Collections.shuffle源码阅读
java.util.Collections
/**
* Randomly permutes the specified list using a default source of
* randomness. All permutations occur with approximately equal
* likelihood.<p>
*
* The hedge "approximately" is used in the foregoing description because
* default source of randomness is only approximately an unbiased source
* of independently chosen bits. If it were a perfect source of randomly
* chosen bits, then the algorithm would choose permutations with perfect
* uniformity.<p>
*
* This implementation traverses the list backwards, from the last element
* up to the second, repeatedly swapping a randomly selected element into
* the "current position". Elements are randomly selected from the
* portion of the list that runs from the first element to the current
* position, inclusive.<p>
*
* This method runs in linear time. If the specified list does not
* implement the {@link RandomAccess} interface and is large, this
* implementation dumps the specified list into an array before shuffling
* it, and dumps the shuffled array back into the list. This avoids the
* quadratic behavior that would result from shuffling a "sequential
* access" list in place.
*
* @param list the list to be shuffled.
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the specified list or
* its list-iterator does not support the <tt>set</tt> operation.
*/
public static void shuffle(List<?> list) {
if (r == null) {
r = new Random();
}
shuffle(list, r);
}
private static Random r;
java.util.Random
/**
* Randomly permute the specified list using the specified source of
* randomness. All permutations occur with equal likelihood
* assuming that the source of randomness is fair.<p>
*
* This implementation traverses the list backwards, from the last element
* up to the second, repeatedly swapping a randomly selected element into
* the "current position". Elements are randomly selected from the
* portion of the list that runs from the first element to the current
* position, inclusive.<p>
*
* This method runs in linear time. If the specified list does not
* implement the {@link RandomAccess} interface and is large, this
* implementation dumps the specified list into an array before shuffling
* it, and dumps the shuffled array back into the list. This avoids the
* quadratic behavior that would result from shuffling a "sequential
* access" list in place.
*
* @param list the list to be shuffled.
* @param rnd the source of randomness to use to shuffle the list.
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the specified list or its
* list-iterator does not support the <tt>set</tt> operation.
*/
public static void shuffle(List<?> list, Random rnd) {
int size = list.size();
if (size < SHUFFLE_THRESHOLD || list instanceof RandomAccess) {
for (int i=size; i>1; i--)
swap(list, i-1, rnd.nextInt(i));
} else {
Object arr[] = list.toArray(); // Shuffle array
for (int i=size; i>1; i--)
swap(arr, i-1, rnd.nextInt(i)); // Dump array back into list
ListIterator it = list.listIterator();
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
it.next();
it.set(arr[i]);
}
}
}
private static final int SHUFFLE_THRESHOLD = 5;
/**
* Swaps the elements at the specified positions in the specified list.
* (If the specified positions are equal, invoking this method leaves
* the list unchanged.)
*
* @param list The list in which to swap elements.
* @param i the index of one element to be swapped.
* @param j the index of the other element to be swapped.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if either <tt>i</tt> or <tt>j</tt>
* is out of range (i < 0 || i >= list.size()
* || j < 0 || j >= list.size()).
* @since 1.4
*/
public static void swap(List<?> list, int i, int j) {
final List l = list; //这一步有什么用
l.set(i, l.set(j, l.get(i)));
}
java.util.List
@org.intellij.lang.annotations.Flow(sourceIsContainer=true)
public abstract E set(int index,
@org.intellij.lang.annotations.Flow(targetIsContainer=true) E element)
Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the specified element (optional operation).
Parameters:
index - index of the element to replace
element - element to be stored at the specified position
Returns:
the element previously at the specified position
/**
* Swaps the two specified elements in the specified array.
*/
private static void swap(Object[] arr, int i, int j) {
Object tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
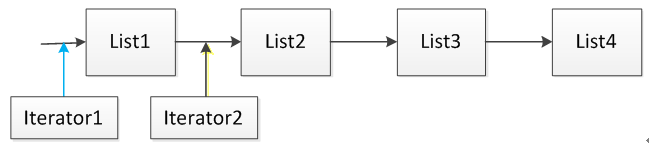
这里假设集合List由四个元素List1、List2、List3和List4组成,当使用语句Iterator it = List.Iterator()时,迭代器it指向的位置是上图中Iterator1指向的位置,当执行语句it.next()之后,迭代器指向的位置后移到上图Iterator2所指向的位置。
首先看一下Iterator和ListIterator迭代器的方法有哪些。
Iterator迭代器包含的方法有:
hasNext():如果迭代器指向位置后面还有元素,则返回 true,否则返回false
next():返回集合中Iterator指向位置后面的元素
remove():删除集合中Iterator指向位置后面的元素
ListIterator迭代器包含的方法有:
add(E e): 将指定的元素插入列表,插入位置为迭代器当前位置之前
hasNext():以正向遍历列表时,如果列表迭代器后面还有元素,则返回 true,否则返回false
hasPrevious():如果以逆向遍历列表,列表迭代器前面还有元素,则返回 true,否则返回false
next():返回列表中ListIterator指向位置后面的元素
nextIndex():返回列表中ListIterator所需位置后面元素的索引
previous():返回列表中ListIterator指向位置前面的元素
previousIndex():返回列表中ListIterator所需位置前面元素的索引
remove():从列表中删除next()或previous()返回的最后一个元素(有点拗口,意思就是对迭代器使用hasNext()方法时,删除ListIterator指向位置后面的元素;当对迭代器使用hasPrevious()方法时,删除ListIterator指向位置前面的元素)
set(E e):从列表中将next()或previous()返回的最后一个元素返回的最后一个元素更改为指定元素e
一.相同点
都是迭代器,当需要对集合中元素进行遍历不需要干涉其遍历过程时,这两种迭代器都可以使用。
二.不同点
1.使用范围不同,Iterator可以应用于所有的集合,Set、List和Map和这些集合的子类型。而ListIterator只能用于List及其子类型。
2.ListIterator有add方法,可以向List中添加对象,而Iterator不能。
3.ListIterator和Iterator都有hasNext()和next()方法,可以实现顺序向后遍历,但是ListIterator有hasPrevious()和previous()方法,可以实现逆向(顺序向前)遍历。Iterator不可以。
4.ListIterator可以定位当前索引的位置,nextIndex()和previousIndex()可以实现。Iterator没有此功能。
5.都可实现删除操作,但是ListIterator可以实现对象的修改,set()方法可以实现。Iterator仅能遍历,不能修改。
三:Iterator和ListIterator用法示例
ListIterator用法:
package com.collection; import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator; public class ListIteratorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> staff = new LinkedList<>();
staff.add("zhuwei");
staff.add("xuezhangbin");
staff.add("taozhiwei");
ListIterator<String> iter = staff.listIterator();
String first = iter.next(); //删除zhuwei
iter.remove(); //把zhuwei改为simei
//iter.set("simei");
System.out.println("first:"+first); iter.add("xiaobai"); //遍历List元素
System.out.println("遍历List中元素,方法一:");
for(String str : staff)
System.out.println(str+" "); iter = staff.listIterator();
System.out.println("遍历List中元素,方法二:");
while(iter.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
} }
http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-11/109950.htm
Collections.shuffle源码阅读的更多相关文章
- Collections.shuffle()源码分析
Java.util.Collections类下有一个静态的shuffle()方法,如下: 1)static void shuffle(List<?> list) 使用默认随机源对列表进行 ...
- System.Collections.Generic 源码阅读总结
ArrayList ,List ArrayList 和 List 都是不限制长度的集合类型 ,List相比ArrayList 就内部实现而言除了泛型本质没有太大区别.不过为避免装箱拆箱问题,尽可能使用 ...
- Spark源码阅读之存储体系--存储体系概述与shuffle服务
一.概述 根据<深入理解Spark:核心思想与源码分析>一书,结合最新的spark源代码master分支进行源码阅读,对新版本的代码加上自己的一些理解,如有错误,希望指出. 1.块管理器B ...
- Flink源码阅读(1.7.2)
目录 Client提交任务 flink的图结构 StreamGraph OptimizedPlan JobGraph ExecutionGraph flink部署与执行模型 Single Job Jo ...
- Bert源码阅读
前言 对Google开源出来的bert代码,来阅读下.不纠结于代码组织形式,而只是梳理下其训练集的生成,训练的self-attention和multi-head的具体实现. 训练集的生成 主要实现在c ...
- ZooKeeper源码阅读——client(二)
原创技术文章,转载请注明:转自http://newliferen.github.io/ 如何连接ZooKeeper集群 要想了解ZooKeeper客户端实现原理,首先需要关注一下客户端的使用方式, ...
- SparkConf加载与SparkContext创建(源码阅读一)
即日起开始spark源码阅读之旅,这个过程是相当痛苦的,也许有大量的看不懂,但是每天一个方法,一点点看,相信总归会有极大地提高的.那么下面开始: 创建sparkConf对象,那么究竟它干了什么了类,从 ...
- java8 ArrayList源码阅读
转载自 java8 ArrayList源码阅读 本文基于jdk1.8 JavaCollection库中有三类:List,Queue,Set 其中List,有三个子实现类:ArrayList,Vecto ...
- JDK1.8源码阅读系列之三:Vector
本篇随笔主要描述的是我阅读 Vector 源码期间的对于 Vector 的一些实现上的个人理解,用于个人备忘,有不对的地方,请指出- 先来看一下 Vector 的继承图: 可以看出,Vector 的直 ...
随机推荐
- Oracle Dataguard三种保护模式
Oracle Dataguard提供了三种数据保护模式,在此分别总结一下三种数据保护模式的特点. 1.最大保护模式1)这种模式提供了最高级别的数据保护能力:2)要求至少一个物理备库收到重做日志后,主库 ...
- maven项目 打可执行jar包
1.pom添加 <build> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</art ...
- hp-ux-ia64:jffi/ffi 编译总结
在HP-UX-IA64下编译JFFI及FFI遇到很多问题,官网jffi文档中也并没有在hp-ux-ia64平台上有编译过. 次文档仅为记录之用.记录编译过程,但并不意味着本人遇到的问题已经解决. 注意 ...
- Drupal 实战
<Drupal 实战> 基本信息 作者: 葛红儒 丛书名: 实战系列 出版社:机械工业出版社 ISBN:9787111429999 上架时间:2013-6-28 出版日期:2013 ...
- HDU1863 畅通project 【最小生成树Prim】
畅通project Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Total ...
- shell 中条件判断
if 中的 -z 到 -d 的意思 2011-09-05 10:30 [ -a FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在则为真. [ -b FILE ] 如果 FILE 存在且是一个块特殊文件则为真. [ ...
- MySQL(13):Select-order by
1. 按照字段值进行排序: 语法: order by 字段 升序|降序(asc|desc) 允许多字段排序,指的是,先按照第一个字段排序,如果说,不能区分,才使用第二个字段,以此类推. ...
- ios 中如何应对UIScrollView快速滑动(暴力用户,暴力测试)
1.实现UIScrollViewDelegate 开始滑动: - (void)scrollViewWillBeginDecelerating:(UIScrollView *)scrollView 滑动 ...
- hdu 1205
#include <stdio.h> int a[1005000]; int main() { int t; scanf("%d",&t); while(t-- ...
- java中Class.forName与new
一.使用Class.forName 1.装载类 Class clazz = Class.forName("xx.xx.xx"); 2.初始化对象 clazz.newInstance ...
