Javac之关于方法的调用1
方法的调用从Attr类的visitApply()方法进入,如下:
/** Visitor method for method invocations.
* NOTE: The method part of an application will have in its type field
* the return type of the method, not the method's type itself!
*/
public void visitApply(JCMethodInvocation tree) {
// The local environment of a method application is
// a new environment nested in the current one.
Env<AttrContext> localEnv = env.dup(tree, env.info.dup());
// The types of the actual method arguments.
List<Type> argtypes;
// The types of the actual method type arguments.
List<Type> typeargtypes = null;
Name methName = TreeInfo.name(tree.meth);
boolean isConstructorCall = methName == names._this || methName == names._super;
if (isConstructorCall) {
// 构造函数的调用
} else {
// 非构造函数的调用
}
chk.validate(tree.typeargs, localEnv);
}
关于JCMethodInvocation的语法结构可查看:http://www.cnblogs.com/extjs4/p/7118730.html
由于构造函数也是一种特殊的函数,所以通过调用TreeInfo.name()方法获取methName后通过与this和super关键字的比较,将构造函数与一般的函数分别进行逻辑判断。
(1)调用构造函数
先来看构造函数的判断逻辑:
// We are seeing a ...this(...) or ...super(...) call.
// Check that this is the first statement in a constructor.
// 对...this(...) 或者...super(...)的调用必须是构造器中的第一个语句
if (checkFirstConstructorStat(tree, env)) {
// Record the fact that this is a constructor call (using isSelfCall).
localEnv.info.isSelfCall = true;
// Attribute arguments, yielding list of argument types.
argtypes = attribArgs(tree.args, localEnv);
typeargtypes = attribTypes(tree.typeargs, localEnv);
// Variable `site' points to the class in which the called constructor is defined.
Type site = env.enclClass.sym.type;
if (methName == names._super) {
// 在Object类的构造函数中不能有super()调用,因为Object是所有类的超类,没有父类
if (site == syms.objectType) {
log.error(tree.meth.pos(), "no.superclass", site);
site = types.createErrorType(syms.objectType);
} else {
site = types.supertype(site);
}
}
if (site.tag == CLASS) {
Type encl = site.getEnclosingType();
while (encl != null && encl.tag == TYPEVAR) {
encl = encl.getUpperBound();
}
if (encl.tag == CLASS) {
if (tree.meth.getTag() == JCTree.SELECT) { // we are calling a nested class
JCTree qualifier = ((JCFieldAccess) tree.meth).selected;
// We are seeing a prefixed call, of the form <expr>.super(...).
// Check that the prefix expression conforms to the outer instance type of the class.
Type type = attribExpr(qualifier, localEnv,encl);
chk.checkRefType(qualifier.pos(),type); // 检查type是否为引用类型
} else if (methName == names._super) { // ???
// qualifier omitted; check for existence of an appropriate implicit qualifier.
rs.resolveImplicitThis(tree.meth.pos(),localEnv, site, true);
}
} else if (tree.meth.getTag() == JCTree.SELECT) {
// 非法限定符; {0}不是内部类
log.error(tree.meth.pos(), "illegal.qual.not.icls",site.tsym);
}
// if we're calling a java.lang.Enum constructor,prefix the implicit String and int parameters
if (site.tsym == syms.enumSym && allowEnums) {
argtypes = argtypes.prepend(syms.intType).prepend(syms.stringType);
}
// Resolve the called constructor under the assumption that we are referring to a superclass instance of the
// current instance (JLS ???).
boolean selectSuperPrev = localEnv.info.selectSuper;
localEnv.info.selectSuper = true; // 在super()的调用环境下要设置selectSuper = true
localEnv.info.varArgs = false; // ???
// 查找到这个要调用的super() 构造函数
Symbol sym = rs.resolveConstructor(tree.meth.pos(), localEnv, site, argtypes, typeargtypes);
localEnv.info.selectSuper = selectSuperPrev;
// Set method symbol to resolved constructor...
TreeInfo.setSymbol(tree.meth, sym);
// ...and check that it is legal in the current context.
// (this will also set the tree's type)
Type mpt = newMethTemplate(argtypes, typeargtypes);
checkId(tree.meth, site, sym, localEnv, MTH,mpt, tree.varargsElement != null);
} // end (site.tag == CLASS)
// Otherwise, `site' is an error type and we do nothing
}
result = tree.type = syms.voidType; // 构造函数做为特殊的方法,其返回类型为void
e.g 1
首先来了解一下内隐类,《Java编程思想》有这么一段话,如下:
由于inner class的构造函数必须连接到一个reference指向outer class对象身上,所以当你继承inner class时,事情便稍微复杂些。问题出在“指向outer class对象”的那个神秘reference必须被初始化。但derived class之内不存在可连接的缺省对象,这个问题的答案是,使用专用语法,明确产生该关联性。
class InnerA {
class InnerB {
class innerC {
}
}
}
class InheritInner extends InnerA.InnerB.innerC {
InheritInner(InnerA.InnerB wi) {
wi.super();
}
}
e.g 2
// 生成x0.super()类型的东西
class A {
class B {
public B(String name){}
}
}
class C{
public void test(){
new A().new B("dd"){
public void m1(){
}
};
}
}
e.g 3
class Outer {
class A {
class B extends A {
public B(String name) {
super();
}
}
}
}
另外还需要知道Enum枚举类的构造函数,如下:
/**
* Sole constructor. Programmers cannot invoke this constructor.
* It is for use by code emitted by the compiler in response to enum type declarations.
*
* @param name - The name of this enum constant, which is the identifier used to declare it.
* @param ordinal - The ordinal of this enumeration constant (its position
* in the enum declaration, where the initial constant is assigned an ordinal of zero).
*/
protected Enum(String name, int ordinal) {
this.name = name;
this.ordinal = ordinal;
}
下面就调用Resolev类的resolveConstructor()方法来继续处理了,方法的代码如下:
/** Resolve constructor.
* @param pos The position to use for error reporting.
* @param env The environment current at the constructor invocation.
* @param site The type of class for which a constructor is searched.
* @param argtypes The types of the constructor invocation's value arguments.
* @param typeargtypes The types of the constructor invocation's type arguments.
*/
Symbol resolveConstructor(DiagnosticPosition pos,
Env<AttrContext> env,
Type site,
List<Type> argtypes,
List<Type> typeargtypes) {
Symbol sym = startResolution();
List<MethodResolutionPhase> steps = methodResolutionSteps;
while (steps.nonEmpty() &&
steps.head.isApplicable(boxingEnabled, varargsEnabled) &&
sym.kind >= ERRONEOUS
){
currentStep = steps.head;
sym = resolveConstructor(pos, env, site, argtypes, typeargtypes,
steps.head.isBoxingRequired(),
env.info.varArgs = steps.head.isVarargsRequired());
// 将获取到的这一步合适的sym方法放入map中
methodResolutionCache.put(steps.head, sym);
steps = steps.tail;
}
if (sym.kind >= AMBIGUOUS) { // if nothing is found return the 'first' error
MethodResolutionPhase errPhase = firstErroneousResolutionPhase();
Symbol symbol = methodResolutionCache.get(errPhase);
sym = access(symbol,pos, site, names.init, true, argtypes, typeargtypes);
env.info.varArgs = errPhase.isVarargsRequired();
}
return sym;
}
关于方法的筛选大概走三步,也就是Phase 1,Phase 2与Phase 3所描述的。
15.12. Method Invocation Expressions
- 15.12.1. Compile-Time Step 1: Determine Class or Interface to Search
- 15.12.2. Compile-Time Step 2: Determine Method Signature
-
- 15.12.2.1. Identify Potentially Applicable Methods
- 15.12.2.2. Phase 1: Identify Matching Arity Methods Applicable by Subtyping
- 15.12.2.3. Phase 2: Identify Matching Arity Methods Applicable by Method Invocation Conversion
- 15.12.2.4. Phase 3: Identify Applicable Variable Arity Methods
- 15.12.2.5. Choosing the Most Specific Method
- 15.12.2.6. Method Result and Throws Types
- 15.12.2.7. Inferring Type Arguments Based on Actual Arguments
- 15.12.2.8. Inferring Unresolved Type Arguments
- 15.12.3. Compile-Time Step 3: Is the Chosen Method Appropriate?
- 15.12.4. Run-Time Evaluation of Method Invocation
通过MethodResolutionStep枚举类也可以看出,代码如下:
enum MethodResolutionPhase {
BASIC(false, false),
BOX(true, false),
VARARITY(true, true);
boolean isBoxingRequired;
boolean isVarargsRequired;
MethodResolutionPhase(boolean isBoxingRequired, boolean isVarargsRequired) {
this.isBoxingRequired = isBoxingRequired;
this.isVarargsRequired = isVarargsRequired;
}
public boolean isBoxingRequired() {
return isBoxingRequired;
}
public boolean isVarargsRequired() {
return isVarargsRequired;
}
// 不能够使用可变参数(varargsEnabled=false) 并且 要求可变参数时(isVarargsRequired=true) 变为不可用
// 不能够使用装箱与拆箱(boxingEnabled=false) 并且 要求装箱与拆箱时(isBoxingRequired=true) 变为不可用
public boolean isApplicable(boolean boxingEnabled, boolean varargsEnabled) {
return (varargsEnabled || !isVarargsRequired) &&
(boxingEnabled || !isBoxingRequired);
}
}
也就是说:
(1)不进行拆箱装箱,没有可变参数变量的声明
(2)允许拆箱装箱,但不允许有可变参数变量的声明
(3)允许可变参数变量声明
关于在resolveConstructor()方法中调用的如下方法:
sym = resolveConstructor(pos, env, site, argtypes, typeargtypes,
steps.head.isBoxingRequired(),
env.info.varArgs = steps.head.isVarargsRequired());
后面将会有详细的说明。
接着调用TreeInfo.setSymbol(tree.meth,sym)方法,截图如下:
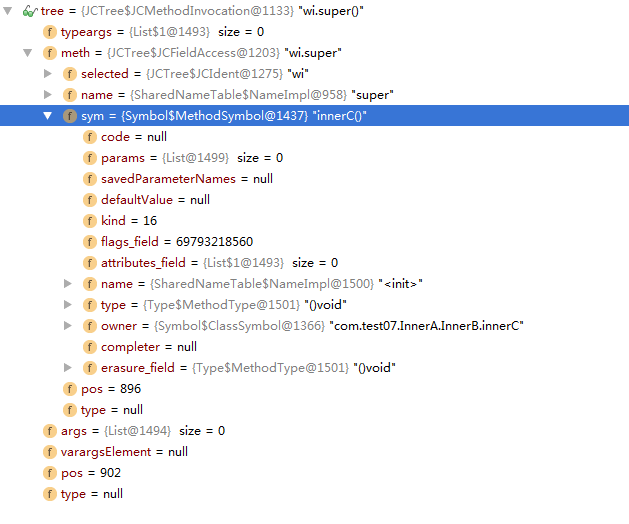
也就是设置了sym属性,如上设置了MethodSymbol,setSymbol()方法的代码如下:
/** If this tree is an identifier or a field, set its symbol, otherwise skip.
*/
public static void setSymbol(JCTree tree, Symbol sym) {
tree = skipParens(tree);
switch (tree.getTag()) {
case JCTree.IDENT:
((JCIdent) tree).sym = sym; break;
case JCTree.SELECT:
((JCFieldAccess) tree).sym = sym; break;
default:
}
}
newMethTemplate()方法的代码如下:
/** Obtain a method type with given argument types.
*/
Type newMethTemplate(List<Type> argtypes, List<Type> typeargtypes) {
// public MethodType(List<Type> argtypes,Type restype,List<Type> thrown,TypeSymbol methodClass)
MethodType mt = new MethodType(argtypes, null, null, syms.methodClass);
// 没有类型参数时方法的Type类型为MethodType,否则为ForAll
return (typeargtypes == null) ? mt : (Type)new ForAll(typeargtypes, mt);
}
有一个重要的方法checkId()方法,非常重要!
(2)普通方法的调用
接着来看普通方法的判断逻辑,如下:
// Otherwise, we are seeing a regular method call.
// Attribute the arguments, yielding list of argument types, ...
argtypes = attribArgs(tree.args, localEnv);
typeargtypes = attribAnyTypes(tree.typeargs, localEnv);
// ... and attribute the method using as a prototype a methodtype
// whose formal argument types is exactly the list of actual
// arguments (this will also set the method symbol).
Type mpt = newMethTemplate(argtypes, typeargtypes);
localEnv.info.varArgs = false;
Type mtype = attribExpr(tree.meth, localEnv, mpt);
if (localEnv.info.varArgs) {
Assert.check(mtype.isErroneous() || tree.varargsElement != null);
}
// Compute the result type.
Type restype = mtype.getReturnType();
if (restype.tag == WILDCARD) {
throw new AssertionError(mtype);
}
// as a special case, array.clone() has a result that is the same as static type of the array being cloned
if (tree.meth.getTag() == JCTree.SELECT &&
allowCovariantReturns &&
methName == names.clone &&
types.isArray(((JCFieldAccess) tree.meth).selected.type)
){
restype = ((JCFieldAccess) tree.meth).selected.type;
}
// as a special case, x.getClass() has type Class<? extends |X|>
if ( allowGenerics &&
methName == names.getClass && // getClass
tree.args.isEmpty()
){
Type qualifier = null;
if(tree.meth.getTag() == JCTree.SELECT){
qualifier = ((JCFieldAccess) tree.meth).selected.type;
}else{
qualifier = env.enclClass.sym.type;
}
Type a = types.erasure(qualifier);
WildcardType wt = new WildcardType(a,BoundKind.EXTENDS,syms.boundClass);
Type b = restype.getEnclosingType();
restype = new ClassType(b,List.<Type>of(wt),restype.tsym);
}
chk.checkRefTypes(tree.typeargs, typeargtypes);
// Check that value of resulting type is admissible in the current context. Also, capture the return type
Type c = capture(restype);
result = check(tree, c, VAL, pkind, pt);
其中有对两类方法的调用进行了特殊的处理,如array.clone()与x.getClass()。举个例子,如下:
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = { 1, 2 };
int b[] = a.clone();
// 获取到的是Class类
Class<? extends Class> m = Test3.class.getClass();
// 获取到的是Test3类
Class<? extends Test3> n = new Test3().getClass();
System.out.println(m); // class java.lang.Class
System.out.println(n); // class com.test07.Test3
System.out.println(n instanceof Class); // true
}
}
在进行数组克隆的判断逻辑时还需要判断allowCovariantReturns标识,由于clone方法在Object的定义如下:
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
返回值类型为Object,而clone()后的返回类型确为int[]类型,所以需要covariant,covariant可以参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/extjs4/p/6305654.html
而对于getClass()方法来说,如果new ClassName().getClass(),那么最后得到的返回结果为Class<? extends |ClassName|>,从如上的实例也可以看出。
最后调用了一个重要的方法check()方法,非常重要!
e.g 1:
public class Test2{
public void m1(){}
public void test(){
// javac warning: Unused type arguments for the non generic method m1() of type Test2;
// it should not be parameterized with arguments <String>
new Test2().<String>m1();
}
}
Javac之关于方法的调用1的更多相关文章
- (转)为什么不能从静态的方法里面调用非静态方法,或变量and类加载机制
1. 程序最终都将在内存中执行,变量只有在内存中占有一席之地时才能被访问. 类的静态成员(变量和方法)属于类本身,在类加载的时候就会分配内存,可以通过类名直接去访问:非静态成员(变量和方法)属于类的对 ...
- JNI-Thread中start方法的调用与run方法的回调分析
前言 在java编程中,线程Thread是我们经常使用的类.那么创建一个Thread的本质究竟是什么,本文就此问题作一个探索. 内容主要分为以下几个部分 1.JNI机制的使用 2.Thread创建线程 ...
- UIView的layoutSubviews和drawRect方法何时调用
首先两个方法都是异步执行.layoutSubviews方便数据计算,drawRect方便视图重绘. layoutSubviews在以下情况下会被调用: 1.init初始化不会触发layoutSubvi ...
- 自己实现一个Native方法的调用
JNI 开始本篇的内容之前,首先要讲一下JNI.Java很好,使用的人很多.应用极广,但是Java不是完美的.Java的不足体现在运行速度要比传统的C++慢上许多之外,还有Java无法直接访问到操作系 ...
- 从vs2010的UnitTestFramework类库提取私有方法反射调用的方法
背景 年龄大点的程序员都知道在vs2010中创建单元测试非常的简单,鼠标定位在方法名字,右键创建单元测试,就会创建一个测试方法,即使是在私有方法上也可以创建测试方法. VS2010以后就没这么简单了, ...
- Unity3D中C#和js方法相互调用
通过查找资料,Unity3D中C#和js要相互调用彼此的方法,js文件必须放在"Standard Assets". "Pro Standard Assets" ...
- Java笔记4-do while循环,break,修饰符,方法的调用
do while循环语法:do{ //循环体}while(条件表达式); 注:它是先执行循环体,后再判断的循环结构. 如:int i = 0;do{ System.out.println(" ...
- paip。java 高级特性 类默认方法,匿名方法+多方法连续调用, 常量类型
paip.java 高级特性 类默认方法,匿名方法+多方法连续调用, 常量类型 作者Attilax 艾龙, EMAIL:1466519819@qq.com 来源:attilax的专栏 地址:http ...
- 虚方法的调用是怎么实现的(单继承VS多继承)
我们知道通过一个指向之类的父类指针可以调用子类的虚方法,因为子类的方法会覆盖父类同样的方法,通过这个指针可以找到对象实例的地址,通过实例的地址可以找到指向对应方法表的指针,而通过这个方法的名字就可以确 ...
随机推荐
- php autoload 笔记
php auotload 实现了类的延迟加载机制,需要的时候在include,平时很少用到.它的实现原理搜了一下如下(不是本人研究的结果): 检查执行器全局变量函数指针autoload_func是否为 ...
- [转]解决Mysql InnoDB: Failing assertion: ret || !assert_on_error问题
国庆回来后,发现mysql停止服务了,没办法继续启动了.查看日志,看到: 131008 09:56:03 mysqld_safe Starting mysqld daemon with databas ...
- 安装Greenplum-perfmon-web监控软件遇到的问题及解决
环境 Product Version Pivotal Greenplum (GPDB) 4.3.x Pivotal Greenplum Command Center (GPCC) Others ...
- angular响应式表单 - 状态字段
用于表单验证的过程: touched,untoched pristine,dirty pending
- hdu X问题 (中国剩余定理不互质)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1573 X问题 Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory ...
- 【题解】 BZOJ4548 小奇的糖果
本文同步在学弟ZCDHJ的个人博客发布,审核需要一段时间. 传送门 考虑题目中获得的糖果并不包含所有的颜色这句话,发现相当于我们可以直接选取某一个颜色强制不能选(这样子一定最优). 然后就可以考虑分开 ...
- Docker 修改镜像源地址
Docker 官方中国区 https://registry.docker-cn.com 网易 http://hub-mirror.c.163.com ustc https://docker.mirro ...
- zun 不能创建 docker 容器,报错: datastore for scope "global" is not initialized
问题:zun不能创建docker容器,报错:datastore for scope "global" is not initialized 解决:修改docker 服务配置文件 ...
- mysql 行转列 (结果集以坐标显示)
create table capacity( type int , numbers int , monthst INT ); select type, sum(case monthst when 1 ...
- Sphinx全文检索
全文检索 一.生活中的数据总体分为: 结构化数据:指具有固定格式或有限长度的数据,如数据库,元数据等. 非结构化数据:指没有固定格式或不定长的数据,如邮件,word文档等. 非结构化数据还有一种叫法: ...
