Tomcat架构解析(三)-----Engine、host、context解析以及web应用加载
上一篇博文介绍了Server的创建,在Server创建完之后,就进入到Engine的创建过程,如下:
一、Engine的创建
1、创建Engine实例

当前次栈顶元素为Service对象,通过Service对象的setContainer()方法,将Engine对象添加到Service中。
2、为Engine添加集群配置

3、为Engine添加生命周期监听器

4、为Engine添加安全配置


二、Host的创建
1、创建Host的实例

addCallMethod(String rule,String methodName,int paraNumber):该方法同样设置对象的属性,但更加灵活,不需要对象具有setter。根据rule规则指定的属性,调用对象的methodName方法,paraNumber参数是表示方法需要的参数个数。
当paraNumber=0时,可以单独使用,不然需要配合addCallParam方法。
2、为Host添加集群

3、为Host添加生命周期管理

4、为Host添加安全配置
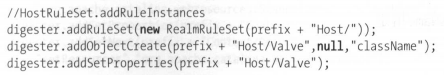
三、Context的解析
Context就对应着具体的web应用,说白了,就是平时开发的各种项目。但是Catalina中的Context配置并不只是在一处配置,一般配置Context有如下几种方式:
a、在Tomcat的server.xml中进行配置Context的相关信息(一般不这么干,因为烦);
b、将应用丢到部署目录(也就是/webapps下),这种比较常见。原理就是Tomcat通过HostConfig对象自动扫描部署目录,以context.xml为基础进行解析创建;
c、在Eclipse或IDEA等开发工具中将web应用部署在Tomcat中,此时Context的相应配置会动态自动的更新到server.xml文件中(开发过程中肯定是这么干了)。
1、Context实例化


后续就是为Context添加生命周期监听器、类加载器、会话管理器、初始化参数、安全配置以及cookie处理器等等。。。
四、web应用加载
当整个server开始启动的时候,肯定要将部署的所有的web应用都加载进来,web应用在Tomcat中的默认实现类为StandardContext,主要过程如下:
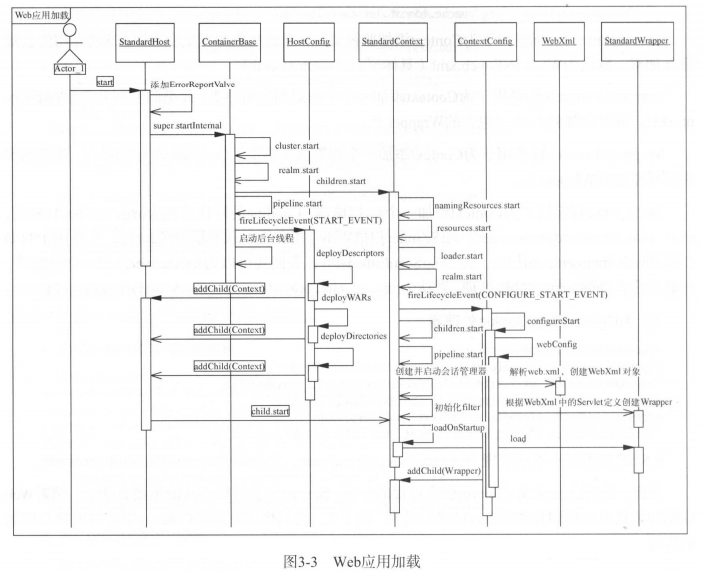
1、StandardHost
加载web应用的入口主要有两个:
a、根据前面的博文可以知道,在Host解析的过程中,如果存在Context子元素,则会解析Context,并将Context添加到Host对象中,作为Host的子容器。当Host启动时(调用start()),由生命周期
管理接口的start()方法默认启动子容器的start()方法;

其中docBase代表web应用所在地址,path则是web应用的访问地址。前面也说到了,这种方式比较烦。。。
b、HostConfig自动扫描部署目录,扫描到web应用之后,创建相关Context实例。
下面来具体解释下StandardHost的启动加载过程:
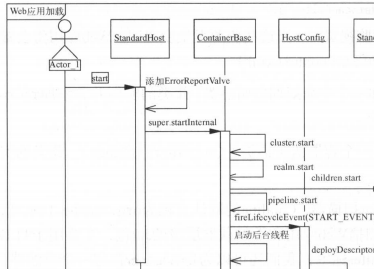
a、添加ErrorReportValve
在服务器处理异常时输出错误页面。当然如果在web.xml中配置了错误页面,则这个是不起作用的,只有web.xml中没有配置错误页面,该配置才有效。当然web.xml中配置错误页面的粒度是针对整个web应用,后者则是针对整个Host,粒度较大。
b、调用StandardHost的父类ContainerBase的startInternal()
该方法启动虚拟机,具体包括:
------如果配置了集群cluster,则启动;
|-----如果配置了安全组件realm,则启动;
|-----启动子容器,当Host中包含子节点时,例如Context;
|-----启动Host持有的pipeline组件;
|-----设置Host的状态为starting,触发start_event生命周期事件。HostConfig监听该事件,扫描部署目录,自动创建StandardContext实例,然后启动这些Context实例;
------启动Host层级的后台任务处理,cluster后台任务处理(检测心跳等等)、realm后台任务处理、pipeline后台任务处理。
2、HostConfig
HostConfig主要作用是自动扫描Tomcat部署目录,创建StandardContext。HostConfig实现了LifecycleListener接口,主要包括start_event、periodic_event、stop_event三个生命周期事件。
a、start_event事件
Host启动时触发,但是要求Host的deplyOnStartUp属性为true,当服务器启动时,部署所有的web应用。该事件处理包括三个步骤:
------Context描述文件部署
|-----web目录部署
------war包部署
b、periodic_event事件
Catalina容器支持定期执行自身以及其子容器的后台处理过程,此种机制能够定时扫描到web应用的变更,并重新加载,后台任务处理完成后,触发periodic_event事件。HostConfig接收到此事件后,若web应用有改动,则重新加载。
五、MapperListener和Mapper
1、MapperListener的初始化
作用:实现了ContainerListener与 LifecycleListener接口,监听tomcat组件的变化,当有Host,Context及Wrapper变更时,调用Mapper相关方法,增加或者删除Host,Context,Wrapper等。
/**
* Initialize associated mapper.
*/
public void init() { // Find any components that have already been initialized since the
// MBean listener won't be notified as those components will have
// already registered their MBeans jiaan
findDefaultHost(); Engine engine = (Engine) connector.getService().getContainer();
engine.addContainerListener(this); Container[] conHosts = engine.findChildren();
for (Container conHost : conHosts) {
Host host = (Host) conHost;
if (!LifecycleState.NEW.equals(host.getState())) {
host.addLifecycleListener(this);
// Registering the host will register the context and wrappers
registerHost(host);
}
}
}
Connector是由Service负责管理,然后给所有的子容器都添加生命周期监听器。然后将Host及其子容器Context,Context的子容器Wrapper注册到MapperListener的Mapper对象。
2、Mapper
Mapper中维护着一个Host数组,每个Host中有一个ContextList,这个ContextList中维护着一个Context数组。每个Context维护着一个defaultWrapper,三个Wrapper数组(exactWrappers、wildcardWrappers、extensionWrappers)。
下面对Host、Context及Wrapper进行功能上的介绍:
Host:代表一个虚拟主机,各Host的name不能相同,appBase代表各虚拟主机的应用发布位置;
Context:代表一个应用,Context可以根据应用的/WEB-INF/web.xml文件中定义的servlet来处理请求。一个Host下可以有多个Context;
Wrapper: 代表一个Servlet或者jsp,它负责管理一个 Servlet,包括的 Servlet 的装载、初始化、执行以及资源回收。
通过MapperListener以及Mapper,当客户端发出请求时,就可以根据url找到对应的Wrapper(就是Servlet),解释如下:
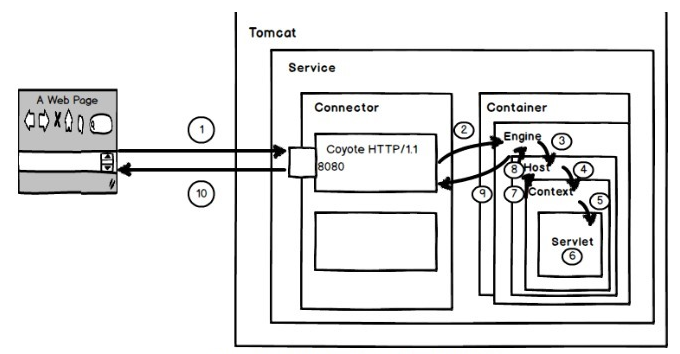
- 1、用户在浏览器中输入网址localhost:8080/test/index.jsp,请求被发送到本机端口8080,被在那里监听的Coyote HTTP/1.1 Connector获得;
- 2、Connector把该请求交给它所在的Service的Engine(Container)来处理,并等待Engine的回应;
- 3、Engine获得请求localhost/test/index.jsp,匹配所有的虚拟主机Host;
- 4、Engine匹配到名为localhost的Host(即使匹配不到也把请求交给该Host处理,因为该Host被定义为该Engine的默认主机),名为localhost的Host获得请求/test/index.jsp,匹配它所拥有的所有Context。Host匹配到路径为/test的Context(如果匹配不到就把该请求交给路径名为“ ”的Context去处理);
- 5、path=“/test”的Context获得请求/index.jsp,在它的mapping table中寻找出对应的Servlet(这地方就是用到了上面的Mapper去找到对应的Servlet对象)。Context匹配到URL Pattern为*、jsp的Servlet,对应于JspServlet类;
- 6、构造HttpServletRequest对象和HttpServletResponse对象,作为参数调用JspServlet的doGet()或doPost(),执行业务逻辑、数据存储等;
- 7、Context把执行完之后的HttpServletResponse对象返回给Host;
- 8、Host把HttpServletResponse对象返回给Engine;
- 9、Engine把HttpServletResponse对象返回Connector;
- 10、Connector把HttpServletResponse对象返回给客户Browser。
大概介绍了Tomcat中的Engine、Host、Context的解析,并且简单介绍了拿到客户端请求如何找到对应的Servlet。下篇博文主要介绍Tomcat如何与客户端建立连接,待续~~~
Tomcat架构解析(三)-----Engine、host、context解析以及web应用加载的更多相关文章
- Tomcat 启动时 警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context}
在Eclipse 中,启动Tomcat 时,出现: 警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting proper ...
- tomcat日志警告WARNING: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'debug' to '0' did not find a matching property.
日志中有警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'debug' to '0' did ...
- 警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'source' to
警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'source' to 警告: [SetPro ...
- 警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context}
警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'source' to'org.eclipse ...
- 警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context}Setting property 'source' to 'org.eclipse
当你用Eclipse运行web项目的时候,你就会看到控制台出现:WARNING: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Set ...
- 警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'source' to 'org.eclipse.jst.jee.server:fhcq-oa' did not find a matching property.
当你在使用Eclipse运行web项目时,你可能会看到控制台出现: 警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Settin ...
- 警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} 解决方法
Tomcat启动时出现红色警告内容 警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'sour ...
- [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'source' to 'org.eclipse.jst.j2ee.server:lovemu' did not find a matching property.
[SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'source' to 'org.eclipse.js ...
- 警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'source' to 'org.eclipse.jst.jee.server:Weixin' did not find a matching property.
警告: [SetPropertiesRule]{Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context} Setting property 'source' to 'org.eclips ...
随机推荐
- sql语句Order by 报错列名不明确
select top 10 column1,column2,column3 from table1 where table1.id not in(select top 0 table1.id from ...
- XML 解析技术
xml 解析方式有两种: dom 解析和 sax 解析: 针对着两种解析方式,有三种解析器: sun公司的 jaxp dom4j 组织的 dom4j jdom 组织的 jdom dom 解析XML : ...
- 基于RBAC权限验证, 中间价middleware实现, views 登录视图代码
废话不多说 上代码: 基础实现: rom django.shortcuts import HttpResponse, redirect, render from django.http import ...
- Struts2把数据封装到集合中之封装到map中
struts框架封装数据可以封装到集合中也可以封装到map中,该篇博客主要讲解将数据封装到map中. 1. 封装复杂类型的参数(集合类型 Collection .Map接口等) 2. 需求:页面中有可 ...
- 转录组分析综述A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis
转录组分析综述 转录组 文献解读 Trinity cufflinks 转录组研究综述文章解读 今天介绍下小编最近阅读的关于RNA-seq分析的文章,文章发在Genome Biology 上的A sur ...
- Ubuntu几种常见乱码解决方法
一.网页中的flash乱码: ubuntu默认浏览器是Firefox,但是Ubuntu默认不安装像flash这种带版权的软件,所以当你浏览像youku或网页播放器时,这种带有 flash ...
- Python之路(第十八篇)shutil 模块、zipfile模块、configparser模块
一.shutil 模块 1.shutil.copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst[, length]) 将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中,需要打开文件 import shutil shutil.co ...
- urllib和requests库
目录 1. Python3 使用urllib库请求网络 1.1 基于urllib库的GET请求 1.2 使用User-Agent伪装后请求网站 1.3 基于urllib库的POST请求,并用Cooki ...
- [ES]elasticsearch章2 ES查询过程解析
es服务端是准确知道每个document分布在哪个shard上: search一个比较复杂的执行模式,因为我们不知道那些document会被匹配到,任何一个shard上都有可能,所以一个search请 ...
- jquery动态出操作select
var citys = {1:'北京',2:'上海',3:'广州',4:'深圳'}; $("#city option:gt(0)").remove(); for(var k in ...
