java基础---设计模式(2)
结构型模式
出处:https://blog.csdn.net/zhangerqing/article/details/8239539
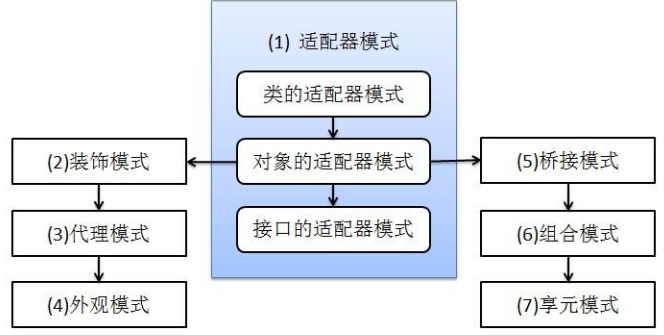
一、适配器模式
适配器模式将某个类的接口转换成客户端期望的另一个接口表示,目的是消除由于接口不匹配所造成的类的兼容性问题 ,包括类的适配器模式、对象的适配器模式、接口
的适配器模式
- 类的适配器模式
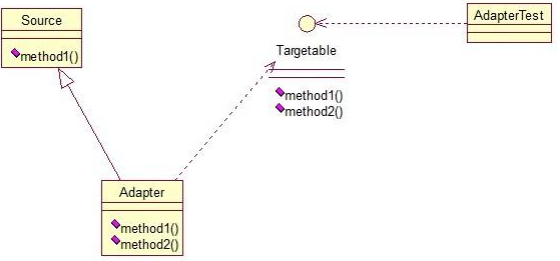
public class Source {
public void method1() {
System.out.println("this is original method!");
}
}
public interface Targetable {
/* 与原类中的方法相同 */
public void method1();
/* 新类的方法 */
public void method2();
}
//实现接口
public class Adapter extends Source implements Targetable {
@Override
public void method2() {
System.out.println("this is the targetable method!");
}
}
//Adapter类继承Source类,实现Targetable接口,下面是测试类:
public class AdapterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Targetable target = new Adapter();
target.method1();
target.method2();
}
}
//this is original method!
//this is the targetable method!
- 对象的适配器模式
将Adapter类作修改,这次不继承Source类,而是持有Source类的实例,以达到解决兼容性的问题

//修改adapter
public class Wrapper implements Targetable { private Source source; public Wrapper(Source source){
super();
this.source = source;
}
@Override
public void method2() {
System.out.println("this is the targetable method!");
} @Override
public void method1() {
source.method1(); //直接调用了对象的method1 进行重写
}
} //测试类:
public class AdapterTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
Source source = new Source();
Targetable target = new Wrapper(source);
target.method1();
target.method2();
}
}
- 接口的适配器模式
借助于一个抽象类,该抽象类实现了该接口所有的方法,而我们不和原始的接口打交道,只和该抽象类取得联系,所以我们写一个类,继承该抽象类,重写我们需要的方法
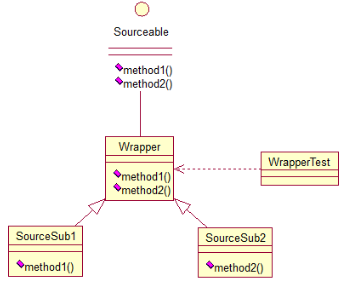
//原接口
public interface Sourceable { public void method1();
public void method2();
} //抽象类Wrapper2实现了接口的方法,重写后方法体为空
public abstract class Wrapper2 implements Sourceable{ public void method1(){}
public void method2(){}
} //子类分别重写需要的方法
public class SourceSub1 extends Wrapper2 {
public void method1(){
System.out.println("the sourceable interface's first Sub1!");
}
}
public class SourceSub2 extends Wrapper2 {
public void method2(){
System.out.println("the sourceable interface's second Sub2!");
}
} public class WrapperTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
Sourceable source1 = new SourceSub1();
Sourceable source2 = new SourceSub2(); source1.method1();
source1.method2();
source2.method1();
source2.method2();
}
} //the sourceable interface's first Sub1! method`()为空,用的abstract里的方法
//the sourceable interface's second Sub2!
总结:
- 类的适配器模式:当希望将一个类转换成满足另一个新接口的类时,可以使用类的适配器模式,创建一个新类,继承原有的类,实现新的接口即可。
- 对象的适配器模式:当希望将一个对象转换成满足另一个新接口的对象时,可以创建一个Wrapper类,持有原类的一个实例,在Wrapper类的方法中,调用实例的方法就行。
- 接口的适配器模式:当不希望实现一个接口中所有的方法时,可以创建一个抽象类Wrapper,实现所有方法,我们写别的类的时候,继承抽象类即可。
二、装饰模式
装饰模式就是给一个对象增加一些新的功能,而且是动态的,要求装饰对象和被装饰对象实现同一个接口,装饰对象持有被装饰对象的实例
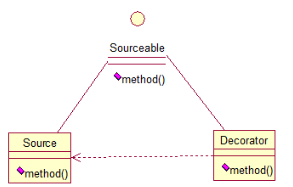
public interface Sourceable {
public void method();
}
//被装饰类
public class Source implements Sourceable {
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("the original method!");
}
}
//装饰类实现接口
public class Decorator implements Sourceable {
private Sourceable source;
public Decorator(Sourceable source){
super();
this.source = source;
}
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("before decorator!");
source.method();
System.out.println("after decorator!");
}
}
//测试类:
public class DecoratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sourceable source = new Source();
Sourceable obj = new Decorator(source);
obj.method();
}
}
//before decorator!
//the original method!
//after decorator!
总结:装饰器模式适用于扩展一个类的功能,能够动态的为一个对象增加功能,而且还能动态撤销。(继承不能做到这一点,继承的功能是静态的,不能动态增删)但产生过多相似的对象,不易排错!
三、代理模式
代理模式就是找一个代理类替原对象进行一些操作
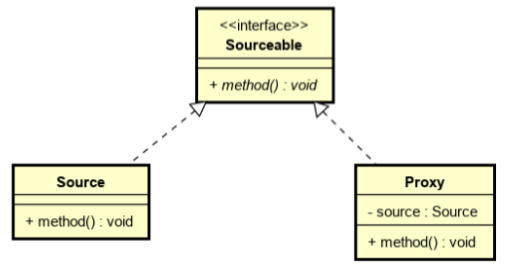
public interface Sourceable {
public void method();
}
public class Source implements Sourceable {
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("the original method!");
}
}
public class Proxy implements Sourceable {
private Source source;
public Proxy(){
super();
this.source = new Source();
}
@Override
public void method() {
before();
source.method();
atfer();
}
private void atfer() {
System.out.println("after proxy!");
}
private void before() {
System.out.println("before proxy!");
}
}
//测试类:
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sourceable source = new Proxy();
source.method();
}
}
//before proxy!
//the original method!
//after proxy!
总结:如果在使用的时候需要对原有的方法进行改进,可以采用一个代理类调用原有方法,并且对产生的结果进行控制,这种方式就是代理模式。
装饰器模式通常的做法是将原始对象作为一个参数传给装饰者的构造器,而代理模式通常在一个代理类中创建一个被代理类的对象
装饰器模式关注于在一个对象上动态的添加方法,然而代理模式关注于控制对对象的访问
四、外观模式
将类与类之间的关系放在一个Facade类中,降低了类类之间的耦合度,该模式中没有涉及到接口
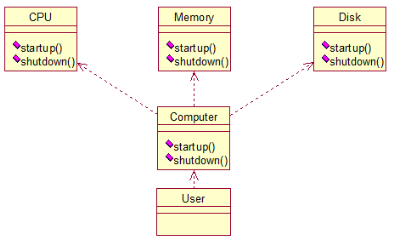
public class CPU {
public void startup(){
System.out.println("cpu startup!");
}
public void shutdown(){
System.out.println("cpu shutdown!");
}
}
public class Memory {
public void startup(){
System.out.println("memory startup!");
}
public void shutdown(){
System.out.println("memory shutdown!");
}
}
public class Disk {
public void startup(){
System.out.println("disk startup!");
}
public void shutdown(){
System.out.println("disk shutdown!");
}
}
public class Computer {
private CPU cpu;
private Memory memory;
private Disk disk;
public Computer(){
cpu = new CPU();
memory = new Memory();
disk = new Disk();
}
public void startup(){
System.out.println("start the computer!");
cpu.startup();
memory.startup();
disk.startup();
System.out.println("start computer finished!");
}
public void shutdown(){
System.out.println("begin to close the computer!");
cpu.shutdown();
memory.shutdown();
disk.shutdown();
System.out.println("computer closed!");
}
}
public class User {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer computer = new Computer();
computer.startup();
computer.shutdown();
}
}
/*start the computer!
cpu startup!
memory startup!
disk startup!
start computer finished!
begin to close the computer!
cpu shutdown!
memory shutdown!
disk shutdown!
computer closed!*/
五、桥接模式
将抽象化与实现化解耦,使得二者可以独立变化
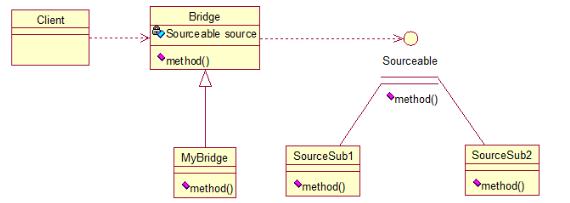
public interface Sourceable {
public void method();
}
//分别定义两个实现类:
public class SourceSub1 implements Sourceable {
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("this is the first sub!");
}
}
public class SourceSub2 implements Sourceable {
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("this is the second sub!");
}
}
//定义一个桥,持有Sourceable的一个实例:
public abstract class Bridge {
private Sourceable source;
public void method(){
source.method();
}
public Sourceable getSource() {
return source;
}
public void setSource(Sourceable source) {
this.source = source;
}
}
public class MyBridge extends Bridge {
public void method(){
getSource().method();
}
}
//测试类:
public class BridgeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bridge bridge = new MyBridge();
/*调用第一个对象*/
Sourceable source1 = new SourceSub1();
bridge.setSource(source1);
bridge.method();
/*调用第二个对象*/
Sourceable source2 = new SourceSub2();
bridge.setSource(source2);
bridge.method();
}
}
//this is the first sub!
//this is the second sub!
六、组合模式
将多个对象组合在一起进行操作,常用于表示树形结构中,例如二叉树,数等
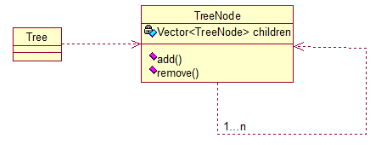
public class TreeNode {
private String name;
private TreeNode parent;
private Vector<TreeNode> children = new Vector<TreeNode>();
public TreeNode(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public TreeNode getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(TreeNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
//添加孩子节点
public void add(TreeNode node){
children.add(node);
}
//删除孩子节点
public void remove(TreeNode node){
children.remove(node);
}
//取得孩子节点
public Enumeration<TreeNode> getChildren(){
return children.elements();
}
}
public class Tree {
TreeNode root = null;
public Tree(String name) {
root = new TreeNode(name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tree tree = new Tree("A");
TreeNode nodeB = new TreeNode("B");
TreeNode nodeC = new TreeNode("C");
nodeB.add(nodeC);
tree.root.add(nodeB);
System.out.println("build the tree finished!");
}
}
七、享元模式
实现对象的共享,即共享池,当系统中对象多的时候可以减少内存的开销,通常与工厂模式一起使用。
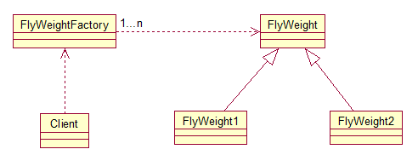
FlyWeightFactory负责创建和管理享元单元,当一个客户端请求时,工厂需要检查当前对象池中是否有符合条件的对象,如果有,就返回已经存在的对象,如果没有,则创建一个新对象,FlyWeight是超类
//数据库连接池源码
public class ConnectionPool { private Vector<Connection> pool; /*公有属性*/
private String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
private String username = "root";
private String password = "root";
private String driverClassName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; private int poolSize = 100;
private static ConnectionPool instance = null;
Connection conn = null; /*构造方法,做一些初始化工作*/
private ConnectionPool() {
pool = new Vector<Connection>(poolSize); for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
try {
Class.forName(driverClassName);
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
pool.add(conn);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} /* 返回连接的连接池 */
public synchronized void release() {
pool.add(conn);
} /* 返回连接池中的一个数据库连接 */
public synchronized Connection getConnection() {
if (pool.size() > 0) {
Connection conn = pool.get(0);
pool.remove(conn);
return conn;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
通过连接池的管理,实现了数据库连接的共享,不需要每一次都重新创建连接,节省了数据库重新创建的开销,提升了系统的性能!
java基础---设计模式(2)的更多相关文章
- java基础---设计模式(1)
出处:https://blog.csdn.net/zhangerqing/article/details/8194653 java的设计模式分为三大类 创建型模式: 工厂方法模式.抽象工厂模式.单例模 ...
- Java基础-设计模式之-代理模式Proxy
代理模式是对象的结构模式.代理模式给某一个对象提供一个代理对象,并由代理对象控制对原对象的引用. 代理模式是常用的Java 设计模式,它的特征是代理类与委托类有同样的接口,代理类主要负责为委托类预处理 ...
- JAVA基础——设计模式之单列模式
一:单例设计模式 Singleton是一种创建型模式,指某个类采用Singleton模式,则在这个类被创建后,只可能产生一个实例供外部访问,并且提供一个全局的访问点. 单例设计模式的特点: 单例类只能 ...
- JAVA基础——设计模式之观察者模式
观察者模式是对象的行为模式,又叫发布-订阅(Publish/Subscribe)模式.模型-视图(Model/View)模式.源-监听器(Source/Listener)模式或从属者(Dependen ...
- JAVA基础——设计模式之简单工厂模式
在阎宏博士的<JAVA与模式>一书中开头是这样描述简单工厂模式的:简单工厂模式是类的创建模式,又叫做静态工厂方法(Static Factory Method)模式.简单工厂模式是由一个工厂 ...
- java基础设计模式1——单例模式
概念:在应用这个模式时,单例对象的类必须保证只有一个实例存在.许多时候整个系统只需要拥有一个的全局对象,这样有利于我们协调系统整体的行为. 单例模式从实现上可以分为饿汉式单例和懒汉式单例两种,前者天生 ...
- JAVA基础——设计模式之装饰者模式
装饰模式 : 对新房进行装修并没有改变房屋的本质,但它可以让房子变得更漂亮.更温馨.更实用. 在软件设计中,对已有对象(新房)的功能进行扩展(装修). 把通用功能封装在装饰器中,用到的地方 ...
- java基础---设计模式(3)
行为型模式 出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhangerqing 行为型模式包括策略模式.模板方法模式.观察者模式.迭代子模式.责任链模式.命令模式.备忘录模式.状态模式.访问者模式 ...
- [Java面经]干货整理, Java面试题(覆盖Java基础,Java高级,JavaEE,数据库,设计模式等)
如若转载请注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/wang-meng/p/5898837.html 谢谢.上一篇发了一个找工作的面经, 找工作不宜, 希望这一篇的内容能够帮助到大 ...
随机推荐
- DDD兴起的原因以及与微服务的关系
DDD为什么能火起来? 我们先不讨论DDD的定义, 先梳理一下DDD火起来的背景, 根据我学习的套路, 永远是为什么为先,再是解决什么问题,是什么东西, 最后如何使用.我们都知道这些年随着设备以及技术 ...
- 安装Keras出现的问题
先是pip install tensorflow 给装好了,但是pip install keras出现如下的问题: 只好搜帖子,参考如下的帖子,我直接 conda install keras wi ...
- Sql server 多列去重复值,相同的只显示一条数据
CREATE TABLE #tp( headerNo VARCHAR(10), machineNO VARCHAR(10), descrption nVARCHAR(20), artNo VARCHA ...
- YOLOv5目标检测源码重磅发布了!
YOLOv5目标检测源码重磅发布了! https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 该存储库代表了对未来对象检测方法的超解析开源研究,并结合了在使用之前的YOLO存储库在 ...
- DMS是临时解决方案?
DMS是临时解决方案? Who Says DMS Is an Interim Solution? 现在是认真对待DMS驱动程序监控系统的时候了. 特斯拉(Tesla)在台湾高速公路上撞上翻倒卡车的镜头 ...
- java接口类
是什么:类似于java中的继承,但是继承只可以继承一个人父类,接口类可以继承多个 作用:解决java继承解决不了的问题 关键字:interface(定义) implements(使用) 注意事项:1. ...
- Python_selenium PO模式下 Tesecase 的相同执行代码做成selenium_base_case公共模块及调用
作用: PO模式下 Tesecase 的相同执行代码做成selenium_base_case公共模块及调用,提高代码简洁度,实现同样效果. 框架结构: 代码简单实践: common模块下 seleni ...
- 【NX二次开发】Block UI 半径尺寸(沿曲线的位置)
属性说明 常规 类型 描述 BlockID String 控件ID Enable Logical 是否可操作 Group Logical ...
- 如何在CentOS 7上搭建LAMP环境(使用YUM或编译)
什么是LAMP? LAMP是Linux,Apache,MySQL和PHP的缩写. 它是一堆应用程序的堆栈,它们在Web服务器上一起工作以托管网站. 话虽如此,每个程序都有不同的目的: 在LAMP中, ...
- Git操作文档
Git 操作文档 Git 是一个十分流行的版本控制系统,Git 和 SVN 区别在于,SVN使用增量文件系统,存储每次提交之间的差异.而 git 使用全量文件系统,存储每次提交的文件的全部内容(sna ...
