AndroidJetpack数据处理之数据库Room和懒加载Paging
数据库工具:Room
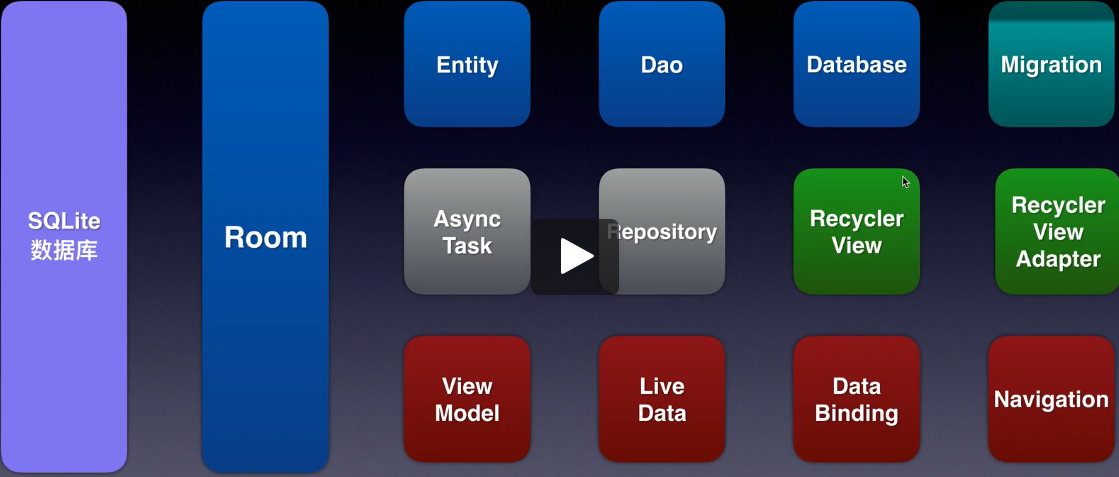
Room结构
导入依赖
app的build.gradle中开启kapt:
apply plugin: 'kotlin-kapt'
并导入以下依赖:
def room_version = '2.2.4'
implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version"
annotationProcessor "androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version" // For Kotlin use kapt instead of annotationProcessor
// Test helpers
testImplementation "androidx.room:room-testing:$room_version"
kapt 'android.arch.persistence.room:compiler:1.1.1'
implementation 'androidx.recyclerview:recyclerview:1.1.0'
//注意:对于基于 Kotlin 的应用,请确保使用 kapt 而不是 annotationProcessor。您还应添加 kotlin-kapt 插件。
基础三大件:Entity,Dao,Database
Entity:数据库的结构
语法
使用@Entity注解Entity类
使用@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true),@ColumuInfo(name = "")注解键
示例
@Entity(tableName = "word_table") //数据库结构
data class Word (
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
var id: Int,
@ColumnInfo(name = "english")
var word: String,
@ColumnInfo(name = "chinese")
var chineseMeaning: String
)
Dao:数据库的操作
语法
使用 @Dao注解接口
使用 @Insert,@Update,@Delete,@Query("DELETE FROM WORD"),@Query("SELECT * FROM WORD ORDER BY ID DESC") 等注解数据库操作
示例
@Dao //数据库操作
interface WordDao {
@Insert
fun insertWords(vararg words: Word)
@Update
fun updateWords(vararg words: Word)
@Delete
fun daleteWords(vararg words: Word)
@Query("DELETE FROM WORD")
fun deleteAllWords()
@Query("SELECT * FROM WORD ORDER BY ID DESC")
fun getAllWords() : LiveData<List<Word>> //使用LiveData,观测数据改变并自动
}
Database:数据库工具类
语法
使用 @Database(entities = [com.example.roomtest.Word::class], version = 1, exportSchema = false) 注解类
尽量使用抽象类并且使用单例模式
示例
@Database(entities = [com.example.roomtest.Word::class], version = 1, exportSchema = false)
//获取数据库实体
abstract class WordDatabase : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun getWordDao() : WordDao
/**
* 单例数据库
*/
companion object {
private var instance: WordDatabase? = null
@Synchronized
fun get(context: Context): WordDatabase {
if (instance == null) {
instance = Room.databaseBuilder(context.applicationContext,
WordDatabase::class.java, "word_database")
.build()
}
return instance!!
}
}
}
进阶
一、使用ViewModel
1,导入ViewModel模板
2,示例
class WordViewModel(application: Application) : AndroidViewModel(application) {
var wordDao: WordDao
var allWordLive: LiveData<List<Word>>
init {
val wordDatabase = WordDatabase.get(application)
wordDao = wordDatabase.getWordDao()
allWordLive = wordDao!!.getAllWords()
}
fun insertWords(vararg words: Word) {
InsertAsyncTask(wordDao!!).execute(*words)
}
fun clearWords() {
ClearAsyncTask(wordDao!!).execute()
}
inner class InsertAsyncTask(val wordDao: WordDao) : BaseAsyncTask(wordDao) {
override fun doInBackground(vararg params: Word): Void? {
wordDao.insertWords(*params)
return null
}
}
inner class UpdateAsyncTask(val wordDao: WordDao) : BaseAsyncTask(wordDao) {
override fun doInBackground(vararg params: Word): Void? {
return null
}
}
inner class DeleteAsyncTask(val wordDao: WordDao) : BaseAsyncTask(wordDao) {
override fun doInBackground(vararg params: Word): Void? {
return null
}
}
inner class ClearAsyncTask(val wordDao: WordDao) : BaseAsyncTask(wordDao) {
override fun doInBackground(vararg params: Word): Void? {
wordDao.deleteAllWords()
return null
}
}
}
以上ViewModel将数据的操作与使用放在一起,还可以继续分层:将数据的使用剥离出去
二、使用仓库Reposity访问数据
示例
/**
* 数据访问
*/
class WordRepository(val context: Context) {
private var allWordsLive : LiveData<List<Word>>
private var wordDao : WordDao
init {
val wordDatabase = WordDatabase.get(context)
wordDao = wordDatabase.getWordDao()
allWordsLive = wordDao.getAllWords()
}
fun insertWords(vararg words: Word) {
InsertAsyncTask(wordDao!!).execute(*words)
}
fun clearWords() {
ClearAsyncTask(wordDao!!).execute()
}
inner class InsertAsyncTask(val wordDao: WordDao) : BaseAsyncTask(wordDao) {
override fun doInBackground(vararg params: Word): Void? {
wordDao.insertWords(*params)
return null
}
}
inner class ClearAsyncTask(val wordDao: WordDao) : BaseAsyncTask(wordDao) {
override fun doInBackground(vararg params: Word): Void? {
wordDao.deleteAllWords()
return null
}
}
}
改造后的ViewModel:
class WordViewModel(application: Application) : AndroidViewModel(application) {
private val wordDao: WordDao
var allWordLive: LiveData<List<Word>>
init {
val wordDatabase = WordDatabase.get(application)
wordDao = wordDatabase.getWordDao()
allWordLive = wordDao!!.getAllWords()
}
fun insertWords(vararg words: Word) {
WordRepository(getApplication()).insertWords(*words)
}
fun clearWords() {
WordRepository(getApplication()).clearWords()
}
}
三、升级数据库
Room.databaseBuilder(context.applicationContext,
WordDatabase::class.java,
"word_database")
.fallbackToDestructiveMigration() //破坏式升级:升级版本后清空原有内容
.addMigrations(MIGRATION_1_2) //无痛改变
.build()
val MIGRATION_1_2 : Migration = object : Migration(1, 2) { //类的参数分别为新旧数据库的版本号
override fun migrate(database: SupportSQLiteDatabase) {
database.execSQL("") //使用SQL语句进行数据库操作
}
}
项目的其他代码
基累BaseAsyncTask:
open class BaseAsyncTask(private val wordDao: WordDao) : AsyncTask<Word, Void, Void>() {
override fun doInBackground(vararg words: Word): Void? {
return null
}
}
Acitvity:
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.TextView
import androidx.lifecycle.LiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.Observer
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProviders
import java.lang.StringBuilder
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var insert: Button
private lateinit var update: Button
private lateinit var delete: Button
private lateinit var clear: Button
private lateinit var content : TextView
private lateinit var wordViewModel: WordViewModel
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
insert = findViewById(R.id.insert)
update = findViewById(R.id.update)
delete = findViewById(R.id.delete)
clear = findViewById(R.id.clear)
content = findViewById(R.id.content)
wordViewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this)[WordViewModel::class.java]
wordViewModel.allWordLive.observe(this, Observer {
var text = StringBuilder()
for (x in it) {
text.append(x.id).append(":").append(x.word).append("=").append(x.chineseMeaning).append("\n")
}
content.text = text.toString()
})
insert.setOnClickListener {
var word1 = Word(0, "Hello", "你好")
var word2 = Word(0, "World", "世界")
wordViewModel.insertWords(word1, word2)
}
clear.setOnClickListener {
wordViewModel.clearWords()
}
}
}
xml布局:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Guideline
android:id="@+id/guideline"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.6" />
<ScrollView
android:id="@+id/scrollView2"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/guideline"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="1.0"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="1.0">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView"
android:textSize="24sp" />
</ScrollView>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Guideline
android:id="@+id/guideline2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.5" />
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Guideline
android:id="@+id/guideline3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.8" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/insert"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="insert"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/guideline3"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/guideline2"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/guideline"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.52" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/update"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="update"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/guideline3"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="@+id/guideline2"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/guideline"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.52" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/clear"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="clear"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/guideline2"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/guideline3" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/delete"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="delete"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="@+id/guideline2"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/guideline3" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
懒加载控件:Paging
声明依赖
def paging_version = "2.1.1"
implementation "androidx.paging:paging-runtime:$paging_version" // For Kotlin use paging-runtime-ktx
// alternatively - without Android dependencies for testing
testImplementation "androidx.paging:paging-common:$paging_version" // For Kotlin use paging-common-ktx
// optional - RxJava support
implementation "androidx.paging:paging-rxjava2:$paging_version" // For Kotlin use paging-rxjava2-ktx
Paging + Room + RecyclerView
数据类型
Dao中,数据使用DataSource.Factory<Key, Value>格式
@Dao
interface StudentDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM student_table ORDER BY id")
fun getAllStudents() : DataSource.Factory<Int, Student>
}
RecycleView的适配器
改用PagedListAdapter<数据类型, Holder>:
class MyPagedAdapter : PagedListAdapter<Student, MyViewHolder>(DIFF_CALLBACK) {
companion object {
private val DIFF_CALLBACK = object : DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Student>() {
override fun areItemsTheSame(oldItem: Student, newItem: Student): Boolean {
return oldItem.id == newItem.id
}
override fun areContentsTheSame(oldItem: Student, newItem: Student):Boolean {
return oldItem.studentNumber == newItem.studentNumber
}
}
}
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): MyViewHolder {
return MyViewHolder(view)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: MyViewHolder, position: Int) {
}
class MyViewHolder(itemView: View) : ViewHolder(itemView) {
}
}
装配数据
private lateinit var studentDao: StudentDao //Dao类
private lateinit var studentDatabase : StudentDatabase //数据库类
private lateinit var pagedAdapter: MyPagedAdapter //适配器类
private lateinit var allStudentsLivePaged : LiveData<PagedList<Student>> //分页数据管理
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
pagedAdapter = MyPagedAdapter()
list.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this, LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL, false)
list.adapter = pagedAdapter
studentDatabase = StudentDatabase.getInstance(this)
studentDao = studentDatabase.getStudentDao()
//第二个参数为一次加载数据的个数
allStudentsLivePaged = LivePagedListBuilder(studentDao.getAllStudents(), 2).build()
}
AndroidJetpack数据处理之数据库Room和懒加载Paging的更多相关文章
- hibernate懒加载(转载)
http://blog.csdn.net/sanjy523892105/article/details/7071139 懒加载详解 懒加载为Hibernate中比较常用的特性之一,下面我们详细来了解下 ...
- Hibernate中的一级缓存、二级缓存和懒加载(转)
1.为什么使用缓存 hibernate使用缓存减少对数据库的访问次数,从而提升hibernate的执行效率.hibernate中有两种类型的缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存. 2.一级缓存 Hibenate中 ...
- Hibernate中的一级缓存、二级缓存和懒加载
1.为什么使用缓存 hibernate使用缓存减少对数据库的访问次数,从而提升hibernate的执行效率.hibernate中有两种类型的缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存. 2.一级缓存 Hibenate中 ...
- Hibernate第八篇【懒加载】
前言 前面在使用Hibernate的时候就提及过了懒加载,但没有好好地说明具体的说明究竟是怎么回事-本博文主要讲解懒加载 什么是拦截器以及为什么要使用懒加载? 懒加载就是当使用数据的时候才去获取数据. ...
- Hibernate懒加载解析
Hibernate懒加载解析 在Hibernate框架中,当我们要访问的数据量过大时,明显用缓存不太合适, 因为内存容量有限 ,为了减少并发量,减少系统资源的消耗,这时Hibernate用懒加载机制来 ...
- @Basic表示一个简单的属性 懒加载,急加载
5.@Basic(fetch=FetchType,optional=true) 可选 @Basic表示一个简单的属性到数据库表的字段的映射,对于没有任何标注的getXxxx()方法,默认 即为 @Ba ...
- hibernate懒加载
Hibernate懒加载解析 hibernatejoinsession数据库sqlobject Hibernate懒加载解析 在Hibernate框架中,当我们要访问的数据量过大时,明显用缓存不太合适 ...
- 四十二:数据库之SQLAlchemy之数据查询懒加载技术
懒加载在一对多,或者多对多的时候,如果要获取多的这一部分的数据的时候,通过一个relationship定义好对应关系就可以全部获取,此时获取到的数据是list,但是有时候不想获取全部数据,如果要进行数 ...
- 在ThinkPHP框架(5.0.24)下引入Ueditor并实现向七牛云对象存储上传图片同时将图片信息保存到MySQL数据库,同时实现lazyload懒加载
这是我花了很多天的时间才得以真正实现的一组需求. 文章后面有完整Demo的GitHub链接. 一. 需求描述 1. 应用是基于ThinkPHP5开发的: 2. 服务器环境是LNMP,PHP版本是7.2 ...
随机推荐
- Redis内部阻塞式操作有哪些?
Redis实例在运行的时候,要和许多对象进行交互,这些不同的交互对象会有不同的操作.下面我们来看看,这些不同的交互对象以及相应的主要操作有哪些. 客户端:键值对的增删改查操作. 磁盘:生成RDB快照. ...
- k8s系列文章第五篇(docker-compose)
更多精彩内容,猛搓这里 目录 一.Docker Compose 1.前言 2.官方介绍 1.Compose 中有两个重要的概念 2.三步骤 3.Compose是Docker官方的开源项目,需要安装! ...
- 本地图片转base64编码
通常获取图片的base64编码都是通过input的上传file属性获取转化,但是有时候需要的是本地图片不经过上传操作,直接拿本地图片转成base64编码就不行了,input上传操作需要人为操作一下,没 ...
- Unsupported major.minor version 52.0解决办法【转】
1.首先解释一下报错原因: stanford parser和jdk版本对应关系 J2SE8=52, J2SE7=51, J2SE6.0=50, J2SE5.0=49, JDK1.4=48, JDK1. ...
- Elasticsearch(9300、9200)未授权访问
下载地址https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.5.0.zip 检测 http://localhost ...
- LATEX学习和IEEE Tran模板介绍
目录 软件的选择 IEEE 模板下载 模板正文 图 表格 公式 算法 参考文献 Latex学习网站:http://www.latexstudio.net/page/tex-documents/ IEE ...
- Cancer Cell | 肿瘤微环境渐进式调控AML治疗抵抗的分子机制
急性髓系白血病 ( acute myeloid leukemia, AML ) 是成年人常见的血液系统恶性肿瘤之一,主要表现为髓系原始细胞克隆性恶性增殖及正常造血细胞功能抑制.在AML基因突变图谱中, ...
- 5年Android开发诉苦:47天21家面试,半年空档期觉得整个人生都被毁了
近日,我在逛某社交论坛时,发现一位做了五年的Android开发将自己这段时间的所有面试经历发表了出来,根据网友自己提供的信息显示,主要面试的地点都在北京,上海等地. 微软和亚马逊刚面试完一面,都是以算 ...
- 【LeetCode】316. 去除重复字母
316. 去除重复字母 知识点:栈:单调 题目描述 给你一个字符串 s ,请你去除字符串中重复的字母,使得每个字母只出现一次.需保证 返回结果的字典序最小(要求不能打乱其他字符的相对位置). 示例 输 ...
- 谈谈网络协议 - 数据链路层( Data Link)
数据链路层( Data Link) 链路:从1个节点到相邻节点的一段物理线路(有线或无线),中间没有其他交换节点 案例 上图可以看出,总共由5条链路组成: 第1条:计算机0 => 路由器0,使用 ...
