Processing (Java) 中实现2D任意图形的鼠标悬停检测 · 2D射线检测 · 模拟按钮 · 点击事件
引言
如果使用Processing开发应用,画面中需要设定一些按钮,而且这些按钮是不规则图形样式,甚至是以一张图片形式呈现,如何判定其轮廓,定义悬停事件、点击事件是非常核心的算法需求。本文浅析这一问题的通用解决方案。因为Processing是Java衍生语言,同样适合java语言体系。
第一项
以最简单的检测情景开始------矩形检测。主要包括检测边界,触发悬停事件和点击事件。
矩形的话只需要考虑四个边坐标和鼠标x、y坐标大小关系,见下文:
// 检查鼠标是否悬停在矩形上
boolean isMouseOver(float mx, float my) {
return mx >= x && mx <= x + width && my >= y && my <= y + height;
}其中的mx、my分别表示mouseX,mouseY。width、height代表矩形的宽和高。
为了方便定义矩形样式,这里diy一个矩形类:
// 自定义矩形类
class Rectangle {
// 矩形的左上角坐标 方便绘制
float x, y;
// 矩形的宽度和高度
float width, height;
// 构造函数,用于初始化矩形的位置和大小
Rectangle(float x, float y, float width, float height) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
// 检查鼠标是否悬停在矩形上
boolean isMouseOver(float mx, float my) {
return mx >= x && mx <= x + width && my >= y && my <= y + height;
}
// 绘制矩形的方法
void draw (){
rect(x,y,width,height);
}
}完整代码如下:
import processing.core.PApplet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class RectangleExample extends PApplet {
// 存储矩形信息的列表
ArrayList<Rectangle> rectangles = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void settings() {
// 设置窗口大小
size(600, 400);
}
@Override
public void setup() {
// 创建一个矩形并添加到列表中
rectangles.add(new Rectangle(100, 100, 200, 150));
}
@Override
public void draw() {
// 设置背景颜色为白色
background(255);
// 遍历所有矩形
for (Rectangle rect : rectangles) {
// 检查鼠标是否悬停在矩形上
if (rect.isMouseOver(mouseX, mouseY)) {
// 鼠标悬停时,设置填充颜色为灰色
fill(200);
} else {
// 鼠标未悬停时,设置填充颜色为黑色
fill(0);
}
// 绘制矩形
rect.draw();
}
}
@Override
public void mouseClicked() {
// 遍历所有矩形
for (Rectangle rect : rectangles) {
// 检查鼠标是否点击在矩形上
if (rect.isMouseOver(mouseX, mouseY)) {
// 鼠标点击在矩形上时,打印消息
println("点击了矩形!");
}
}
}
// 自定义矩形类
class Rectangle {
// 矩形的左上角坐标
float x, y;
// 矩形的宽度和高度
float width, height;
// 构造函数,用于初始化矩形的位置和大小
Rectangle(float x, float y, float width, float height) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
// 检查鼠标是否悬停在矩形上
boolean isMouseOver(float mx, float my) {
return mx >= x && mx <= x + width && my >= y && my <= y + height;
}
// 绘制矩形的方法
void draw (){
rect(x,y,width,height);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PApplet.main(RectangleExample.class);
}
}结果如下:

第二项
不规则多边形检测。主要包括检测轮廓,触发悬停事件和点击事件。
首先定义一个多边形:
// 定义多边形的顶点
float[][] polygon = {
{100, 100},
{200, 50},
{300, 200},
{250, 300},
{150, 250}
};然后编写判断鼠标位置与多边形区域是否相遇,也就是是否悬停于多边形之上,类似三维世界中的射线检测方法:
/**
* 判断点是否在多边形内,使用射线法。
*
* @param x 点的 x 坐标
* @param y 点的 y 坐标
* @param polygon 多边形的顶点数组
* @return 如果点在多边形内返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
public boolean isPointInPolygon(float x, float y, float[][] polygon) {
boolean inside = false;
int j = polygon.length - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < polygon.length; i++) {
if ((polygon[i][1] > y) != (polygon[j][1] > y) &&
x < (polygon[j][0] - polygon[i][0]) * (y - polygon[i][1]) / (polygon[j][1] - polygon[i][1]) + polygon[i][0]) {
inside = !inside;
}
j = i;
}
return inside;
}然后就好办了,悬停事件以及点击事件:
// 判断鼠标是否在多边形内
if (isPointInPolygon(mouseX, mouseY, polygon)) {
fill(0, 255, 0); // 鼠标在多边形内,设置填充颜色为绿色
} else {
fill(255, 0, 0); // 鼠标在多边形外,设置填充颜色为红色
}
} /**
* 处理鼠标点击事件
*/
public void mouseClicked() {
if (isPointInPolygon(mouseX, mouseY, polygon)) {
println("鼠标在多边形内点击");
}
}最后的代码:
import processing.core.PApplet;
public class MainSketch1 extends PApplet {
// 定义多边形的顶点
float[][] polygon = {
{100, 100},
{200, 50},
{300, 200},
{250, 300},
{150, 250}
};
@Override
public void settings() {
super.settings();
size(600,400);
}
@Override
public void setup() {
super.setup();
}
/**
* 绘制循环,用于更新和绘制窗口内容。
* 此方法在 setup() 方法之后自动重复调用。
*/
public void draw() {
// 设置背景颜色为白色(RGB 值:255, 255, 255)
background(255);
// 在窗口的左上角 (0, 0) 位置绘制加载的图像 img
// 绘制多边形
beginShape();
for (float[] point : polygon) {
vertex(point[0], point[1]);
}
endShape(CLOSE);
// 判断鼠标是否在多边形内
if (isPointInPolygon(mouseX, mouseY, polygon)) {
fill(0, 255, 0); // 鼠标在多边形内,设置填充颜色为绿色
} else {
fill(255, 0, 0); // 鼠标在多边形外,设置填充颜色为红色
}
}
/**
* 判断点是否在多边形内,使用射线法。
*
* @param x 点的 x 坐标
* @param y 点的 y 坐标
* @param polygon 多边形的顶点数组
* @return 如果点在多边形内返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
public boolean isPointInPolygon(float x, float y, float[][] polygon) {
boolean inside = false;
int j = polygon.length - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < polygon.length; i++) {
if ((polygon[i][1] > y) != (polygon[j][1] > y) &&
x < (polygon[j][0] - polygon[i][0]) * (y - polygon[i][1]) / (polygon[j][1] - polygon[i][1]) + polygon[i][0]) {
inside = !inside;
}
j = i;
}
return inside;
}
/**
* 处理鼠标点击事件
*/
public void mouseClicked() {
if (isPointInPolygon(mouseX, mouseY, polygon)) {
println("鼠标在多边形内");
}
}
/**
* 程序的入口点,启动 MainSketch 类的 Processing 应用程序。
*
* @param args 命令行参数
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 调用 Processing 库的 main 方法,传入 MainSketch 类的 Class 对象以启动应用程序
PApplet.main(MainSketch1.class); // 启动入口
}
}如下图:
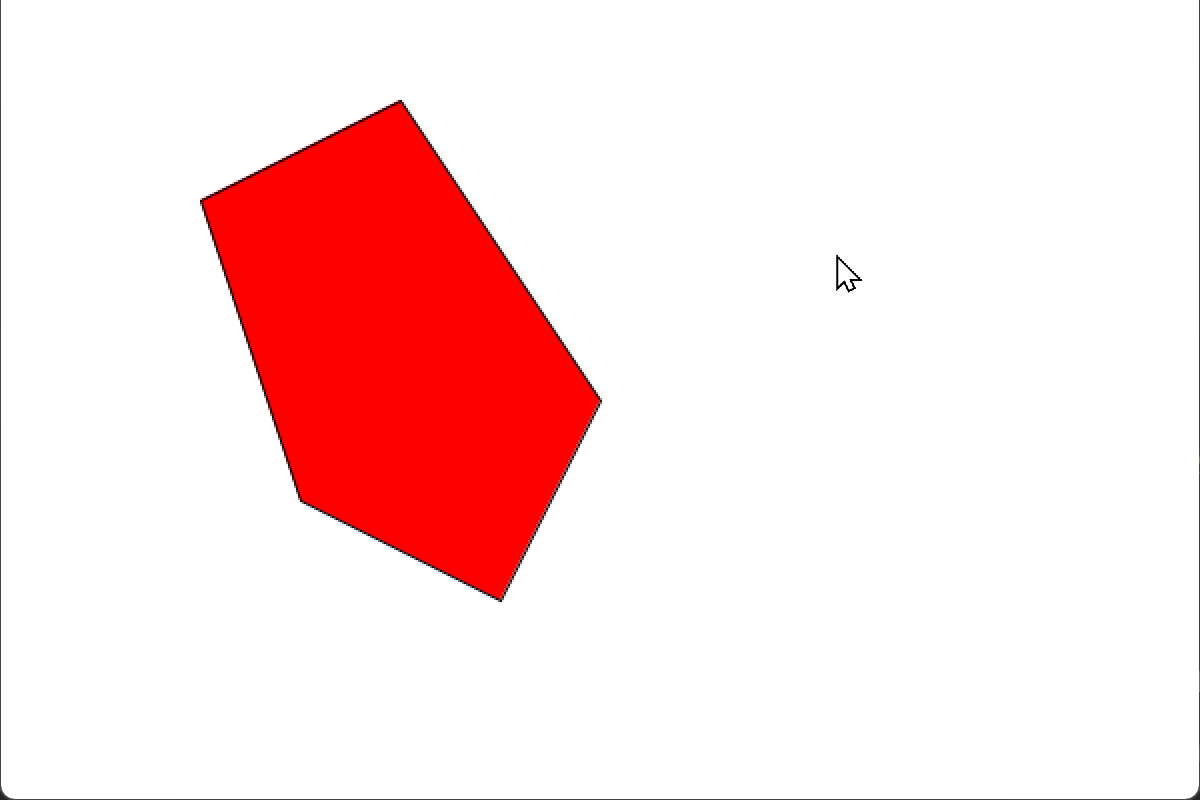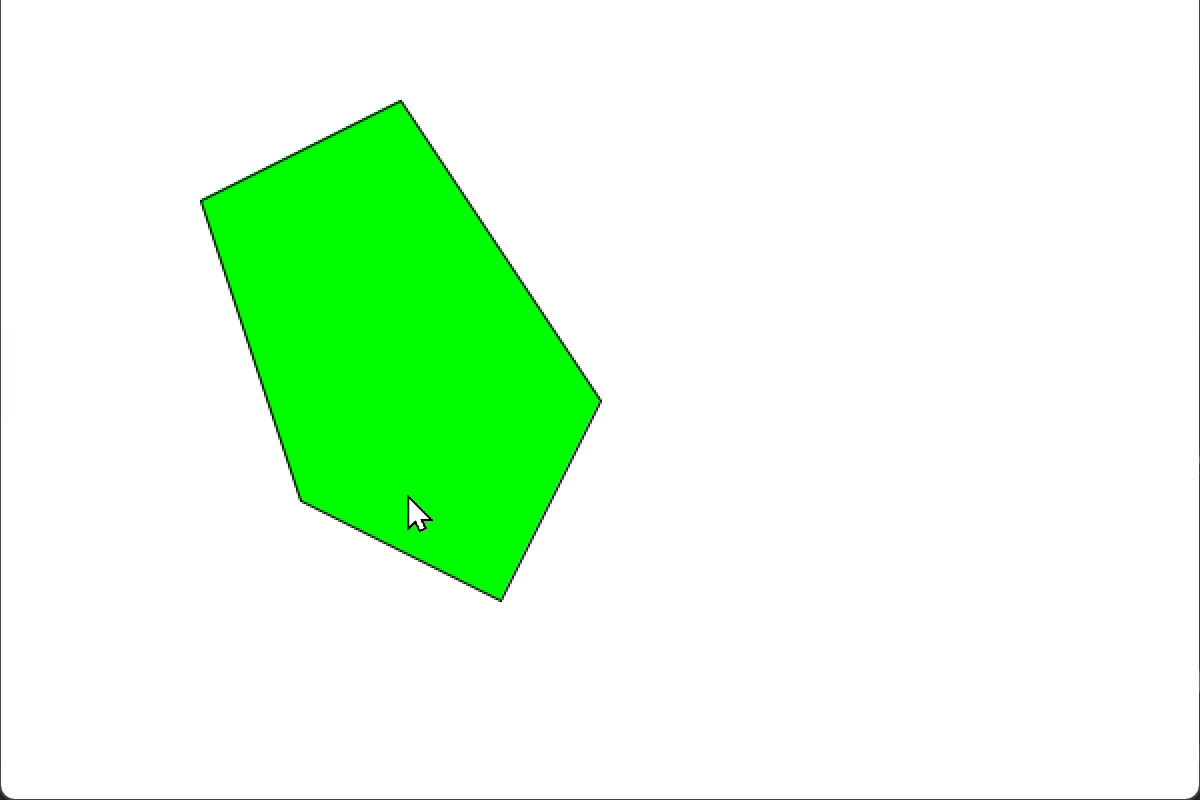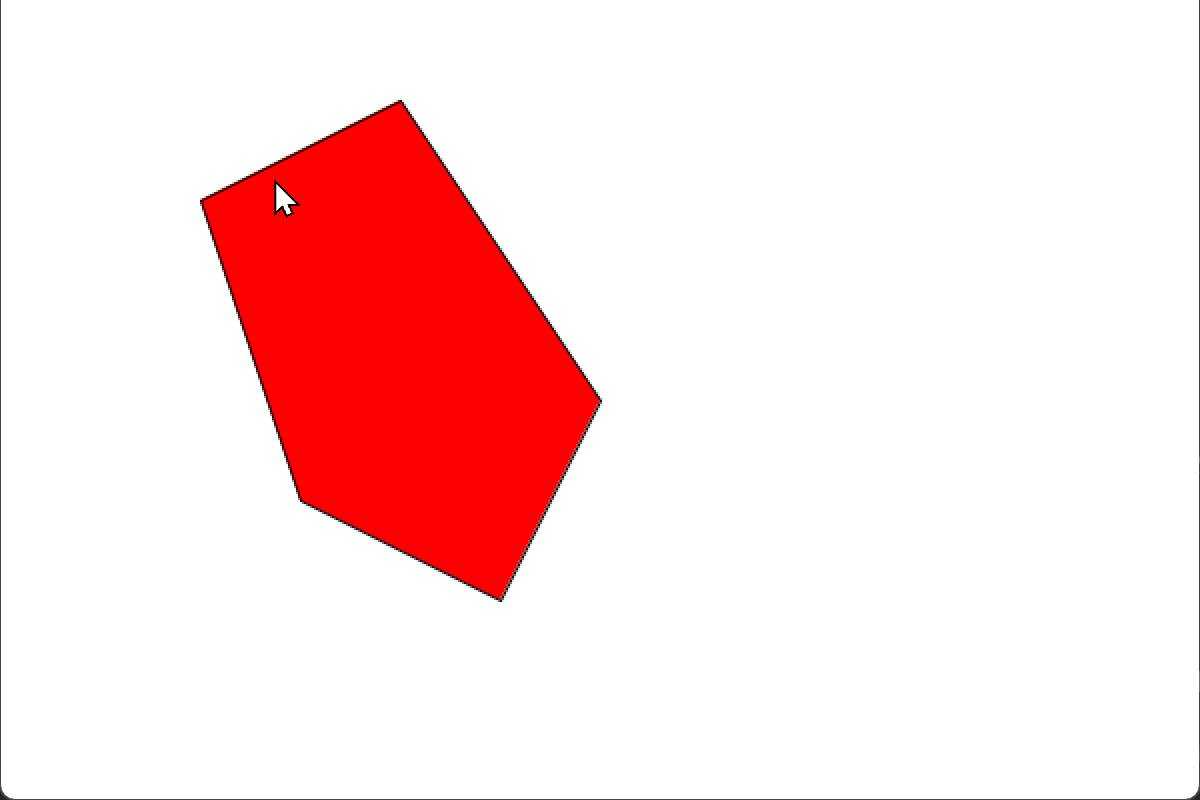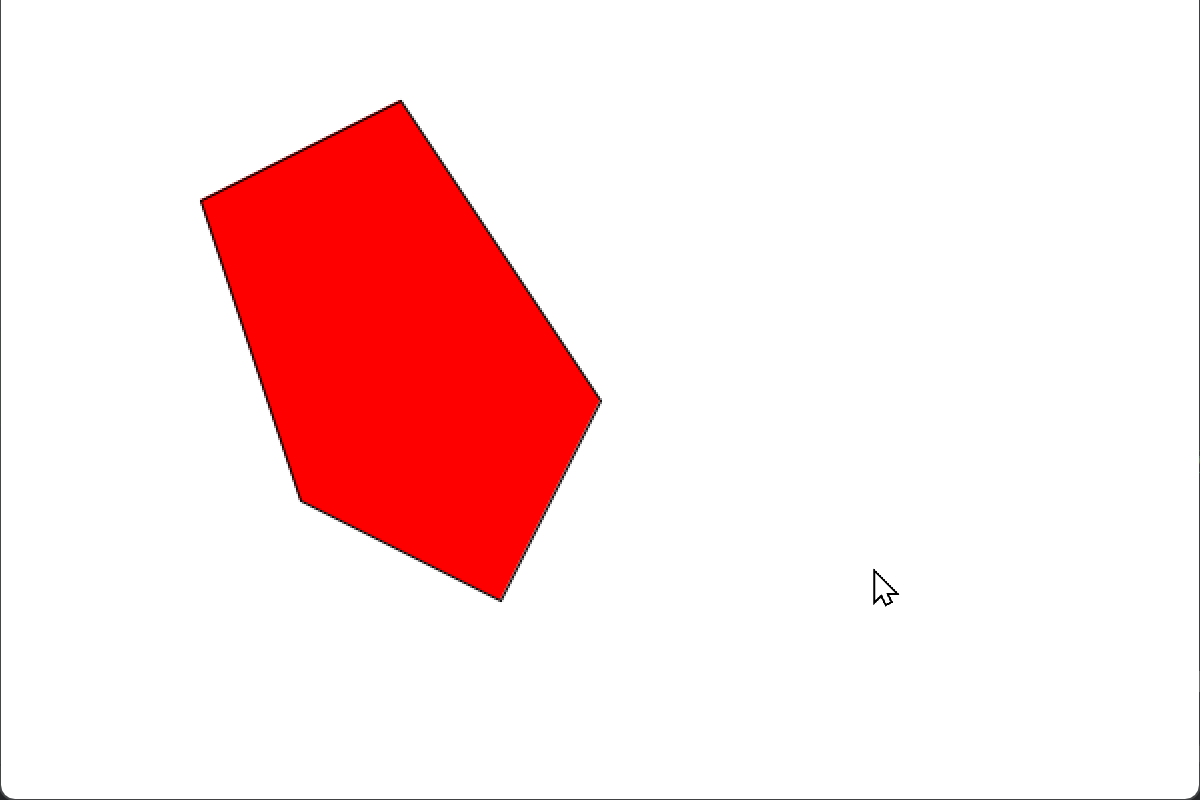
第三项
接下来,我们导入一张带通道的.PNG图片,轮廓不规则。鼠标悬停,图片变黑白,且有描边效果。

然后编写算法,计算鼠标是否悬停。其实可以采用第二项的方法,把轮廓抽象成多个点构成的多边形,然后检测。下面我用另一种讨巧的方法-----通过alpha通道值判断。见代码:
/**
* 判断鼠标是否在图片的不透明区域内 即悬停
* @param mouseX 鼠标的 x 坐标
* @param mouseY 鼠标的 y 坐标
* @param img 图片对象
* @param imgX 图片的 x 坐标
* @param imgY 图片的 y 坐标
* @return 如果鼠标在图片的不透明区域内返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
public boolean isMouseInImageOpaqueArea(int mouseX, int mouseY, PImage img, int imgX, int imgY) {
if (mouseX >= imgX && mouseX < imgX + img.width &&
mouseY >= imgY && mouseY < imgY + img.height) {
int localX = mouseX - imgX;
int localY = mouseY - imgY;
int pixel = img.get(localX, localY);
return alpha(pixel) > 0;
}
return false;
}而计算轮廓,也就是不透明边界,方便做描边处理,见下:
// 预计算不透明区域的边界
private void precomputeBoundaries() {
boundaries = new ArrayList<>();
for (int y = 0; y < img.height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < img.width; x++) {
int pixel = img.get(x, y);
if (alpha(pixel) > 0) {
// 检查当前像素是否为边界像素
boolean isBoundary = false;
// 检查相邻像素的透明度
if (x > 0 && alpha(img.get(x - 1, y)) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (x < img.width - 1 && alpha(img.get(x + 1, y)) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (y > 0 && alpha(img.get(x, y - 1)) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (y < img.height - 1 && alpha(img.get(x, y + 1)) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (isBoundary) {
boundaries.add(new Point(x, y)); // 存储边界点
}
}
}
}
}当有了这两个算法支持,接下来的任务就顺利多了,见完整代码:
import processing.core.PApplet;
import processing.core.PImage;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
//自定义数据类 ---- 点
class Point {
int x;
int y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public class ImageSketch extends PApplet {
PImage img;
int imgX, imgY;
List<Point> boundaries; // 存储不透明区域的边界点
/**
* 判断鼠标是否在图片的不透明区域内
* @param mouseX 鼠标的 x 坐标
* @param mouseY 鼠标的 y 坐标
* @param img 图片对象
* @param imgX 图片的 x 坐标
* @param imgY 图片的 y 坐标
* @return 如果鼠标在图片的不透明区域内返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
public boolean isMouseInImageOpaqueArea(int mouseX, int mouseY, PImage img, int imgX, int imgY) {
if (mouseX >= imgX && mouseX < imgX + img.width &&
mouseY >= imgY && mouseY < imgY + img.height) {
int localX = mouseX - imgX;
int localY = mouseY - imgY;
int pixel = img.get(localX, localY);
return alpha(pixel) > 0;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void settings() {
size(800, 600);
}
@Override
public void setup() {
// 加载 PNG 图片
img = loadImage("img.png");
img.resize(300,300);
imgX = (width - img.width) / 2;
imgY = (height - img.height) / 2;
precomputeBoundaries(); // 预计算不透明区域的边界
}
@Override
public void draw() {
background(255);
PImage displayImg = img;
boolean isMouseInImgOpaqueArea;
isMouseInImgOpaqueArea = isMouseInImageOpaqueArea(mouseX,mouseY,img,imgX,imgY);
if (isMouseInImgOpaqueArea) {
// 鼠标悬停时将图片转换为灰度图
displayImg = img.get();
displayImg.filter(GRAY);
for (Point p : boundaries) {
point(p.x + imgX, p.y + imgY); // 绘制边界点
}
}
stroke(0); // 设置描边颜色为黑色
strokeWeight(2); // 设置描边宽度为 2 像素
noFill(); // 不填充内部
// 绘制图片
image(displayImg, imgX, imgY);
}
// 预计算不透明区域的边界
private void precomputeBoundaries() {
boundaries = new ArrayList<>();
for (int y = 0; y < img.height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < img.width; x++) {
int pixel = img.get(x, y);
if (alpha(pixel) > 0) {
// 检查当前像素是否为边界像素
boolean isBoundary = false;
// 检查相邻像素的透明度
if (x > 0 && alpha(img.get(x - 1, y)) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (x < img.width - 1 && alpha(img.get(x + 1, y)) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (y > 0 && alpha(img.get(x, y - 1)) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (y < img.height - 1 && alpha(img.get(x, y + 1)) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (isBoundary) {
boundaries.add(new Point(x, y)); // 存储边界点
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PApplet.main("ImageSketch");
}
}效果如下:

第四项
假如场景更复杂,图片有变化,比如位置、旋转,那么如何解决?
当图片旋转时,鼠标悬停和点击检测会变得更加复杂,因为图片的坐标系统发生了变化。为了实现旋转图片的检测,需要重点考虑以下方面:
- 记录旋转角度:需要一个变量来记录图片的旋转角度。
- 旋转坐标转换:在检测鼠标是否在图片不透明区域内时,需要将鼠标坐标转换到图片的旋转坐标系中。
- 更新绘制逻辑:在绘制图片和边界时需考虑旋转角度。
我们先把事件处理好:
@Override
public void mousePressed() {
if (isMouseInImageOpaqueArea(mouseX, mouseY, img, imgX, imgY, rotationAngle)) {
isDragging = true;
// 计算鼠标点击位置相对于图片中心的偏移量
float centeredMouseX = mouseX - (imgX + img.width / 2);
float centeredMouseY = mouseY - (imgY + img.height / 2);
// 将偏移量转换到旋转后的坐标系
float rotatedMouseX = centeredMouseX * cos(-rotationAngle) - centeredMouseY * sin(-rotationAngle);
float rotatedMouseY = centeredMouseX * sin(-rotationAngle) + centeredMouseY * cos(-rotationAngle);
// 记录鼠标点击位置相对于图片的偏移量
offsetX = (int) rotatedMouseX;
offsetY = (int) rotatedMouseY;
}
}
@Override
public void mouseDragged() {
if (isDragging) {
// 计算鼠标相对于图片中心的当前偏移量
float centeredMouseX = mouseX - (imgX + img.width / 2);
float centeredMouseY = mouseY - (imgY + img.height / 2);
// 将当前偏移量转换到旋转后的坐标系
float rotatedMouseX = centeredMouseX * cos(-rotationAngle) - centeredMouseY * sin(-rotationAngle);
float rotatedMouseY = centeredMouseX * sin(-rotationAngle) + centeredMouseY * cos(-rotationAngle);
// 计算鼠标拖动的偏移量
float deltaX = rotatedMouseX - offsetX;
float deltaY = rotatedMouseY - offsetY;
// 将拖动的偏移量转换回全局坐标系
float globalDeltaX = deltaX * cos(rotationAngle) - deltaY * sin(rotationAngle);
float globalDeltaY = deltaX * sin(rotationAngle) + deltaY * cos(rotationAngle);
// 更新图片的位置
imgX += (int) globalDeltaX;
imgY += (int) globalDeltaY;
}
}
// 鼠标释放
@Override
public void mouseReleased() {
isDragging = false;
}
// 键盘事件
@Override
public void keyPressed() {
if (key == 'r') {
rotationAngle += PI / 16; // 按 'r' 键旋转图片
}
}检测悬停与否,重点考虑坐标系的变化:
/*
* 判断鼠标是否在图片的不透明区域内
* @param mouseX 鼠标的 x 坐标
* @param mouseY 鼠标的 y 坐标
* @param img 图片对象
* @param imgX 图片的 x 坐标
* @param imgY 图片的 y 坐标
* @param angle 图片的旋转角度
* @return 如果鼠标在图片的不透明区域内返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
public boolean isMouseInImageOpaqueArea(int mouseX, int mouseY, PImage img, int imgX, int imgY, float angle) {
// 先将鼠标坐标转换到以图片中心为原点的坐标系
float centeredMouseX = mouseX - (imgX + img.width / 2);
float centeredMouseY = mouseY - (imgY + img.height / 2);
// 再进行旋转转换
float rotatedMouseX = centeredMouseX * cos(-angle) - centeredMouseY * sin(-angle);
float rotatedMouseY = centeredMouseX * sin(-angle) + centeredMouseY * cos(-angle);
// 将旋转后的坐标转换回以图片左上角为原点的坐标系
rotatedMouseX += img.width / 2;
rotatedMouseY += img.height / 2;
if (rotatedMouseX >= 0 && rotatedMouseX < img.width &&
rotatedMouseY >= 0 && rotatedMouseY < img.height) {
int localX = (int) rotatedMouseX;
int localY = (int) rotatedMouseY;
int pixel = img.get(localX, localY);
return alpha(pixel) > 0;
}
return false;
}另外,移动旋转操作,使用translate和rotate函数:
translate(imgX + img.width / 2, imgY + img.height / 2); // 将原点移动到图片中心
rotate(rotationAngle); // 旋转图片完整代码参考如下:
import processing.core.PApplet;
import processing.core.PImage;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ImageSketchRotated extends PApplet {
PImage img;
int imgX, imgY;
List<Point> boundaries; // 存储不透明区域的边界点
boolean isDragging = false;
int offsetX, offsetY;
float rotationAngle = 0; // 图片的旋转角度
class Point {
int x;
int y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
/**
* 判断鼠标是否在图片的不透明区域内
* @param mouseX 鼠标的 x 坐标
* @param mouseY 鼠标的 y 坐标
* @param img 图片对象
* @param imgX 图片的 x 坐标
* @param imgY 图片的 y 坐标
* @param angle 图片的旋转角度
* @return 如果鼠标在图片的不透明区域内返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
public boolean isMouseInImageOpaqueArea(int mouseX, int mouseY, PImage img, int imgX, int imgY, float angle) {
// 先将鼠标坐标转换到以图片中心为原点的坐标系
float centeredMouseX = mouseX - (imgX + img.width / 2);
float centeredMouseY = mouseY - (imgY + img.height / 2);
// 再进行旋转转换
float rotatedMouseX = centeredMouseX * cos(-angle) - centeredMouseY * sin(-angle);
float rotatedMouseY = centeredMouseX * sin(-angle) + centeredMouseY * cos(-angle);
// 将旋转后的坐标转换回以图片左上角为原点的坐标系
rotatedMouseX += img.width / 2;
rotatedMouseY += img.height / 2;
if (rotatedMouseX >= 0 && rotatedMouseX < img.width &&
rotatedMouseY >= 0 && rotatedMouseY < img.height) {
int localX = (int) rotatedMouseX;
int localY = (int) rotatedMouseY;
int pixel = img.get(localX, localY);
return alpha(pixel) > 0;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void settings() {
size(800, 600);
}
@Override
public void setup() {
// 加载 PNG 图片
img = loadImage("img.png");
img.resize(300, 300);
imgX = (width - img.width) / 2;
imgY = (height - img.height) / 2;
precomputeBoundaries(); // 预计算不透明区域的边界
}
@Override
public void draw() {
background(255);
pushMatrix(); // 保存当前的变换矩阵
translate(imgX + img.width / 2, imgY + img.height / 2); // 将原点移动到图片中心
rotate(rotationAngle); // 旋转图片
translate(-img.width / 2, -img.height / 2); // 将原点移回图片左上角
// 检查鼠标是否悬停在图片上
boolean isMouseInImgOpaqueArea = isMouseInImageOpaqueArea(mouseX, mouseY, img, imgX, imgY, rotationAngle);
PImage displayImg = img;
if (isMouseInImgOpaqueArea) {
// 鼠标悬停时将图片转换为灰度图
displayImg = img.get();
displayImg.filter(GRAY);
for (Point p : boundaries) {
point(p.x, p.y); // 绘制边界点
}
}
stroke(0); // 设置描边颜色为黑色
strokeWeight(2); // 设置描边宽度为 2 像素
noFill(); // 不填充内部
// 绘制图片
image(displayImg, 0, 0);
popMatrix(); // 恢复之前的变换矩阵
}
@Override
public void mousePressed() {
if (isMouseInImageOpaqueArea(mouseX, mouseY, img, imgX, imgY, rotationAngle)) {
isDragging = true;
// 计算鼠标点击位置相对于图片中心的偏移量
float centeredMouseX = mouseX - (imgX + img.width / 2);
float centeredMouseY = mouseY - (imgY + img.height / 2);
// 将偏移量转换到旋转后的坐标系
float rotatedMouseX = centeredMouseX * cos(-rotationAngle) - centeredMouseY * sin(-rotationAngle);
float rotatedMouseY = centeredMouseX * sin(-rotationAngle) + centeredMouseY * cos(-rotationAngle);
// 记录鼠标点击位置相对于图片的偏移量
offsetX = (int) rotatedMouseX;
offsetY = (int) rotatedMouseY;
}
}
@Override
public void mouseDragged() {
if (isDragging) {
// 计算鼠标相对于图片中心的当前偏移量
float centeredMouseX = mouseX - (imgX + img.width / 2);
float centeredMouseY = mouseY - (imgY + img.height / 2);
// 将当前偏移量转换到旋转后的坐标系
float rotatedMouseX = centeredMouseX * cos(-rotationAngle) - centeredMouseY * sin(-rotationAngle);
float rotatedMouseY = centeredMouseX * sin(-rotationAngle) + centeredMouseY * cos(-rotationAngle);
// 计算鼠标拖动的偏移量
float deltaX = rotatedMouseX - offsetX;
float deltaY = rotatedMouseY - offsetY;
// 将拖动的偏移量转换回全局坐标系
float globalDeltaX = deltaX * cos(rotationAngle) - deltaY * sin(rotationAngle);
float globalDeltaY = deltaX * sin(rotationAngle) + deltaY * cos(rotationAngle);
// 更新图片的位置
imgX += (int) globalDeltaX;
imgY += (int) globalDeltaY;
}
}
@Override
public void mouseReleased() {
isDragging = false;
}
// 预计算不透明区域的边界
private void precomputeBoundaries() {
boundaries = new ArrayList<>();
int[] pixels = img.pixels; // 提前加载像素数据
for (int y = 0; y < img.height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < img.width; x++) {
int index = y * img.width + x; // 计算像素在数组中的索引
int pixel = pixels[index];
if (alpha(pixel) > 0) {
// 检查当前像素是否为边界像素
boolean isBoundary = false;
// 检查相邻像素的透明度
if (x > 0 && alpha(pixels[index - 1]) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (x < img.width - 1 && alpha(pixels[index + 1]) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (y > 0 && alpha(pixels[index - img.width]) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (y < img.height - 1 && alpha(pixels[index + img.width]) == 0) isBoundary = true;
if (isBoundary) {
boundaries.add(new Point(x, y)); // 存储边界点
}
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void keyPressed() {
if (key == 'r') {
rotationAngle += PI / 16; // 按 'r' 键旋转图片
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PApplet.main("ImageSketchRotated");
}
}效果如下:
接着说
一般的应用,有了这几个通用方法,想必能够应付了。写到这里,笔者突然想到另一种讨巧的解决方法,一种“笨办法”,但或许可以节省性能开销-------使用一张蒙版层来辅助检测边界,计算区域。
准备好素材,一张原图(地图样板),一张特殊区域图(蒙版)

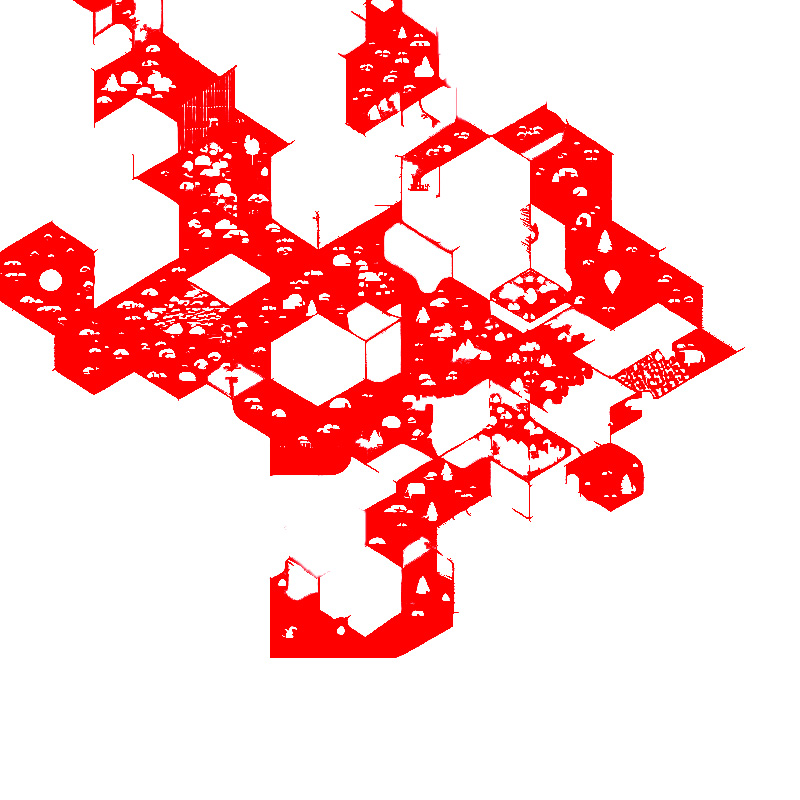
有了蒙版做辅助,就以它切入。去计算蒙版图片的每个像素值。如果是红色(R:255 G:0 B:0,或者放宽范围) ,那么就是我们想要的区域。算法如下:
/**
* 检查鼠标是否悬停在特殊区域
* @return 如果鼠标悬停在特殊区域返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
private boolean isMouseOverSpecialArea() {
if (mouseX >= 0 && mouseX < width && mouseY >= 0 && mouseY < height) {
int pixel = maskImage.get(mouseX, mouseY);
// 检查蒙版图对应位置是否为红色
return red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50;
}
return false;
}鼠标如果悬停特殊区域,那么该区域标红。其他代码照样,如下图:
import processing.core.PApplet;
import processing.core.PImage;
public class MapInteraction33 extends PApplet {
PImage mapImage;
PImage maskImage;
public void settings() {
size(800, 800);
}
public void setup() {
// 加载地图图片
mapImage = loadImage("ditu.png");
// 加载蒙版图
maskImage = loadImage("mask.jpg");
// 确保图片大小一致
mapImage.resize(width, height);
maskImage.resize(width, height);
}
public void draw() {
background(255);
// 绘制地图
image(mapImage, 0, 0);
// 检查鼠标是否悬停在特殊区域
if (isMouseOverSpecialArea()) {
// 绘制红色覆盖层,仅覆盖特殊区域
fill(255, 0, 0, 100); // 红色半透明
noStroke();
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
int pixel = maskImage.get(x, y);
if (red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50) {
rect(x, y, 1, 1);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 检查鼠标是否悬停在特殊区域
* @return 如果鼠标悬停在特殊区域返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
private boolean isMouseOverSpecialArea() {
if (mouseX >= 0 && mouseX < width && mouseY >= 0 && mouseY < height) {
int pixel = maskImage.get(mouseX, mouseY);
// 检查蒙版图对应位置是否为红色
return red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50;
}
return false;
}
public void mousePressed() {
if (isMouseOverSpecialArea()) {
// 处理点击事件
println("Clicked on the special area!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PApplet.main("MapInteraction33");
}
}绘制特殊区域高亮显示,其实可以随意发挥,这里可以优化一下代码,提前线计算好区域信息,减少性能消耗:
// 提前处理蒙版图,记录红色区域的像素位置
specialAreaPoints = new ArrayList<>();
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
int pixel = maskImage.get(x, y);
if (red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50) {
specialAreaPoints.add(new Point(x, y));
}
}
}然后再Draw...
fill(255, 0, 0, 100); // 红色半透明
noStroke();
for (Point point : specialAreaPoints) {
rect(point.x, point.y, 1, 1);
}完整代码:
import processing.core.PApplet;
import processing.core.PImage;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MapInteraction extends PApplet {
PImage mapImage;
PImage maskImage;
List<Point> specialAreaPoints; // 存储特殊区域位置
class Point {
int x;
int y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public void settings() {
size(800, 800);
}
public void setup() {
// 加载地图图片
mapImage = loadImage("ditu.png");
// 加载蒙版图
maskImage = loadImage("mask.jpg");
// 确保图片大小一致
mapImage.resize(width, height);
maskImage.resize(width, height);
// 提前处理蒙版图,记录红色区域的像素位置
specialAreaPoints = new ArrayList<>();
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
int pixel = maskImage.get(x, y);
if (red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50) {
specialAreaPoints.add(new Point(x, y));
}
}
}
}
public void draw() {
background(255);
// 绘制地图
image(mapImage, 0, 0);
// 检查鼠标是否悬停在特殊区域
if (isMouseOverSpecialArea()) {
// 绘制红色覆盖层,仅覆盖特殊区域
fill(255, 0, 0, 100); // 红色半透明
noStroke();
for (Point point : specialAreaPoints) {
rect(point.x, point.y, 1, 1);
}
}
}
/**
* 检查鼠标是否悬停在特殊区域
* @return 如果鼠标悬停在特殊区域返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
private boolean isMouseOverSpecialArea() {
if (mouseX >= 0 && mouseX < width && mouseY >= 0 && mouseY < height) {
int pixel = maskImage.get(mouseX, mouseY);
// 检查蒙版图对应位置是否为红色
return red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50;
}
return false;
}
public void mousePressed() {
if (isMouseOverSpecialArea()) {
// 处理点击事件
println("Clicked on the special area!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PApplet.main("MapInteraction");
}
}效果如下:
如果继续美化,可以加一些辉光效果,辉光算法如下:
/**
* 计算特殊区域的边界
* @return 边界点列表
*/
private List<Point> calculateBoundary() {
List<Point> boundary = new ArrayList<>();
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
int pixel = maskImage.get(x, y);
if (red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50) {
// 检查当前像素是否为边界像素
boolean isBoundary = false;
if (x > 0 && !isRed(maskImage.get(x - 1, y))) isBoundary = true;
if (x < width - 1 && !isRed(maskImage.get(x + 1, y))) isBoundary = true;
if (y > 0 && !isRed(maskImage.get(x, y - 1))) isBoundary = true;
if (y < height - 1 && !isRed(maskImage.get(x, y + 1))) isBoundary = true;
if (isBoundary) {
boundary.add(new Point(x, y));
}
}
}
}
return boundary;
} /**
* 绘制辉光效果
*/
private void drawGlowEffect() {
// 创建一个与窗口大小相同的临时图像
PImage glowImage = createImage(width, height, ARGB);
glowImage.loadPixels();
// 将特殊区域绘制到临时图像上,增强颜色透明度
for (Point p : specialAreaBoundary) {
int index = p.y * width + p.x;
glowImage.pixels[index] = color(255, 0, 0, 255); // 增大透明度
}
glowImage.updatePixels();
glowImage.filter(BLUR, 2); // 增大模糊半径
tint(255,255);
image(glowImage, 0, 0);
// 对临时图像应用模糊滤镜,增大模糊半径
glowImage.filter(BLUR, 4); // 增大模糊半径
tint(255,255);
image(glowImage, 0, 0);
// 设置混合模式为 ADD,多次叠加辉光图像
blendMode(ADD);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { // 多次叠加
image(glowImage, 0, 0);
}
// 恢复默认混合模式
blendMode(BLEND);
}完整代码:
import processing.core.PApplet;
import processing.core.PImage;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import processing.opengl.*;
public class MapInteractionwithglow extends PApplet {
class Point {
int x;
int y;
Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
PImage mapImage;
PImage maskImage;
List<Point> specialAreaBoundary;
ArrayList<MapInteractionwithglow.Point> specialAreaPoints = new ArrayList<>();
public void settings() {
size(800, 800);
}
public void setup() {
// 加载地图图片
mapImage = loadImage("ditu.png");
// 加载蒙版图
maskImage = loadImage("mask.jpg");
// 确保图片大小一致
mapImage.resize(width, height);
maskImage.resize(width, height);
// 提前计算特殊区域的边界
specialAreaBoundary = calculateBoundary();
// 提前处理蒙版图,记录红色区域的像素位置
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
int pixel = maskImage.get(x, y);
if (red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50) {
specialAreaPoints.add(new MapInteractionwithglow.Point(x, y));
}
}
}
}
public void draw() {
background(255);
// 绘制地图
image(mapImage, 0, 0);
// 检查鼠标是否悬停在特殊区域
if (isMouseOverSpecialArea()) {
fill(255, 0, 0, 60); // 红色半透明
noStroke();
for (MapInteractionwithglow.Point point : specialAreaPoints) {
rect(point.x, point.y, 1, 1);
}
// 绘制辉光效果
drawGlowEffect();
}
}
/**
* 绘制辉光效果
*/
private void drawGlowEffect() {
// 创建一个与窗口大小相同的临时图像
PImage glowImage = createImage(width, height, ARGB);
glowImage.loadPixels();
// 将特殊区域绘制到临时图像上,增强颜色透明度
for (Point p : specialAreaBoundary) {
int index = p.y * width + p.x;
glowImage.pixels[index] = color(255, 0, 0, 255); // 增大透明度
}
glowImage.updatePixels();
glowImage.filter(BLUR, 2); // 增大模糊半径
tint(255,255);
image(glowImage, 0, 0);
// 对临时图像应用模糊滤镜,增大模糊半径
glowImage.filter(BLUR, 4); // 增大模糊半径
tint(255,255);
image(glowImage, 0, 0);
// 设置混合模式为 ADD,多次叠加辉光图像
blendMode(ADD);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { // 多次叠加
image(glowImage, 0, 0);
}
// 恢复默认混合模式
blendMode(BLEND);
}
/**
* 计算特殊区域的边界
* @return 边界点列表
*/
private List<Point> calculateBoundary() {
List<Point> boundary = new ArrayList<>();
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
int pixel = maskImage.get(x, y);
if (red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50) {
// 检查当前像素是否为边界像素
boolean isBoundary = false;
if (x > 0 && !isRed(maskImage.get(x - 1, y))) isBoundary = true;
if (x < width - 1 && !isRed(maskImage.get(x + 1, y))) isBoundary = true;
if (y > 0 && !isRed(maskImage.get(x, y - 1))) isBoundary = true;
if (y < height - 1 && !isRed(maskImage.get(x, y + 1))) isBoundary = true;
if (isBoundary) {
boundary.add(new Point(x, y));
}
}
}
}
return boundary;
}
/**
* 检查像素是否为红色
* @param pixel 像素颜色
* @return 如果是红色返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
private boolean isRed(int pixel) {
return red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50;
}
/**
* 检查鼠标是否悬停在特殊区域
* @return 如果鼠标悬停在特殊区域返回 true,否则返回 false
*/
private boolean isMouseOverSpecialArea() {
if (mouseX >= 0 && mouseX < width && mouseY >= 0 && mouseY < height) {
int pixel = maskImage.get(mouseX, mouseY);
// 检查蒙版图对应位置是否为红色
return red(pixel) > 200 && green(pixel) < 50 && blue(pixel) < 50;
}
return false;
}
public void mousePressed() {
if (isMouseOverSpecialArea()) {
// 处理点击事件
println("Clicked on the special area!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PApplet.main("MapInteractionwithglow");
}
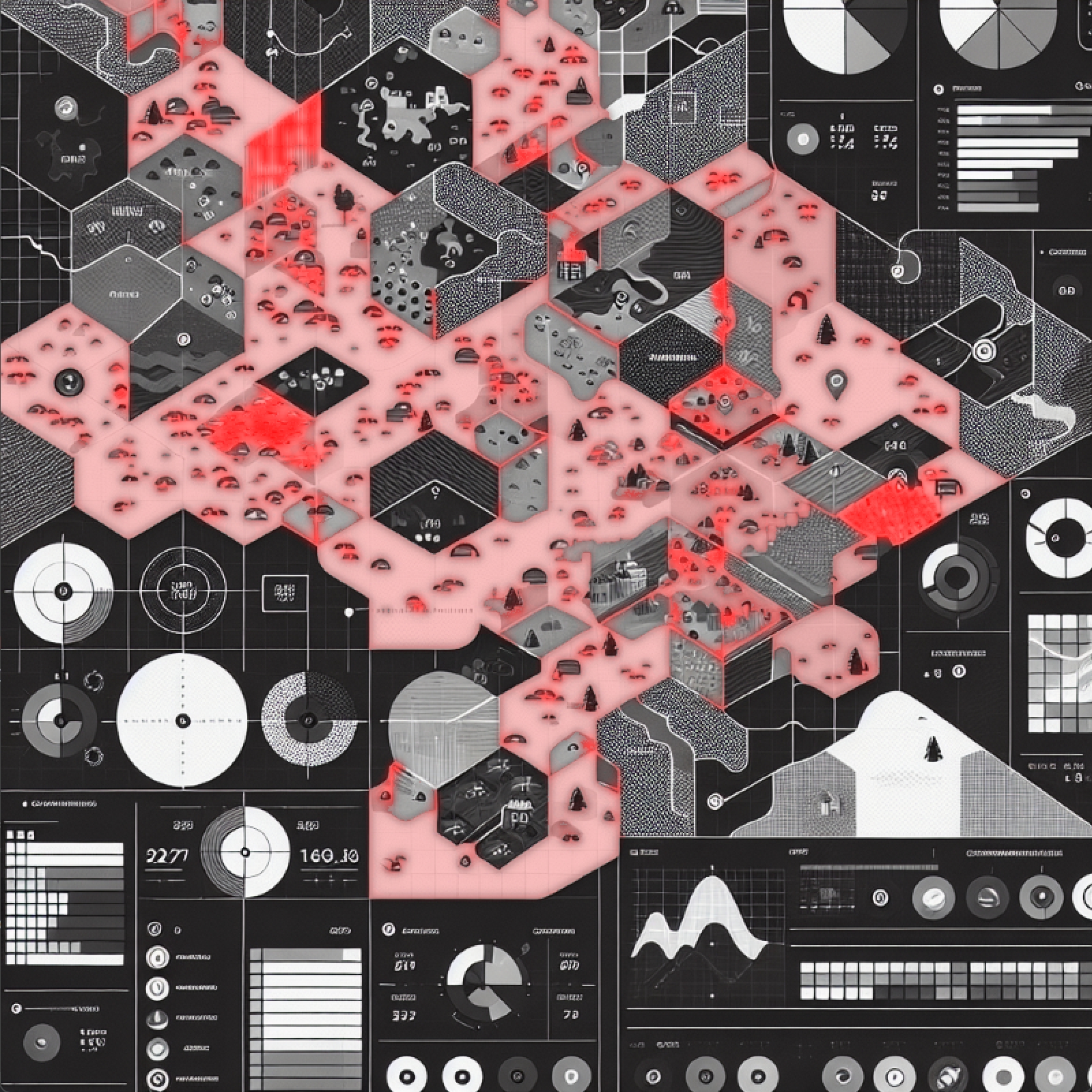
}效果:

尾声
从规则四边形(矩形)到不规则多边形,再延伸到png透明通道图片,最后举了地图检测的例子。一般场景下足以应付检测问题了。
想要深入研究,大致可以参考经典游戏《英雄无敌3》中,回到城堡选中建筑物时的交互体验,不过游戏中的解决方案看来是很科学高效的,或许是调用了OpenGL图形接口的相关算法。未来有机会还需继续探究算法。
Processing (Java) 中实现2D任意图形的鼠标悬停检测 · 2D射线检测 · 模拟按钮 · 点击事件的更多相关文章
- Android Listview中Button按钮点击事件冲突解决办法
今天做项目时,ListView中含有了Button组件,心里一早就知道肯定会有冲突,因为以前就遇到过,并解决过,可惜当时没有记录下来. 今天在做的时候,继续被这个问题郁闷了一把,后来解决后,赶紧来记录 ...
- 四种方式写按钮点击事件和Android 中常用的布局
1.匿名内部类的方式 2.创建一个类实现onClickListener,实现onClick方法,设置控件点击时传一个类的对象 3.让当前类实现onClickListener,设置控件点击事件时传递一个 ...
- c#在代码中再次调用按钮点击事件
在一个按钮事件中调用另一个按钮(button1)的点击事件,可以直接如下: button1.PerformClick() 也称之为 以编程方式调用按钮的click事件
- java中十进制转换为任意进制
次笔试时候遇到的关于十进制转换成十三进制的编程题. 先说说简单的思路吧: 1.十进制数 num 转换为 n进制 num%n结果肯定为n进制数的最后一位 结果存入一个数组中 2.进入一个循环num!=0 ...
- java中并不是任意多个接口都可以实现多实现
interface A{ public abstract void show(); } interface B{ public abstract int show(); } public class ...
- WPF中,输入完密码回车提交 ,回车触发按钮点击事件
类似与winform中窗体的AcceptButton属性,在wpf中,需要将按钮的IsDefault设置为true就行.
- Javascript(jQuery)中绑定页面上所有按钮点击事件的几种方式
方法一:使用document对象查找所有的按钮 [javascript] view plain copy 在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片 //按照dom的方式添加事件处理 function B ...
- angular JS中使用jquery datatable 自定义搜索按钮点击事件 和mRender的 ng-click事件
'use strict'; app.controller('DataTableCtrl', function ($scope, $compile) { $scope.searchFiles = { n ...
- ASPxGridView中Command列自定义按钮点击事件概要
其中CustomButtonClick="ButtonClick",e.buttonID可以获取到自定义按钮的id e.visibleIndex获取到行的索引 grdList.Ge ...
- 关于android中,菜单按钮点击事件首次执行之后再次执行需要双击按钮的问题
有时候在获取事件的时候,需要双击才能获取,解决方法很简单,把返回值设为true,那么这个事件就不会再分发了,我预计是设为其他值会继续分发,造成事件的相应混乱
随机推荐
- 解决phpmyadmin导入MYSQL数据库限制大小为50M的问题
有时候想导入的数据库太大.但是遭到的限制 解决phpmyadmin导入MYSQL数据库限制大小为50M的问题 转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/wesky/p/10609340. ...
- Qt编写地图综合应用36-覆盖物折线
一.前言 折线图目前应用最广的也是用来绘制各种轨迹,折线图其实就是后面动态轨迹图.飞机航线图的前身,公用的一个方法addPolyline,折线图可以设置颜色.粗细.透明度等属性,如果开启了悬浮绘图工具 ...
- Qt通用方法及类库6
函数名 //判断是否是IP地址 static bool isIP(const QString &ip); //判断是否是MAC地址 static bool isMac(const QStrin ...
- lottie-web动画库在HTML5页面中和在vue项目中的两种使用方式
本文主要介绍lottie-web动画库在HTML5页面中和在vue项目中的两种使用方式. 1.在HTML5页面中的使用方式 具体使用步骤详见下面的代码: <!DOCTYPE html> & ...
- 第三方JavaScript库有时会附带*.map文件的所用
第三方JavaScript库有时会附带*.map文件的所用:起到对源***.js文件进行源码转换和压缩的作用. 详见参考链接:JavaScript Source Map 详解
- 昔日移动端IM明星 “米聊” 即将停止服务
2021年1月19日,小米旗下米聊宣布,将于2021年2月19日12点停止米聊的服务. 1.以下消息来自米聊官网 2.关于米聊 米聊是小米科技出品的一款免费即时通讯工具,推出时间为:2010年12 ...
- 基于开源IM即时通讯框架MobileIMSDK:RainbowChat-iOS端v6.0版已发布
关于MobileIMSDK MobileIMSDK 是一套专门为移动端开发的开源IM即时通讯框架,超轻量级.高度提炼,一套API优雅支持UDP .TCP .WebSocket 三种协议,支持iOS.A ...
- 【Java 温故而知新系列】基础知识-02 数据基本类型
1.Java基本数据类型 Java语言是强类型语言,对于每一种数据都定义了明确的具体的数据类型,在内存中分配了不同大小的内存空间. 基本数据类型 数值型:整数类型(byte,short,int,lon ...
- CSP2024 游记
前文 Day -1 上午考试了,多少分忘了. 晚上老师布置模板题. Day 0 继续前一天的模板题,并没有 AK. Day 1 J 组 先看 T1,发现是一道简单的水题,切了. 再看 T2,也是水题, ...
- Android性能测试(内存、cpu、fps、流量、GPU、电量)——adb篇
adb 常用命令 获取连接设备号:adb devices 列出设备所有已安装的包名 (不需root权限) adb shell "pm list packages",可以加上 ...
