Caffe源码理解1:Blob存储结构与设计
博客:blog.shinelee.me | 博客园 | CSDN
Blob作用
据Caffe官方描述:
A Blob is a wrapper over the actual data being processed and passed along by Caffe, and also under the hood provides synchronization capability between the CPU and the GPU. Mathematically, a blob is an N-dimensional array stored in a C-contiguous fashion.
Caffe stores and communicates data using blobs. Blobs provide a unified memory interface holding data; e.g., batches of images, model parameters, and derivatives for optimization.
Blobs conceal the computational and mental overhead of mixed CPU/GPU operation by synchronizing from the CPU host to the GPU device as needed. Memory on the host and device is allocated on demand (lazily) for efficient memory usage.
Blob是Caffe中的基础数据结构,主要作用如下:
- 存储和传输数据,对外提供统一的内存接口。在Caffe中,输入图像、每层的权重和反向传播时的梯度、每层的输入和输出等都以
Blob形式管理 - 隐藏CPU和GPU之间数据同步的细节(通过
SyncedMemory实现),用户使用时不需要自己管理CPU和GPU间的数据同步
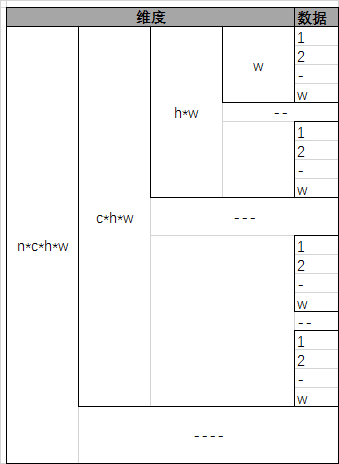
在逻辑上,Blob是个\(N_d\)维张量。当\(N_d=4\)时,Blob的shape定义为\(N * C * H * W\),即\(Num * Channel * Height * Width\),可以表示输入图像Batch、卷积层的kernel参数、卷积层的输入输出map等;当\(N_d=2\)时,可以表示全连接层的权重,\(N_{out} * N_{in}\);当\(N_d=1\)时,可以表示卷积层和全连接层的bias参数。
具体地,
- \(N_d=4\),
Blob表示输入图像时,\(N\)为当前批次的图片数量即MiniBatchNum,\(C\)为图像的通道数,RGB图\(C=3\),\(H\)和\(W\)为图像的高和宽。 - \(N_d=4\),
Blob表示卷积层的输入输出时,\(N=1\),\(C\)为特征图的数量,\(H\)和\(W\)为特征图的高和宽。 - \(N_d=4\),
Blob表示卷积层kernel参数时,\(N\)为当前层输出特征图的数量,其与卷积核数量相同,\(C\)为当前层输入特征图的数量,其与一个卷积核的层数相同,\(H\)和\(W\)为卷积核的高和宽,每个卷积是三维的即\(C*H*W\)。 - \(N_d=2\),
Blob表示全连接层的权重时,shape为\(N_{out} * N_{in}\)的二维矩阵,\(N_{out}\)为输出数量,\(N_{in}\)为输入数量。 - \(N_d=1\),
Blob为长度为\(N\)的向量,表示卷积层bias参数时,\(N\)为卷积核数量(与输出特征图数量相同),表示全连接层bias参数时,\(N\)为输出数量(与上面的\(N_{out}\)相同)。
主要成员变量
shared_ptr<SyncedMemory> data_; // 数据,存储图像、参数、输入输出等
shared_ptr<SyncedMemory> diff_; // 反向传播时的梯度,训练阶段update时参数的更新量
shared_ptr<SyncedMemory> shape_data_; // GPU shape,与下面的shape是相同的
vector<int> shape_; // shape,data和diff相同
int count_; // 张量中的元素数量,比如 N*C*H*W
int capacity_; // 容量,当前分配内存的大小,当reshape时,可能需要扩容
Blob存储结构
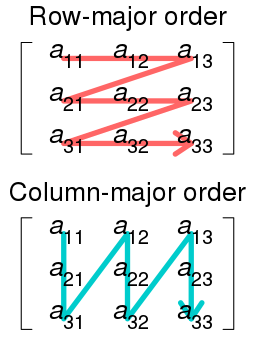
Blob的data_和diff_对应的数据区,在内存中均以行有先的方式存储(C语言风格)。行优先和列优先的存储方式如下图所示,9个数连续存储,表示同一个矩阵,但是存储顺序不同,图片来自WIKI:
当输入图像为1张RGB图时,shape为\(1*3*4*5\),其存储顺序如下图所示,图片素材来自链接。channel维上,0为R,1为G、2为B,先在R上行有先存储,再在G上行有先存储,最后在B上行有先存储。这里仅作示意,在caffe中实际存储顺序为BGR。
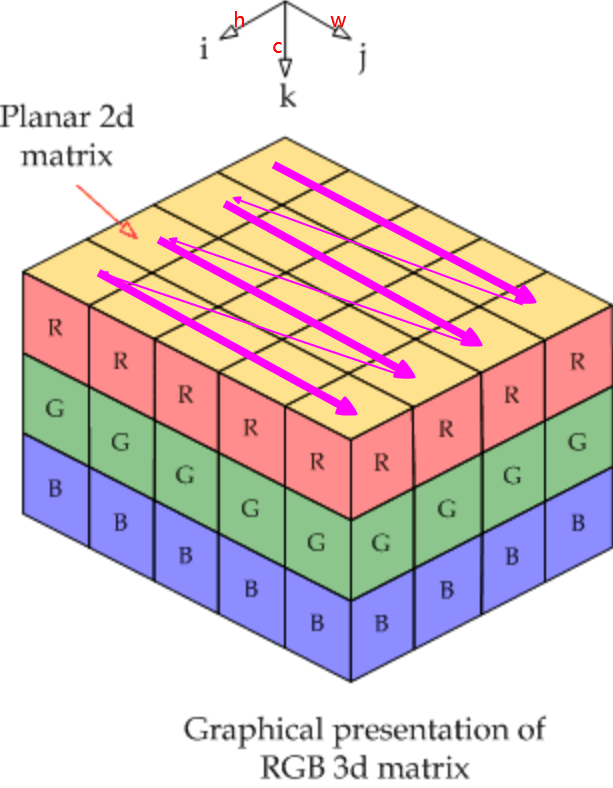
当\(N=4\)时,\(Num * Channel * Height * Width\),Blob在\(Width\)维上连续存储,如下图所示:
理解了上图,再理解多维Blob的拼接、裁剪等操作就很容易了。
通过Blob的offset成员函数可以获得\((n, c, h, w)\)处的偏移量,偏移的计算方式与行优先存储是一致的,代码如下:
inline int offset(const int n, const int c = 0, const int h = 0,
const int w = 0) const {
CHECK_GE(n, 0);
CHECK_LE(n, num());
CHECK_GE(channels(), 0);
CHECK_LE(c, channels());
CHECK_GE(height(), 0);
CHECK_LE(h, height());
CHECK_GE(width(), 0);
CHECK_LE(w, width());
return ((n * channels() + c) * height() + h) * width() + w;
}
CPU与GPU间的数据传递
const Dtype* cpu_data() const; // 不可修改数据,return (const Dtype*)data_->cpu_data();
const Dtype* gpu_data() const; // return (const Dtype*)data_->gpu_data();
Dtype* mutable_cpu_data(); // 可修改数据,return static_cast<Dtype*>(data_->mutable_cpu_data());
Dtype* mutable_gpu_data(); // static_cast<Dtype*>(data_->mutable_gpu_data());
Caffe中通过上述方式来获取CPU和GPU上的数据区指针,在调用函数时,SyncedMemory会自行判断是否需要同步数据(具体是如何判断的,在讲SyncedMemory时再详细说明),当访问CPU(GPU)侧数据时,如果GPU(CPU)侧数据(可能)更新过,则将数据同步至CPU(GPU)。可参考下面示例代码来理解何时会发生数据同步,示例代码来自Caffe官网。
// Assuming that data are on the CPU initially, and we have a blob.
const Dtype* foo;
Dtype* bar;
foo = blob.gpu_data(); // data copied cpu->gpu.
foo = blob.cpu_data(); // no data copied since both have up-to-date contents.
bar = blob.mutable_gpu_data(); // no data copied.
// ... some operations ...
bar = blob.mutable_gpu_data(); // no data copied when we are still on GPU.
foo = blob.cpu_data(); // data copied gpu->cpu, since the gpu side has modified the data
foo = blob.gpu_data(); // no data copied since both have up-to-date contents
bar = blob.mutable_cpu_data(); // still no data copied.
bar = blob.mutable_gpu_data(); // data copied cpu->gpu.
bar = blob.mutable_cpu_data(); // data copied gpu->cpu.
只要调用了mutable函数,即便没有实际修改数据,再调用另一侧的mutable函数,也会发生数据同步。因此,在明确不修改数据时,尽量调用const函数,只有在操纵数据时才调用mutable函数。
主要成员函数
Blob的主要成员函数有:
- 基本函数,包括构造函数、set和get类函数、逻辑判断等
Reshape函数,用于设置Blob的shape,分配内存Update函数,用于在网络训练时更新参数使用,\(data = data - diff\)Blob运算函数,用于切片统计、求L1范数、L2范数、数乘等- 辅助函数,proto导入导出等
下面重点介绍其中主要的成员函数。
template <typename Dtype>
class Blob {
public:
Blob()
: data_(), diff_(), count_(0), capacity_(0) {}
/// @brief Deprecated; use <code>Blob(const vector<int>& shape)</code>.
explicit Blob(const int num, const int channels, const int height,
const int width);
explicit Blob(const vector<int>& shape);
// ......
}
在Blob的构造函数中,会调用Reshape函数,给shape成员变量赋值以及分配初始内存。在Layer::Reshape或者Layer::Forward时,也会调用Reshape函数来设置输出Blob的维度,如果reshape了整个网络的输入Blob,则需要调用Net::Forward或者Net::Reshape来重新确定每一层相关Blob的shape(从bottom到top逐层推算得出)。当Blob size发生改变时,只有在内存不够才会再分配内存,具体代码如下
template <typename Dtype>
bool Blob<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<int>& shape) {
CHECK_LE(shape.size(), kMaxBlobAxes);
count_ = 1;
shape_.resize(shape.size());
if (!shape_data_ || shape_data_->size() < shape.size() * sizeof(int)) {
shape_data_.reset(new SyncedMemory(shape.size() * sizeof(int)));
}
int* shape_data = static_cast<int*>(shape_data_->mutable_cpu_data());
for (int i = 0; i < shape.size(); ++i) {
CHECK_GE(shape[i], 0);
if (count_ != 0) {
CHECK_LE(shape[i], INT_MAX / count_) << "blob size exceeds INT_MAX";
}
count_ *= shape[i];
shape_[i] = shape[i];
shape_data[i] = shape[i];
}
// 不够时分配内存,原内存会释放(shared_ptr)
if (count_ > capacity_) {
capacity_ = count_;
data_.reset(new SyncedMemory(capacity_ * sizeof(Dtype)));
diff_.reset(new SyncedMemory(capacity_ * sizeof(Dtype)));
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
在网络训练阶段,根据损失函数以及反向传播得到的梯度,获得每层参数的更新量diff_,会调用Update函数来更新参数,如下
template <typename Dtype>
void Blob<Dtype>::Update() {
// We will perform update based on where the data is located.
switch (data_->head()) {
case SyncedMemory::HEAD_AT_CPU:
// perform computation on CPU
// data = data - diff, axpy: y = ax + y
caffe_axpy<Dtype>(count_, Dtype(-1),
static_cast<const Dtype*>(diff_->cpu_data()),
static_cast<Dtype*>(data_->mutable_cpu_data()));
break;
case SyncedMemory::HEAD_AT_GPU:
case SyncedMemory::SYNCED:
#ifndef CPU_ONLY
// perform computation on GPU
caffe_gpu_axpy<Dtype>(count_, Dtype(-1),
static_cast<const Dtype*>(diff_->gpu_data()),
static_cast<Dtype*>(data_->mutable_gpu_data()));
#else
NO_GPU;
#endif
break;
default:
LOG(FATAL) << "Syncedmem not initialized.";
}
}
值得一提的是,Blob维度索引支持负数,-1表示最后一个维度,与Python相同,实现代码如下,在需要访问某个维度时,先使用CanonicalAxisIndex获得真正维度,比如CanonicalAxisIndex(-1)。
// axis_index the axis index.
// If 0 <= index < num_axes(), return index.
// If -num_axes <= index <= -1, return (num_axes() - (-index))
inline int CanonicalAxisIndex(int axis_index) const {
CHECK_GE(axis_index, -num_axes())
<< "axis " << axis_index << " out of range for " << num_axes()
<< "-D Blob with shape " << shape_string();
CHECK_LT(axis_index, num_axes())
<< "axis " << axis_index << " out of range for " << num_axes()
<< "-D Blob with shape " << shape_string();
if (axis_index < 0) {
return axis_index + num_axes();
}
return axis_index;
}
其他函数,只取代表。
// set get
// 省略基本的set和get函数,如上面提到的const和mutable函数
// 返回(n, c, h, w)处的数据,return cpu_data()[offset(n, c, h, w)]
inline Dtype data_at(const int n, const int c, const int h, const int w) const;
inline Dtype diff_at(const int n, const int c, const int h, const int w) const;
void ShareData(const Blob& other); // 与另一Blob共享data,类似浅拷贝
void ShareDiff(const Blob& other); // 与另一Blob共享diff
// 从另一Blob拷贝,类似深拷贝
void Blob<Dtype>::CopyFrom(const Blob& source, bool copy_diff, bool reshape);
// 切片元素数量统计,count *= shape(i)
inline int count(int start_axis, int end_axis) const;
// proto序列化与反序列化
void FromProto(const BlobProto& proto, bool reshape = true); // 从proto导入
void ToProto(BlobProto* proto, bool write_diff = false) const; // 导出为proto
// 运算
Dtype asum_data() const; // data L1 norm
Dtype asum_diff() const; // diff L1 norm
Dtype sumsq_data() const; // data L2 norm
Dtype sumsq_diff() const; // diff L2 norm
void scale_data(Dtype scale_factor); // data 数乘,in place
void scale_diff(Dtype scale_factor); // diff 数乘,in place
// 逻辑判断
bool ShapeEquals(const BlobProto& other); // 判断shape是否相同
以上。
参考
- Blobs, Layers, and Nets: anatomy of a Caffe model
- Row- and column-major order
- Caffe: a fast open framework for deep learning
Caffe源码理解1:Blob存储结构与设计的更多相关文章
- Caffe源码理解2:SyncedMemory CPU和GPU间的数据同步
目录 写在前面 成员变量的含义及作用 构造与析构 内存同步管理 参考 博客:blog.shinelee.me | 博客园 | CSDN 写在前面 在Caffe源码理解1中介绍了Blob类,其中的数据成 ...
- Caffe源码理解3:Layer基类与template method设计模式
目录 写在前面 template method设计模式 Layer 基类 Layer成员变量 构造与析构 SetUp成员函数 前向传播与反向传播 其他成员函数 参考 博客:blog.shinelee. ...
- Caffe学习系列(17): caffe源码分析 vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom(转)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_14975217/article/details/51524042 Blob:4个维度 n x c x h x w: bottom[0] .bot ...
- caffe源码分析 vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom
Blob:4个维度 n x c x h x w: bottom[0] .bottom[1]代表该层有几个输入. bottom[0]->count(): 输入中,元素的总维数(个数) bottom ...
- caffe源码 理解链式法则
网络结构 首先我们抽象理解下一个网络结构是怎样的,如下图所示 F1,F2,F3为某种函数 input为输入数据,output为输出数据 X1,X2为为中间的层的输入输出数据 总体来说有以下关系 X1 ...
- caffe源码阅读
参考网址:https://www.cnblogs.com/louyihang-loves-baiyan/p/5149628.html 1.caffe代码层次熟悉blob,layer,net,solve ...
- caffe源码学习之Proto数据格式【1】
前言: 由于业务需要,接触caffe已经有接近半年,一直忙着阅读各种论文,重现大大小小的模型. 期间也总结过一些caffe源码学习笔记,断断续续,这次打算系统的记录一下caffe源码学习笔记,巩固一下 ...
- caffe源码学习
本文转载自:https://buptldy.github.io/2016/10/09/2016-10-09-Caffe_Code/ Caffe简介 Caffe作为一个优秀的深度学习框架网上已经有很多内 ...
- Caffe源码中caffe.proto文件分析
Caffe源码(caffe version:09868ac , date: 2015.08.15)中有一些重要文件,这里介绍下caffe.proto文件. 在src/caffe/proto目录下有一个 ...
随机推荐
- td默认文字超出后显示..,点击tr时td文字显示完整
做项目时,产品提的需求,table表格里面,每一列限制文字超出宽度后显示省略号,等点击td时,文字显示完整,今天整理了一下代码,积累一下 备注:1.邮箱和网址,在td里面不会自动换行,需要增加word ...
- Java学习导航
由于最近在系统的重新学习Java,为了便于日后复习,给个人博客中Java内容做一个目录. Java基础:Java虚拟机(JVM) Java基础:内存模型 Java基础:JVM垃圾回收算法 Java基础 ...
- mybatis源码解读(五)——sql语句的执行流程
还是以第一篇博客中给出的例子,根据代码实例来入手分析. static { InputStream inputStream = MybatisTest.class.getClassLoader().ge ...
- 洛谷 P1613 解题报告
P1613 跑路 题目描述 小\(A\)的工作不仅繁琐,更有苛刻的规定,要求小\(A\)每天早上在\(6:00\)之前到达公司,否则这个月工资清零.可是小\(A\)偏偏又有赖床的坏毛病.于是为了保住自 ...
- 通过jstack与jmap分析一次cpu打满的线上故障
一.发现问题 下面是线上机器的cpu使用率,可以看到从4月8日开始,随着时间cpu使用率在逐步增高,最终使用率达到100%导致线上服务不可用,后面重启了机器后恢复. 二.排查思路 简单分析下可能出问题 ...
- .NET之IOC控制反转运用
当前场景: 如果有不同的用户.使用同一个系统.而不同的客户有某些不同的需求.在不改变系统主体的情况下,可以直接使用IOC控制反转依赖搭建项目 1.添加接口层 目前里面只有一个会员的类.里面有一个登录接 ...
- spring+activemq中多个consumer同时处理消息时遇到的性能问题
最近在做数据对接的工作,用到了activemq,我需要从activemq中接收消息并处理,但是我处理数据的步骤稍微复杂,渐渐的消息队列中堆的数据越来越多,就想到了我这边多开几个线程来处理消息. 可是会 ...
- JXP
JSX 初识:它是JavaScript的语法扩展,建议在React中使用它来描述UI的外观. 考虑这个变量声明: 在JSX中嵌入表达式 可以通过将其包含在大括号中来嵌入JSX中的任何JavaScr ...
- SSM-SpringMVC-18:SpringMVC中参数自动装配
------------吾亦无他,唯手熟尔,谦卑若愚,好学若饥------------- 在处理方法中,参数写上之后,只要符合特定规则,就可以自动装配 首先 其次是:自定义的参数的自动装配: 案例如 ...
- Re:从零开始的领域驱动设计
领域驱动的火爆程度不用我赘述,但是即便其如此得耳熟能详,但大多数人对其的认识,还只是停留在知道它的缩写是DDD,知道它是一种软件思想,或者知道它和微服务有千丝万缕的关系.Eric Evans对DDD的 ...
