[转帖]How does a CPU work?
How does a CPU work?
https://milapneupane.com.np/2019/07/06/how-does-a-cpu-work/
CPU, also known as the microprocessor is the heart and/or brain of a computer. Lets Deep dive into the core of the computer to help us write computer programs efficiently.
“A tool is usually more simple than a machine; it is generally used with the hand, whilst a machine is frequently moved by animal or steam power.”
– Charles Babbage
A computer is a machine powered mostly by electricity but its flexibility and programability has helped achieve the simplicity of a tool.
CPU is the heart and/or the brain of a computer. It executes the instructions that are provided to it. Its main job is to perform arithmetic and logical operations and orchestrate the instructions together. Before diving into the main parts let’s start by looking what are the main components of a CPU and what there roles are:
Two main components of a processor
- Control unit — CU
- Arithmetic and logical unit — ALU
CONTROL UNIT — CU
Control unit CU is the part of CPU that helps orchestrate the execution of instructions. It tells what to do. According to the instruction, it helps activate the wires connecting CPU to different other parts of computer including the ALU. Control unit is the first component of CPU to receive the instruction for processing.
There are two types of control unit:
- hardwired control units.
- microprogrammable (microprogrammed) control units.
Hardwired control units are the hardware and needs the change in hardware to add modify it’s working where as microprogrammable control unit can be programmed to change its behavior. Hardwired CU are faster in processing instruction whereas microprogrammable as more flexible.
ARITHMETIC AND LOGICAL UNIT — ALU
Arithmetic and logical unit ALU as name suggest does all the arithmetic and logical computations. ALU performs the operations like addition, subtraction. ALU consists of logic circuitry or logic gates which performs these operations.
Most logic gates take in two input and produces one output
Bellow is an example of half adder circuit which takes in two inputs and outputs the result. Here A and B are the input, S is the output and C is the carry.
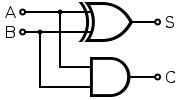 Half source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adder_(electronics)#/media/File:Half_Adder.svg
Half source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adder_(electronics)#/media/File:Half_Adder.svg
Storage — Registers and Memory
Main job of CPU is to execute the instructions provided to it. To process these instructions most of the time, it needs data. Some data are intermediate data, some of them are inputs and other is the output. These data along with the instructions are stored in the following storage:
REGISTERS
Register is a small set of place where the data can be stored. A register is a combination of latches. Latches also known as flip-flops are combinations of logic gates which stores 1 bit of information.
A latch has two input wire, write and input wire and one output wire. We can enable the write wire to make changes to the stored data. When the write wire is disabled the output always remains the same.
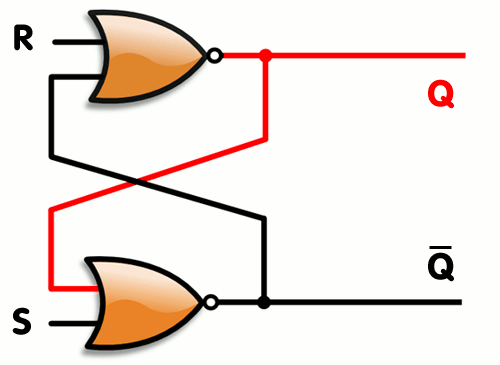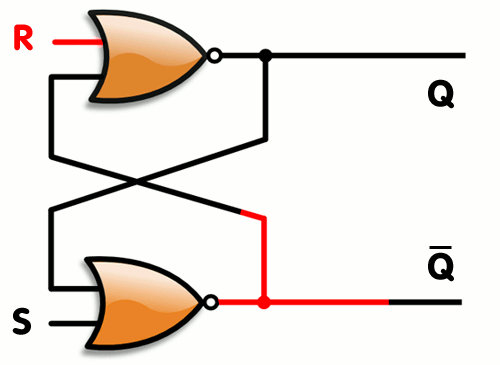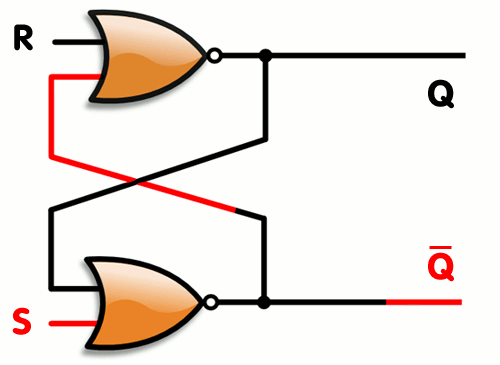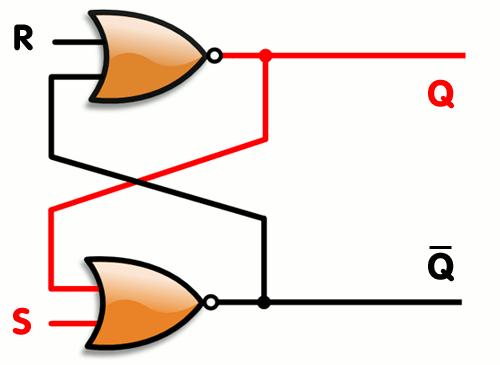 An SR latch, constructed from a pair of cross-coupled NOR gates
An SR latch, constructed from a pair of cross-coupled NOR gates
CPU has registers to store the data of output. Sending to main memory(RAM) would be slow as it is the intermediate data. This data is send to other register which is connected by a BUS. A register can store instruction, output data, storage address or any kind of data.
MEMORY(RAM)
Ram is a collection of register arranged and compact together in an optimized way so that it can store a higher number of data. RAM(Random Access Memory) are volatile and it’s data get’s lost when we turn off the power. As RAM is a collection of register to read/write data a RAM takes input of 8bit address, data input for the actual data to be stored and finally read and write enabler which works as it is for the latches.
What are Instructions
Instruction is the granular level computation a computer can perform. There are various types of instruction a CPU can process.
Instructions include:
- Arithmetic such as add and subtract
- Logic instructions such as and, or, and not
- Data instructions such as move, input, output, load, and store
- Control Flow instructions such as goto, if … goto, call, and return
- Notify CPU that the program has ended Halt
Instruction are provided to computer using assembly language or are generated by compiler or are interpreted in some high level languages.
These instruction are hardwired inside CPU. ALU contains the arithmetic and logical where as the control flow are managed by CU.
In one clock cycle computers can perform one instruction but modern computers can perform more than one.
A group of instructions a computer can perform is called an instruction set.
CPU clock
Clock cycle
The speed of a computer is determined by its clock cycle. It is the number of clock periods per second a computer works on. A single clock cycles are very small like around 250 * 10 *-12 sec. Higher the clock cycle faster the processor is.
CPU clock cycle is measure in gHz(Gigahertz). 1gHz is equal to 10 ⁹ Hz(hertz). A hertz means a second. So 1Gigahertz means 10 ⁹ cycles per second.
The faster the clock cycle, the more instructions the CPU can execute.Clock cycle = 1/clock rateCPU Time = number of clock cycle / clock rate
This means to improve CPU time we can increase clock rate or decrease number of clock cycle by optimizing the instruction we provide to CPU. Some processor provide the ability to increase the clock cycle but since it is physical changes there might be over heating and even smokes/fires.
How does an instruction get executed
Instructions are stored on the RAM in a sequential order. For a hypothetical CPU Instruction consists of OP code(operational code) and memory or register address.
There are two registers inside a Control Unit Instruction register(IR) which loads the OP code of the instruction and Instruction address register which loads the address of the current executing instruction. There are other registers inside a CPU which stores the value stored in the address of the last 4 bits of a instruction.
Let’s take an example of a set of instruction which adds two number. The following are the instructions along with there description:
STEP 1 — LOAD_A 8:
The instruction is saved in RAM initially as let’s say <1100 1000>. The first 4 bit is the op code. This determines the instruction. This instruction is fetched into the IR of the control unit. The instruction is decode to be load_A which means it needs to load the data in the address 1000 which is the last 4 bit of the instruction to register A.
STEP 2 — LOAD_B 2
Similar to above this loads the the data in memory address 2 (0010) to CPU register B.
STEP 3 — ADD B A
Now the next instruction is to add these two numbers. Here the CU tells ALU to perform the add operation and save the result back to register A.
STEP 4 — STORE_A 23
This is a very simple set of instruction that helps add two numbers.
We have successfully added two numbers!
BUS
All the data between CPU, register, memory and IO devise are transferred via bus. To load the data to memory that it has just added, the CPU puts the memory address to address bus and the result of the sum to data bus and enables the right signal in control bus. In this way the data is loaded to memory with the help of the bus.
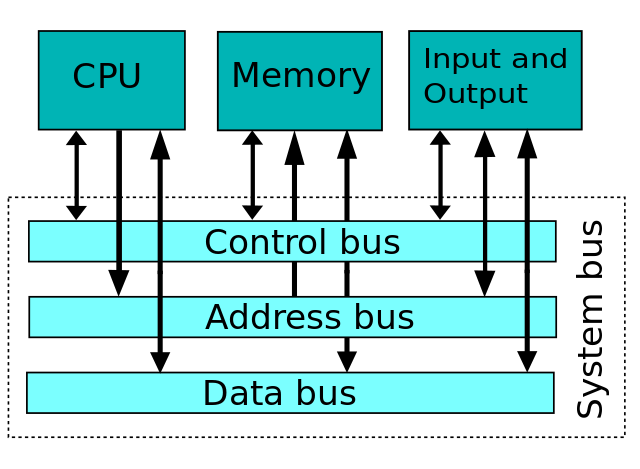 Photo src: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bus_(computing)#/media/File:Computer_system_bus.svg
Photo src: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bus_(computing)#/media/File:Computer_system_bus.svg
CACHE
CPU also has mechanism to prefetch the instruction to its cached. As we know there are millions of instruction a processor can complete within a second. This means that there will be more time spent in fetching the instruction from RAM than executing them. So the CPU cache prefetches some of the instruction and also data so that the execution gets fast.
If the data in cache and operating memory is different the data is marked as a dirty bit.
INSTRUCTION PIPELINING
Modern CPU uses Instruction pipelining for parallelization in instruction execution. Fetch, Decode, Execute. When one instruction is in decode phase the CPU can process another instruction for fetch phase.
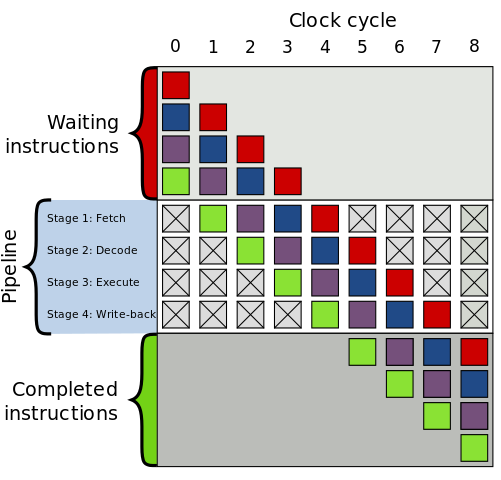 photo source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Instruction_pipelining#/media/File:Pipeline,_4_stage.svg
photo source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Instruction_pipelining#/media/File:Pipeline,_4_stage.svg
This has one problem when one instruction is dependent on another. So processors execute the instruction that are not dependent and in different order.
MULTI CORE COMPUTER
It is basically the different CPU but has some shared resource like the cache.
Performance
Performance of CPU is determined by it’s execution time.Performance = 1/execution time
let’s say it takes 20ms for a program to execute. The performance of CPU is 1/20 = 0.05msRelative performance = execution time 1/ execution time 2
The factor that comes under consideration for a CPU performance is the instruction execution time and the CPU clock speed. So to increase the performance of a program we either need to to increase the clock speed or decrease the number of instruction in a program. The processor speed is limited and modern computer’s with multi core can support millions of instructions a second. But if the program we have written has a lot of instructions this will decrease the overall performance.
Big O notation determines with the given input how the performance will be affected.
There are a lot of optimization done in CPU to make it faster and perform as much as it can. While writing any program we need to consider how reducing the number of instruction we provide to CPU will increase the performance of computer program.
[转帖]How does a CPU work?的更多相关文章
- [转帖]NUMA架构的CPU -- 你真的用好了么?
NUMA架构的CPU -- 你真的用好了么? 本文从NUMA的介绍引出常见的NUMA使用中的陷阱,继而讨论对于NUMA系统的优化方法和一些值得关注的方向. 文章欢迎转载,但转载时请保留本段文字,并置于 ...
- [转帖]linux下的CPU、内存、IO、网络的压力测试
linux下的CPU.内存.IO.网络的压力测试 https://www.cnblogs.com/zhuochong/p/10185881.html 一.对CPU进行简单测试: 1.通过bc命令计算特 ...
- [转帖]超能课堂 CPU制作过程
http://www.expreview.com/50814.html 一般来说,我们对IC芯片的了解仅限于它概念,但是对于已经应用到各式各样的数码产品中IC芯片是怎么来的?大家可能只知道制作IC芯片 ...
- [转帖]双剑合璧:CPU+GPU异构计算完全解析
引用自:http://tech.sina.com.cn/mobile/n/2011-06-20/18371792199.shtml 这篇文章写的深入浅出,把异构计算的思想和行业趋势描述的非常清楚,难得 ...
- 【转帖】如果进入CPU的世界,时间会是怎样的?
如果进入CPU的世界,时间会是怎样的? 2018-02-26 20:52:46 world6 阅读数 1295更多 分类专栏: 网络 缓存服务 架构 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 ...
- [转帖]Oracle 补丁体系(PSR/PSU/CPU) 及 opatch 工具 介绍
Oracle 补丁体系(PSR/PSU/CPU) 及 opatch 工具 介绍 原文:http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/article/details/58095 ...
- [转帖]CPU Cache 机制以及 Cache miss
CPU Cache 机制以及 Cache miss https://www.cnblogs.com/jokerjason/p/10711022.html CPU体系结构之cache小结 1.What ...
- [转帖]震惊,用了这么多年的 CPU 利用率,其实是错的
震惊,用了这么多年的 CPU 利用率,其实是错的 2018年12月22日 08:43:09 Linuxer_ 阅读数:50 https://blog.csdn.net/juS3Ve/article/d ...
- [转帖]关于CPU Cache -- 程序猿需要知道的那些事
关于CPU Cache -- 程序猿需要知道的那些事 很早之前读过作者的blog 记得作者在facebook 工作.. 还写过mysql相关的内容 大拿 本文将介绍一些作为程序猿或者IT从业者应该知道 ...
随机推荐
- 二进制上的数位dpPOJ 3252
Round number POJ - 3252 题目大意:一个"round number" 数的定义是,将它转化成2进制后,0的个数大于等于1的个数,要求的就是在[s,f]范围内& ...
- numpy中np.max() 和 np.maximum() 的区别
np.max(a, axis=None, out=None, keepdims=False) # 接收一个参数a # 取a 在 axis方向上的最大值 np.maximum(x, y) # 接收两个参 ...
- ValseWebninar 报告汇总
ValseWebninar为计算机视觉.图像处理.模式识别与机器学习等研究领域内的华人青年学者提供深入学术交流的舞台. 20191218:基于视觉和常识的深度推理 主持人: 主讲人: 2019 ...
- Fire Game (FZU 2150)(BFS)
题解:一开始想错了,以为只要烧完就是那个答案,但是这不是最优的结果,需要每两个点都bfs一遍,找到如果能够全部烧完,找到花费时间最小的,如果不能return -1.在bfs的时候,记录答案的方法参考了 ...
- 服务器上class文件是新的,但就是执行的老代码
故事是这样的. 上周末回老家,n个测试和开发找我,说我写的代码哪儿哪儿不行,吓得我赶紧打开电脑,连上阿里云数据库,修改了代码,测试们拉包重新测试后,还是不行,通过看打出的日志,还是执行的修改之前的代码 ...
- Linux网络编程二、tcp连接API
一.服务端 1.创建套接字: int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol); domain:指定协议族,通常选用AF_INET. type:指定sock ...
- JavaWeb_(Struts2框架)Servlet与Struts区别
JavaWeb_(SSH)使用Servlet实现用户的登陆 传送门 JavaWeb_(SSH)使用Struts框架实现用户的登陆 传送门 MySQL数据库中存在Gary用户,密码为123:第一次登陆时 ...
- DB 分库分表的基本思想和切分策略
DB 分库分表的基本思想和切分策略 一.基本思想 Sharding的基本思想就要把一个数据库切分成多个部分放到不同的数据库(server)上,从而缓解单一数据库的性能问题.不太严格的讲,对于海量数据的 ...
- oracle表结构表数据导入导出
--------------------------------------imp/exp------------------------------------------------------- ...
- XPATH了解
特殊标签 找SVG这种特殊标签可以使用[name()='svg'],如//[name()='svg']/[name()='line'][2] 文本 找标签内的文本时可以使用: //*[text()=' ...
