初识Hibernate 缓存
生活就像一杯咖啡,让你我慢慢的品尝,品尝它的苦涩和甘甜......
一、什么是Hibernate缓存。
解析:白话来说就是缓存数据的容器
官方标准点缓存:是计算机领域的概念,它介于应用程序和永久性数据存储源之间。
作用:降低应用程序直接读写数据库的频率,从而提高程序的运行性能。缓存中的数据是数据存储源中数据的拷贝。缓存的物理介质通常是内存。
二、缓存一般分为三个类
一级缓存
二级缓存
查看缓存
三、一级缓存
场景一:使用同一个session连续查询两次同一个对象
/查询学生信息
public static void select(){ //由班级查询该班级学生信息
Session session=HibernateUtil.currentSession();
Grade grade=(Grade) session.get(Grade.class, );
//输出班级信息
System.out.println(grade.getGname());
Grade grade2=(Grade) session.get(Grade.class, );
//输出班级信息
System.out.println(grade2.getGname());
}
执行结果:

场景一:在第一次查询完毕后,关闭session对象,重新开启一个session然后继续查询同一个对象
//查询学生信息
public static void select(){ //由班级查询该班级学生信息
Session session=HibernateUtil.currentSession();
Grade grade=(Grade) session.get(Grade.class, );
//输出班级信息
System.out.println(grade.getGname());
//关闭session
HibernateUtil.closeSession();
//重新获取session
session=HibernateUtil.currentSession();
Grade grade2=(Grade) session.get(Grade.class, );
//输出班级信息
System.out.println(grade2.getGname());
}
执行结果:

解析:
1:当我没有关闭session时用的同一个session两次访问同一个对象时,只会向DB端发送一条sql语句
* 原因:因为我第一次访问数据库的时候Hibernate会自动的将我查询出来的结果保留一份查询出来的对象到一级缓存
并且这个额对象是根据OID唯一标识的,也可以理解为数据库中的主键值,然后当我再一次访问一个对象时,Hibernate
机制会自动的先去一级缓存中查找看有没有OID与我要查询的OID相同的对象,如果有的话,则直接从一级缓存中 拿数据
如果没有相同的OID则说明缓存中没有我要的记录,那么就会直接去访问DB端了,这样的话,又会重新发送一条sql
2:当我第一次查询完数据后立即关闭session,这时重新开启一个session来访问同一个对象,这时我们会发现它居然向数据库发送了两条Sql语句。这是为什么呢?
* 原因:其实原因很简单,因为我们虽然说是访问的同一个对象,但是我们随即就关闭了这个session而重新开启了一个session,
此时我们访问时的session是不一致的也就是说是两个不同的session发出的请求,这样理解的话,我们就不难理解了。
所以总结出,一级缓存是一个会话级别的缓存,当一次回话结束后该会话里的缓存则会全部的销毁,所有我们自然就只能重新发送一条sql啦。
3补充以下方法支持一级缓存

四、二级缓存
(一)配置二级缓存
1.引入如下jar包。
ehcache-1.2.3.jar 核心库
backport-util-concurrent.jar
commons-logging.jar
2.配置Hibernate.cfg.xml开启二级缓存
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
3.配置二级缓存的供应商
<property name="hibernate.cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider</property>
4.指定使用二级缓存的类
方案一:在*.hbm.xml中配置
在<class元素的子元素下添加chche子节点,但该配置仅会缓存对象的简单属性,若希望缓存集合属性中的元素,必须在set元素中添加<cache>子元素
<class name="Student" table="STUDENT">
<cache usage="read-write"/>
方案二:在大配置文件(hibernate.cfg.xml)中配置
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="cn.happy.entity.Student"/>
<collection-cache usage="read-write" collection=""/>--可注释如果配置不成功
注意大配置的书写位置
Multiple annotations found at this line:
- The content of element type "session-factory" must match "(property*,mapping*,(class-cache|collection-
cache)*,event*,listener*)".
- Start tag of element <session-factory>
*5.在src下添加ehcache.xml文件,从etc获取文件即可。
<ehcache>
<!-- Sets the path to the directory where cache .data files are created.
If the path is a Java System Property it is replaced by
its value in the running VM.
The following properties are translated:
user.home - User's home directory
user.dir - User's current working directory
java.io.tmpdir - Default temp file path -->
<diskStore path="d:/tmp"/>
<!--Default Cache configuration. These will applied to caches programmatically created through
the CacheManager.
The following attributes are required for defaultCache:
maxInMemory - Sets the maximum number of objects that will be created in memory
eternal - Sets whether elements are eternal. If eternal, timeouts are ignored and the element
is never expired.
timeToIdleSeconds - Sets the time to idle for an element before it expires. Is only used
if the element is not eternal. Idle time is now - last accessed time
timeToLiveSeconds - Sets the time to live for an element before it expires. Is only used
if the element is not eternal. TTL is now - creation time
overflowToDisk - Sets whether elements can overflow to disk when the in-memory cache
has reached the maxInMemory limit.
-->
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory=""
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds=""
timeToLiveSeconds=""
overflowToDisk="true"
/>
<!--Predefined caches. Add your cache configuration settings here.
If you do not have a configuration for your cache a WARNING will be issued when the
CacheManager starts
The following attributes are required for defaultCache:
name - Sets the name of the cache. This is used to identify the cache. It must be unique.
maxInMemory - Sets the maximum number of objects that will be created in memory
eternal - Sets whether elements are eternal. If eternal, timeouts are ignored and the element
is never expired.
timeToIdleSeconds - Sets the time to idle for an element before it expires. Is only used
if the element is not eternal. Idle time is now - last accessed time
timeToLiveSeconds - Sets the time to live for an element before it expires. Is only used
if the element is not eternal. TTL is now - creation time
overflowToDisk - Sets whether elements can overflow to disk when the in-memory cache
has reached the maxInMemory limit.
-->
<!-- Sample cache named sampleCache1
This cache contains a maximum in memory of elements, and will expire
an element if it is idle for more than minutes and lives for more than
minutes.
If there are more than elements it will overflow to the
disk cache, which in this configuration will go to wherever java.io.tmp is
defined on your system. On a standard Linux system this will be /tmp"
-->
<cache name="sampleCache1"
maxElementsInMemory=""
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds=""
timeToLiveSeconds=""
overflowToDisk="true"
/>
<!-- Sample cache named sampleCache2
This cache contains elements. Elements will always be held in memory.
They are not expired. -->
<cache name="sampleCache2"
maxElementsInMemory=""
eternal="true"
timeToIdleSeconds=""
timeToLiveSeconds=""
overflowToDisk="false"
/> -->
<!-- Place configuration for your caches following -->
</ehcache>
(二)二级缓存散装数据原理图
解析:每次从二级缓存中取出的对象,都是一个新的对象。
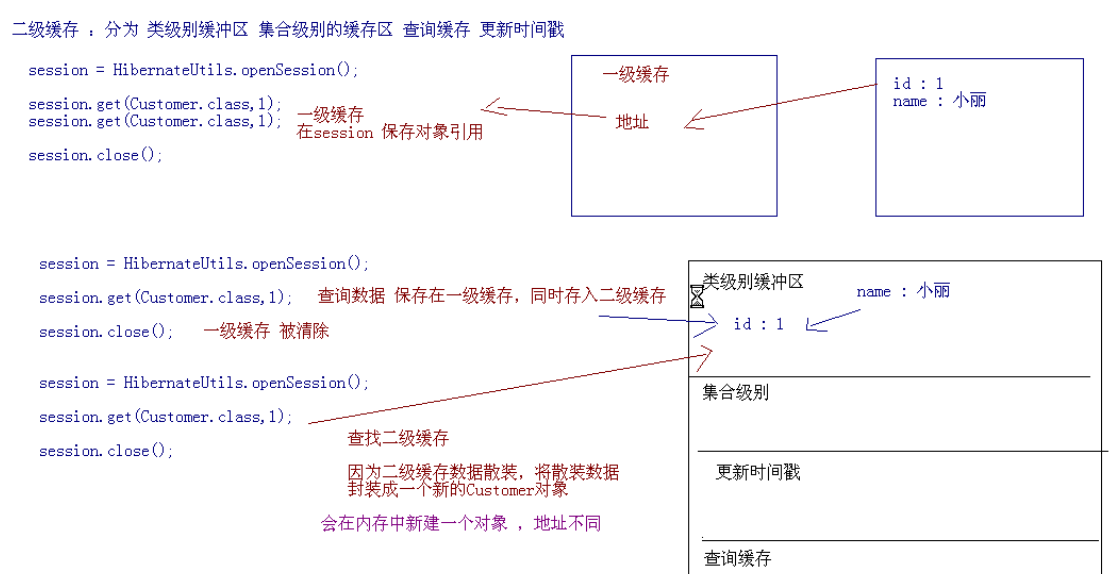
(三)什么样的数据适合放入二级缓存中?
1很少被修改的数据
2不是很重要的数据,允许出现偶尔并发的数据
3不会被并发访问的数据
4参考数据,指的是供应用参考的常量数据,它的实列数目有限,它的实列被许多其他类的实列引用,实列极少或者从来不会被修改。
讲述几乎结束了!!!
初识Hibernate 缓存的更多相关文章
- Hibernate 缓存机制浅析
1. 为什么要用 Hibernate 缓存? Hibernate是一个持久层框架,经常访问物理数据库. 为了降低应用程序对物理数据源访问的频次,从而提高应用程序的运行性能. 缓存内的数据是对物理数据源 ...
- hibernate缓存机制(转)
原文出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/wean/archive/2012/05/16/2502724.html 一.why(为什么要用Hibernate缓存?) Hibernate是 ...
- 【转】hibernate缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存
什么是缓存? 缓存是介于物理数据源与应用程序之间,是对数据库中的数据复制一份临时放在内存中的容器,其作用是为了减少应用程序对物理数据源访问的次数,从而提高了应用程序的运行性能.Hibernate在进行 ...
- Hibernate缓存(转)
来自:http://www.cnblogs.com/wean/archive/2012/05/16/2502724.html 一.why(为什么要用Hibernate缓存?) Hibernate是一个 ...
- Hibernate缓存原理与策略
Hibernate缓存原理: 对于Hibernate这类ORM而言,缓存显的尤为重要,它是持久层性能提升的关键.简单来讲Hibernate就是对JDBC进行封装,以实现内部状态的管理,OR关系的映射等 ...
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记93:Hibernate学习之路---Hibernate 缓存介绍,缓存级别,使用二级缓存的情况,二级缓存的架构集合缓存,二级缓存的并发策略,实现步骤,集合缓存,查询缓存,时间戳缓存
本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当于学习笔记 ②将自己的经验分享给大家,相互学习,互相交流,不可商用 内容难免出现问题,欢迎指正,交流,探讨,可以留言,也可以通过以下方式联系. 本人互联网技术爱 ...
- Hibernate缓存原理与策略 Hibernate缓存原理:
Hibernate缓存原理: 对于Hibernate这类ORM而言,缓存显的尤为重要,它是持久层性能提升的关键.简单来讲Hibernate就是对JDBC进行封装,以实现内部状态的管理,OR关系的映射等 ...
- Hibernate 缓存机制
一.why(为什么要用Hibernate缓存?) Hibernate是一个持久层框架,经常访问物理数据库. 为了降低应用程序对物理数据源访问的频次,从而提高应用程序的运行性能. 缓存内的数据是对物理数 ...
- hibernate缓存说明
hibernate缓存说明: 1.一级缓存(session级别缓存) 一级缓存,不是用来提升性能,是用来处理事务的 2.二级缓存(sessionFactory级别缓存): 二级缓存,对 ...
随机推荐
- 【译】怎样编写移动优先的CSS
原文:How To Write Mobile-first CSS 作者: 译者:huansky 构建响应式网站是今天前端开发人员必备的技能. 当我们谈论响应式网站时,移动优先这个词立刻就会浮现. 我们 ...
- 【QQ技术】群文件报毒怎样下载?~ 变相绕过QQ复杂检验过程
刚才又人问我,要是群文件被鉴定为病毒那怎么下载? 我简单说一下吧: 其实qq客户端过滤比较严的,而web段却还是老一套,很多人说出现这个情况其实是腾讯已经把他库里面的文件删了,其实不然 如果源删了,那 ...
- CSS颜色模式转换器的实现
前面的话 在CSS中,颜色的表示方式主要包括关键字.16进制.RGB模式.RGBA模式.HSL模式.HSLA模式.关于颜色模式的详细信息移步至此.本文就16进制.RGB模式及HSL模式的互相转换进行实 ...
- javascript学习目录
类型系统 [1]基本数据类型 [2]引用类型中的对象Object [3]引用类型中的数组Array [4]引用类型中的时间Date [5]函数Function [6]正则表达式RegExp [7]包装 ...
- PHP实现简易blog
最近,有时间看了点PHP的代码.参考PHP100教程做了简单的blog,网易云课堂2012年的教程,需要的可以找一下,这里面简单的记录一下. 首先是集成环境,这里选用的WAMP:http://www. ...
- SQL Server安全(4/11):许可(Permissions)
在保密你的服务器和数据,防备当前复杂的攻击,SQL Server有你需要的一切.但在你能有效使用这些安全功能前,你需要理解你面对的威胁和一些基本的安全概念.这篇文章提供了基础,因此你可以对SQL Se ...
- GitHub一代:我们都是开源控
我们是新的GitHub一代?GitHub塑造了新式开源文化?嗯,看看十几年开源控.Getable CTO Mikeal Rogers 是怎么说的吧: GitHub本来想做一个开源软件协作平台,结果做着 ...
- golang内存分配
golang内存分配 new一个对象的时候,入口函数是malloc.go中的newobject函数 func newobject(typ *_type) unsafe.Pointer { flags ...
- 常用的一些SQL语句整理,也许有你想要的。
本篇文章是对一些常用的sql语句进行了总结与分析,需要的朋友参考下,也许会有你需要的. 1.SQL行列转换 问题:假设有张学生成绩表(tb)如下:姓名 课程 分数张三 语文 74张三 数学 83张三 ...
- 关于CodeFirst异常:无法确定类型'XXX'和类型‘YYY’之间的关联的主体端,必须使用关系 Fluent API 或数据注释显式配置此关联的主体端。
此错误的原因是,你配置两个实体间的关系为一对一 然而我认为的一对一关系是,两者之间必须存在一个主体, 也就是说,你不能表1的外键是表2的主键并且表1的主键是表2的外键, 这样不符合数据库式吧? 我想多 ...
