libpcap使用
首先先介绍一下本次实验的环境:
Ubuntu 11.04,IP:192.168.1.1,广播地址:192.168.1.255,子网掩码:255.255.255.0
可以使用下面的命令设置:
sudo ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.1 broadcast 192.168.1.255 netmask 255.255.255.0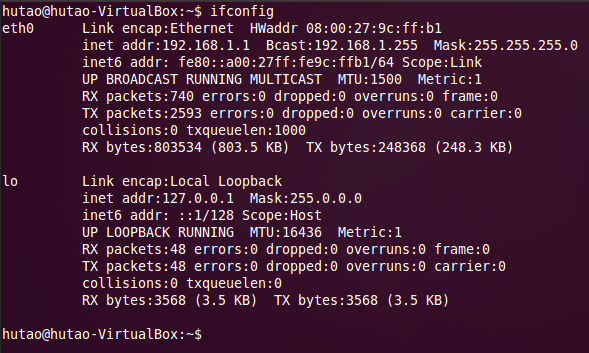
1.安装
在http://www.tcpdump.org/下载libpcap(tcpdump的源码也可以从这个网站下载)
解压
./configure
make
sudo make install
2.使用
安装好libpcap后,我们要使用它啦,先写一个简单的程序,并介绍如何使用libpcap库编译它:
Makefile:
- all: test.c
- gcc -g -Wall -o test test.c -lpcap
- clean:
- rm -rf *.o test
其后的程序的Makefile均类似,故不再重复
test1.c
- #include <pcap.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- char errBuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE], * device;
- device = pcap_lookupdev(errBuf);
- if(device)
- {
- printf("success: device: %s\n", device);
- }
- else
- {
- printf("error: %s\n", errBuf);
- }
- return 0;
- }
可以成功编译,不过运行的时候却提示找不到libpcap.so.1,因为libpcap.so.1默认安装到了/usr/local/lib下,我们做一个符号链接到/usr/lib/下即可:
运行test的时候输出"no suitable device found",原因是我们没有以root权限运行,root权限运行后就正常了:
下面开始正式讲解如何使用libpcap:
首先要使用libpcap,我们必须包含pcap.h头文件,可以在/usr/local/include/pcap/pcap.h找到,其中包含了每个类型定义的详细说明。
1.获取网络接口
首先我们需要获取监听的网络接口:
我们可以手动指定或让libpcap自动选择,先介绍如何让libpcap自动选择:
char * pcap_lookupdev(char * errbuf)
上面这个函数返回第一个合适的网络接口的字符串指针,如果出错,则errbuf存放出错信息字符串,errbuf至少应该是PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE个字节长度的。注意,很多libpcap函数都有这个参数。
pcap_lookupdev()一般可以在跨平台的,且各个平台上的网络接口名称都不相同的情况下使用。
如果我们手动指定要监听的网络接口,则这一步跳过,我们在第二步中将要监听的网络接口字符串硬编码在pcap_open_live里。
2.释放网络接口
在操作为网络接口后,我们应该要释放它:
void pcap_close(pcap_t * p)
该函数用于关闭pcap_open_live()获取的pcap_t的网络接口对象并释放相关资源。
3.打开网络接口
获取网络接口后,我们需要打开它:
pcap_t * pcap_open_live(const char * device, int snaplen, int promisc, int to_ms, char * errbuf)
上面这个函数会返回指定接口的pcap_t类型指针,后面的所有操作都要使用这个指针。
第一个参数是第一步获取的网络接口字符串,可以直接使用硬编码。
第二个参数是对于每个数据包,从开头要抓多少个字节,我们可以设置这个值来只抓每个数据包的头部,而不关心具体的内容。典型的以太网帧长度是1518字节,但其他的某些协议的数据包会更长一点,但任何一个协议的一个数据包长度都必然小于65535个字节。
第三个参数指定是否打开混杂模式(Promiscuous Mode),0表示非混杂模式,任何其他值表示混合模式。如果要打开混杂模式,那么网卡必须也要打开混杂模式,可以使用如下的命令打开eth0混杂模式:
ifconfig eth0 promisc
第四个参数指定需要等待的毫秒数,超过这个数值后,第3步获取数据包的这几个函数就会立即返回。0表示一直等待直到有数据包到来。
第五个参数是存放出错信息的数组。
4.获取数据包
打开网络接口后就已经开始监听了,那如何知道收到了数据包呢?有下面3种方法:
a)
u_char * pcap_next(pcap_t * p, struct pcap_pkthdr * h)
如果返回值为NULL,表示没有抓到包
第一个参数是第2步返回的pcap_t类型的指针
第二个参数是保存收到的第一个数据包的pcap_pkthdr类型的指针
pcap_pkthdr类型的定义如下:
- struct pcap_pkthdr
- {
- struct timeval ts; /* time stamp */
- bpf_u_int32 caplen; /* length of portion present */
- bpf_u_int32 len; /* length this packet (off wire) */
- };
注意这个函数只要收到一个数据包后就会立即返回
b)
int pcap_loop(pcap_t * p, int cnt, pcap_handler callback, u_char * user)
第一个参数是第2步返回的pcap_t类型的指针
第二个参数是需要抓的数据包的个数,一旦抓到了cnt个数据包,pcap_loop立即返回。负数的cnt表示pcap_loop永远循环抓包,直到出现错误。
第三个参数是一个回调函数指针,它必须是如下的形式:
void callback(u_char * userarg, const struct pcap_pkthdr * pkthdr, const u_char * packet)
第一个参数是pcap_loop的最后一个参数,当收到足够数量的包后pcap_loop会调用callback回调函数,同时将pcap_loop()的user参数传递给它
第二个参数是收到的数据包的pcap_pkthdr类型的指针
第三个参数是收到的数据包数据
c)
int pcap_dispatch(pcap_t * p, int cnt, pcap_handler callback, u_char * user)
这个函数和pcap_loop()非常类似,只是在超过to_ms毫秒后就会返回(to_ms是pcap_open_live()的第4个参数)
例子:
test2:
- #include <pcap.h>
- #include <time.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- char errBuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE], * devStr;
- /* get a device */
- devStr = pcap_lookupdev(errBuf);
- if(devStr)
- {
- printf("success: device: %s\n", devStr);
- }
- else
- {
- printf("error: %s\n", errBuf);
- exit(1);
- }
- /* open a device, wait until a packet arrives */
- pcap_t * device = pcap_open_live(devStr, 65535, 1, 0, errBuf);
- if(!device)
- {
- printf("error: pcap_open_live(): %s\n", errBuf);
- exit(1);
- }
- /* wait a packet to arrive */
- struct pcap_pkthdr packet;
- const u_char * pktStr = pcap_next(device, &packet);
- if(!pktStr)
- {
- printf("did not capture a packet!\n");
- exit(1);
- }
- printf("Packet length: %d\n", packet.len);
- printf("Number of bytes: %d\n", packet.caplen);
- printf("Recieved time: %s\n", ctime((const time_t *)&packet.ts.tv_sec));
- pcap_close(device);
- return 0;
- }

打开两个终端,先ping 192.168.1.10,由于我们的ip是192.168.1.1,因此我们可以收到广播的数据包,另一个终端运行test,就会抓到这个包。
下面的这个程序会把收到的数据包内容全部打印出来,运行方式和上一个程序一样:
test3:
- #include <pcap.h>
- #include <time.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- void getPacket(u_char * arg, const struct pcap_pkthdr * pkthdr, const u_char * packet)
- {
- int * id = (int *)arg;
- printf("id: %d\n", ++(*id));
- printf("Packet length: %d\n", pkthdr->len);
- printf("Number of bytes: %d\n", pkthdr->caplen);
- printf("Recieved time: %s", ctime((const time_t *)&pkthdr->ts.tv_sec));
- int i;
- for(i=0; i<pkthdr->len; ++i)
- {
- printf(" %02x", packet[i]);
- if( (i + 1) % 16 == 0 )
- {
- printf("\n");
- }
- }
- printf("\n\n");
- }
- int main()
- {
- char errBuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE], * devStr;
- /* get a device */
- devStr = pcap_lookupdev(errBuf);
- if(devStr)
- {
- printf("success: device: %s\n", devStr);
- }
- else
- {
- printf("error: %s\n", errBuf);
- exit(1);
- }
- /* open a device, wait until a packet arrives */
- pcap_t * device = pcap_open_live(devStr, 65535, 1, 0, errBuf);
- if(!device)
- {
- printf("error: pcap_open_live(): %s\n", errBuf);
- exit(1);
- }
- /* wait loop forever */
- int id = 0;
- pcap_loop(device, -1, getPacket, (u_char*)&id);
- pcap_close(device);
- return 0;
- }

从上图可以看出,如果我们没有按Ctrl+c,test会一直抓到包,因为我们将pcap_loop()设置为永远循环
由于ping属于icmp协议,并且发出icmp协议数据包之前必须先通过arp协议获取目的主机的mac地址,因此我们抓到的包是arp协议的,而arp协议的数据包长度正好是42字节(14字节的以太网帧头+28字节的arp数据)。具体内容请参考相关网络协议说明。
5.分析数据包
我们既然已经抓到数据包了,那么我们要开始分析了,这部分留给读者自己完成,具体内容可以参考相关的网络协议说明。在本文的最后,我会示范性的写一个分析arp协议的sniffer,仅供参考。要特别注意一点,网络上的数据是网络字节顺序的,因此分析前需要转换为主机字节顺序(ntohs()函数)。
6.过滤数据包
我们抓到的数据包往往很多,如何过滤掉我们不感兴趣的数据包呢?
几乎所有的操作系统(BSD, AIX, Mac OS, Linux等)都会在内核中提供过滤数据包的方法,主要都是基于BSD Packet Filter(BPF)结构的。libpcap利用BPF来过滤数据包。
过滤数据包需要完成3件事:
a) 构造一个过滤表达式
b) 编译这个表达式
c) 应用这个过滤器
a)
BPF使用一种类似于汇编语言的语法书写过滤表达式,不过libpcap和tcpdump都把它封装成更高级且更容易的语法了,具体可以man tcpdump,以下是一些例子:
src host 192.168.1.177
只接收源ip地址是192.168.1.177的数据包
dst port 80
只接收tcp/udp的目的端口是80的数据包
not tcp
只接收不使用tcp协议的数据包
tcp[13] == 0x02 and (dst port 22 or dst port 23)
只接收SYN标志位置位且目标端口是22或23的数据包(tcp首部开始的第13个字节)
icmp[icmptype] == icmp-echoreply or icmp[icmptype] == icmp-echo
只接收icmp的ping请求和ping响应的数据包
ehter dst 00:e0:09:c1:0e:82
只接收以太网mac地址是00:e0:09:c1:0e:82的数据包
ip[8] == 5
只接收ip的ttl=5的数据包(ip首部开始的第8个字节)
b)
构造完过滤表达式后,我们需要编译它,使用如下函数:
int pcap_compile(pcap_t * p, struct bpf_program * fp, char * str, int optimize, bpf_u_int32 netmask)
fp:这是一个传出参数,存放编译后的bpf
str:过滤表达式
optimize:是否需要优化过滤表达式
metmask:简单设置为0即可
c)
最后我们需要应用这个过滤表达式:
int pcap_setfilter(pcap_t * p, struct bpf_program * fp)
第二个参数fp就是前一步pcap_compile()的第二个参数
应用完过滤表达式之后我们便可以使用pcap_loop()或pcap_next()等抓包函数来抓包了。
下面的程序演示了如何过滤数据包,我们只接收目的端口是80的数据包:
test4.c
- #include <pcap.h>
- #include <time.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- void getPacket(u_char * arg, const struct pcap_pkthdr * pkthdr, const u_char * packet)
- {
- int * id = (int *)arg;
- printf("id: %d\n", ++(*id));
- printf("Packet length: %d\n", pkthdr->len);
- printf("Number of bytes: %d\n", pkthdr->caplen);
- printf("Recieved time: %s", ctime((const time_t *)&pkthdr->ts.tv_sec));
- int i;
- for(i=0; i<pkthdr->len; ++i)
- {
- printf(" %02x", packet[i]);
- if( (i + 1) % 16 == 0 )
- {
- printf("\n");
- }
- }
- printf("\n\n");
- }
- int main()
- {
- char errBuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE], * devStr;
- /* get a device */
- devStr = pcap_lookupdev(errBuf);
- if(devStr)
- {
- printf("success: device: %s\n", devStr);
- }
- else
- {
- printf("error: %s\n", errBuf);
- exit(1);
- }
- /* open a device, wait until a packet arrives */
- pcap_t * device = pcap_open_live(devStr, 65535, 1, 0, errBuf);
- if(!device)
- {
- printf("error: pcap_open_live(): %s\n", errBuf);
- exit(1);
- }
- /* construct a filter */
- struct bpf_program filter;
- pcap_compile(device, &filter, "dst port 80", 1, 0);
- pcap_setfilter(device, &filter);
- /* wait loop forever */
- int id = 0;
- pcap_loop(device, -1, getPacket, (u_char*)&id);
- pcap_close(device);
- return 0;
- }
在下面的这一个例子中,客户机通过tcp的9732端口连接服务器,发送字符'A',之后服务器将'A'+1即'B'返回给客户机,具体实现可以参考:http://blog.csdn.net/htttw/article/details/7519964
服务器的ip是192.168.56.101,客户机的ip是192.168.56.1
服务器:
Makefile:
- all: tcp_client.c tcp_server.c
- gcc -g -Wall -o tcp_client tcp_client.c
- gcc -g -Wall -o tcp_server tcp_server.c
- clean:
- rm -rf *.o tcp_client tcp_server
tcp_server:
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/socket.h>
- #include <netinet/in.h>
- #include <arpa/inet.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #define PORT 9832
- #define SERVER_IP "192.168.56.101"
- int main()
- {
- /* create a socket */
- int server_sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
- struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
- server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
- server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(SERVER_IP);
- server_addr.sin_port = htons(PORT);
- /* bind with the local file */
- bind(server_sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
- /* listen */
- listen(server_sockfd, 5);
- char ch;
- int client_sockfd;
- struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
- socklen_t len = sizeof(client_addr);
- while(1)
- {
- printf("server waiting:\n");
- /* accept a connection */
- client_sockfd = accept(server_sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, &len);
- /* exchange data */
- read(client_sockfd, &ch, 1);
- printf("get char from client: %c\n", ch);
- ++ch;
- write(client_sockfd, &ch, 1);
- /* close the socket */
- close(client_sockfd);
- }
- return 0;
- }
tcp_client:
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/socket.h>
- #include <netinet/in.h>
- #include <arpa/inet.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #define PORT 9832
- #define SERVER_IP "192.168.56.101"
- int main()
- {
- /* create a socket */
- int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
- struct sockaddr_in address;
- address.sin_family = AF_INET;
- address.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(SERVER_IP);
- address.sin_port = htons(PORT);
- /* connect to the server */
- int result = connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&address, sizeof(address));
- if(result == -1)
- {
- perror("connect failed: ");
- exit(1);
- }
- /* exchange data */
- char ch = 'A';
- write(sockfd, &ch, 1);
- read(sockfd, &ch, 1);
- printf("get char from server: %c\n", ch);
- /* close the socket */
- close(sockfd);
- return 0;
- }
运行方法如下,首先在服务器上运行tcp_server,然后运行我们的监听器,然后在客户机上运行tcp_client,注意,我们可以先清空arp缓存,这样就可以看到整个通信过程(包括一开始的arp广播)
在客户机上运行下列命令来清空记录服务器的arp缓存:
sudo arp -d 192.168.56.101
arp -a后发现已经删除了记录服务器的arp缓存
抓包的结果如下所示,由于包太多了,无法全部截图,因此我把所有内容保存在下面的文本中了:
全部的包如下:
- hutao@hutao-VirtualBox:~/test3$ sudo ./test
- success: device: eth0
- id: 1
- Packet length: 60
- Number of bytes: 60
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- ff ff ff ff ff ff 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 06 00 01
- 08 00 06 04 00 01 0a 00 27 00 00 00 c0 a8 38 01
- 00 00 00 00 00 00 c0 a8 38 65 00 00 00 00 00 00
- 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
- id: 2
- Packet length: 42
- Number of bytes: 42
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 27 9c ff b1 08 06 00 01
- 08 00 06 04 00 02 08 00 27 9c ff b1 c0 a8 38 65
- 0a 00 27 00 00 00 c0 a8 38 01
- id: 3
- Packet length: 74
- Number of bytes: 74
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 08 00 27 9c ff b1 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 45 00
- 00 3c d4 af 40 00 40 06 74 55 c0 a8 38 01 c0 a8
- 38 65 8e 20 26 68 79 e1 63 8c 00 00 00 00 a0 02
- 39 08 d4 13 00 00 02 04 05 b4 04 02 08 0a 00 14
- b7 23 00 00 00 00 01 03 03 06
- id: 4
- Packet length: 74
- Number of bytes: 74
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 27 9c ff b1 08 00 45 00
- 00 3c 00 00 40 00 40 06 49 05 c0 a8 38 65 c0 a8
- 38 01 26 68 8e 20 b6 c4 e6 e5 79 e1 63 8d a0 12
- 38 90 f1 e5 00 00 02 04 05 b4 04 02 08 0a 00 57
- a1 2c 00 14 b7 23 01 03 03 05
- id: 5
- Packet length: 66
- Number of bytes: 66
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 08 00 27 9c ff b1 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 45 00
- 00 34 d4 b0 40 00 40 06 74 5c c0 a8 38 01 c0 a8
- 38 65 8e 20 26 68 79 e1 63 8d b6 c4 e6 e6 80 10
- 00 e5 fb c1 00 00 01 01 08 0a 00 14 b7 24 00 57
- a1 2c
- id: 6
- Packet length: 67
- Number of bytes: 67
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 08 00 27 9c ff b1 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 45 00
- 00 35 d4 b1 40 00 40 06 74 5a c0 a8 38 01 c0 a8
- 38 65 8e 20 26 68 79 e1 63 8d b6 c4 e6 e6 80 18
- 00 e5 ba b7 00 00 01 01 08 0a 00 14 b7 25 00 57
- a1 2c 41
- id: 7
- Packet length: 66
- Number of bytes: 66
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 27 9c ff b1 08 00 45 00
- 00 34 47 cb 40 00 40 06 01 42 c0 a8 38 65 c0 a8
- 38 01 26 68 8e 20 b6 c4 e6 e6 79 e1 63 8e 80 10
- 01 c5 f1 dd 00 00 01 01 08 0a 00 57 a1 2e 00 14
- b7 25
- id: 8
- Packet length: 67
- Number of bytes: 67
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 27 9c ff b1 08 00 45 00
- 00 35 47 cc 40 00 40 06 01 40 c0 a8 38 65 c0 a8
- 38 01 26 68 8e 20 b6 c4 e6 e6 79 e1 63 8e 80 18
- 01 c5 f1 de 00 00 01 01 08 0a 00 57 a1 2e 00 14
- b7 25 42
- id: 9
- Packet length: 66
- Number of bytes: 66
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 27 9c ff b1 08 00 45 00
- 00 34 47 cd 40 00 40 06 01 40 c0 a8 38 65 c0 a8
- 38 01 26 68 8e 20 b6 c4 e6 e7 79 e1 63 8e 80 11
- 01 c5 f1 dd 00 00 01 01 08 0a 00 57 a1 2e 00 14
- b7 25
- id: 10
- Packet length: 66
- Number of bytes: 66
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 08 00 27 9c ff b1 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 45 00
- 00 34 d4 b2 40 00 40 06 74 5a c0 a8 38 01 c0 a8
- 38 65 8e 20 26 68 79 e1 63 8e b6 c4 e6 e7 80 10
- 00 e5 fb bc 00 00 01 01 08 0a 00 14 b7 25 00 57
- a1 2e
- id: 11
- Packet length: 66
- Number of bytes: 66
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 08 00 27 9c ff b1 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 45 00
- 00 34 d4 b3 40 00 40 06 74 59 c0 a8 38 01 c0 a8
- 38 65 8e 20 26 68 79 e1 63 8e b6 c4 e6 e7 80 11
- 00 e5 fb bb 00 00 01 01 08 0a 00 14 b7 25 00 57
- a1 2e
- id: 12
- Packet length: 66
- Number of bytes: 66
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 27 9c ff b1 08 00 45 00
- 00 34 47 ce 40 00 40 06 01 3f c0 a8 38 65 c0 a8
- 38 01 26 68 8e 20 b6 c4 e6 e8 79 e1 63 8f 80 10
- 01 c5 f1 dd 00 00 01 01 08 0a 00 57 a1 2e 00 14
- b7 25
- id: 13
- Packet length: 66
- Number of bytes: 66
- Recieved time: Sat Apr 28 19:57:50 2012
- 08 00 27 9c ff b1 0a 00 27 00 00 00 08 00 45 00
- 00 34 d4 b4 40 00 40 06 74 58 c0 a8 38 01 c0 a8
- 38 65 8e 20 26 68 79 e1 63 8f b6 c4 e6 e8 80 10
- 00 e5 fb b9 00 00 01 01 08 0a 00 14 b7 26 00 57
- a1 2e
仔细研究即可发现服务器与客户机是如何通过tcp通信的。
下面的这个程序可以获取eth0的ip和子网掩码等信息:
test5:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <pcap.h>
- #include <errno.h>
- #include <netinet/in.h>
- #include <arpa/inet.h>
- int main()
- {
- /* ask pcap to find a valid device for use to sniff on */
- char * dev; /* name of the device */
- char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
- dev = pcap_lookupdev(errbuf);
- /* error checking */
- if(!dev)
- {
- printf("pcap_lookupdev() error: %s\n", errbuf);
- exit(1);
- }
- /* print out device name */
- printf("dev name: %s\n", dev);
- /* ask pcap for the network address and mask of the device */
- bpf_u_int32 netp; /* ip */
- bpf_u_int32 maskp; /* subnet mask */
- int ret; /* return code */
- ret = pcap_lookupnet(dev, &netp, &maskp, errbuf);
- if(ret == -1)
- {
- printf("pcap_lookupnet() error: %s\n", errbuf);
- exit(1);
- }
- /* get the network address in a human readable form */
- char * net; /* dot notation of the network address */
- char * mask; /* dot notation of the network mask */
- struct in_addr addr;
- addr.s_addr = netp;
- net = inet_ntoa(addr);
- if(!net)
- {
- perror("inet_ntoa() ip error: ");
- exit(1);
- }
- printf("ip: %s\n", net);
- /* do the same as above for the device's mask */
- addr.s_addr = maskp;
- mask = inet_ntoa(addr);
- if(!mask)
- {
- perror("inet_ntoa() sub mask error: ");
- exit(1);
- }
- printf("sub mask: %s\n", mask);
- return 0;
- }
结果如图:
int pcap_lookupnet(const char * device, bpf_u_int32 * netp, bpf_u_int32 * maskp, char * errbuf)
可以获取指定设备的ip地址,子网掩码等信息
netp:传出参数,指定网络接口的ip地址
maskp:传出参数,指定网络接口的子网掩码
pcap_lookupnet()失败返回-1
我们使用inet_ntoa()将其转换为可读的点分十进制形式的字符串
本文的绝大部分来源于libpcap的官方文档:libpcapHakin9LuisMartinGarcia.pdf,可以在官网下载,文档只有9页,不过很详细,还包括了数据链路层,网络层,传输层,应用层等的分析。很好!
更多参考可以man pcap
最后为了方便大家,本文的所有代码和上述的pdf文档都一并上传上来了:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/htttw/4264686
完成!
libpcap使用的更多相关文章
- 基于Linux平台的libpcap源码分析和优化
目录 1..... libpcap简介... 1 2..... libpcap捕包过程... 2 2.1 数据包基本捕包流程... 2 2.2 libpcap捕包过程... ...
- 给libpcap增加一个新的捕包方法
libpcap是一个网络数据包捕获函数库,功能非常强大,提供了系统独立的用户级别网络数据包捕获接口,Libpcap可以在绝大多数类unix 平台下工作.大多数网络监控软件都以它为基础,著名的tcpdu ...
- Ubuntu下libpcap安装
1.首先按下面的博客教程下载和安装四个软件包: 点击打开链接 2.这四个软件都安装好之后按下面教程新建Makefile文件和test.c文件: 点击打开链接 Makefie: all: test.c ...
- libpcap和WinPcap
能从物理上访问网络上的流量后,你需要用软件把它记录下来.这里,我们探究记录.解析和分析被捕获的数据包中最常用的软件库:libpcap和WinPcap.也将介绍包括tcpdump.Wireshark等基 ...
- libpcap/wwinpcap
winpcap(windows packet capture)是windows平台下一个免费,公共的网络访问系统.开发winpcap这个项目的目的在于为win32应用程序提供访问网络底层的能力.win ...
- CentOS安装libpcap
1.安装GCC: yum -y install gcc-c++ 2.安装flex: yum -y install flex 没有flex,直接安装libpcap会提示"Your o ...
- libpcap 主要函数及过程详解
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-21556133-id-120228.html libpcap(Packet Capture Library),即数据包捕获函数库,是Uni ...
- 基于 libpcap库的sniffer程序
基于 libpcap库的sniffer程序 Libpcap库是WireSharek和Tcpdump抓包程序的基础,利用libcap我们自己也可以实现自己的抓包程序,在网络上实时抓包分析,或者利用处理的 ...
- Develop a Packet Sniffer with libpcap
Develop a Packet Sniffer with libpcap: http://vichargrave.com/develop-a-packet-sniffer-with-libpcap/
随机推荐
- directUI
MFC界面开发中,习惯了使用控件,亦或者是自绘制控件来美化界面,但操作起来繁琐,还不太美观.DirectUI的出现,对于界面开发,给了我们一个新的选择,目前很多公司使用了该技术对其产品进行了美化,效果 ...
- iOS: 学习笔记实例, 用代码控制视图创建与切换
1. 创建iOS, Single View Application.2. 修改YYViewController.m // // YYViewController.m // DynamicViewDem ...
- Lambda表达式, 可以让我们的代码更优雅.
在C#中, 适当地使用Lambda表达式, 可以让我们的代码更优雅. 通过lambda表达式, 我们可以很方便地创建一个delegate: 下面两个语句是等价的 Code highlighting p ...
- servlet跳转jsp
ackage com.monkey.servlet; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; import java.io.*; im ...
- Noah的学习笔记之Python篇:命令行解析
Noah的学习笔记之Python篇: 1.装饰器 2.函数“可变长参数” 3.命令行解析 注:本文全原创,作者:Noah Zhang (http://www.cnblogs.com/noahzn/) ...
- windows相关小知识
获得本机MAC1 快捷键win+R打开运行窗口, 输入cmd回车进入控制台2 输入ipconfig -all 找到本地连接中的物理地址 根据IP获得MAC方法:1 进入cmd控制台,执行:ping ...
- Dataguard配置前提条件
Data Guard配置前提条件 配置Data Guard必须保证以下前提条件: 1.Data Guard是Oracle企业版的组件.Oracle标准版里没有这个控件.所以Data Guard配置所使 ...
- Contest20140711 loop 数论
loop|loop.in|loop.out 题目描述: 有N个点. 现在重复这样的操作: 随机找一个出度为0的点p1,随机找一个入度为0的点p2,连一条有向边从p1指向p2.直到没有出度为0的点. 统 ...
- BZOJ 4008 亚瑟王
Description 小K不慎被LL邪教洗脑了,洗脑程度深到他甚至想要从亚瑟王邪教中脱坑. 他决定,在脱坑之前,最后再来打一盘亚瑟王.既然是最后一战,就一定要打得漂亮.众所周知,亚瑟王是一个看脸的游 ...
- ‘char *' differs in levels of indirection from 'int'
这个问题是有与和系统变量重名导致的,如 char* ans = (char*) malloc(10);系统变量是一个int.
