IO多路复用之select总结(转载)
1、基本概念
IO多路复用是指内核一旦发现进程指定的一个或者多个IO条件准备读取,它就通知该进程。IO多路复用适用如下场合:
(1)当客户处理多个描述字时(一般是交互式输入和网络套接口),必须使用I/O复用。
(2)当一个客户同时处理多个套接口时,而这种情况是可能的,但很少出现。
(3)如果一个TCP服务器既要处理监听套接口,又要处理已连接套接口,一般也要用到I/O复用。
(4)如果一个服务器即要处理TCP,又要处理UDP,一般要使用I/O复用。
(5)如果一个服务器要处理多个服务或多个协议,一般要使用I/O复用。
与多进程和多线程技术相比,I/O多路复用技术的最大优势是系统开销小,系统不必创建进程/线程,也不必维护这些进程/线程,从而大大减小了系统的开销。
2、select函数
该函数准许进程指示内核等待多个事件中的任何一个发送,并只在有一个或多个事件发生或经历一段指定的时间后才唤醒。函数原型如下:
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/time.h> int select(int maxfdp1,fd_set *readset,fd_set *writeset,fd_set *exceptset,const struct timeval *timeout)
返回值:就绪描述符的数目,超时返回0,出错返回-1
函数参数介绍如下:
(1)第一个参数maxfdp1指定待测试的描述字个数,它的值是待测试的最大描述字加1(因此把该参数命名为maxfdp1),描述字0、1、2...maxfdp1-1均将被测试。
因为文件描述符是从0开始的。
(2)中间的三个参数readset、writeset和exceptset指定我们要让内核测试读、写和异常条件的描述字。如果对某一个的条件不感兴趣,就可以把它设为空指针。struct fd_set可以理解为一个集合,这个集合中存放的是文件描述符,可通过以下四个宏进行设置:
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *fdset); //清空集合
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //将一个给定的文件描述符加入集合之中
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //将一个给定的文件描述符从集合中删除
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); // 检查集合中指定的文件描述符是否可以读写
(3)timeout告知内核等待所指定描述字中的任何一个就绪可花多少时间。其timeval结构用于指定这段时间的秒数和微秒数。
struct timeval{
long tv_sec; //seconds
long tv_usec; //microseconds
};
这个参数有三种可能:
(1)永远等待下去:仅在有一个描述字准备好I/O时才返回。为此,把该参数设置为空指针NULL。
(2)等待一段固定时间:在有一个描述字准备好I/O时返回,但是不超过由该参数所指向的timeval结构中指定的秒数和微秒数。
(3)根本不等待:检查描述字后立即返回,这称为轮询。为此,该参数必须指向一个timeval结构,而且其中的定时器值必须为0。
原理图:

3、测试程序
写一个TCP回射程序,程序的功能是:客户端向服务器发送信息,服务器接收并原样发送给客户端,客户端显示出接收到的信息。
服务端程序如下:

1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <errno.h>
5 #include <netinet/in.h>
6 #include <sys/socket.h>
7 #include <sys/select.h>
8 #include <sys/types.h>
9 #include <netinet/in.h>
10 #include <arpa/inet.h>
11 #include <unistd.h>
12 #include <assert.h>
13
14 #define IPADDR "127.0.0.1"
15 #define PORT 8787
16 #define MAXLINE 1024
17 #define LISTENQ 5
18 #define SIZE 10
19
20 typedef struct server_context_st
21 {
22 int cli_cnt; /*客户端个数*/
23 int clifds[SIZE]; /*客户端的个数*/
24 fd_set allfds; /*句柄集合*/
25 int maxfd; /*句柄最大值*/
26 } server_context_st;
27 static server_context_st *s_srv_ctx = NULL;
28 /*===========================================================================
29 * ==========================================================================*/
30 static int create_server_proc(const char* ip,int port)
31 {
32 int fd;
33 struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
34 fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM,0);
35 if (fd == -1) {
36 fprintf(stderr, "create socket fail,erron:%d,reason:%s\n",
37 errno, strerror(errno));
38 return -1;
39 }
40
41 /*一个端口释放后会等待两分钟之后才能再被使用,SO_REUSEADDR是让端口释放后立即就可以被再次使用。*/
42 int reuse = 1;
43 if (setsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &reuse, sizeof(reuse)) == -1) {
44 return -1;
45 }
46
47 bzero(&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr));
48 servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
49 inet_pton(AF_INET,ip,&servaddr.sin_addr);
50 servaddr.sin_port = htons(port);
51
52 if (bind(fd,(struct sockaddr*)&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr)) == -1) {
53 perror("bind error: ");
54 return -1;
55 }
56
57 listen(fd,LISTENQ);
58
59 return fd;
60 }
61
62 static int accept_client_proc(int srvfd)
63 {
64 struct sockaddr_in cliaddr;
65 socklen_t cliaddrlen;
66 cliaddrlen = sizeof(cliaddr);
67 int clifd = -1;
68
69 printf("accpet clint proc is called.\n");
70
71 ACCEPT:
72 clifd = accept(srvfd,(struct sockaddr*)&cliaddr,&cliaddrlen);
73
74 if (clifd == -1) {
75 if (errno == EINTR) {
76 goto ACCEPT;
77 } else {
78 fprintf(stderr, "accept fail,error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
79 return -1;
80 }
81 }
82
83 fprintf(stdout, "accept a new client: %s:%d\n",
84 inet_ntoa(cliaddr.sin_addr),cliaddr.sin_port);
85
86 //将新的连接描述符添加到数组中
87 int i = 0;
88 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
89 if (s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] < 0) {
90 s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] = clifd;
91 s_srv_ctx->cli_cnt++;
92 break;
93 }
94 }
95
96 if (i == SIZE) {
97 fprintf(stderr,"too many clients.\n");
98 return -1;
99 }
100
101 }
102
103 static int handle_client_msg(int fd, char *buf)
104 {
105 assert(buf);
106 printf("recv buf is :%s\n", buf);
107 write(fd, buf, strlen(buf) +1);
108 return 0;
109 }
110
111 static void recv_client_msg(fd_set *readfds)
112 {
113 int i = 0, n = 0;
114 int clifd;
115 char buf[MAXLINE] = {0};
116 for (i = 0;i <= s_srv_ctx->cli_cnt;i++) {
117 clifd = s_srv_ctx->clifds[i];
118 if (clifd < 0) {
119 continue;
120 }
121 /*判断客户端套接字是否有数据*/
122 if (FD_ISSET(clifd, readfds)) {
123 //接收客户端发送的信息
124 n = read(clifd, buf, MAXLINE);
125 if (n <= 0) {
126 /*n==0表示读取完成,客户都关闭套接字*/
127 FD_CLR(clifd, &s_srv_ctx->allfds);
128 close(clifd);
129 s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] = -1;
130 continue;
131 }
132 handle_client_msg(clifd, buf);
133 }
134 }
135 }
136 static void handle_client_proc(int srvfd)
137 {
138 int clifd = -1;
139 int retval = 0;
140 fd_set *readfds = &s_srv_ctx->allfds;
141 struct timeval tv;
142 int i = 0;
143
144 while (1) {
145 /*每次调用select前都要重新设置文件描述符和时间,因为事件发生后,文件描述符和时间都被内核修改啦*/
146 FD_ZERO(readfds);
147 /*添加监听套接字*/
148 FD_SET(srvfd, readfds);
149 s_srv_ctx->maxfd = srvfd;
150
151 tv.tv_sec = 30;
152 tv.tv_usec = 0;
153 /*添加客户端套接字*/
154 for (i = 0; i < s_srv_ctx->cli_cnt; i++) {
155 clifd = s_srv_ctx->clifds[i];
156 /*去除无效的客户端句柄*/
157 if (clifd != -1) {
158 FD_SET(clifd, readfds);
159 }
160 s_srv_ctx->maxfd = (clifd > s_srv_ctx->maxfd ? clifd : s_srv_ctx->maxfd);
161 }
162
163 /*开始轮询接收处理服务端和客户端套接字*/
164 retval = select(s_srv_ctx->maxfd + 1, readfds, NULL, NULL, &tv);
165 if (retval == -1) {
166 fprintf(stderr, "select error:%s.\n", strerror(errno));
167 return;
168 }
169 if (retval == 0) {
170 fprintf(stdout, "select is timeout.\n");
171 continue;
172 }
173 if (FD_ISSET(srvfd, readfds)) {
174 /*监听客户端请求*/
175 accept_client_proc(srvfd);
176 } else {
177 /*接受处理客户端消息*/
178 recv_client_msg(readfds);
179 }
180 }
181 }
182
183 static void server_uninit()
184 {
185 if (s_srv_ctx) {
186 free(s_srv_ctx);
187 s_srv_ctx = NULL;
188 }
189 }
190
191 static int server_init()
192 {
193 s_srv_ctx = (server_context_st *)malloc(sizeof(server_context_st));
194 if (s_srv_ctx == NULL) {
195 return -1;
196 }
197
198 memset(s_srv_ctx, 0, sizeof(server_context_st));
199
200 int i = 0;
201 for (;i < SIZE; i++) {
202 s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] = -1;
203 }
204
205 return 0;
206 }
207
208 int main(int argc,char *argv[])
209 {
210 int srvfd;
211 /*初始化服务端context*/
212 if (server_init() < 0) {
213 return -1;
214 }
215 /*创建服务,开始监听客户端请求*/
216 srvfd = create_server_proc(IPADDR, PORT);
217 if (srvfd < 0) {
218 fprintf(stderr, "socket create or bind fail.\n");
219 goto err;
220 }
221 /*开始接收并处理客户端请求*/
222 handle_client_proc(srvfd);
223 server_uninit();
224 return 0;
225 err:
226 server_uninit();
227 return -1;
228 }

客户端程序如下:

1 #include <netinet/in.h>
2 #include <sys/socket.h>
3 #include <stdio.h>
4 #include <string.h>
5 #include <stdlib.h>
6 #include <sys/select.h>
7 #include <time.h>
8 #include <unistd.h>
9 #include <sys/types.h>
10 #include <errno.h>
11
12 #define MAXLINE 1024
13 #define IPADDRESS "127.0.0.1"
14 #define SERV_PORT 8787
15
16 #define max(a,b) (a > b) ? a : b
17
18 static void handle_recv_msg(int sockfd, char *buf)
19 {
20 printf("client recv msg is:%s\n", buf);
21 sleep(5);
22 write(sockfd, buf, strlen(buf) +1);
23 }
24
25 static void handle_connection(int sockfd)
26 {
27 char sendline[MAXLINE],recvline[MAXLINE];
28 int maxfdp,stdineof;
29 fd_set readfds;
30 int n;
31 struct timeval tv;
32 int retval = 0;
33
34 while (1) {
35
36 FD_ZERO(&readfds);
37 FD_SET(sockfd,&readfds);
38 maxfdp = sockfd;
39
40 tv.tv_sec = 5;
41 tv.tv_usec = 0;
42
43 retval = select(maxfdp+1,&readfds,NULL,NULL,&tv);
44
45 if (retval == -1) {
46 return ;
47 }
48
49 if (retval == 0) {
50 printf("client timeout.\n");
51 continue;
52 }
53
54 if (FD_ISSET(sockfd, &readfds)) {
55 n = read(sockfd,recvline,MAXLINE);
56 if (n <= 0) {
57 fprintf(stderr,"client: server is closed.\n");
58 close(sockfd);
59 FD_CLR(sockfd,&readfds);
60 return;
61 }
62
63 handle_recv_msg(sockfd, recvline);
64 }
65 }
66 }
67
68 int main(int argc,char *argv[])
69 {
70 int sockfd;
71 struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
72
73 sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
74
75 bzero(&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr));
76 servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
77 servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
78 inet_pton(AF_INET,IPADDRESS,&servaddr.sin_addr);
79
80 int retval = 0;
81 retval = connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr));
82 if (retval < 0) {
83 fprintf(stderr, "connect fail,error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
84 return -1;
85 }
86
87 printf("client send to server .\n");
88 write(sockfd, "hello server", 32);
89
90 handle_connection(sockfd);
91
92 return 0;
93 }

4、程序结果
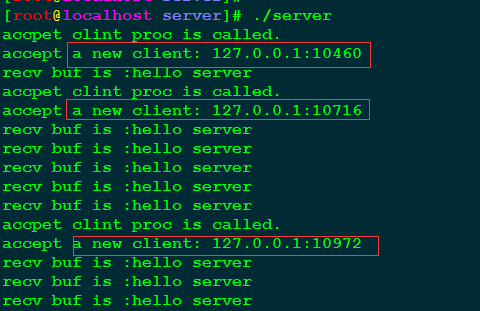
启动服务程序,执行三个个客户程序进行测试,结果如下图所示:
IO多路复用之select总结(转载)的更多相关文章
- IO多路复用之select、poll、epoll
本文转载自IO多路复用之select.poll.epoll 导语 IO多路复用:通过一种机制,一个进程可以监视多个描述符,一旦某个描述符就绪(一般是读就绪或者写就绪),能够通知程序进行相应的读写操作. ...
- IO多路复用之select
IO多路复用之select总结 1.基本概念 IO多路复用是指内核一旦发现进程指定的一个或者多个IO条件准备读取,它就通知该进程.IO多路复用适用如下场合: (1)当客户处理多个描述字时(一般是交 ...
- 网络通信 --> IO多路复用之select、poll、epoll详解
IO多路复用之select.poll.epoll详解 目前支持I/O多路复用的系统调用有 select,pselect,poll,epoll,I/O多路复用就是通过一种机制,一个进程可以监视 ...
- python网络编程——IO多路复用之select
1 IO多路复用的概念 原生socket客户端在与服务端建立连接时,即服务端调用accept方法时是阻塞的,同时服务端和客户端在收发数据(调用recv.send.sendall)时也是阻塞的.原生so ...
- 【python】-- IO多路复用(select、poll、epoll)介绍及实现
IO多路复用(select.poll.epoll)介绍及select.epoll的实现 IO多路复用中包括 select.pool.epoll,这些都属于同步,还不属于异步 一.IO多路复用介绍 1. ...
- Python——IO多路复用之select模块epoll方法
Python——IO多路复用之select模块epoll方法 使用epoll方法实现IO多路复用,使用方法基本与poll方法一致,epoll效率要高于select和poll. .├── epoll_c ...
- Python——IO多路复用之select模块poll方法
Python——IO多路复用之select模块poll方法 使用poll方法实现IO多路复用 .├── poll_client.py├── poll_server.py└── settings.py ...
- Python——IO多路复用之select模块select方法
Python——IO多路复用之select模块select方法 使用select模块的select方法实现Python——IO多路复用 实现同时将终端输入的文本以及客户端传输的文本写入文本文件中: w ...
- IO多路复用(select、poll、epoll)介绍及select、epoll的实现
IO多路复用(select.poll.epoll)介绍及select.epoll的实现 IO多路复用中包括 select.pool.epoll,这些都属于同步,还不属于异步 一.IO多路复用介绍 1. ...
随机推荐
- 关于Jmeter线程组的设置,看这一篇就够了
一.事件背景 个人感觉自己做性能测试,可以说是轻车熟路了,而且工作多年一直都是这一套测试思路及体系,从未质疑过自己,也许是狮子座的迷之自信吧! 也就在上周让我对自己的测试方法及体系产生了质疑! 为什么 ...
- python函数初体验
函数 函数参数w 形式参数>>>>(被指定具体的值)默认参数, 实际参数是调用时候的实际指定参数 我们把函数⾥⾯的参数叫形式函数,函数实际调⽤的时候,赋予的参数叫实际函数 定义 ...
- 年底巩固下 CS 知识「GitHub 热点速览 v.21.49」
作者:HelloGitHub-小鱼干 期末到了!是时候来一波 CS 复习资料了,从本科基础知识开始到实用编程技术.本周 GitHub 热点趋势榜给你提供了最全的复习资料:清华的 CS 四年学习资料.W ...
- C++中的字符串输入getline
http://www.cnblogs.com/wanghao111/archive/2009/09/05/1560822.html 1 #include <iostream> 2 #inc ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day4
一.获取登录后页面信息的两种方法 1.第一种方法: 人为把有效cookies加到请求头中,代码如下 import urllib.request # 确定url url = "https:// ...
- 【leetcode】451. Sort Characters By Frequency
Given a string s, sort it in decreasing order based on the frequency of the characters. The frequenc ...
- linux之wc命令详解
Linux系统中wc(Word Count)命令的功能为统计指定文件中的字节数.字数.行数,并将统计结果显示输出. 1.命令格式 wc [options] 文件... 2.命令功能 统计指定文件中的字 ...
- [学习总结]1、View的scrollTo 和 scrollBy 方法使用说明和区别
参考资料:http://blog.csdn.net/vipzjyno1/article/details/24577023 非常感谢这个兄弟! 先查看这2个方法的源码: scrollTo: 1 /** ...
- 接口测试 python+PyCharm 环境搭建
1.配置Python环境变量 a:我的电脑->属性->高级系统设置->环境变量->系统变量中的PATH变量. 变量名:PATH 修改变量值为:;C:\Python27 ...
- vue-cli2嵌入html
1.使用iframe <!-- 相对路径/绝对路径 --> <iframe src="../../../static/zsw.html"></ifra ...
