使用jdk8 stream简化集合操作
使用stream的前提是对lambda表达式和函数式接口有一定的了解,同时对方法引用和普通传参的区别有一定的认识。
stream的三大特性:1、不存储数据2、不改变源数据3、延时执行。
stream优点:1、简化代码2、使用并行流可以利用多核特性,提升效率。
stream上的所有操作分为两类:中间操作和结束操作,中间操作只是一种标记,只有结束操作才会触发实际计算。
常用api如下
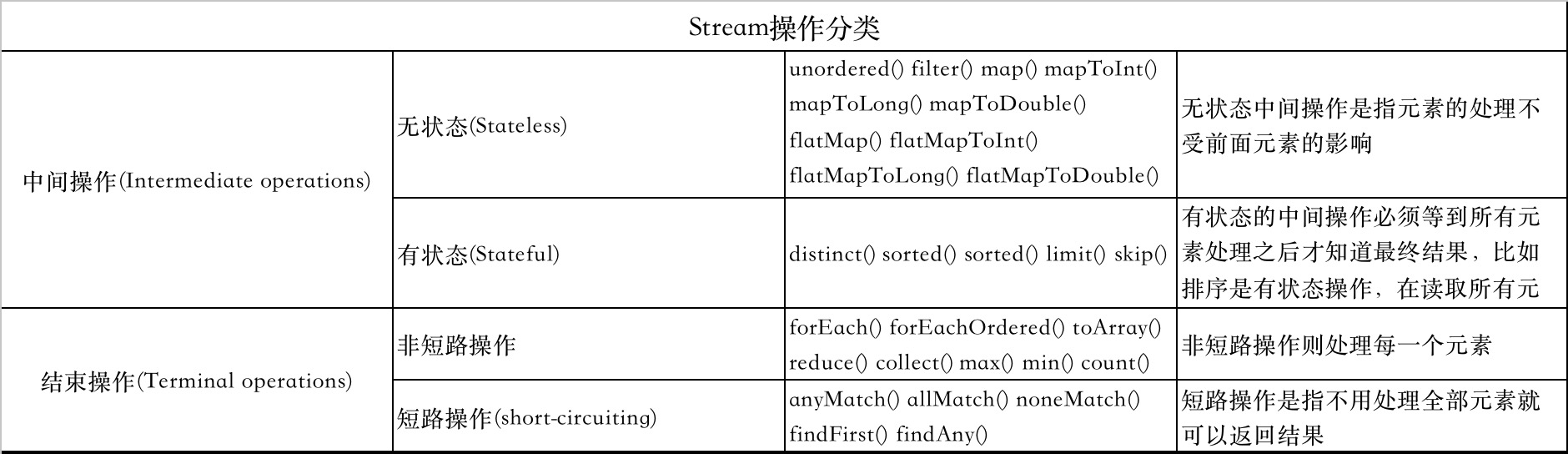
中间操作
filter:过滤流,过滤流中的元素,返回一个符合条件的Stream
map:转换流,将一种类型的流转换为另外一种流。(mapToInt、mapToLong、mapToDouble 返回int、long、double基本类型对应的Stream)
flatMap:简单的说,就是一个或多个流合并成一个新流。(flatMapToInt、flatMapToLong、flatMapToDouble 返回对应的IntStream、LongStream、DoubleStream流。)
distinct:返回去重的Stream。
sorted:返回一个排序的Stream。
peek:主要用来查看流中元素的数据状态。
limit:返回前n个元素数据组成的Stream。属于短路操作
skip:返回第n个元素后面数据组成的Stream。
结束操作
forEach: 循环操作Stream中数据。
toArray: 返回流中元素对应的数组对象。
reduce: 聚合操作,用来做统计。
collect: 聚合操作,封装目标数据。
min、max、count: 聚合操作,最小值,最大值,总数量。
anyMatch: 短路操作,有一个符合条件返回true。
allMatch: 所有数据都符合条件返回true。
noneMatch: 所有数据都不符合条件返回true。
findFirst: 短路操作,获取第一个元素。
findAny: 短路操作,获取任一元素。
forEachOrdered: 暗元素顺序执行循环操作。
流的创建demo
package com.example.test.stream; import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
import java.util.stream.Stream; public class StreamCreate { public static void main(String[] args) { unLimitStream2();
} public static void testArrayStream(){
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
IntStream intStream = Arrays.stream(arr);
Student[] students = new Student[]{Student.builder().name("zhangsan").age(12).score(12).build(),Student.builder().name("zhangsan").age(12).score(12).build()};
Stream<Student> studentStream = Arrays.stream(students);
Stream<Integer> integerStream =Stream.of(1,2,5,4,6);
Stream<int[]> intArrayStrean = Stream.of(arr,arr);
intArrayStrean.forEach(System.out::println);
} public static void testCollectionStream(){
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("sdf","sdfdsf","ertert","sdfdsf");
//创建普通流
Stream<String> stringStream = strings.stream();
//创建并行流
Stream<String> parallelStream = strings.parallelStream();
} public static void emptyStream(){
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.empty();
} public static void unLimitStream(){
Stream.generate((() -> "number" + new Random().nextInt())).limit(20).forEach(System.out::println); } public static void unLimitStream2(){
Stream.iterate(0,x ->x+1).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
Stream.iterate(0,x ->x).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
流的操作demo
package com.example.test.stream; import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream; public class OpepateStream { private static String[] arr = new String[]{"b","ab","abc","abcd","abcde"}; public static void main(String[] args) { testFlatMap();
} public static void testMap(){
String[] str = {"sdf","sdfdsFFF","dfsGdsf"};
Stream.of(str).map(t ->t.toUpperCase()).forEach(System.out::println);
}
public static void filter(){
String[] str = {"sdf","sdfdsFFF","dfsGdsf"};
Stream.of(str).filter(t -> ! t.equals("sdf")).forEach(System.out::println);
} public static void testFlatMap(){
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("beijing changcheng", "beijing gugong", "beijing tiantan", "gugong tiananmen"); list.stream().map(item -> Arrays.stream(item.split(" "))).forEach(System.out::println);
list.stream().flatMap(item -> Arrays.stream(item.split(" "))).forEach(System.out::println);
List<Integer> a=new ArrayList<>();
a.add(1);
a.add(2);
List<Integer> b=new ArrayList<>();
b.add(3);
b.add(4);
List<Integer> figures=Stream.of(a,b).flatMap(u->u.stream()).collect(Collectors.toList());
figures.forEach(f->System.out.println(f)); } public static void sort(){
String[] arr1 = {"abc","a","bc","abcd"};
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(String::length).reversed()).forEach(System.out::println);
} public static void sort2(){
String[] arr1 = {"abc","a","bc","abcd"};
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(String::length).reversed()).forEach(System.out::println);
} public static void sort3(){
String[] arr1 = {"abc","a","bc","abcd"};
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(OpepateStream::com1).thenComparing(String::length)).forEach(System.out::println);
} public static char com1(String x){
return x.charAt(0);
}
public static void testMaxAndMin(){
Optional<String> option = Stream.of(arr).max(Comparator.comparing(String::length));
option.ifPresent(System.out::println);
Stream.of(arr).min(Comparator.comparing(String::length)).ifPresent(System.out::println);
} public static void findFirst(){
String str = Stream.of(arr).parallel().filter(t -> t.length()>3).findFirst().orElse("noting");
System.out.println(str);
} public static void testFindAny(){
Optional<String> optional = Stream.of(arr).parallel().filter(x->x.length()>3).findAny();
optional.ifPresent(System.out::println);
} public static void reduceTest(){
Optional<Integer> optional = Stream.of(1,2,3).reduce((x,y) -> x+y);
optional.ifPresent(System.out::println);
} public static Optional<Double> inverse(Double x) {
return x == 0 ? Optional.empty() : Optional.of(1 / x);
} public static Optional<Double> squareRoot(Double x) {
return x < 0 ? Optional.empty() : Optional.of(Math.sqrt(x));
} public static void testStream2() {
double x = 4d;
Optional<Double> result1 = inverse(x).flatMap(OpepateStream::squareRoot);
result1.ifPresent(System.out::println);
Optional<Double> result2 = Optional.of(4.0).flatMap(OpepateStream::inverse).flatMap(OpepateStream::squareRoot);
result2.ifPresent(System.out::println);
} public static void testToMap(){
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build());
}
}
};
studentList.add(Student.builder().name("student08").age(12).score(1000).build());
studentList.add(Student.builder().name("student08").age(12).score(234).build());
studentList.add(Student.builder().name("student08").age(12).score(123).build());
studentList.add(Student.builder().name("student08").age(12).score(3000).build());
Map<String,Integer> map = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Student::getName,Student::getScore,(a,b) -> b));
map.forEach((x,y) -> System.out.println(x + "->" + y)); } public static void toAssign(){
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build());
}
}
};
HashSet<Student> s = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
s.forEach(System.out::println);
} public static void aggregation(){
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build());
}
}
};
IntSummaryStatistics summaryStatistics = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Student::getScore));
System.out.println("getAverage->"+summaryStatistics.getAverage());
System.out.println("getMax->"+summaryStatistics.getMax());
System.out.println("getMin->"+summaryStatistics.getMin());
System.out.println("getCount->"+summaryStatistics.getCount());
System.out.println("getSum->"+summaryStatistics.getSum());
} public static void group(){
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build());
}
}
};
Map<Boolean,Integer> map = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy((x -> x.getScore()>50) ,Collectors.summingInt(Student::getScore)));
map.forEach((x,y) -> {
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
});
Map<String,Set<Integer>> map4 = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getName,Collectors.mapping(Student::getScore,Collectors.toSet())));
map4.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y));
} public static void group1(){
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build());
}
}
};
Map<Boolean,Integer> map = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy((x -> x.getScore()>50) ,Collectors.summingInt(Student::getScore)));
map.forEach((x,y) -> {
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
});
Map<String,List<Student>> map4 = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getName));
map4.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y));
} }
并行流
package com.example.test.stream;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class ParalellTest {
public void peek1(int x) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":->peek1->" + x);
}
public void peek2(int x) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":->peek2->" + x);
}
public void peek3(int x) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":->final result->" + x);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ParalellTest paralellTest = new ParalellTest();
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.iterate(1,x -> x+1).limit(10);
stream.peek(paralellTest::peek1).filter(x -> x>5)
.peek(paralellTest::peek2).filter(x -> x<9)
.peek(paralellTest::peek3).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.iterate(1,x -> x+1).limit(10).parallel();
stream2.peek(paralellTest::peek1).filter(x -> x>5)
.peek(paralellTest::peek2).filter(x -> x<9)
.peek(paralellTest::peek3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
综合应用
package com.example.test.stream; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream; public class StreamTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
test2();
} public static void test1(){
Random random = new Random();
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build());
}
}
};
List<String> names = studentList.stream().filter(t -> t.getScore()>50)
.sorted(Comparator.comparingDouble(Student::getScore).reversed())
.map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(names);
} public static void test2(){
List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
add(Student.builder().name("student" + i).age(12).score(i).build());
}
}
};
Stream<Student> stream = studentList.stream().filter(StreamTest::filter)
.sorted(Comparator.comparingDouble(Student::getScore).reversed());
System.out.println("--------------");
System.out.println(stream.map(Student::getName).collect(Collectors.toList())); } private static boolean filter(Student student){
System.out.println("123123123");
return student.getScore() >50;
}
}
使用jdk8 stream简化集合操作的更多相关文章
- C# 使用 Index 和 Range 简化集合操作
C# 使用 Index 和 Range 简化集合操作 Intro 有的语言数组的索引值是支持负数的,表示从后向前索引,比如:arr[-1] 从 C# 8 开始,C# 支持了数组的反向 Index,和 ...
- JAVA8 Stream集合操作:中间方法和完结方法
StreamLambda为java8带了闭包,这一特性在集合操作中尤为重要:java8中支持对集合对象的stream进行函数式操作,此外,stream api也被集成进了collection api, ...
- Java8 新特性之集合操作Stream
Java8 新特性之集合操作Stream Stream简介 Java 8引入了全新的Stream API.这里的Stream和I/O流不同,它更像具有Iterable的集合类,但行为和集合类又有所不同 ...
- Java 8 Lambda 表达式及 Stream 在集合中的用法
简介 虽然 Java 8 已经发布有一段时间了,但是关于 Java 8 中的 Lambda 表达式最近才开始系统的学习,刚开始就被 Stream 的各种骚操作深深的吸引住了,简直漂亮的不像 Java. ...
- 试水jdk8 stream
jdk8出来日子不短了,jdk11都出来了,不过用的最多的不过是1.5罢了. 今年终于鼓起勇气认真对待它,在18年记录下学习stream,画上一个圆. 先看个图 Java8中有两大最为重要的改变.第一 ...
- JDK8 Stream 数据流效率分析
JDK8 Stream 数据流效率分析 Stream 是Java SE 8类库中新增的关键抽象,它被定义于 java.util.stream (这个包里有若干流类型: Stream<T> ...
- 恕我直言你可能真的不会java第11篇-Stream API终端操作
一.Java Stream管道数据处理操作 在本号之前写过的文章中,曾经给大家介绍过 Java Stream管道流是用于简化集合类元素处理的java API.在使用的过程中分为三个阶段.在开始本文之前 ...
- Java8中的Stream流式操作 - 入门篇
作者:汤圆 个人博客:javalover.cc 前言 之前总是朋友朋友的叫,感觉有套近乎的嫌疑,所以后面还是给大家改个称呼吧 因为大家是来看东西的,所以暂且叫做官人吧(灵感来自于民间流传的四大名著之一 ...
- 函数式Android编程(II):Kotlin语言的集合操作
原文标题:Functional Android (II): Collection operations in Kotlin 原文链接:http://antonioleiva.com/collectio ...
随机推荐
- Fences_3.08破解安装
Fences_3.08破解安装 一.总结 一句话总结: 找破解软件去吾爱破解论坛,非常节约时间 二.Fences_3.08破解安装(亲测有效) 来源:吾爱破解论坛 百度网盘下载地址:链接:https: ...
- JDK&JRE
JDK是提供给Java开发人员使用的,其中包含了java的开发工具,也包括了JRE.所以安装了JDK,就不用在单独安装JRE了. 其中的开发工具:编译工具(javac.exe) 打包工具(jar.ex ...
- The magic method __set() must have public visibility and cannot be static in
魔术方法 __set 用private 封装后出现问题 private function __set(){} 就是这个格式 10 错误信息就是这个:The magic method __set() m ...
- osg #ifdef _WIN32 osg
#ifdef _WIN32 #include <Windows.h> #endif // _WIN32 #include <osgViewer/Viewer> #include ...
- jmeter 查看结果树,获取响应体写法校验是否提取写法是否正确的方法
JSON Path Expression里面写入提出值的写法,点击Test测试提取
- div和span显示在同一行
div和span标签的区别 div 是块级元素标签,独占一行,后面跟的内容换行显示 span 是内联元素标签,后面可以跟其他显示内容,不独占一行 display属性可以改变内联元素和块级元素的状态 ...
- 动态PHP电商网站伪静态的 Nginx反向代理Cache缓存终极设置
转自: http://www.ttlsa.com/nginx/dynamic-php-nginx-cache/
- javascript——URI的编解码方法
有效的URI(统一资源标示符)是不能包含某些字符的,如空格,所以需要进行编码,编码方法有:encodeURI()和encodeURIComponent(), 对编的码进行解码方法有:decodeURI ...
- Ext.net中Combobox如何绑定数据库中的值
]; ]; " /> </Items> </ext:ComboBox>
- linux EXT4格式分区扩容
1.查看现有的分区大小 2.关机增加磁盘大小为100G 3.查看磁盘扩容后状态 lsblk或dh -TH 4.进行分区扩展磁盘,保留根目录的起止位置. 5.删除根分区,不要保存 6.创建分区, ...
