Spring中基于注解的IOC(二):案例与总结
2.Spring的IOC案例
创建maven项目
导入依赖
pom.xml
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
4.0.0
cn.cqu
xmlIOC
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
org.springframework
spring-context
5.0.2.RELEASE
commons-dbutils
commons-dbutils
1.4
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.6
c3p0
c3p0
0.9.1.2
junit
junit
4.12
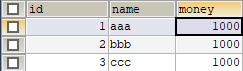
创建数据库
CREATE TABLE account(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR(40),
money FLOAT
)CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
INSERT INTO account(NAME,money)VALUES('aaa',1000);
INSERT INTO account(NAME,money)VALUES('bbb',1000);
INSERT INTO account(NAME,money)VALUES('ccc',1000);
Account.java
package cn.cqu.domain;
public class Account {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private float money;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(float money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
IAccountDao.java
package cn.cqu.dao;
import cn.cqu.domain.Account;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 账户的持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 查询所有
* @return
*/
List findAllAccount();
/**
* 查询一个
* @param accountId
* @return
*/
Account findById(Integer accountId);
/**
* 插入
* @param account
*/
void saveAccount(Account account);
/**
* 更新
* @param account
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
/**
* 删除
* @param accountId
*/
void deleteAccount(Integer accountId);
}
AccountDaoImpl.java
package cn.cqu.dao.impl;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import cn.cqu.domain.Account;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import java.util.List;
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private QueryRunner runner;
public QueryRunner getRunner() {
return runner;
}
public void setRunner(QueryRunner runner) {
this.runner = runner;
}
public List findAllAccount() {
try {
return runner.query("select * from account",new BeanListHandler(Account.class));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Account findById(Integer accountId) {
try {
return runner.query("select * from account where id = ?",new BeanHandler(Account.class),accountId);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
try {
runner.update("insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)",account.getName(),account.getMoney());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
runner.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
try {
runner.update("delete from account where id=?",accountId);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
IAccountService.java
package cn.cqu.service;
import cn.cqu.domain.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface IAccountService {
/**
* 查询所有
* @return
*/
List findAllAccount();
/**
* 查询一个
* @param accountId
* @return
*/
Account findById(Integer accountId);
/**
* 插入
* @param account
*/
void saveAccount(Account account);
/**
* 更新
* @param account
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
/**
* 删除
* @param accountId
*/
void deleteAccount(Integer accountId);
}
AccountServiceImpl.java
package cn.cqu.service.impl;
import cn.cqu.domain.Account;
import cn.cqu.service.IAccountService;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import java.util.List;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IAccountDao dao;
public IAccountDao getDao() {
return dao;
}
public void setDao(IAccountDao dao) {
this.dao = dao;
}
public List findAllAccount() {
return dao.findAllAccount();
}
public Account findById(Integer accountId) {
return dao.findById(accountId);
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
dao.saveAccount(account);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
dao.updateAccount(account);
}
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
dao.deleteAccount(accountId);
}
}
bean.xml
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
AccountServiceTest.java
package cn.cqu.test;
import cn.cqu.domain.Account;
import cn.cqu.service.IAccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置
*/
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Test
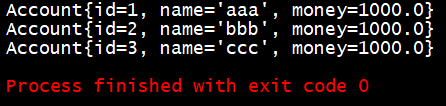
public void testFindAll()
{
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//3.执行方法
List accounts = as.findAllAccount();
for (Account account:accounts)
{
System.out.println(account);
}
}
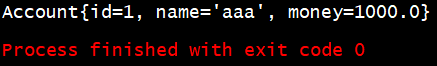
@Test
public void testFindById()
{
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//3.执行方法
Account account = as.findById(1);
System.out.println(account);
}
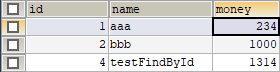
@Test
public void testSaveAccount()
{
Account account =new Account();
account.setName("testFindById");
account.setMoney(1314);
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//3.执行方法
as.saveAccount(account);
}
@Test
public void testUpdate()
{
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//3.执行方法
Account account = as.findById(1);
account.setMoney(234);
as.updateAccount(account);
}
@Test
public void testDelete()
{
//1.获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.得到业务层对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
//3.执行方法
as.deleteAccount(3);
}
}
使用注解对上述部分代码进行改造
AccountDaoImpl.java
package cn.cqu.dao.impl;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import cn.cqu.domain.Account;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Autowired
private QueryRunner runner;
public List findAllAccount() {
try {
return runner.query("select * from account",new BeanListHandler(Account.class));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Account findById(Integer accountId) {
try {
return runner.query("select * from account where id = ?",new BeanHandler(Account.class),accountId);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
try {
runner.update("insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)",account.getName(),account.getMoney());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
runner.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
try {
runner.update("delete from account where id=?",accountId);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
AccountServiceImpl.java
package cn.cqu.service.impl;
import cn.cqu.domain.Account;
import cn.cqu.service.IAccountService;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private IAccountDao dao;
public List findAllAccount() {
return dao.findAllAccount();
}
public Account findById(Integer accountId) {
return dao.findById(accountId);
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
dao.saveAccount(account);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
dao.updateAccount(account);
}
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
dao.deleteAccount(accountId);
}
}
bean.xml
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
运行结果同上
3.Spring的新注解
我们依然离不开 spring 的xml 配置文件,那么能不能不写这个 bean.xml,所有配置都用注解来实现呢?
我们发现,之所以我们现在离不开 xml 配置文件,是因为:
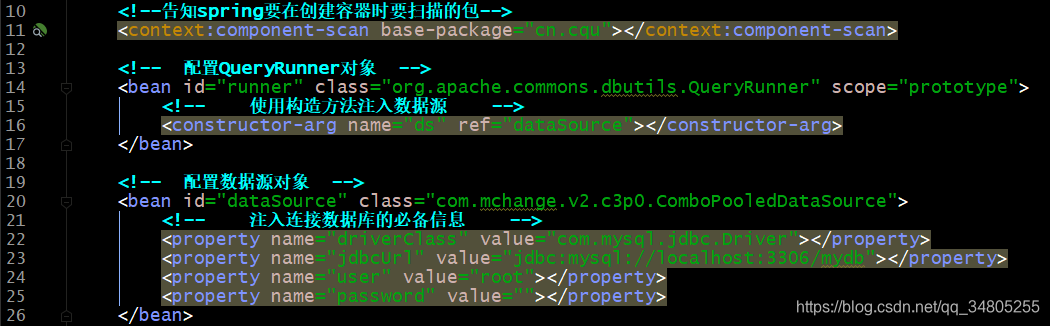
原因1:
如果他要也能用注解配置,那么我们就离脱离 xml 文件又进了一步。
原因2:
数据源和 QueryRunner的配置也需要靠注解来实现。
因为QueryRunner是dbutils下的jar包,我们想给它加注解是加不了的
dataSource也是同样的道理
1.首先对如下进行注解改造

创建一个专门的类,大致如下
package cn.cqu.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* 此类的类名和它所在包名由自己命名均可
*
* 该类是一个配置类,它的作用和bean.xml是一样的
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "cn.cqu")
public class SpringConfiguration {
}
(1) @Configuration
作用:无锡人流手术多少钱 http://www.chnk120.com/
用于指定当前类是一个 spring 配置类,当创建容器时会从该 类上加载注解。获取容器时需要使用
AnnotationApplicationContext(有@Configuration注解的类.class)
属性:
value:用于指定配置类的字节码
细节:
当配置类作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建的参数时,该注解可以不写
(2)@ComponentScan或@ComponentScans
作用:
@ComponentScan用于指定一个通过注解指定Spring在创建容器时要扫描的包
@ComponentScans用于指定多个通过注解指定Spring在创建容器时要扫描的包
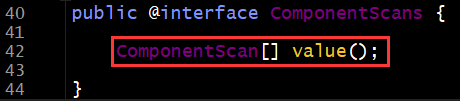
属性:
value或basePackages:用于指定创建容器时要扫描的包
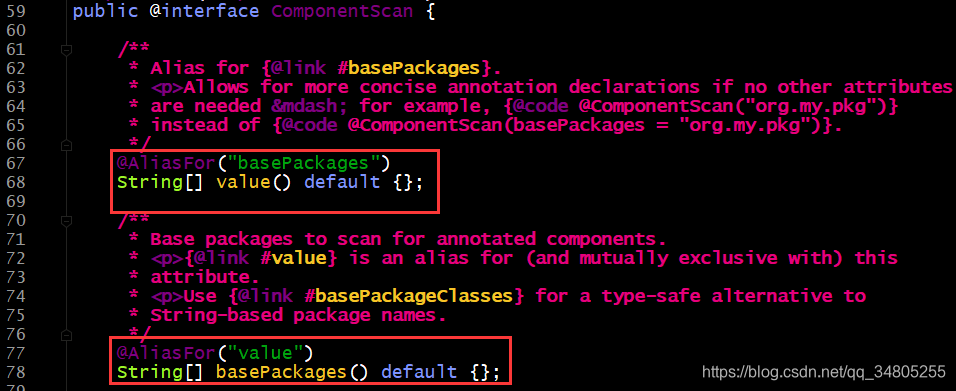
我们使用此注解就等同于在bean.xml中配置了

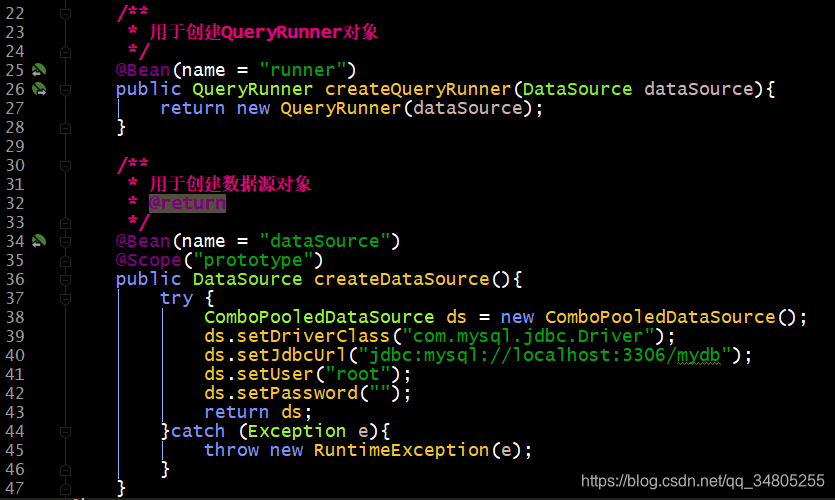
2.接下来我们对如下进行改造
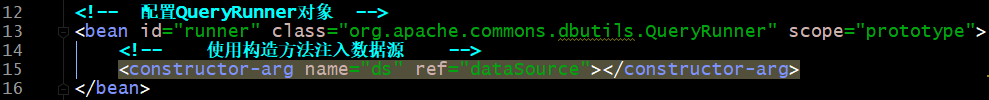
其实以上配置有两步:
1.创建QueryRunner对象
2.存入Sping的IOC容器中
在该类中添加创建QueryRunner对象的方法,即完成上述的第一步创建QueryRunner对象
使用下面的Bean完成第二步
(3)@Bean
作用:
用于把当前方法的返回值作为bean对象存入Spring的IOC容器中
属性:
name:用于指定bean的id,当不写时是当前方法的名称
细节:
当我们使用注解配置方法时,如果方法有参数,spring框架会去容器中查找有没有可用的bean对象,查找的方式和Autowired注解的作用是一样的
同样我们也可以使用@Scope来指定作用范围
(4)@Import
作用:
用于导入其他的配置类
通过这种方法,可以将配置写在多个类当中,而设置一个主配置类,然后通过注解@Import将其他的配置类导入到主配置类中聚合在一起相当于一个bean.xml
属性:
value:用于指定其他配置类的字节码
当我们使用Import之后,有Import注解的类就是主配置类或父配置类,而导入的都是子配置类
同时它也支持并列的配置关系,我们只需要在使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext创建容器时,将多个配置类的字节码都作为它的参数

4.SpringIOC总结
对Spring依赖总结:
变化集中转移到配置(配置文件或注解)中
Spring框架内部依赖于配置
自定义类依赖于不变(String)
从而编译时依赖转运行时依赖,降低耦合
Spring中基于注解的IOC(二):案例与总结的更多相关文章
- Spring中基于注解的IOC(一):基础介绍
1. Spring中的常用注解 注解配置和xml配置要实现的功能都是一样的,都要降低程序的耦合,只是配置的形式不一样 xml中配置示例: 注解分类: 1.用于创建对象的注解 它们的作用就和在xml中编 ...
- Spring 框架的概述以及Spring中基于XML的IOC配置
Spring 框架的概述以及Spring中基于XML的IOC配置 一.简介 Spring的两大核心:IOC(DI)与AOP,IOC是反转控制,DI依赖注入 特点:轻量级.依赖注入.面向切面编程.容器. ...
- 10 Spring框架--基于注解的IOC配置
1.工程环境搭建 2.基于注解的IOC配置 IOC注解的分类 (1)用于创建对象的 他们的作用就和在XML配置文件中编写一个<bean>标签实现的功能是一样的@Component: 作用: ...
- spring中基于注解使用AOP
本文内容:spring中如何使用注解实现面向切面编程,以及如何使用自定义注解. 一个场景 比如用户登录,每个请求发起之前都会判断用户是否登录,如果每个请求都去判断一次,那就重复地做了很多事情,只要是有 ...
- spring中基于注解使用ehcache
继续上篇,这篇介绍服务层缓存,基于注解的方式使用ehcache 注解的标签主要有4个:@Cacheable.@CacheEvict.@CachePut.@Caching,他们的用法是: @Cachea ...
- spring的基于注解的IOC配置
1.配置文件配置 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http: ...
- Spring中基于注解方式管理bean
操作步骤 第一步:导入相关jar包 spring IoC的基本包 Spring支持注解的Jar包 第二步:创建Spring配置文件,ApplicationContext.xml 引入约束和开启注解扫描 ...
- spring基于注解的IoC以及IoC的案例
1.Spring中IoC的常用注解 1.1明确: (1)基于注解的配置和xml的配置要实现的功能都是一样的,都是要降低程序之间的耦合,只是配置的形式不一样 2.案例:使用xml方式和注解方式实现单表的 ...
- 阶段3 2.Spring_05.基于XML的IOC的案例1_4 注解IOC案例-把自己编写的类使用注解配置
注解改造案例 复制之前的xml配置的pom.xml里面的依赖. 复制com文件 bean.xml配置文件也拷贝过来 测试类也复制过来 开始基于注解的IOC配置 右键项目,选择maven.选择更新 更新 ...
随机推荐
- offsetWidth的bug
#div1{width:200px;border:1px solid red;} 这个时候如果用 offsetWidth 提取 #div1 的宽 得到的值是 202: 也就是说 offsetWidt ...
- 【redis】设置密码
1.第一种方式 (当前这种linux配置redis密码的方法是一种临时的,如果redis重启之后密码就会失效,) (1)首先进入redis,如果没有开启redis则需要先开启:[root@iZ94jz ...
- Android 开发基础入门篇: android studio安装教程
下载地址 http://www.android-studio.org/ 注意: 安装主要分两种情况,下载的自带SDK和不带SDK两种 然后又分为安装版,就是.exe和解压版 两种的区别...解压版,, ...
- ESA2GJK1DH1K基础篇: 移植官方MQTT包,让TCP实现MQTT功能(以GPRS模块为例)
前言 这节代码将在这一节的基础上实现 拷贝第一节测试里面的MQTT文件夹到当前工程 当前工程建个MQTT的文件夹,用于存放那个MQTT文件夹里面的内容 添加文件到里面 注意:::: 实际源码拷贝位置 ...
- C 题解———2019.10.16
现在很痛苦,等过阵子回头看看,会发现其实那都不算事. [题目描述]定义一个排列 a 的价值为满足|a[i]-i|<=1 的 i 的数量.给出三个正整数 n,m,p,求出长度为 n 且价值恰好为 ...
- ACT开发初步(二)——XML
由于pc无法发文,先挖坑,慢慢填
- Java 并发系列之十:java 并发框架(2个)
1. Fork/Join框架 2. Executor框架 3. ThreadPoolExecutor 4. ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 5. FutureTask 6. t ...
- 运维-安装rabbitmq 集群
服务器: online-platform-rabbitmq-01 online-platform-rabbitmq-02 online-platform-rabbitmq-03 绑定HOSTS: ...
- salt 安装
list: centos 6.5 x86_64 172.18.39.28 mast.test.com 172.18.39.27 mini.test.com master:#sudo yum insta ...
- SQL工具 Red Gate
Red Gate提供了很多对于sql server的工具. 这边介绍两个:Sql Prompt和Sql doc Sql Prompt:智能提示sql语句等等 Sql doc:生成数据库文档页面 Red ...
