Pytorch基础(6)----参数初始化
一、使用Numpy初始化:【直接对Tensor操作】
对Sequential模型的参数进行修改:
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn # 定义一个 Sequential 模型
net1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(30, 40),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(40, 50),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(50, 10)
) # 访问第一层的参数
w1 = net1[0].weight
b1 = net1[0].bias
print(w1) #对第一层Linear的参数进行修改:
# 定义第一层的参数 Tensor 直接对其进行替换
net1[0].weight.data = torch.from_numpy(np.random.uniform(3, 5, size=(40, 30)))
print(net1[0].weight)
23
24 #若模型中相同类型的层都需要初始化成相同的方式,一种更高效的方式:使用循环去访问:
25 for layer in net1:
26 if isinstance(layer, nn.Linear): # 判断是否是线性层
27 param_shape = layer.weight.shape
28 layer.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(np.random.normal(0, 0.5, size=param_shape))
29 # 定义为均值为 0,方差为 0.5 的正态分布
对Module模型 的参数初始化:
对于 Module 的参数初始化,其实也非常简单,如果想对其中的某层进行初始化,可以直接像 Sequential 一样对其 Tensor 进行重新定义,其唯一不同的地方在于,如果要用循环的方式访问,需要介绍两个属性,children 和 modules,下面我们举例来说明:
1、创建Module模型类:
class sim_net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(sim_net, self).__init__()
self.l1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(30, 40),
nn.ReLU()
) self.l1[0].weight.data = torch.randn(40, 30) # 直接对某一层初始化 self.l2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(40, 50),
nn.ReLU()
) self.l3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(50, 10),
nn.ReLU()
) def forward(self, x):
x = self.l1(x)
x =self.l2(x)
x = self.l3(x)
return x
2、创建模型对象:
net2 = sim_net()
3、访问children:
# 访问 children
for i in net2.children():
print(i)
#打印的结果:
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=30, out_features=40)
(1): ReLU()
)
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=40, out_features=50)
(1): ReLU()
)
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=50, out_features=10)
(1): ReLU()
)
4、访问modules:
# 访问 modules
for i in net2.modules():
print(i) #打印的结果
sim_net(
(l1): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=30, out_features=40)
(1): ReLU()
)
(l2): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=40, out_features=50)
(1): ReLU()
)
(l3): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=50, out_features=10)
(1): ReLU()
)
)
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=30, out_features=40)
(1): ReLU()
)
Linear(in_features=30, out_features=40)
ReLU()
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=40, out_features=50)
(1): ReLU()
)
Linear(in_features=40, out_features=50)
ReLU()
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=50, out_features=10)
(1): ReLU()
)
Linear(in_features=50, out_features=10)
ReLU()
通过上面的例子,可以看到:
children 只会访问到模型定义中的第一层,因为上面的模型中定义了三个 Sequential,所以只会访问到三个 Sequential,而 modules 会访问到最后的结构,比如上面的例子,modules 不仅访问到了 Sequential,也访问到了 Sequential 里面,这就对我们做初始化非常方便。
5、采用循环初始化:
for layer in net2.modules():
if isinstance(layer, nn.Linear):
param_shape = layer.weight.shape
layer.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(np.random.normal(0, 0.5, size=param_shape))
二、torch.nn.init初始化
PyTorch 还提供了初始化的函数帮助我们快速初始化,就是 torch.nn.init,其操作层面仍然在 Tensor 上。先介绍一种初始化方法:
Xavier 初始化方法:
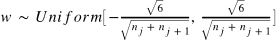
其中 和
表示该层的输入和输出数目。
这种非常流行的初始化方式叫 Xavier,方法来源于 2010 年的一篇论文 Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks,其通过数学的推到,证明了这种初始化方式可以使得每一层的输出方差是尽可能相等的。
torch.nn.init:
from torch.nn import init init.xavier_uniform(net1[0].weight) # 这就是上面我们讲过的 Xavier 初始化方法,PyTorch 直接内置了其实现 #这就直接修改了net1[0].weight的值
Pytorch基础(6)----参数初始化的更多相关文章
- pytorch对模型参数初始化
1.使用apply() 举例说明: Encoder :设计的编码其模型 weights_init(): 用来初始化模型 model.apply():实现初始化 # coding:utf- from t ...
- PyTorch常用参数初始化方法详解
1. 均匀分布 torch.nn.init.uniform_(tensor, a=0, b=1) 从均匀分布U(a, b)中采样,初始化张量. 参数: tensor - 需要填充的张量 a - 均匀分 ...
- PyTorch模型读写、参数初始化、Finetune
使用了一段时间PyTorch,感觉爱不释手(0-0),听说现在已经有C++接口.在应用过程中不可避免需要使用Finetune/参数初始化/模型加载等. 模型保存/加载 1.所有模型参数 训练过程中,有 ...
- 【转载】 pytorch自定义网络结构不进行参数初始化会怎样?
原文地址: https://blog.csdn.net/u011668104/article/details/81670544 ------------------------------------ ...
- pytorch和tensorflow的爱恨情仇之参数初始化
pytorch和tensorflow的爱恨情仇之基本数据类型 pytorch和tensorflow的爱恨情仇之张量 pytorch和tensorflow的爱恨情仇之定义可训练的参数 pytorch版本 ...
- DL基础补全计划(五)---数值稳定性及参数初始化(梯度消失、梯度爆炸)
PS:要转载请注明出处,本人版权所有. PS: 这个只是基于<我自己>的理解, 如果和你的原则及想法相冲突,请谅解,勿喷. 前置说明 本文作为本人csdn blog的主站的备份.(Bl ...
- [源码解析] PyTorch分布式(6) -------- DistributedDataParallel -- 初始化&store
[源码解析] PyTorch分布式(6) ---DistributedDataParallel -- 初始化&store 目录 [源码解析] PyTorch分布式(6) ---Distribu ...
- pytorch基础教程1
0.迅速入门:根据上一个博客先安装好,然后终端python进入,import torch ******************************************************* ...
- [人工智能]Pytorch基础
PyTorch基础 摘抄自<深度学习之Pytorch>. Tensor(张量) PyTorch里面处理的最基本的操作对象就是Tensor,表示的是一个多维矩阵,比如零维矩阵就是一个点,一维 ...
随机推荐
- 依据矩阵的二维相关系数进行OCR识别
我想通过简单的模板匹配来进行图像识别. 把预处理好的字符图片,分别与A到Z的样本图片进行模板匹配. 结果最大的表明相关性最大,就能够识别字符图片了. 在实际应用中.我用了openCV的matchTem ...
- Gulp帮你自己主动搞定coffee和scss的compile
今天继续说说gulp的watch,能够自己主动搞定非常多事情.不用每次都去敲命令了! 上次说到用gulp能够非常方便的进行css,js,html的压缩.而且能够对coffee和scss进行编译. cs ...
- Chrome development tools学习笔记(3)
(上次DOM的部分做了些补充,欢迎查看Chrome development tools学习笔记(2)) 利用DevTools Elements工具来调试页面样式 CSS(Cascading Style ...
- MySql 同一个列中的内容进行批量改动
问题重现: MySql 数据库中,一给列的内容中包含 ".wmv" 须要将 "." 后的wmv格式 换为"flv" 解决的方法 up ...
- Qt graphic item日记
今天在用用graphic view 加入graphic item的时候要引入一个context menu,自然就要对context menu上的action进行slot处理.可是graphic ite ...
- Java-CyclicBarrier的简单样例
内容:一个主任务等待两个子任务,通过CyclicBarrier的await()实现.此Runnable任务在CyclicBarrier的数目达到后,全部其他线程被唤醒前被运行. public clas ...
- luogu2320 鬼谷子的钱袋
题目大意 鬼谷子决定将自己的金币数好并用一个个的小钱袋装好,以便在他现有金币的支付能力下,任何数目的金币他都能用这些封闭好的小钱的组合来付账.求钱袋数最少,并且不有两个钱袋装有相同的大于1的金币数的装 ...
- luogu2763 试题库问题 二分匹配
关键词:二分匹配 本题用有上下界的网络流可以解决,但编程复杂度有些高. 每个类需要多少题,就设置多少个类节点.每个题节点向其所属的每一个类节点连一条边.这样就转化成了二分匹配问题. #include ...
- SqlServer 自动备份策略设置
企业管理器中的Tools,Database Maintenance Planner,可以设置数据库的定期自动备份计划.并通过启动Sql server Agent来自动运行备份计划.具体步骤如下: 1. ...
- hdu 2988(最小生成树 kruskal算法)
Dark roads Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total ...
