Netty源码分析之NioEventLoop(二)—NioEventLoop的启动
上篇文章中我们对Netty中NioEventLoop创建流程与源码进行了跟踪分析。本篇文章中我们接着分析NioEventLoop的启动流程;
Netty中会在服务端启动和新连接接入时通过chooser选择器,分别为NioServerSocketChannel与NioSocketChannel选择绑定一个NioEventLoop,接下来我们就分别从这两个方面梳理NioEventLoop的启动源码
一、服务端启动
首先我们结合下图看下Netty服务启动过程中,NioServerSocketChannel绑定的NioEventLoop启动流程
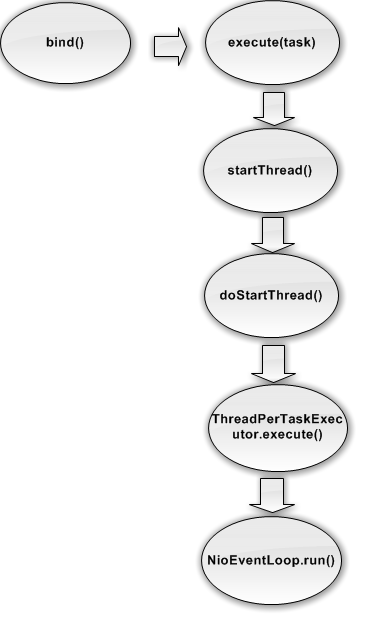
bind()部分源码我们在之前服务端启动过程中进行过说明,我们进一步跟踪进入doBind0()方法中可以看到channel.eventLoop().execute的执行,需要说明的是这里其实启动的NioServerSocketChannel绑定的 bossGroup,用来负责处理新连接接入的。
/**
* read by jsf
*
* @param regFuture
* @param channel
* @param localAddress
* @param promise
*/
private static void doBind0(final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel, final SocketAddress localAddress,
final ChannelPromise promise) {
//该方法向 NioServerSocketChannel 的 eventLoop 提交了一个任务,当 future(其实就是 promise) 成功后执行
//NioServerSocketChannel 的 bind 方法,并添加一个关闭监听器。我们主要关注 bind 方法。
// This method is invoked before channelRegistered() is triggered. Give user
// handlers a chance to set up
// the pipeline in its channelRegistered() implementation.
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) { channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}
进入NioEventLoop父类SingleThreadEventExecutor中的execute方法,改方法通过inEventLoop()会首先判断当前的线程是否是NioEventLoop本身绑定的线程,结合inEventLoop的代码可以看到NioEventLoop本身线程还未初始化为空,这里返回false,执行启动线程操作,同时会任务放入任务队列中。
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
} //首先判断当前线程是否是该EventLoop绑定的线程
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
//把传入的任务加入任务对立
addTask(task);
if (!inEventLoop) {//如果不是同一条线程
startThread();
if (isShutdown() && removeTask(task)) {
reject();
}
} if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
@Override
public boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread) {
return thread == this.thread;
}
继续跟踪进入startThread()方法中
private void startThread() {
if (state == ST_NOT_STARTED) {
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_NOT_STARTED, ST_STARTED)) {
try {
doStartThread();
} catch (Throwable cause) {
STATE_UPDATER.set(this, ST_NOT_STARTED);
PlatformDependent.throwException(cause);
}
}
}
}
在 doStartThread()中主要实现了以下功能:
1、执行传入的ThreadPerTaskExecutor的execute方法,创建一个新的线程,并与这个NioEventLoop对象绑定;
2、在开启的线程中执行SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run(),也就是NioEventLoop的run方法,开始NioEventLoop的执行操作;
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
//线程执行器通过线程工厂创建线程
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//开启线程,并赋值
thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (interrupted) {
thread.interrupt();
}
boolean success = false;
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
//执行NioEventLoop的run方法
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception from an event executor: ", t);
} finally {
for (;;) {
int oldState = state;
if (oldState >= ST_SHUTTING_DOWN || STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, oldState, ST_SHUTTING_DOWN)) {
break;
}
}
// Check if confirmShutdown() was called at the end of the loop.
if (success && gracefulShutdownStartTime == 0) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Buggy " + EventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + " implementation; " +
SingleThreadEventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + ".confirmShutdown() must " +
"be called before run() implementation terminates.");
}
}
try {
// Run all remaining tasks and shutdown hooks.
for (;;) {
if (confirmShutdown()) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
try {
cleanup();
} finally {
STATE_UPDATER.set(SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, ST_TERMINATED);
threadLock.release();
if (!taskQueue.isEmpty()) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("An event executor terminated with " +
"non-empty task queue (" + taskQueue.size() + ')');
}
}
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
}
}
});
}
OK到这一步,基于服务端启动绑定端口的NioServerSocketChannel,也就是服务端Channel绑定的NioEventLoop已经启动。
二、新连接接入
首先我们结合下图看下当有客户端接入时,创建NioSocketChannel,然后绑定NioEventLoop并启动的流程
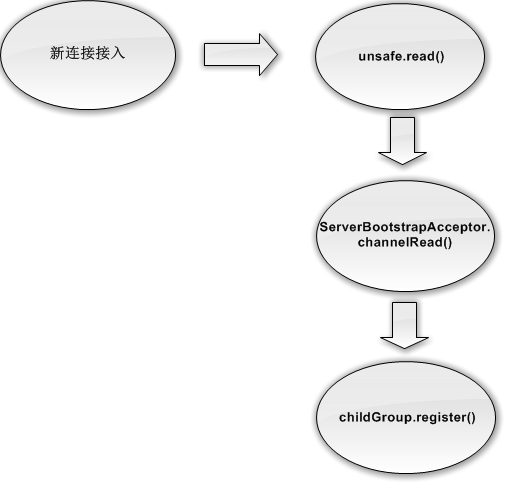
服务端启动时会在NioServerSocketChannel的任务链中添加ServerBootstrapAcceptor对象,这就是用来处理新新连接接入的
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) throws Exception {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
// 服务端NioServerSocketChannel的pipeline中添加ServerBootstrapAcceptor
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
在新连接接入事件触发时,执行unsafe.read();
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
if (!k.isValid()) {
final EventLoop eventLoop;
try {
eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();
} catch (Throwable ignored) {
// If the channel implementation throws an exception because there is no event loop, we ignore this
// because we are only trying to determine if ch is registered to this event loop and thus has authority
// to close ch.
return;
}
// Only close ch if ch is still registered to this EventLoop. ch could have deregistered from the event loop
// and thus the SelectionKey could be cancelled as part of the deregistration process, but the channel is
// still healthy and should not be closed.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/5125
if (eventLoop != this || eventLoop == null) {
return;
}
// close the channel if the key is not valid anymore
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
return;
}
try {
int readyOps = k.readyOps();
// We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise
// the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
// remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
// Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
// Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
// Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead
// to a spin loop
//新连接接入
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}
unsafe.read()的具体实现为NioMessageUnsafe中的read(),在read()方法中主要实现了两个功能:
1、创建客户端Channel,也就是NioSocketChannel;
2、开始服务端NioServerSocketChannel的任务链传递,首先执行之前已经加入任务链的ServerBootstrapAcceptor中的channelRead
@Override
public void read() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
final ChannelConfig config = config();
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config); boolean closed = false;
Throwable exception = null;
try {
try {
do {
//这里创建客户端连接,也就是NioSocketChannelChannel
int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
if (localRead == 0) {
break;
}
if (localRead < 0) {
closed = true;
break;
} allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
} int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
//在这里开始NioServerSocketChannel的任务链传递,会首先执行ServerBootstrapAcceptor中的channelRead
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
readBuf.clear();
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete(); if (exception != null) {
closed = closeOnReadError(exception); pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(exception);
} if (closed) {
inputShutdown = true;
if (isOpen()) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
} finally {
// Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet.
// This could be for two reasons:
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
接下来在ServerBootstrapAcceptor中的channelRead中会获取到传入的NioSocketChannel,针对NioSocketChannel主要会执行以下操作:
1、配置childHandler任务链;
2、配置childOptions;
3、为NioSocketChannel分配NioEventLoop
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
final Channel child = (Channel) msg; //配置childHandler任务链
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler); //配置childOptions
setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger); for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
} try {
//为新连接分配NioEventLoop,并启动执行
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
看以看到EventLoopGroup中register具体实实现:
1、关于next(),我们之前讲过是专门用来分配NioEventLoop;
2、register()主要负责了EventLoop的绑定和启动;
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(ChannelPromise promise) {
return next().register(promise);
}
@Override
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (eventLoop == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("eventLoop");
}
if (isRegistered()) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("registered to an event loop already"));
return;
}
if (!isCompatible(eventLoop)) {
promise.setFailure(
new IllegalStateException("incompatible event loop type: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName()));
return;
} //与NioEventLoop绑定
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop; //首先判断线程是否一致,当前线程是NioServerSocketChannel的线程,与当前创建NioSocketChannel的eventLoop线程不一致
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
//在这里NioEventLoop启动
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(
"Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}",
AbstractChannel.this, t);
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}
上面代码中的 eventLoop.execute我们已经分析过,经过一系列的流程,最后会执行NioEventLoop的run方法开始轮询感兴趣的IO事件。
以上我们主要从服务启动与客户端连接两个方面分析了NioEventLoop的启动流程与源码,其实也就对应NioServerSocketChannel与NioSocketChannel分别绑定的NioEventLoop,其中有错误和不足之处还请指正与海涵。
关注微信公众号,查看更多技术文章。

Netty源码分析之NioEventLoop(二)—NioEventLoop的启动的更多相关文章
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第1节: NioEventLoopGroup之创建线程执行器
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 概述: 通过上一章的学习, 我们了解了Server启动的大致流程, 有很多组件与模块并没有细讲, 从这个章开始, 我们开始详细剖析netty的各个 ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第2节: NioEventLoopGroup之NioEventLoop的创建
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第二节: NioEventLoopGroup之NioEventLoop的创建 回到上一小节的MultithreadEventExecutorG ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第3节: 初始化线程选择器
Netty源码分析第二章:NioEventLoop 第三节:初始化线程选择器 回到上一小节的MultithreadEventExecutorGroup类的构造方法: protected Multi ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第4节: NioEventLoop线程的启动
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第四节: NioEventLoop线程的启动 之前的小节我们学习了NioEventLoop的创建以及线程分配器的初始化, 那么NioEvent ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第5节: 优化selector
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第五节: 优化selector 在剖析selector轮询之前, 我们先讲解一下selector的创建过程 回顾之前的小节, 在创建NioEv ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第6节: 执行select操作
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第六节: 执行select操作 分析完了selector的创建和优化的过程, 这一小节分析select相关操作 跟到跟到select操作的入口 ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第7节: 处理IO事件
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第七节:处理IO事件 上一小节我们了解了执行select()操作的相关逻辑, 这一小节我们继续学习select()之后, 轮询到io事件的相关 ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第8节: 执行任务队列
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第八节: 执行任务队列 继续回到NioEventLoop的run()方法: protected void run() { for (;;) ...
- Netty 源码分析系列(二)Netty 架构设计
前言 上一篇文章,我们对 Netty做了一个基本的概述,知道什么是Netty以及Netty的简单应用. Netty 源码分析系列(一)Netty 概述 本篇文章我们就来说说Netty的架构设计,解密高 ...
- Netty源码分析 (三)----- 服务端启动源码分析
本文接着前两篇文章来讲,主要讲服务端类剩下的部分,我们还是来先看看服务端的代码 /** * Created by chenhao on 2019/9/4. */ public final class ...
随机推荐
- 解题:UOJ #46 玄学
题面 二进制分组,修改把区间拆开丢在后面,合并的时候归并最后两块:查询在对应节点上二分答案 #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #includ ...
- EasyUI实战篇之datagrid:如何重新设置datagrid所配置的属性(options)并重新查询列表(relaod)
http://www.stepday.com/topic/?873 今天在使用EasyUI的datagrid列表组件想实现一个列表的展现,且列表上方有搜索条件,初始化的时候我是这样配置的: 1.< ...
- django-simple-captcha 验证码插件
官方文档:http://django-simple-captcha.readthedocs.io/en/latest/usage.html#installation github:https://gi ...
- Golang异常处理-panic与recover
Golang异常处理-panic与recover 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 在程序设计中,容错是相当重要的一部分工作,在 Go中它是通过错误处理来实现的,err ...
- spring cloud 微服务架构 简介
Spring Cloud 1. Spring Cloud 简介 Spring Cloud是在Spring Boot的基础上构建的,用于简化分布式系统构建的工具集,为开发人员提供快速建立分布式系统中的 ...
- python---补充django中文报错(2),Django3.5出错
今天是要Django3.5设置项目,结果出现中文报错,虽然之前分析过py2.7的报错原因,但是在py3之后reload不在使用,需要引入: from importlib import reload 但 ...
- LaTeX文章结构
%导言 %\documentclass{article} %ctexbook \documentclass{ctexbook} \title{\heiti 监督学习} % 黑体 \author{\ka ...
- VS之解决方案文件夹
Visual Studio提供了一种特殊的文件夹,它可以帮助组织大型解决方案.它们的名称也恰如其分,叫做“解决方案文件夹”. 注意 解决方案文件夹是解决方案资源管理器中的一种组织工具,创建这样的文 ...
- js 隐藏代码生成工具
昨天写了篇<js 奇葩技巧之隐藏代码>,今天来写个工具方便大家生成吧.在昨天算法基础上优化了解码算法,采用立即函数运行.有两种模式可供选择: 1. eval 全局模式,比如你定义的 va ...
- PHP 设计模式 单例模式 工厂模式 注册模式
1.工厂模式,工厂方法或者类生成对象,而不是在代码中直接new 2.单例模式,使某个类的对象仅允许创建一个 3.注册模式,全局共享和交换对象 项目文件目录 入口文件 index.php <?ph ...
