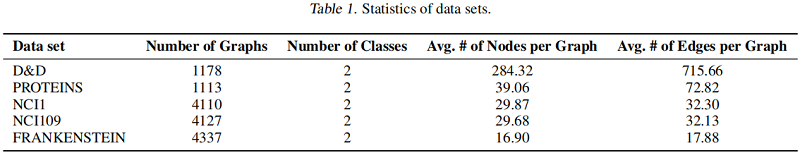
数据集
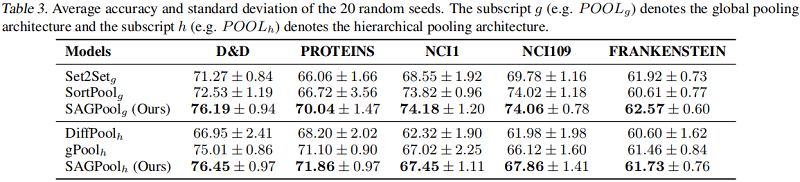
基线实验
SAGPool 的变体
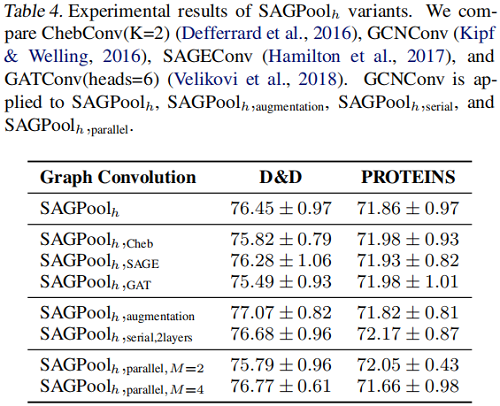
4 Conclusion
本文提出了一种基于自注意的SAGPool图池化方法。我们的方法具有以下特征:分层池、同时考虑节点特征和图拓扑、合理的复杂度和端到端表示学习。SAGPool使用一致数量的参数,而不管输入图的大小如何。我们工作的扩展可能包括使用可学习的池化比率来获得每个图的最优聚类大小,并研究每个池化层中多个注意掩模的影响,其中最终的表示可以通过聚合不同的层次表示来获得。
论文解读(SAGPool)《Self-Attention Graph Pooling》的更多相关文章
- 论文解读《Deep Attention-guided Graph Clustering with Dual Self-supervision》
论文信息 论文标题:Deep Attention-guided Graph Clustering with Dual Self-supervision论文作者:Zhihao Peng, Hui Liu ...
- 论文解读GALA《Symmetric Graph Convolutional Autoencoder for Unsupervised Graph Representation Learning》
论文信息 Title:<Symmetric Graph Convolutional Autoencoder for Unsupervised Graph Representation Learn ...
- 论文解读(ChebyGIN)《Understanding Attention and Generalization in Graph Neural Networks》
论文信息 论文标题:Understanding Attention and Generalization in Graph Neural Networks论文作者:Boris Knyazev, Gra ...
- 论文解读(GraphMAE)《GraphMAE: Self-Supervised Masked Graph Autoencoders》
论文信息 论文标题:GraphMAE: Self-Supervised Masked Graph Autoencoders论文作者:Zhenyu Hou, Xiao Liu, Yukuo Cen, Y ...
- 论文解读(KP-GNN)《How Powerful are K-hop Message Passing Graph Neural Networks》
论文信息 论文标题:How Powerful are K-hop Message Passing Graph Neural Networks论文作者:Jiarui Feng, Yixin Chen, ...
- 论文解读(SR-GNN)《Shift-Robust GNNs: Overcoming the Limitations of Localized Graph Training Data》
论文信息 论文标题:Shift-Robust GNNs: Overcoming the Limitations of Localized Graph Training Data论文作者:Qi Zhu, ...
- 论文解读(LG2AR)《Learning Graph Augmentations to Learn Graph Representations》
论文信息 论文标题:Learning Graph Augmentations to Learn Graph Representations论文作者:Kaveh Hassani, Amir Hosein ...
- 论文解读(GCC)《Efficient Graph Convolution for Joint Node RepresentationLearning and Clustering》
论文信息 论文标题:Efficient Graph Convolution for Joint Node RepresentationLearning and Clustering论文作者:Chaki ...
- 论文解读(AGC)《Attributed Graph Clustering via Adaptive Graph Convolution》
论文信息 论文标题:Attributed Graph Clustering via Adaptive Graph Convolution论文作者:Xiaotong Zhang, Han Liu, Qi ...
随机推荐
- 分布式集群中为什么会有 Master?
在分布式环境中,有些业务逻辑只需要集群中的某一台机器进行执行,其他的机 器可以共享这个结果,这样可以大大减少重复计算,提高性能,于是就需要进行 leader 选举.
- 什么是 spring 的内部 bean?
只有将 bean 用作另一个 bean 的属性时,才能将 bean 声明为内部 bean. 为了定义 bean,Spring 的基于 XML 的配置元数据在 <property> 或 &l ...
- 客户端回调 Watcher ?
客户端 SendThread 线程接收事件通知,交由 EventThread 线程回调 Watcher. 客户端的 Watcher 机制同样是一次性的,一旦被触发后,该 Watcher 就失效了.
- zookeeper 的应用
不建议使用(单独)zookeeper 做分布式队列,有几点原因,以下原因摘抄于curator的官网: 1.zookeeper有1MB的传输限制.而在队列中,拥有很多的数据节点,通常包括数千个,如果有较 ...
- ctfhub 双写绕过 文件头检查
双写绕过 进入环境 上传一句话木马 上传路径感觉不对检查源代码 从此处可以看出需要双写绕过 使用bp抓包 此处这样修改即可双写绕过 使用蚁剑连接 即可找到flag 文件头检查 进入环境 上传一句话木马 ...
- HTML 初学整理
一.HTML简介 HTML的概念 HTML是HyperText Markup Language(超文本标记语言)的简写,超文本标记语言,标准通用标记语言下的一个应用."超文本"就是 ...
- Pullword 中文分词
安装 npm install pullword 使用 var defaultOptions = { url: 'http://api.pullword.com/post.php', /* api ...
- 一个抽取百度定位的教程(下载百度地图Demo+配置+抽取)
效果展示 已经下载Demo的可以直接到第五步,已经配置好的并可以运行的可以直接到第七步. 1.在浏览器搜索 " 百度定位API ",点击下面这个链接 2.翻到最下面找到并点击 &q ...
- Python实现简单用户注册信息管理系统
运行效果: 注意:运行前请在同一目录下创建一个userdata.bin用于保存用户数据 源代码: 1 # coding:utf-8 2 ''' 3 用户注册信息管理系统 4 功能包括: 5 1.查看全 ...
- Python入门-import导入模块功能
1.啥是模块 模块(module):用来实现或者多个功能的Python代码,(包含变量.函数.类),本质就是*.py后缀文件. 包(package):定义了一个由模块和子包组成的Python应用程序执 ...
