基本类型包装类、System类、Math类、Arrays类、大数据运算
1 基本类型包装类
Java中想对8种基本数据类型进行复杂操作很困难。
实际程序界面上用户输入的数据都是以字符串类型进行存储的。
程序开发中,需要把字符串转换成指定的基本数据类型。
1.1基本数据类型对象包装类
定义:java将基本数据类型值封装成了对象,提供更多的操作基本数值的功能。
8种基本类型对应的包装类:
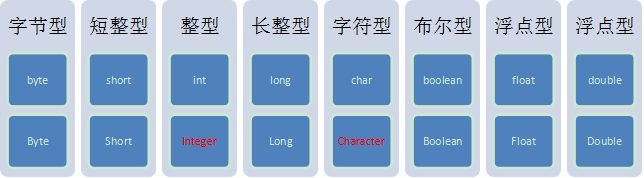
Tips:int对应的是Integer,char对应的Character,其他6个都是基本类型首字母大写。
1.2字符串与基本数据类型的转换
1.2.1字符串转成基本类型(这些方法分别在8个类里面)

例:
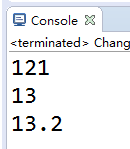
public class Changes {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="12";
System.out.println(str+1);
//字符串转int
int strInt=Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(strInt+1);
//字符串转double
String s2="12.2";
double s2d=Double.parseDouble(s2);
System.out.println(s2d+1);
}
}
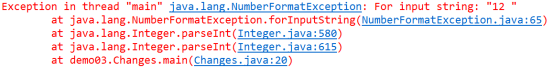
注意必须是正确的数值,如果乱写会报格式异常:

1.2.2基本数值转成字符串(三种方式)
1)基本类型直接与””相连接 (直接与空串连接)
2)调用String的valueOf方法(静态方法)

3)包装类的toString方法(只有第一个是Object的重写)

例:
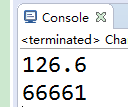
//基本数据类型转字符串
public class Change2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//直接加空串
String s1=12+""; //valueOf方法
String s2=String.valueOf(6.6);
System.out.println(s1+s2); //toString方法
String s3=Integer.toString(6666);
System.out.println(s3+1);
}
}
1.3基本类型和对应的包装类对象转换
1.3.1基本数值---->包装对象(两种方法)
1)1构造方法
2)valueof方法
1.3.2包装对象---->基本数值(重要)
intValue方法
例:
public class Change3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//基本类型转包装类
//1构造方法
Integer in=new Integer(12);
Integer in2=new Integer("123");
//2valueof方法
Integer in3=Integer.valueOf(45);
Integer in4=Integer.valueOf("456");
//包装类转基本类型
int i=in.intValue();
}
}
1.4自动装箱拆箱
基本类型可以使用运算符直接进行计算,但是引用类型不可以。
引用数据类型变量的值必须是new出来的内存空间地址值。
1.4.1概念
自动拆箱:对象自动直接转成基本数值
自动装箱:基本数值自动直接转成对象
例:
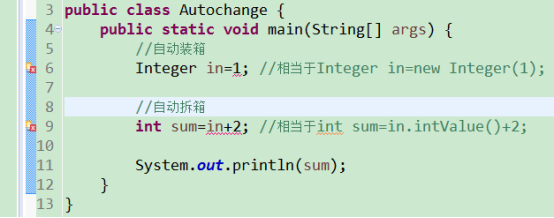
public class Autochange {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//自动装箱
Integer in=1; //相当于Integer in=new Integer(1);
//自动拆箱
int sum=in+2; //相当于int sum=in.intValue()+2;
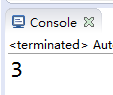
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
前面学过集合,例如ArrayList<Integer>,里面的类型是Integer,但是当用add()方法时,
加进去的是数字,这就是自动装箱。
1.4.2 jdk1.5以后自动装箱拆箱才可以用
例:在项目上,右键---Properties,
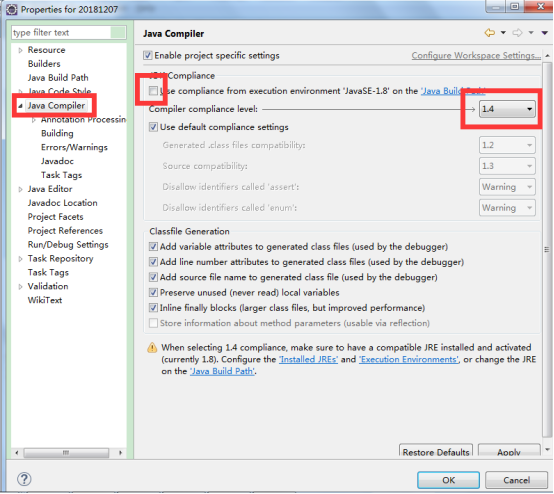
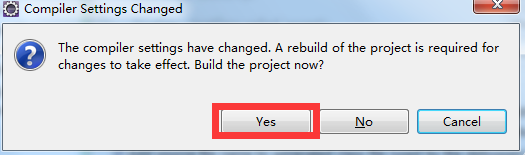
可以看到报错了。
1.4.3自动装箱byte常量池
例:
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer in1=128;
Integer in2=128;
System.out.println(in1==in2);
System.out.println(in1.equals(in2));
}
}
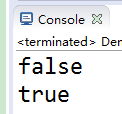
虽然是自动装箱,但是地址不同,只是值相同。
但是,如果是:
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//byte范围内
Integer in3=50;
Integer in4=50;
System.out.println(in3==in4); //指向同一个地址
System.out.println(in3.equals(in4));
}
}
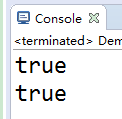
当数据在byte范围内,数据在常量池中,进行自动装箱,不会新创建对象空间而是使用已有的空间。所以地址也相同了。
2 System类
2.1定义
System类代表程序所在系统,提供了对应的一些系统属性信息,和系统操作。
System类不能手动创建对象,因为构造方法被private修饰。
System类中的都是static方法,类名访问即可。
2.2字段
(这个以后学习IO流时再了解)
2.3常用方法
1)currentTimeMillis() 获取当前系统时间与1970年01月01日00:00点之间的毫秒差值
2)exit(int status) 用来结束正在运行的Java程序。参数是数值,传入0为正常状态,其他为异常状态。
例:
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if(i==5){
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}
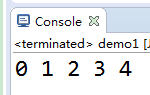
3)gc() 用来运行JVM中的垃圾回收器,完成内存中垃圾的清除。
(gc的链接)
4)getProperty(String key) 用来获取指定键(字符串名称)中所记录的系统属性信息
例:
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取系统所有属性信息
System.out.println(System.getProperties());
}
}

5)复制数组

例:
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] src={1,2,3,4,5};
int[] desc=new int[5];
System.arraycopy(src, 1, desc, 1, 3); //两个数组长度一定要对才行
for(int i=0;i<desc.length;i++){
System.out.print(desc[i]+" ");
}
}
}
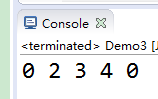
注意数组长度,否则会报数组越界异常。
2.4练习
1)验证for循环打印数字1-9999所需要使用的时间(毫秒)
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long before=System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=1;i<10000;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
long after=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("程序执行的时间为"+(after-before));
}
}

2)将src数组中前3个元素,复制到dest数组的前3个位置上
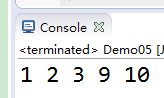
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] src={1,2,3,4,5};
int[] dest={6,7,8,9,10};
System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, 3);
for(int i=0;i<dest.length;i++){
System.out.print(dest[i]+" ");
}
}
}
4)循环,随机生成100-999之间的的三位数并进行打印该数,当该数能被10整除时,结束运行的程序
import java.util.Random;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r=new Random();
while(true){
int n=r.nextInt(900)+100;
System.out.println(n);
if(n%10==0){
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
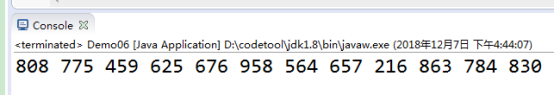
3 Math类
数学工具类
类似这样的工具类,其所有方法均为静态方法,并且一般不会创建对象。
3.1常用方法

例:
public class MathTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//向上取整
System.out.println(Math.ceil(2.6));
//向下取整
System.out.println(Math.floor(2.6));
//取次幂
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 10));
//取随机数
System.out.println(Math.random());
//四舍五入
System.out.println(Math.round(2.3));
System.out.println(Math.round(2.5));
}
}
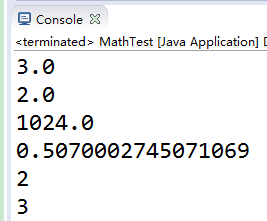
注意:除了四舍五入,其他的返回值都是double
记忆:



4 Arrays类
此类包含用来操作数组(比如排序和搜索)的各种方法。需要注意,如果指定数组引用为 null,则访问此类中的方法都会抛出空指针异常NullPointerException。
(null.调用 都是空指针异常)
4.1常用方法

例:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
method1();
method2();
method3();
} //查找一个有序数组中某个值的位置
public static void method1(){
int[] arr={1,5,9,11,13,15};
System.out.println("method1的结果为:"+Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 11));
} //升序排序
public static void method2(){
System.out.println("method2的结果为:");
int[] arr={1,8,2,7,5,10,9};
Arrays.sort(arr);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
} System.out.println();
char[] ch={'z','a','c','A'};
Arrays.sort(ch);
for(int i=0;i<ch.length;i++){
System.out.print(ch[i]+" ");
}
} //数组转字符串
public static void method3(){
System.out.println();
int[] arr={1,5,6,8,2,3};
String str=Arrays.toString(arr);
System.out.println("method1的结果为:"+str);
}
}

说明:
1)sort方法,数组中的元素升序排序(字符数组是按ASCII值排)
2)toString方法,数组转为(带着数组格式的)String
3)binarySearch,底层采用二分查找的算法(https://baike.so.com/doc/6740981-6955489.html)
必须是有序数组
如果该值不存在,则返回下标=-该值应该所在的位置-1
例:
public static void method1(){
int[] arr={1,5,9,11,13,15};
System.out.println("Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 12));
}
结果为-5
4.2练习:
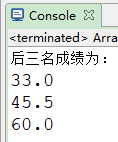
定义一个方法,接收一个数组,数组中存储10个学生考试分数,该方法要求返回考试分数最低的后三名考试分数。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArraysTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] score={100,60,78,99,77.5,45.5,90,97,33,88.5};
double[] score2=sorts(score); System.out.println("后三名成绩为:");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.println(score2[i]);
}
} public static double[] sorts(double[] score){
Arrays.sort(score);
return score;
}
}
5大数据运算
java中long型为最大整数类型。超过long型的整数已经不能被称为整数了,它们被封装成BigInteger对象。
在BigInteger类中,实现四则运算都是方法来实现,并不是采用运算符。
5.1常用构造方法

5.2运算
例:
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
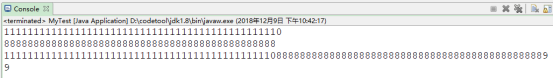
BigInteger bin1=new BigInteger("1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111");
BigInteger bin2=new BigInteger("9999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999");
//加法
System.out.println(bin1.add(bin2));
//减法
System.out.println(bin2.subtract(bin1));
//乘法
System.out.println(bin1.multiply(bin2));
//除法
System.out.println(bin2.divide(bin1));
}
}
5.3 BigDecimal类
例:
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(0.09 + 0.01);
System.out.println(1.0 - 0.32);
System.out.println(1.015 * 100);
System.out.println(1.301 / 100);
}
}
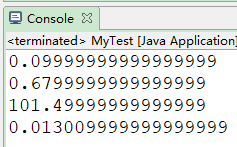
结果总是进不上位,是丢失精度的。
double和float类型在运算中很容易丢失精度,造成数据的不准确性,所以java提供BigDecimal类可以实现浮点数据的高精度运算。
5.3.1常用构造方法

建议浮点数据以字符串形式给出,因为参数结果是可以预知的。
5.3.2除法运算的保留和选择舍入模式

对于浮点数据的除法运算,和整数不同,可能出现无限不循环小数,因此需要对所需要的位数进行保留和选择舍入模式。
scale是保留的小数位数
第二个参数中:向上取整,向下取整,四舍五入,比较常用。
例:
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
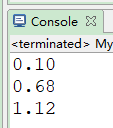
BigDecimal bd1=new BigDecimal("0.09");
BigDecimal bd2=new BigDecimal("0.01");
System.out.println(bd1.add(bd2)); BigDecimal bd3=new BigDecimal("1.0");
BigDecimal bd4=new BigDecimal("0.32");
System.out.println(bd3.subtract(bd4)); BigDecimal bd5=new BigDecimal("111.301");
BigDecimal bd6=new BigDecimal("100");
System.out.println(bd5.divide(bd6, 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING)); //保留两位小数,向上取整
}
}
基本类型包装类、System类、Math类、Arrays类、大数据运算的更多相关文章
- 17_常用API_第17天(包装类、System、Math、Arrays、大数据运算)_讲义
今日内容介绍 1.基本类型包装类 2.System类 3.Math类 4.Arrays类 5.大数据运算 01基本数据类型对象包装类概述 *A:基本数据类型对象包装类概述 *a.基本类型包装类的产生 ...
- 7、包装类、System、Math、Arrays、大数据运算
基本类型封装 基本数据类型对象包装类概述 *A:基本数据类型对象包装类概述 *a.基本类型包装类的产生 在实际程序使用中,程序界面上用户输入的数据都是以字符串类型进行存储的.而程序开发中,我们需要把字 ...
- 常用API(包装类、System、Math、Arrays、大数据运算)
常用API 今日内容介绍 u 基本类型包装类 u System u Math u Arrays u BigInteger u BigDecimal 第1章 基本类型包装类 大家回想下,在第二天我们学习 ...
- java基础(17):包装类、System、Math、Arrays、大数据运算
1. 基本类型包装类 大家回想下,在第三篇文章中我们学习Java中的基本数据类型时,说Java中有8种基本的数据类型,可是这些数据是基本数据,想对其进行复杂操作,变的很难.怎么办呢? 1.1 基本类型 ...
- JAVA基础之基本类型包装类、System类、Math类、Arrays类及大数据运算
个人理解: 为了方便运算及调用一些方法,我们需要将基本类型的数值转换为对象:不过转换的时候需要特别注意好它们的类型到底是什么,需要调用方法的类名是哪个!特别注意是Byte常量池的相关问题(==):gc ...
- Java—包装类/System类/Math类/Arrays类/大数据运算/Collection接口/Iterator迭代器
基本类型包装类 8种基本类型对应的包装类如: 将字符串转成基本类型: 将基本数值转成字符串有3种方式: 基本类型直接与””相连接即可:34+" " 调用String的valueOf ...
- Java常用类:包装类,String,日期类,Math,File,枚举类
Java常用类:包装类,String,日期类,Math,File,枚举类
- [Day17]常用API(System、Math、Arrays、BigInteger、BigDecimal)
1.基本类型包装类 1.1 8种基本类型对应的包装类 字节型 byte Byte 短整型 short Short 整型 int Integer 长整型 long Long 字符型 char Chara ...
- java 基本类型包装类,system类,Math类,Assrays类,大数据运算
实现字符串与基本数据之间转换 将字符串转成基本数据类型方法 例如:将字符串转成成int类型 String str ="123"; int a =Integer.parseInt(s ...
随机推荐
- 优化EF的性能
Entity Framework的性能优化: 1.使用MergeOption.NoTracking (发现添加这个代码后, 导致"The object cannot be deleted ...
- jquery中attr() & prop() 的区别与其实现方法
$(function(){ $('#check').attr('checked'); // undefind ???一头雾水 }) 在jquery中 attr 本来就是用来设置或者获取属性的,可是上面 ...
- UDK更改启动画面及载入动画
转自:http://www.unrealchina.org/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=246&extra=page%3D1 方法很简单: 1.更改启动画 ...
- strlen("汉字")的值是多少
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/gogor/article/details/4470775 strlen("汉字")的值是多少? 这个问题的答案与系统所采用的字符编 ...
- S5pv210 HDMI 接口在 Linux 3.0.8 驱动框架解析
作者:liukun321 咕唧咕唧 日期:2014.1.18 转载请标明作者.出处:http://blog.csdn.net/liukun321/article/details/18452663 本文 ...
- how to run faster
题目大意: 已知 $$ b_i = \sum_{j=1}^n {(i,j)^d [i,j]^c x_j}$$,给定 $b_i$ 求解 $x_i$ 解法: 考虑 $f(n) = \sum_{d|n}{f ...
- 通用后台管理系统UI模板-AdminLTE简介及构造动态菜单栏
AdminLTE是一款基于bootstrap的后台管理系统的通用模板UI,它的样式美观且较为符合大多数后台管理系统的需求,典型的上|左右|下的布局形式.并且提供了一整套我们开发的时候可能用到的UI样式 ...
- UE4 c++ 创建刚体Cube
1 新建一个Actor,一会用蓝图继承这个 TCubeActor.h #pragma once #include "CoreMinimal.h" #include "Ga ...
- poj3191(进制转换)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3191 题意:将一个数转换为-2为基数的数 思路:套路,看代码就好了 代码: #include <iostream> usi ...
- uoj#37. 【清华集训2014】主旋律(状压dp+容斥)
传送门 第一眼容斥,然后我就死活容不出来了-- 记\(f_i\)为点集\(i\)中的点强联通的方案数,那么就是总的方案数减去使\(i\)不连通的方案数 如果\(i\)不连通的话,我们可以枚举缩点之后拓 ...
