spring remoting源码分析--Hessian分析
1. Caucho
1.1 概况
spring-remoting代码的情况如下:

本节近分析caucho模块。
1.2 分类
其中以hession为例,Hessian远程服务调用过程:
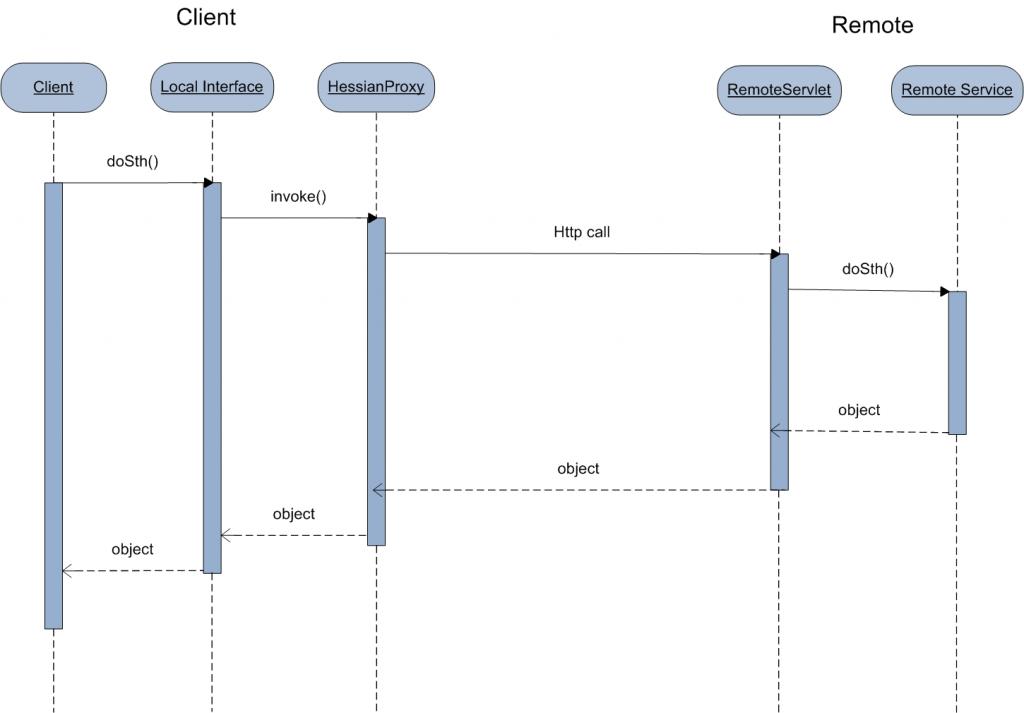
Hessian远程服务调用过程
1.2.1 客户端
BurlapProxyFactoryBean,BurlapClientInterceptor;
HessianProxyFactoryBean,HessianClientInterceptor;
HessianProxyFactoryBean继承自HessianClientInterceptor,间接封装了HessianProxyFactory。HessianProxyFactory是hessian的client实现类,
示例:
public interface Basic {
public String hello();
}
import com.caucho.hessian.client.HessianProxyFactory;
public class BasicClient {
public static void main(String []args)
throws Exception
{
String url = "http://www.caucho.com/hessian/test/basic";
HessianProxyFactory factory = new HessianProxyFactory();
Basic basic = (Basic) factory.create(Basic.class, url);
System.out.println("Hello: " + basic.hello());
}
}
create方法如下:
/**
* Creates a new proxy with the specified URL. The returned object
* is a proxy with the interface specified by api.
*
* <pre>
* String url = "http://localhost:8080/ejb/hello");
* HelloHome hello = (HelloHome) factory.create(HelloHome.class, url);
* </pre>
*
* @param api the interface the proxy class needs to implement
* @param url the URL where the client object is located.
*
* @return a proxy to the object with the specified interface.
*/
public Object create(Class<?> api, URL url, ClassLoader loader)
{
if (api == null)
throw new NullPointerException("api must not be null for HessianProxyFactory.create()");
InvocationHandler handler = null; handler = new HessianProxy(url, this, api); return Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader,
new Class[] { api,
HessianRemoteObject.class },
handler);
}
其中HessianProxy实现了java的动态代理
/**
* Proxy implementation for Hessian clients. Applications will generally
* use HessianProxyFactory to create proxy clients.
*/
public class HessianProxy implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final Logger log
= Logger.getLogger(HessianProxy.class.getName()); protected HessianProxyFactory _factory; private WeakHashMap<Method,String> _mangleMap
= new WeakHashMap<Method,String>(); private Class<?> _type;
private URL _url; /**
* Protected constructor for subclassing
*/
protected HessianProxy(URL url, HessianProxyFactory factory)
{
this(url, factory, null);
} /**
* Protected constructor for subclassing
*/
protected HessianProxy(URL url,
HessianProxyFactory factory,
Class<?> type)
{
_factory = factory;
_url = url;
_type = type;
}
}
最重要的invoke方法如下:
/**
* Handles the object invocation.
*
* @param proxy the proxy object to invoke
* @param method the method to call
* @param args the arguments to the proxy object
*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object []args)
throws Throwable
{
String mangleName; synchronized (_mangleMap) {
mangleName = _mangleMap.get(method);
} if (mangleName == null) {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?> []params = method.getParameterTypes(); // equals and hashCode are special cased
if (methodName.equals("equals")
&& params.length == 1 && params[0].equals(Object.class)) {
Object value = args[0];
if (value == null || ! Proxy.isProxyClass(value.getClass()))
return Boolean.FALSE; Object proxyHandler = Proxy.getInvocationHandler(value); if (! (proxyHandler instanceof HessianProxy))
return Boolean.FALSE; HessianProxy handler = (HessianProxy) proxyHandler; return new Boolean(_url.equals(handler.getURL()));
}
else if (methodName.equals("hashCode") && params.length == 0)
return new Integer(_url.hashCode());
else if (methodName.equals("getHessianType"))
return proxy.getClass().getInterfaces()[0].getName();
else if (methodName.equals("getHessianURL"))
return _url.toString();
else if (methodName.equals("toString") && params.length == 0)
return "HessianProxy[" + _url + "]"; if (! _factory.isOverloadEnabled())
mangleName = method.getName();
else
mangleName = mangleName(method); synchronized (_mangleMap) {
_mangleMap.put(method, mangleName);
}
} InputStream is = null;
HessianConnection conn = null; try {
if (log.isLoggable(Level.FINER))
log.finer("Hessian[" + _url + "] calling " + mangleName); conn = sendRequest(mangleName, args); is = getInputStream(conn); if (log.isLoggable(Level.FINEST)) {
PrintWriter dbg = new PrintWriter(new LogWriter(log));
HessianDebugInputStream dIs
= new HessianDebugInputStream(is, dbg); dIs.startTop2(); is = dIs;
} AbstractHessianInput in; int code = is.read(); if (code == 'H') {
int major = is.read();
int minor = is.read(); in = _factory.getHessian2Input(is); Object value = in.readReply(method.getReturnType()); return value;
}
else if (code == 'r') {
int major = is.read();
int minor = is.read(); in = _factory.getHessianInput(is); in.startReplyBody(); Object value = in.readObject(method.getReturnType()); if (value instanceof InputStream) {
value = new ResultInputStream(conn, is, in, (InputStream) value);
is = null;
conn = null;
}
else
in.completeReply(); return value;
}
else
throw new HessianProtocolException("'" + (char) code + "' is an unknown code");
} catch (HessianProtocolException e) {
throw new HessianRuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if (is != null)
is.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.log(Level.FINE, e.toString(), e);
} try {
if (conn != null)
conn.destroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.log(Level.FINE, e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
发送http请求
/**
* Sends the HTTP request to the Hessian connection.
*/
protected HessianConnection sendRequest(String methodName, Object []args)
throws IOException
{
HessianConnection conn = null; conn = _factory.getConnectionFactory().open(_url);
boolean isValid = false; try {
addRequestHeaders(conn); OutputStream os = null; try {
os = conn.getOutputStream();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new HessianRuntimeException(e);
} if (log.isLoggable(Level.FINEST)) {
PrintWriter dbg = new PrintWriter(new LogWriter(log));
HessianDebugOutputStream dOs = new HessianDebugOutputStream(os, dbg);
dOs.startTop2();
os = dOs;
} AbstractHessianOutput out = _factory.getHessianOutput(os); out.call(methodName, args);
out.flush(); conn.sendRequest(); isValid = true; return conn;
} finally {
if (! isValid && conn != null)
conn.destroy();
}
}
创建http连接代码
/**
* Opens a new or recycled connection to the HTTP server.
*/
public HessianConnection open(URL url)
throws IOException
{
if (log.isLoggable(Level.FINER))
log.finer(this + " open(" + url + ")"); URLConnection conn = url.openConnection(); // HttpURLConnection httpConn = (HttpURLConnection) conn;
// httpConn.setRequestMethod("POST");
// conn.setDoInput(true); long connectTimeout = _proxyFactory.getConnectTimeout(); if (connectTimeout >= 0)
conn.setConnectTimeout((int) connectTimeout); conn.setDoOutput(true); long readTimeout = _proxyFactory.getReadTimeout(); if (readTimeout > 0) {
try {
conn.setReadTimeout((int) readTimeout);
} catch (Throwable e) {
}
}
1.2.2 服务器端
HessianExporter及其实现类HessianServiceExporter,SimpleHessianServiceExporter.
hessian服务端示例
package hessian.test;
import com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianServlet;
public class BasicService extends HessianServlet implements Basic {
public String hello()
{
return "Hello, world";
}
}
我们来看一下:
HessianServiceExporter
/**
* Servlet-API-based HTTP request handler that exports the specified service bean
* as Hessian service endpoint, accessible via a Hessian proxy.
*
* <p><b>Note:</b> Spring also provides an alternative version of this exporter,
* for Sun's JRE 1.6 HTTP server: {@link SimpleHessianServiceExporter}.
*
* <p>Hessian is a slim, binary RPC protocol.
* For information on Hessian, see the
* <a href="http://www.caucho.com/hessian">Hessian website</a>.
* <b>Note: As of Spring 4.0, this exporter requires Hessian 4.0 or above.</b>
*
* <p>Hessian services exported with this class can be accessed by
* any Hessian client, as there isn't any special handling involved.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 13.05.2003
* @see HessianClientInterceptor
* @see HessianProxyFactoryBean
* @see org.springframework.remoting.httpinvoker.HttpInvokerServiceExporter
* @see org.springframework.remoting.rmi.RmiServiceExporter
*/
处理客户端请求的方法:
/**
* Processes the incoming Hessian request and creates a Hessian response.
*/
@Override
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException { if (!"POST".equals(request.getMethod())) {
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(request.getMethod(),
new String[] {"POST"}, "HessianServiceExporter only supports POST requests");
} response.setContentType(CONTENT_TYPE_HESSIAN);
try {
invoke(request.getInputStream(), response.getOutputStream());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new NestedServletException("Hessian skeleton invocation failed", ex);
}
}
invoke调用
/**
* Actually invoke the skeleton with the given streams.
* @param skeleton the skeleton to invoke
* @param inputStream the request stream
* @param outputStream the response stream
* @throws Throwable if invocation failed
*/
protected void doInvoke(HessianSkeleton skeleton, InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream)
throws Throwable { ClassLoader originalClassLoader = overrideThreadContextClassLoader();
try {
InputStream isToUse = inputStream;
OutputStream osToUse = outputStream; if (this.debugLogger != null && this.debugLogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
PrintWriter debugWriter = new PrintWriter(new CommonsLogWriter(this.debugLogger));
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
HessianDebugInputStream dis = new HessianDebugInputStream(inputStream, debugWriter);
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
HessianDebugOutputStream dos = new HessianDebugOutputStream(outputStream, debugWriter);
dis.startTop2();
dos.startTop2();
isToUse = dis;
osToUse = dos;
} if (!isToUse.markSupported()) {
isToUse = new BufferedInputStream(isToUse);
isToUse.mark(1);
} int code = isToUse.read();
int major;
int minor; AbstractHessianInput in;
AbstractHessianOutput out; if (code == 'H') {
// Hessian 2.0 stream
major = isToUse.read();
minor = isToUse.read();
if (major != 0x02) {
throw new IOException("Version " + major + "." + minor + " is not understood");
}
in = new Hessian2Input(isToUse);
out = new Hessian2Output(osToUse);
in.readCall();
}
else if (code == 'C') {
// Hessian 2.0 call... for some reason not handled in HessianServlet!
isToUse.reset();
in = new Hessian2Input(isToUse);
out = new Hessian2Output(osToUse);
in.readCall();
}
else if (code == 'c') {
// Hessian 1.0 call
major = isToUse.read();
minor = isToUse.read();
in = new HessianInput(isToUse);
if (major >= 2) {
out = new Hessian2Output(osToUse);
}
else {
out = new HessianOutput(osToUse);
}
}
else {
throw new IOException("Expected 'H'/'C' (Hessian 2.0) or 'c' (Hessian 1.0) in hessian input at " + code);
} if (this.serializerFactory != null) {
in.setSerializerFactory(this.serializerFactory);
out.setSerializerFactory(this.serializerFactory);
}
if (this.remoteResolver != null) {
in.setRemoteResolver(this.remoteResolver);
} try {
skeleton.invoke(in, out);
}
finally {
try {
in.close();
isToUse.close();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
// ignore
}
try {
out.close();
osToUse.close();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
// ignore
}
}
}
finally {
resetThreadContextClassLoader(originalClassLoader);
}
}
调用skeleton的invoke方法
/**
* Invoke the object with the request from the input stream.
*
* @param in the Hessian input stream
* @param out the Hessian output stream
*/
public void invoke(Object service,
AbstractHessianInput in,
AbstractHessianOutput out)
throws Exception
{
ServiceContext context = ServiceContext.getContext(); // backward compatibility for some frameworks that don't read
// the call type first
in.skipOptionalCall(); // Hessian 1.0 backward compatibility
String header;
while ((header = in.readHeader()) != null) {
Object value = in.readObject(); context.addHeader(header, value);
} String methodName = in.readMethod();
int argLength = in.readMethodArgLength(); Method method; method = getMethod(methodName + "__" + argLength); if (method == null)
method = getMethod(methodName); if (method != null) {
}
else if ("_hessian_getAttribute".equals(methodName)) {
String attrName = in.readString();
in.completeCall(); String value = null; if ("java.api.class".equals(attrName))
value = getAPIClassName();
else if ("java.home.class".equals(attrName))
value = getHomeClassName();
else if ("java.object.class".equals(attrName))
value = getObjectClassName(); out.writeReply(value);
out.close();
return;
}
else if (method == null) {
out.writeFault("NoSuchMethodException",
escapeMessage("The service has no method named: " + in.getMethod()),
null);
out.close();
return;
} Class<?> []args = method.getParameterTypes(); if (argLength != args.length && argLength >= 0) {
out.writeFault("NoSuchMethod",
escapeMessage("method " + method + " argument length mismatch, received length=" + argLength),
null);
out.close();
return;
} Object []values = new Object[args.length]; for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
// XXX: needs Marshal object
values[i] = in.readObject(args[i]);
} Object result = null; try {
result = method.invoke(service, values);
} catch (Exception e) {
Throwable e1 = e;
if (e1 instanceof InvocationTargetException)
e1 = ((InvocationTargetException) e).getTargetException(); log.log(Level.FINE, this + " " + e1.toString(), e1); out.writeFault("ServiceException",
escapeMessage(e1.getMessage()),
e1);
out.close();
return;
} // The complete call needs to be after the invoke to handle a
// trailing InputStream
in.completeCall(); out.writeReply(result); out.close();
}
反射触发类的方法。
BurlapExporter及其实现类BurlapServiceExporter,SimpleBurlapServiceExporter,因已经depressed,故略。
1.3 小结
Spring封装了hessian客户端和服务端的通用代码,把实现者和调用者作为bean放到spring容器中管理,简化了开发。分析源码的过程中,发现在客户端使用了动态代理,在服务端使用反射,让我们加深了对java基础知识的理解。
spring remoting源码分析--Hessian分析的更多相关文章
- Spring系列(五):Spring AOP源码解析
一.@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解 在主配置类中添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,开启aop支持,那么@EnableAspectJAutoProxy到底做了什 ...
- spring 事务源码赏析(一)
在本系列中,我们会分析:1.spring是如何开启事务的.2.spring是如何在不影响业务代码的情况下织入事务逻辑的.3.spirng事务是如何找到相应的的业务代码的.4.spring事务的传播行为 ...
- Spring Security 源码分析(四):Spring Social实现微信社交登录
社交登录又称作社会化登录(Social Login),是指网站的用户可以使用腾讯QQ.人人网.开心网.新浪微博.搜狐微博.腾讯微博.淘宝.豆瓣.MSN.Google等社会化媒体账号登录该网站. 前言 ...
- spring事务源码分析结合mybatis源码(一)
最近想提升,苦逼程序猿,想了想还是拿最熟悉,之前也一直想看但没看的spring源码来看吧,正好最近在弄事务这部分的东西,就看了下,同时写下随笔记录下,以备后查. spring tx源码分析 这里只分析 ...
- spring AOP源码分析(三)
在上一篇文章 spring AOP源码分析(二)中,我们已经知道如何生成一个代理对象了,那么当代理对象调用代理方法时,增强行为也就是拦截器是如何发挥作用的呢?接下来我们将介绍JDK动态代理和cglib ...
- Spring AOP 源码分析 - 拦截器链的执行过程
1.简介 本篇文章是 AOP 源码分析系列文章的最后一篇文章,在前面的两篇文章中,我分别介绍了 Spring AOP 是如何为目标 bean 筛选合适的通知器,以及如何创建代理对象的过程.现在我们的得 ...
- Spring AOP 源码分析 - 创建代理对象
1.简介 在上一篇文章中,我分析了 Spring 是如何为目标 bean 筛选合适的通知器的.现在通知器选好了,接下来就要通过代理的方式将通知器(Advisor)所持有的通知(Advice)织入到 b ...
- Spring AOP 源码分析 - 筛选合适的通知器
1.简介 从本篇文章开始,我将会对 Spring AOP 部分的源码进行分析.本文是 Spring AOP 源码分析系列文章的第二篇,本文主要分析 Spring AOP 是如何为目标 bean 筛选出 ...
- Spring AOP 源码分析系列文章导读
1. 简介 前一段时间,我学习了 Spring IOC 容器方面的源码,并写了数篇文章对此进行讲解.在写完 Spring IOC 容器源码分析系列文章中的最后一篇后,没敢懈怠,趁热打铁,花了3天时间阅 ...
随机推荐
- C#异步编程(一)
异步编程简介 前言 本人学习.Net两年有余,是第一次写博客,虽然写的很认真,当毕竟是第一次,肯定会有很多不足之处, 希望大家照顾照顾新人,有错误之处可以指出来,我会虚心接受的. 何谓异步 与同步相对 ...
- ASP.NET Core 折腾笔记二:自己写个完整的Cache缓存类来支持.NET Core
背景: 1:.NET Core 已经没System.Web,也木有了HttpRuntime.Cache,因此,该空间下Cache也木有了. 2:.NET Core 有新的Memory Cache提供, ...
- redis 学习笔记(2)
redis-cluster 简介 redis-cluster是一个分布式.容错的redis实现,redis-cluster通过将各个单独的redis实例通过特定的协议连接到一起实现了分布式.集群化的目 ...
- asp.net mvc 验证码
效果图 验证码类 namespace QJW.VerifyCode { //用法: //public FileContentResult CreateValidate() //{ // Validat ...
- EC笔记:第4部分:20、传递引用代替传值
考虑以下场景: #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; struct Person { strin ...
- JavaScript学习笔记(三)——this、原型、javascript面向对象
一.this 在JavaScript中this表示:谁调用它,this就是谁. JavaScript是由对象组成的,一切皆为对象,万物皆为对象.this是一个动态的对象,根据调用的对象不同而发生变化, ...
- 微信小程序开发日记——高仿知乎日报(中)
本人对知乎日报是情有独钟,看我的博客和github就知道了,写了几个不同技术类型的知乎日报APP要做微信小程序首先要对html,css,js有一定的基础,还有对微信小程序的API也要非常熟悉 我将该教 ...
- HTML5 Page Visibility
什么是 Page Visibility ? Page Visibility 即页面可见性,通过 visibilityState 的值检测页面当前是否可见.当一个网站是可见或点击选中的状态时 Page ...
- 安卓自定义组合控件--toolbar
最近在学习安卓APP的开发,用到了toolbar这个控件, 最开始使用时include layout这种方法,不过感觉封装性不好,就又改成了自定义组合控件的方式. 使用的工具为android stud ...
- docker4dotnet #4 使用Azure云存储构建高速 Docker registry
使用Docker来构建应用程序最常见的操作就是 docker run 或者 docker pull了,但是由于众所周知的原因,在国内想要高速稳定的获取docker hub上面的资源并不是件容易的事情, ...
