Python 3 利用 Dlib 19.7 和 sklearn机器学习模型 实现人脸微笑检测
0. 引言
利用机器学习的方法训练微笑检测模型,输入一张人脸照片,判断是否微笑;
精度在 95% 左右( 使用的数据集中 69 张没笑脸,65 张有笑脸 );
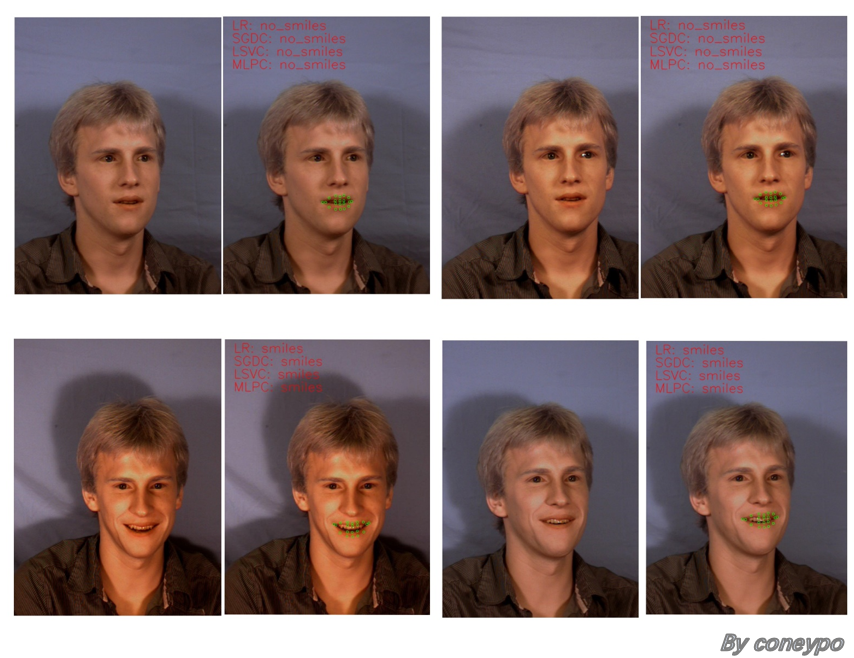

图1 测试图像与检测结果
项目实现的笑脸识别,并不是通过 计算嘴唇角度,满足一定弧度认定为笑脸进行判定,
而是通过机器学习模型,让模型去 学习人脸嘴唇的坐标和判定笑脸的关系:
输入: 人脸嘴唇的坐标
输出: 有没笑脸
借助 Dlib 进行 人脸嘴部 20 个特征点坐标( 40 维特征)的提取,然后根据这 40 维输入特征 作为 模型输入, 1 维特征( 1 代表有微笑 / 0 代表没微笑)作为 输出,进行 Machine Learning 建模;
利用几种机器学习模型进行建模,达到一个二分类(分类 有/无 笑脸)的目的,然后分析模型识别精度和性能,并且可以识别给定图片的人脸是否微笑;
源码:
GitHub: https://github.com/coneypo/Smile_Detector
1. get_features.py :
get_features(img_rd, pos_49to68) # 输入人脸图像路径,利用 Dlib 的 “shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat” 提取嘴部20个特征点坐标的40个特征值;
write_into_CSV() # 将40维特征输入和1维的输出标记(1代表有微笑/0代表没微笑)写入 CSV 文件中;
2. ML_ways_sklearn.py :
pre_data() # 读取 CSV 中的数据,然后提取出训练集 X_train 和测试集 X_test 3. show_lip.py :
显示某人嘴唇的位置
4. check_smiles.py:
输入给定测试图像,用 ML 模型检测其 有/无笑脸;
用到的几种机器学习分类模型:
model_LR() , Logistic Regression, (线性模型)中的逻辑斯特回归
model_Linear SVC() ,Support Vector Classification, (支持向量机)中的线性支持向量分类
model_MLPC() , Multi-Layer Perceptron Classification, (神经网络)多层感知机分类
model_SGDC() , Stochastic Gradient Descent Classification,(线性模型)随机梯度法求解
1. 开发环境
Python: 3.6.3
Dlib: 19.7
OpenCv, NumPy, sklearn, pandas, os, csv 等
get_features.py 中调用的库:
import dlib # 人脸识别的库 Dlib
import numpy as np # 数据处理的库 Numpy
import cv2 # 图像处理的库 OpenCv
import os # 读取文件
import csv # csv操作
ML_ways_sklearn.py 中调用的库:
# pd 读取 CSV
import pandas as pd # 分割数据
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 用于数据预加工标准化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression # 线性模型中的Logistic回归模型
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier # 神经网络模型中的多层网络模型
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC # SVM模型中的线性SVC模型
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier # 线性模型中的随机梯度下降模型
使用的人脸来自于 The MUCT Face Database(Link:http://www.milbo.org/muct/)
(The MUCT database was prepared by Stephen Milborrow, John Morkel, and Fred Nicolls in December 2008 at the University Of Cape Town. We would like to send out a thanks to the people who allowed their faces to be used.)
2. 设计流程
工作内容主要以下两大块:提取人脸特征 和 建模;
整体的设计流程如下图所示:
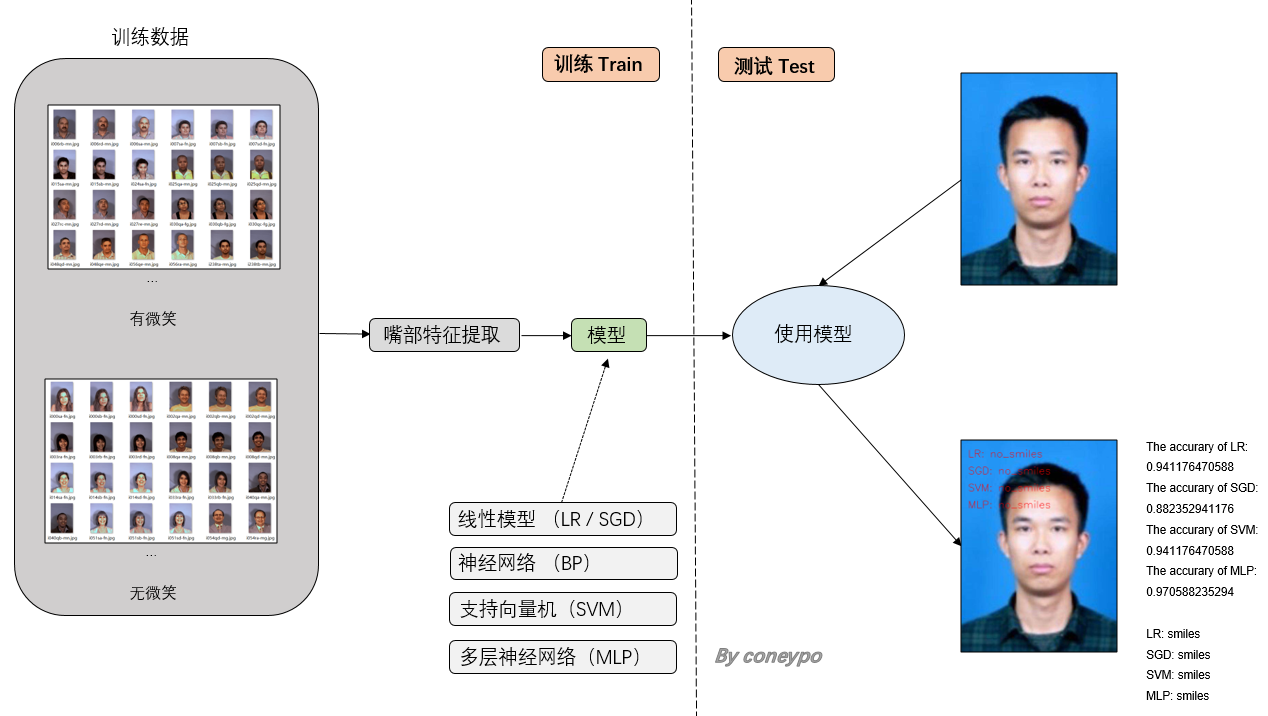
图 2 总体设计流程图
2.1 提取人脸特征:
该部分的设计流程图:
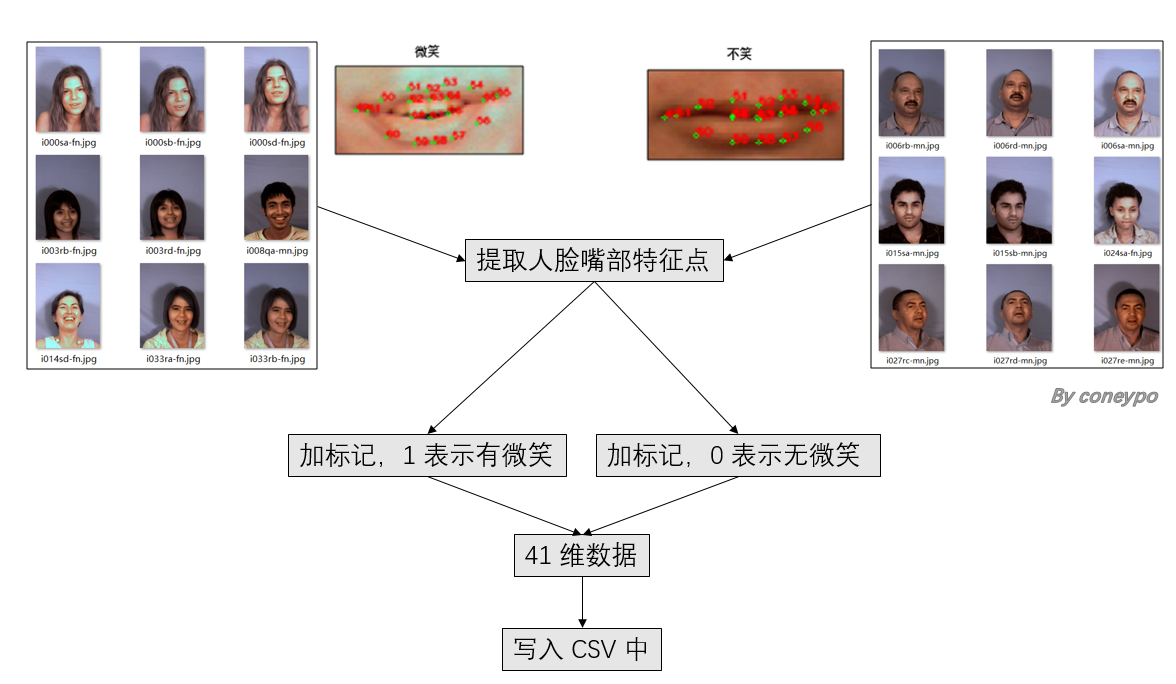
图 3 人脸提取特征部分流程图
先在项目目录下建立两个文件夹,分别存放
有笑脸的人脸的路径 : path_images_with_smiles = "data_imgs/database/smiles/"
无笑脸的人脸的路径: path_images_no_smiles = "data_imgs/database/no_smiles/"
这样之后读取的时候就可以知道人脸的标记有/无人脸;
关于利用 Dlib 进行人脸 68个特征点的提取,在我之前另一篇博客里面介绍过 (link: http://www.cnblogs.com/AdaminXie/p/7905888.html);
本项目中只使用其中嘴部 20个特征点的坐标作为特征输入,20个点的序号如下图所示:
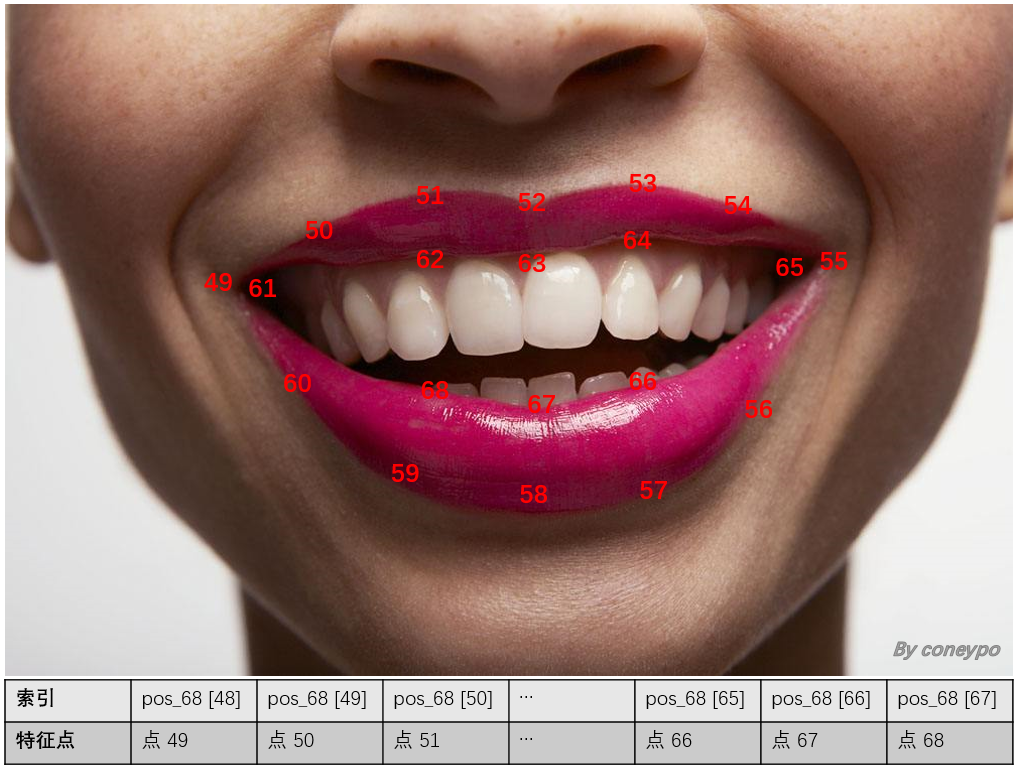
图 4 Dlib 标定的嘴部特征点序号
20 个特征点 40 个坐标值的提取,由 get_features() 函数实现;
输入是图像文件所在路径,返回的的是数组 pos_49to68(40个为特征点坐标值)
# 输入图像文件所在路径,返回一个41维数组(包含提取到的40维特征和1维输出标记)
def get_features(img_rd): # 输入: img_rd: 图像文件
# 输出: pos_49to68: feature 49 to feature 68, 20 feature points in all, 40 points # read img file
img = cv2.imread(img_rd)
# 取灰度
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 计算 68 点坐标
pos_68 = []
rects = detector(img_gray, 0)
landmarks = np.matrix([[p.x, p.y] for p in predictor(img, rects[0]).parts()]) for idx, point in enumerate(landmarks):
# 68点的坐标
pos = (point[0, 0], point[0, 1])
pos_68.append(pos) pos_49to68 = []
# 将点 49-68 写入 CSV
# 即 pos_68[48]-pos_68[67]
for i in range(48, 68):
pos_49to68.append(pos_68[i][0])
pos_49to68.append(pos_68[i][1]) return pos_49to68
然后就遍历两个存放有/无笑脸的文件夹,读取图像文件,然后利用 get_features() 函数得到特征值,写入 CSV 中:
def write_into_CSV():
with open(path_csv+"data.csv", "w", newline="") as csvfile:
writer = csv.writer(csvfile) # 处理带笑脸的图像
print("######## with smiles #########")
for i in range(len(imgs_smiles)):
print("img:", path_pic_smiles, imgs_smiles[i]) # 用来存放41维特征
features_csv_smiles = [] # append "1" means "with smiles"
get_features(path_pic_smiles+imgs_smiles[i], features_csv_smiles)
features_csv_smiles.append(1)
print("features:", features_csv_smiles, "\n") # 写入CSV
writer.writerow(features_csv_smiles) # 处理不带笑脸的图像
print("######## no smiles #########")
for i in range(len(imgs_no_smiles)):
print("img", path_pic_no_smiles, imgs_no_smiles[i]) # 用来存放41维特征
features_csv_no_smiles = [] # append "0" means "no smiles"
get_features(path_pic_no_smiles+imgs_no_smiles[i], features_csv_no_smiles)
features_csv_no_smiles.append(0)
print("features:", features_csv_no_smiles, "\n") # 写入CSV
writer.writerow(features_csv_no_smiles)
会得到一个 41 列的 CSV 文件,前 40 列为 40 维的输入特征,第 41 列为笑脸标记。
show_lip.py
# Created on: 2018-01-27
# Updated on: 2018-09-06 # Author: coneypo
# Blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/AdaminXie/
# Github: https://github.com/coneypo/Smile_Detector # draw the positions of someone's lip import dlib # 人脸识别的库 Dlib
import cv2 # 图像处理的库 OpenCv
from get_features import get_features # return the positions of feature points path_test_img = "data_imgs/test_imgs/i064rc-mn.jpg" detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat') pos_49to68 = get_features(path_test_img) img_rd = cv2.imread(path_test_img) # draw on the lip points
for i in range(0, len(pos_49to68), 2):
print(pos_49to68[i],pos_49to68[i+1])
cv2.circle(img_rd, tuple([pos_49to68[i],pos_49to68[i+1]]), radius=1, color=(0,255,0)) cv2.namedWindow("img_read", 2)
cv2.imshow("img_read", img_rd)
cv2.waitKey(0)
2.2 ML 建模和测试
这部分机器学习模型使用比较简单,之前的特征提取已经完成,写入了 CSV 文件中;接下来就是要从 CSV 中将想要的数据集提取出来,利用 sklearn 进行机器学习建模。
2.2.1 数据预加工
利用 pands.read_csv 读取 CSV 文件,然后利用 train_test_split 进行数据分割;
得到 训练集:X_train, y_train 和 测试集:X_test, y_test
# 从 csv 读取数据
def pre_data():
# 41维表头
column_names = []
for i in range(0, 40):
column_names.append("feature_" + str(i + 1))
column_names.append("output") # read csv
rd_csv = pd.read_csv("data_csv/data.csv", names=column_names) # 输出 csv 文件的维度
# print("shape:", rd_csv.shape) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( # input 0-40
# output 41
rd_csv[column_names[0:40]],
rd_csv[column_names[40]], # 25% for test, 75% for train
test_size=0.25,
random_state=33) return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
2.2.2 机器学习建模
几种建模方法在 sklearn 中实现的代码类似,所以在此只介绍 LR, logistic regression, 逻辑斯特回归分类,它是属于线性模型一种;
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
利用 LR.fit 训练数据:LR.fit(X_train_LR, y_train_LR),利用 LR.predict 预测标记:y_predict_LR = LR_predict(X_test_LR);
返回 ss_LR 和 LR,需要这两个返回值,是因为之后要利用它们对给定图像的进行检测,之后 2.2.3 节会介绍;
# LR, logistic regression, 逻辑斯特回归分类(线性模型)
def model_LR():
# get data
X_train_LR, X_test_LR, y_train_LR, y_test_LR = pre_data() # 数据预加工
# 标准化数据,保证每个维度的特征数据方差为1,均值为0。使得预测结果不会被某些维度过大的特征值而主导
ss_LR = StandardScaler()
X_train_LR = ss_LR.fit_transform(X_train_LR)
X_test_LR = ss_LR.transform(X_test_LR) # 初始化 LogisticRegression
LR = LogisticRegression() # 调用 LogisticRegression 中的 fit() 来训练模型参数
LR.fit(X_train_LR, y_train_LR) # save LR model
joblib.dump(LR, path_models + "model_LR.m") # 评分函数
score_LR = LR.score(X_test_LR, y_test_LR)
# print("The accurary of LR:", score_LR) return (ss_LR)
我的数据集里面是69张没笑脸,65张有笑脸,测试精度如下,精度在95%附近:
The accurary of LR: 0.941176470588
The accurary of SGD: 0.882352941176
The accurary of SVM: 0.941176470588
The accurary of MLP: 0.970588235294
2.2.3 测试单张图片
现在我们已经建好机器学习模型,在 2.2.2 中可以利用 sklearn 机器学习模型的 score 函数得到模型精度;
但是如果想检测给定图像的笑脸,需要进行该部分工作:path_test_pic 就是需要进行检测的文件路径,需要精确到图像文件,比如 “F:/pic/test.pic”;
然后调用 get_features.py 中的 get_features() 函数进行特征提取,得到给定图像的40维特征数组 pos_49_68;
check_smile.py:
# Created on: 2018-01-27
# Updated on: 2018-09-07
# Author: coneypo
# Blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/AdaminXie/
# Github: https://github.com/coneypo/Smile_Detector # use the saved model
from sklearn.externals import joblib from get_features import get_features
import ML_ways_sklearn import cv2 # path of test img
path_test_img = "data_imgs/test_imgs/test1.jpg" # 提取单张40维度特征
pos_49to68_test = get_features(path_test_img) # path of models
path_models = "data_models/" print("The result of"+path_test_img+":")
print('\n') # ######### LR ###########
LR = joblib.load(path_models+"model_LR.m")
ss_LR = ML_ways_sklearn.model_LR()
X_test_LR = ss_LR.transform([pos_49to68_test])
y_predict_LR = str(LR.predict(X_test_LR)[0]).replace('', "no smile").replace('', "with smile")
print("LR:", y_predict_LR) # ######### LSVC ###########
LSVC = joblib.load(path_models+"model_LSVC.m")
ss_LSVC = ML_ways_sklearn.model_LSVC()
X_test_LSVC = ss_LSVC.transform([pos_49to68_test])
y_predict_LSVC = str(LSVC.predict(X_test_LSVC)[0]).replace('', "no smile").replace('', "with smile")
print("LSVC:", y_predict_LSVC) # ######### MLPC ###########
MLPC = joblib.load(path_models+"model_MLPC.m")
ss_MLPC = ML_ways_sklearn.model_MLPC()
X_test_MLPC = ss_MLPC.transform([pos_49to68_test])
y_predict_MLPC = str(MLPC.predict(X_test_MLPC)[0]).replace('', "no smile").replace('', "with smile")
print("MLPC:", y_predict_MLPC) # ######### SGDC ###########
SGDC = joblib.load(path_models+"model_SGDC.m")
ss_SGDC = ML_ways_sklearn.model_SGDC()
X_test_SGDC = ss_SGDC.transform([pos_49to68_test])
y_predict_SGDC = str(SGDC.predict(X_test_SGDC)[0]).replace('', "no smile").replace('', "with smile")
print("SGDC:", y_predict_SGDC) img_test = cv2.imread(path_test_img) img_height = int(img_test.shape[0])
img_width = int(img_test.shape[1]) # show the results on the image
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
cv2.putText(img_test, "LR: "+y_predict_LR, (int(img_height/10), int(img_width/10)), font, 0.8, (84, 255, 159), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_test, "LSVC: "+y_predict_LSVC, (int(img_height/10), int(img_width/10*2)), font, 0.8, (84, 255, 159), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_test, "MLPC: "+y_predict_MLPC, (int(img_height/10), int(img_width/10)*3), font, 0.8, (84, 255, 159), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_test, "SGDC: "+y_predict_SGDC, (int(img_height/10), int(img_width/10)*4), font, 0.8, (84, 255, 159), 1, cv2.LINE_AA) cv2.namedWindow("img", 2)
cv2.imshow("img", img_test)
cv2.waitKey(0)
3. 实现效果
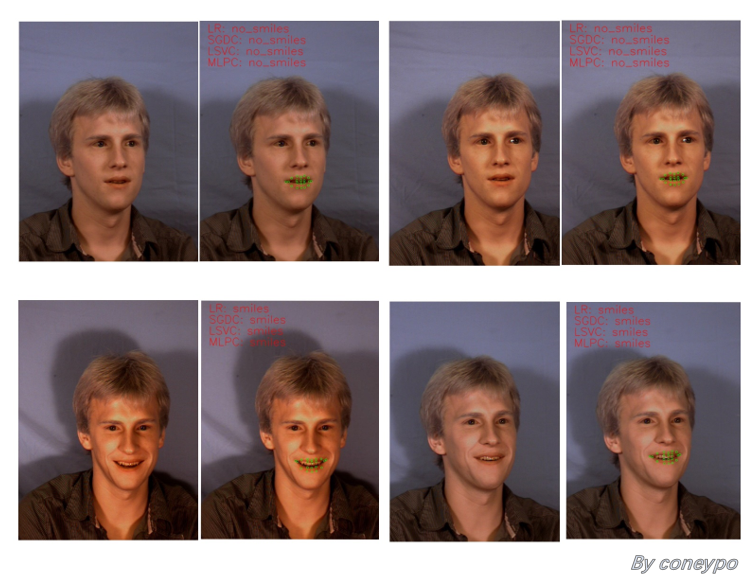

图 5 同一个人不同表情的笑脸检测结果
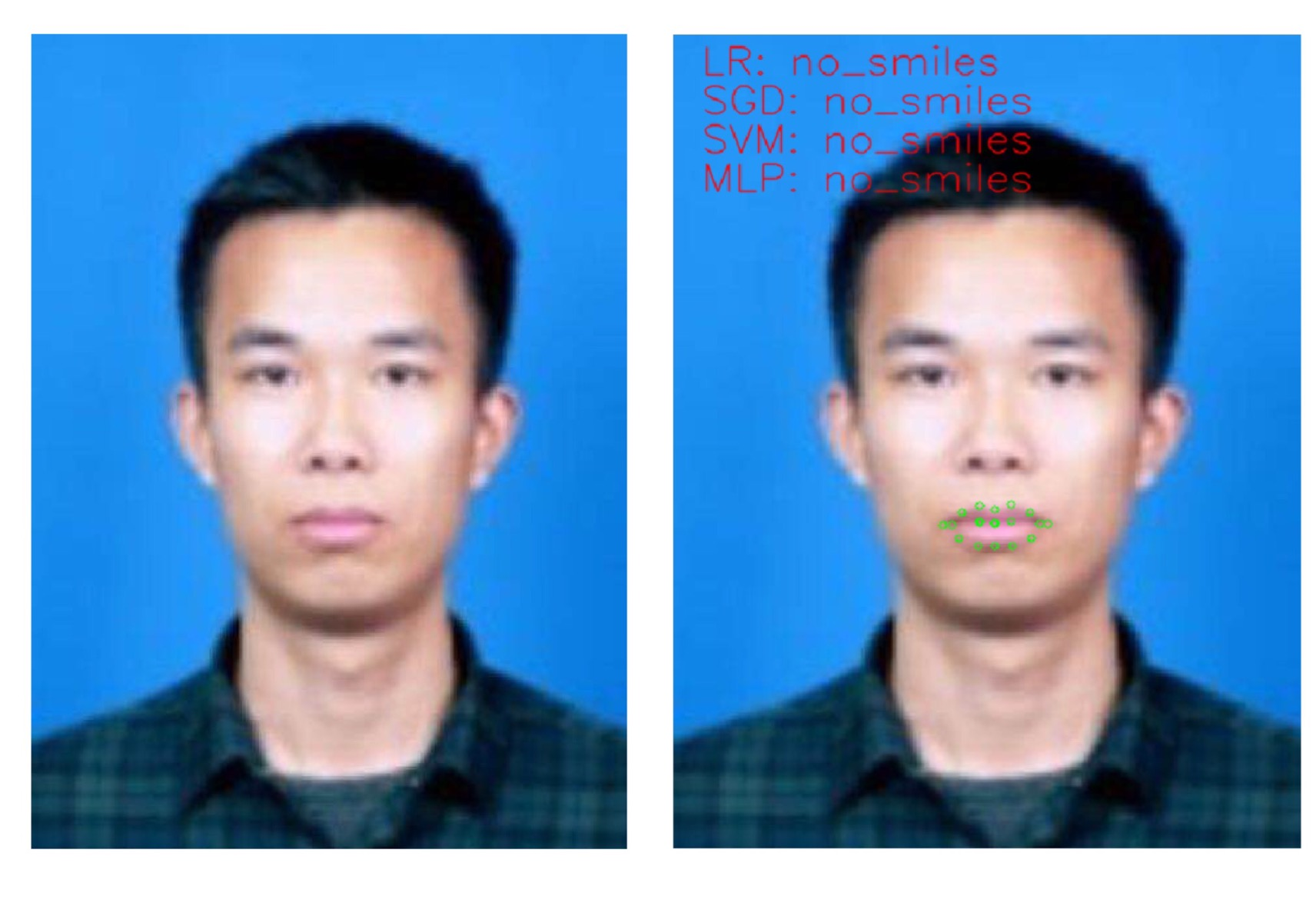


图 6 检测到没微笑


图 7 检测到有微笑
4. 总结
数据集中有无笑脸是自己进行分类的,而且有写的表情不太好界定,所以选取的是一些笑容比较明显的照片作为有笑脸,所以可能出来模型在检测一些微笑上有误差;
笑容检测模型的数据集测试精度在 95% 左右,比较理想;
其实人脸笑容检测的话,光靠嘴部特征去判断不太合适,要结合整张人脸特征点进行训练,改进的话也比较简单;
# 源码上传到了 GitHub,我也在不断更新优化,如果对您有帮助或者感兴趣欢迎 Star 支持我: https://github.com/coneypo/Smile_Detector
# 请尊重他人劳动成果,转载或者使用源码请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/AdaminXie
# 交流学习可以联系邮箱 coneypo@foxmail.com
Python 3 利用 Dlib 19.7 和 sklearn机器学习模型 实现人脸微笑检测的更多相关文章
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 19.7 实现人脸识别和剪切
0.引言 利用python开发,借助Dlib库进行人脸识别,然后将检测到的人脸剪切下来,依次排序显示在新的图像上: 实现的效果如下图所示,将图1原图中的6张人脸检测出来,然后剪切下来,在图像窗口中依次 ...
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 19.7 实现摄像头人脸识别
0.引言 利用python开发,借助Dlib库捕获摄像头中的人脸,提取人脸特征,通过计算欧氏距离来和预存的人脸特征进行对比,达到人脸识别的目的: 可以自动从摄像头中抠取人脸图片存储到本地: 根据抠取的 ...
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 19.7 进行人脸检测
0. 引言 / Overview 介绍 Dlib 中基于 HOG,Histogram of Oriented Gradients / 方向梯度直方图 实现 Face Detect / 人脸检测 的两个 ...
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 实现摄像头实时人脸检测和平铺显示
1. 引言 在某些场景下,我们不仅需要进行实时人脸检测追踪,还要进行再加工:这里进行摄像头实时人脸检测,并对于实时检测的人脸进行初步提取: 单个/多个人脸检测,并依次在摄像头窗口,实时平铺显示检测到的 ...
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 实现摄像头人脸检测特征点标定
0. 引言 利用 Python 开发,借助 Dlib 库捕获摄像头中的人脸,进行实时人脸 68 个特征点标定: 支持多张人脸: 有截图功能: 图 1 工程效果示例( gif ) 图 2 工程效果示例( ...
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 实现人脸检测和剪切
0. 引言 利用 Python 开发,借助 Dlib 库进行人脸检测 / face detection 和剪切: 1. crop_faces_show.py : 将检测到的人脸剪切下来,依次排序平 ...
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 和 sklearn 人脸笑脸检测机器学习建模
0. 引言 利用机器学习的方法训练微笑检测模型,输入一张人脸照片,判断是否微笑: 精度在 95% 左右( 使用的数据集中 69 张没笑脸,65 张有笑脸 ): 图1 测试图像与检测结果 项目实现的笑脸 ...
- Python 3 利用机器学习模型 进行手写体数字检测
0.引言 介绍了如何生成手写体数字的数据,提取特征,借助 sklearn 机器学习模型建模,进行识别手写体数字 1-9 模型的建立和测试. 用到的几种模型: 1. LR,Logistic Regres ...
- Python 3.6.3 利用 Dlib 19.7 和 opencv 实现人脸68点定位 进行人脸识别
0.引言 介绍利用Dlib官方给的人脸识别预测器"shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat"进行68点标定,利用OpenCv进行图像化处理,在人脸 ...
随机推荐
- 搭建PHP本地服务器(XAMPP)
1.下载XAMPP集成包 https://www.apachefriends.org/download.html2.启动前修改配置文件httpd.conf的端口号,例如:Listen 80803.启动 ...
- 房上的猫:类和对象>万物皆对象
众所周知:java是一门面向对象的编程语言 本章将介绍基础的类和对象 一.对象 对象是用来描述客观事物的一个实体,由一组属性和方法构成二.封装 封装就是把一个事物包装起来,并尽可能隐藏内部细节三.类 ...
- [js高手之路]面向对象版本匀速运动框架
这篇文章的效果,需要看过以下3篇文章: [js插件开发教程]一步步开发一个可以定制配置的隔行变色小插件 [js高手之路]匀速运动与实例实战(侧边栏,淡入淡出) [js高手之路]打造通用的匀速运动框架 ...
- Java贪吃蛇感想
暑假敲代码的效率真的不高呀,一个这种小游戏从最开始构思到最后实施代码,从最开始的Demo版本到最后的第四版本,花了一个星期了.本想再更新一个版本,加入双人对战模式,还想写个AI版,可是我估计按照现在我 ...
- 配置apache的文件访问路径
本例中,我们让apache访问"F:/testObject/php"路径: 一.修改http.conf文件配置 访问路径:"apache/conf/httpd.conf& ...
- JavaScript Html页面加载完成
//一.Html页面加载完成的JS写法 //1. $(function () { alert("窗体Html页面加载完成方法一"); }); //2. $(document ...
- for循环找出2到100的质数(素数)
思路: 1,一个数只有1和它本身两个因数,这个数叫质数. 2.注意:缩进这里else是for循环这个上下文的. 代码: for num in range(2,100): #为大循环变量num提供2-1 ...
- Js默认参数(多参数情况)
js function example(settings) { var defaultSetting = { name: '小红', age: '30', sex: '女', phone: '1008 ...
- Mysql安装与主从配置
安装MySql 操作系统:Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard MySql版本:mysql-5.7.17-winx64 第一步:解压mysql-5.7.17-winx64.z ...
- mysql数据库表结构与表约束
表结构操作: 添加单列:alter table tb_name add [column] col_name 添加一列: alter table `sudty` add `aaa` int; 添加多列: ...
