JUC 并发编程--02,生产者和消费者 synchronized的写法 , juc的写法. Condition的用法
synchronized的写法
class PCdemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//多个线程操作同一资源
Data data = new Data();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-1").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-2").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-3").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-4").start();
}
}
//这是一个资源类,
class Data {
private int num = 0;
//加1
public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {
while(num != 0){
this.wait();
}
num++;
System.out.println("当前线程名字:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "加1 操作, num为" + num);
this.notifyAll();
}
//减1
public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
while(num == 0){
this.wait();
}
num--;
System.out.println("当前线程名字:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "减1 操作, num为" + num);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
结果:
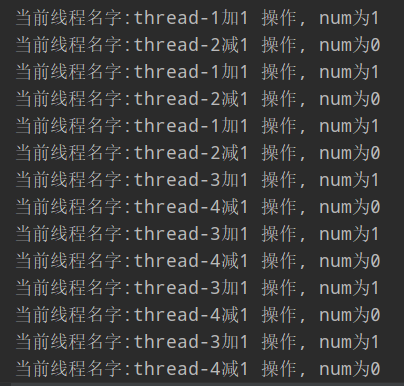
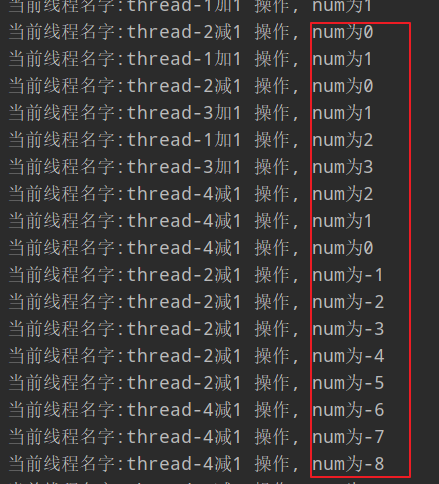
这里需要注意一个概念: 虚假唤醒,就是说线程被唤醒了, 但不会被通知 如果把资源类Data中的 increment, decrement方法中的while 换为: if, 那么运行的时候, 二个线程的结果是正常的, 如果二个以上就会出错,结果为
JUC 版本的 生产者和消费者问题
public class JucPCdemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//JUC 版本的 就是来替代 synchronized版本的
DataJ data = new DataJ();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-1").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-2").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-3").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-4").start();
}
}
class DataJ{
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
private int num = 0;
//加1
public void increment() throws InterruptedException {
//先加锁
lock.lock();
try {
while(num != 0){
condition.await();//这个替代 this.wait()
}
num++;
System.out.println("当前线程名字:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "加1 操作, num为" + num);
condition.signalAll();// 这个来替代 this.notifyAll();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
//减1
public void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
//先加锁
lock.lock();
try {
while(num == 0){
condition.await();//这个替代 this.wait();
}
num--;
System.out.println("当前线程名字:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "减1 操作, num为" + num);
condition.signalAll();// 这个来替代 this.notifyAll();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
结果同样是正确的
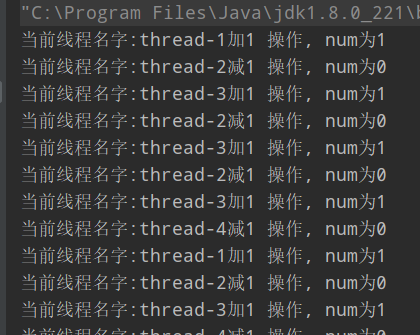
然而 Condition 更强大的是精确通知和精确唤醒, 之前的运行结果线程之间是随机运行的,如果让线程 1,2,3,4 依次循环有序执行, 就要用到Condition
public class JucPCdemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//JUC 版本的 就是来替代 synchronized版本的
//4个线程依次循环有序执行, num 初始值为0, 线程1--A, 线程2--B, 线程3--C, 线程4--D
DataC data = new DataC();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.printA();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-1").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.printB();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-2").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.printC();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-3").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
data.printD();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"thread-4").start();
}
}
class DataC{
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();//对应A
private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();//对应B
private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();//对应C
private Condition condition4 = lock.newCondition();//对应D
private String str = "A";
public void printA() throws InterruptedException {
//先加锁
lock.lock();
try {
while(! "A".equals(str)){
condition1.await();//只要不是 A 就等待
}
System.out.println("当前线程名字:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "对应str为" + str);
str = "B";
condition2.signal();//这里指定唤醒 线程2 对应B
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void printB() throws InterruptedException {
//先加锁
lock.lock();
try {
while(!"B".equals(str)){
condition2.await();//只要不是B 就等待
}
System.out.println("当前线程名字:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "对应str为" + str);
str = "C";
condition3.signal();//这里指定唤醒 线程3 对应C
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void printC() throws InterruptedException {
//先加锁
lock.lock();
try {
while(! "C".equals(str)){
condition3.await();//只要不是C 就等待
}
System.out.println("当前线程名字:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "对应str为" + str);
str = "D";
condition4.signal();//这里指定唤醒 线程4 对应D
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void printD() throws InterruptedException {
//先加锁
lock.lock();
try {
while(! "D".equals(str)){
condition4.await();//只要不是D 就等待
}
System.out.println("当前线程名字:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "对应str为" + str);
str = "A";
condition1.signal();//这里指定唤醒 线程1 对应A
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
运行结果为;

JUC 并发编程--02,生产者和消费者 synchronized的写法 , juc的写法. Condition的用法的更多相关文章
- Java并发编程(4)--生产者与消费者模式介绍
一.前言 这种模式在生活是最常见的,那么它的场景是什么样的呢? 下面是我假象的,假设有一个仓库,仓库有一个生产者和一个消费者,消费者过来消费的时候会检测仓库中是否有库存,如果没有了则等待生产,如果有就 ...
- JUC 并发编程--01,线程,进程,经典卖票案例, juc的写法
进程: 就是一个程序, 里面包含多个线程, 比如一个QQ程序 线程: 进程中最小的调度单元, 比如 QQ中的自动保存功能 并发: 多个线程操作同一资源, 抢夺一个cpu的执行片段, 快速交替 并行: ...
- 并发编程 02—— ConcurrentHashMap
Java并发编程实践 目录 并发编程 01—— ThreadLocal 并发编程 02—— ConcurrentHashMap 并发编程 03—— 阻塞队列和生产者-消费者模式 并发编程 04—— 闭 ...
- JUC并发编程学习笔记
JUC并发编程学习笔记 狂神JUC并发编程 总的来说还可以,学到一些新知识,但很多是学过的了,深入的部分不多. 线程与进程 进程:一个程序,程序的集合,比如一个音乐播发器,QQ程序等.一个进程往往包含 ...
- JUC并发编程与高性能内存队列disruptor实战-上
JUC并发实战 Synchonized与Lock 区别 Synchronized是Java的关键字,由JVM层面实现的,Lock是一个接口,有实现类,由JDK实现. Synchronized无法获取锁 ...
- 并发编程的锁机制:synchronized和lock
1. 锁的种类 锁的种类有很多,包括:自旋锁.自旋锁的其他种类.阻塞锁.可重入锁.读写锁.互斥锁.悲观锁.乐观锁.公平锁.可重入锁等等,其余就不列出了.我们重点看如下几种:可重入锁.读写锁.可中断锁. ...
- JUC并发编程基石AQS之主流程源码解析
前言 由于AQS的源码太过凝练,而且有很多分支比如取消排队.等待条件等,如果把所有的分支在一篇文章的写完可能会看懵,所以这篇文章主要是从正常流程先走一遍,重点不在取消排队等分支,之后会专门写一篇取消排 ...
- python并发编程02 /多进程、进程的创建、进程PID、join方法、进程对象属性、守护进程
python并发编程02 /多进程.进程的创建.进程PID.join方法.进程对象属性.守护进程 目录 python并发编程02 /多进程.进程的创建.进程PID.join方法.进程对象属性.守护进程 ...
- python 并发编程 多进程 生产者消费者模型介绍
一 生产者消费者模型介绍 为什么要使用生产者消费者模型 生产者指的是生产数据的任务,消费者指的是处理数据的任务, 生产数据目的,是为了给消费者处理. 在并发编程中,如果生产者处理速度很快,而消费者处理 ...
随机推荐
- UVA11021麻球繁衍
题意: 有K只麻球,每只生存一天就会死亡,每只麻球在死之前有可能生下一些麻球,生i个麻球的概率是pi,问m天后所有的麻球都死亡的概率是多少? 思路: 涉及到全概率公式,因为麻球的 ...
- UVA10763交换学生
题意: 给你N组关系,每组关系是a,b,最后问你所有的a,b出现的次数和所有的b,a出现的此时是否全部都一样. 思路: 水题,直接开了个二维的map标记,map<int ...
- Windows PE 重定位表编程(枚举重定位地址)
原理之前单独总结过,在这里: http://blog.csdn.net/u013761036/article/details/54051347 下面是枚举重定位信息的代码: // ReLocation ...
- Git解决中文乱码问题
git status 乱码 解决方法: git config --global core.quotepath false git commit 乱码 解决方法: git config --global ...
- 基于蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)的多维可加性指标的异常根因定位
摘要:本文是我在从事AIOps研发工作中做的基于MCTS的多维可加性指标的异常根因定位方案,方案基于清华大学AIOPs实验室提出的Hotspot算法,在此基础上做了适当的修改. 1 概述 ...
- Java 中 RMI 的使用
RMI 介绍 RMI (Remote Method Invocation) 模型是一种分布式对象应用,使用 RMI 技术可以使一个 JVM 中的对象,调用另一个 JVM 中的对象方法并获取调用结果.这 ...
- linux下符号链接和硬链接的区别
存在2众不同类型的链接,软链接和硬链接,修改其中一个,硬链接指向的是节点(inode),软链接指向的是路径(path) 软连接文件 软连接文件也叫符号连接,这个文件包含了另一个文件的路径名,类似于wi ...
- [2021BUAA软工助教]个人第一次阅读作业小结
BUAA个人阅读作业小结 一.作业要求 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/buaa/BUAA_SE_2021_LR/homework/11776 二.评分规则 言之有物,按 ...
- [刷题] 70 Climbing Stairs
要求 楼梯共有n个台阶,每次上一个台阶或两个台阶,一共有多少种上楼梯的方法? 示例 输入:n=3 [1,1,1],[1,2,],[2,1] 输出:n=3 实现 自顶向下(递归) 递归 1 class ...
- Sqoop 安装部署
1. 上传并解压 Sqoop 安装文件 将 sqoop-1.4.7.bin__hadoop-2.6.0.tar.gz 安装包上传到 node-01 的 /root/ 目录下并将其解压 [root@no ...
