DeepLearning.ai-Week4-Deep Learning & Art: Neural Style Transfer
1 - Task
- Implement the neural style transfer algorithm
- Generate novel artistic images using your algorithm
2 - Import Packages
import os
import sys
import scipy.io
import scipy.misc
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow
from PIL import Image
from nst_utils import *
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf %matplotlib inline
3 - Problem Statement

4 - Transfer Learning
加载已经在ImageNet数据集上训练好的VGG网络。
model = load_vgg_model("pretrained-model/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat")
print(model)
Result:
{'conv5_3': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_14:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool1': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool:0' shape=(1, 150, 200, 64) dtype=float32>, 'conv5_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_13:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv3_3': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_6:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv3_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_5:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_9:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool3': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_2:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_3': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_10:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool5': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_4:0' shape=(1, 10, 13, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv3_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_4:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv5_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_12:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv2_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_3:0' shape=(1, 150, 200, 128) dtype=float32>, 'conv5_4': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_15:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'input': <tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(1, 300, 400, 3) dtype=float32_ref>, 'conv3_4': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_7:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_8:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_4': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_11:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool2': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_1:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 128) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool4': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_3:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv1_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu:0' shape=(1, 300, 400, 64) dtype=float32>, 'conv2_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_2:0' shape=(1, 150, 200, 128) dtype=float32>, 'conv1_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_1:0' shape=(1, 300, 400, 64) dtype=float32>}
5 - Neural Style Transfer
实现NST算法有如下几个步骤:
- Build the content cost function J_{content}(C,G)
- Build the style cost function J_{style}(S,G)$
- Put it together to get J(G)=α J_{content}(C,G)+β J_{style}(S,G)
5.1 - Computing the content cost
浏览浏览图片。
content_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/louvre.jpg")
imshow(content_image)
Result:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x21eca6026d8>

5.1.1 - How do you ensure the generated image G matches the content of the image C?
内容损失函数如下:
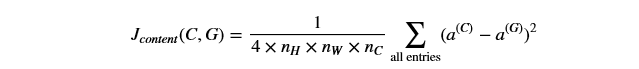
实现compute_content_cost()方法有如下步骤:
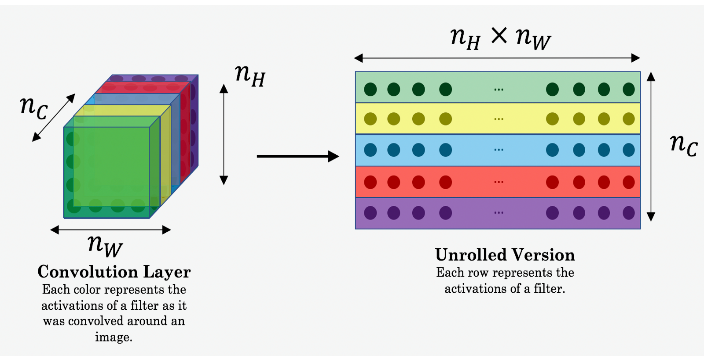
- Retrieve dimensions from a_G:
- To retrieve dimensions from a tensor X, use:
X.get_shape().as_list()
- To retrieve dimensions from a tensor X, use:
- Unroll a_C and a_G as explained in the picture above
- Compute the content cost:
# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_content_cost def compute_content_cost(a_C, a_G):
"""
Computes the content cost Arguments:
a_C -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing content of the image C
a_G -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing content of the image G Returns:
J_content -- scalar that you compute using equation 1 above.
""" ### START CODE HERE ###
# Retrieve dimensions from a_G (≈1 line)
m, n_H, n_W, n_C = a_G.get_shape().as_list() # Reshape a_C and a_G (≈2 lines)
a_C_unrolled = tf.reshape(a_C, (n_H*n_W, n_C))
a_G_unrolled = tf.reshape(a_G, (n_H*n_W, n_C))# compute the cost with tensorflow (≈1 line)
J_content = 1 / (4*n_H*n_W*n_C) * tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(a_C_unrolled, a_G_unrolled)))
### END CODE HERE ### return J_content
tf.reset_default_graph() with tf.Session() as test:
tf.set_random_seed(1)
a_C = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4)
a_G = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4)
J_content = compute_content_cost(a_C, a_G)
print("J_content = " + str(J_content.eval()))
Result:
J_content = 6.76559
5.2 - Computing the style cost
预览图片。
style_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/monet_800600.jpg")
imshow(style_image)
Result:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x21eccaeff28>

5.2.1 - Style matrix
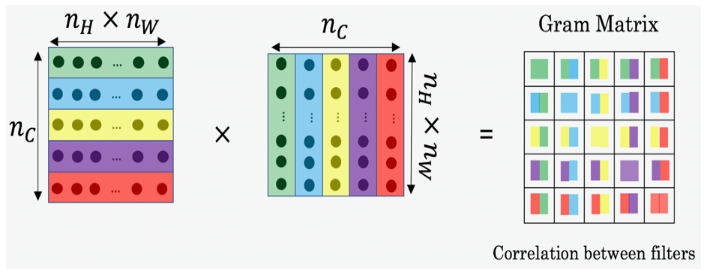
# GRADED FUNCTION: gram_matrix
# G_A = AA^T
def gram_matrix(A):
"""
Argument:
A -- matrix of shape (n_C, n_H*n_W) Returns:
GA -- Gram matrix of A, of shape (n_C, n_C)
""" ### START CODE HERE ### (≈1 line)
GA = tf.matmul(A, tf.transpose(A))
### END CODE HERE ### return GA
tf.reset_default_graph() with tf.Session() as test:
tf.set_random_seed(1)
A = tf.random_normal([3, 2*1], mean=1, stddev=4)
GA = gram_matrix(A) print("GA = " + str(GA.eval()))
Result:
GA = [[ 6.42230511 -4.42912197 -2.09668207]
[ -4.42912197 19.46583748 19.56387138]
[ -2.09668207 19.56387138 20.6864624 ]]
5.2.2 - Style cost
风格损失函数如下:
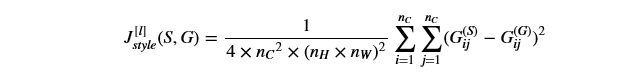
实现compute_layer_style_cost()方法有如下步骤:
- Retrieve dimensions from the hidden layer activations a_G:
- To retrieve dimensions from a tensor X, use:
X.get_shape().as_list()
- To retrieve dimensions from a tensor X, use:
- Unroll the hidden layer activations a_S and a_G into 2D matrices, as explained in the picture above.
- Compute the Style matrix of the images S and G. (Use the function you had previously written.)
- Compute the Style cost:
# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_layer_style_cost def compute_layer_style_cost(a_S, a_G):
"""
Arguments:
a_S -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing style of the image S
a_G -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing style of the image G Returns:
J_style_layer -- tensor representing a scalar value, style cost defined above by equation (2)
""" ### START CODE HERE ###
# Retrieve dimensions from a_G (≈1 line)
m, n_H, n_W, n_C = a_G.get_shape().as_list() # Reshape the images to have them of shape (n_C, n_H*n_W) (≈2 lines)
a_S = tf.reshape(a_S, [n_H*n_W, n_C])
a_G = tf.reshape(a_G, [n_H*n_W, n_C]) # Computing gram_matrices for both images S and G (≈2 lines)
GS = gram_matrix(tf.transpose(a_S))
GG = gram_matrix(tf.transpose(a_G)) # Computing the loss (≈1 line)
J_style_layer = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(GS, GG))) / (4*tf.square(tf.to_float(n_H*n_W*n_C))) ### END CODE HERE ### return J_style_layer
tf.reset_default_graph() with tf.Session() as test:
tf.set_random_seed(1)
a_S = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4)
a_G = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4)
J_style_layer = compute_layer_style_cost(a_S, a_G) print("J_style_layer = " + str(J_style_layer.eval()))
Result:
J_style_layer = 9.19028
5.2.3 - Style Weights
STYLE_LAYERS = [
('conv1_1', 0.2),
('conv2_1', 0.2),
('conv3_1', 0.2),
('conv4_1', 0.2),
('conv5_1', 0.2)]
通过如下公式综合不同层的style costs:
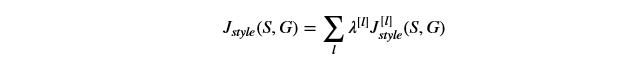
def compute_style_cost(model, STYLE_LAYERS):
"""
Computes the overall style cost from several chosen layers Arguments:
model -- our tensorflow model
STYLE_LAYERS -- A python list containing:
- the names of the layers we would like to extract style from
- a coefficient for each of them Returns:
J_style -- tensor representing a scalar value, style cost defined above by equation (2)
""" # initialize the overall style cost
J_style = 0 for layer_name, coeff in STYLE_LAYERS: # Select the output tensor of the currently selected layer
out = model[layer_name] # Set a_S to be the hidden layer activation from the layer we have selected, by running the session on out
a_S = sess.run(out) # Set a_G to be the hidden layer activation from same layer. Here, a_G references model[layer_name]
# and isn't evaluated yet. Later in the code, we'll assign the image G as the model input, so that
# when we run the session, this will be the activations drawn from the appropriate layer, with G as input.
a_G = out # Compute style_cost for the current layer
J_style_layer = compute_layer_style_cost(a_S, a_G) # Add coeff * J_style_layer of this layer to overall style cost
J_style += coeff * J_style_layer return J_style
5.3 - Defining the total cost to optimize
总的损失函数表示如下:
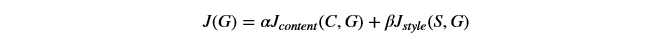
# GRADED FUNCTION: total_cost def total_cost(J_content, J_style, alpha = 10, beta = 40):
"""
Computes the total cost function Arguments:
J_content -- content cost coded above
J_style -- style cost coded above
alpha -- hyperparameter weighting the importance of the content cost
beta -- hyperparameter weighting the importance of the style cost Returns:
J -- total cost as defined by the formula above.
""" ### START CODE HERE ### (≈1 line)
J = alpha * J_content + beta * J_style
### END CODE HERE ### return J
tf.reset_default_graph() with tf.Session() as test:
np.random.seed(3)
J_content = np.random.randn()
J_style = np.random.randn()
J = total_cost(J_content, J_style)
print("J = " + str(J))
Result:
J = 35.34667875478276
6 - Solving the optimization problem
实现神经风格迁移需要实现以下内容:
- Create an Interactive Session
- Load the content image
- Load the style image
- Randomly initialize the image to be generated
- Load the VGG16 model
- Build the TensorFlow graph:
- Run the content image through the VGG16 model and compute the content cost
- Run the style image through the VGG16 model and compute the style cost
- Compute the total cost
- Define the optimizer and the learning rate
- Initialize the TensorFlow graph and run it for a large number of iterations, updating the generated image at every step.
# Reset the graph
tf.reset_default_graph() # Start interactive session
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# load, reshape, and normalize "content" image
content_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/louvre_small.jpg")
content_image = reshape_and_normalize_image(content_image)
# load, reshape, and normalize "style" image
style_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/monet.jpg")
style_image = reshape_and_normalize_image(style_image)
# initialize the "generated" Image as a noisy image created from the content_image
generated_image = generate_noise_image(content_image)
imshow(generated_image[0])
# load the VGG16 model
model = load_vgg_model("pretrained-model/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat")
- Assign the content image to be the input to the VGG model.
- Set a_C to be the tensor giving the hidden layer activation for layer "conv4_2".
- Set a_G to be the tensor giving the hidden layer activation for the same layer.
- Compute the content cost using a_C and a_G.
# Assign the content image to be the input of the VGG model.
sess.run(model['input'].assign(content_image)) # Select the output tensor of layer conv4_2
out = model['conv4_2'] # Set a_C to be the hidden layer activation from the layer we have selected
a_C = sess.run(out) # Set a_G to be the hidden layer activation from same layer. Here, a_G references model['conv4_2']
# and isn't evaluated yet. Later in the code, we'll assign the image G as the model input, so that
# when we run the session, this will be the activations drawn from the appropriate layer, with G as input.
a_G = out # Compute the content cost
J_content = compute_content_cost(a_C, a_G)
# Assign the input of the model to be the "style" image
sess.run(model['input'].assign(style_image)) # Compute the style cost
J_style = compute_style_cost(model, STYLE_LAYERS)
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
J = total_cost(J_content, J_style, alpha=10, beta=40)
### END CODE HERE ###
# define optimizer (1 line)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(2.0) # define train_step (1 line)
train_step = optimizer.minimize(J)
def model_nn(sess, input_image, num_iterations = 200):
# Initialize global variables (you need to run the session on the initializer)
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
### END CODE HERE ###
# Run the noisy input image (initial generated image) through the model. Use assign().
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
sess.run(model["input"].assign(input_image))
### END CODE HERE ###
for i in range(num_iterations):
# Run the session on the train_step to minimize the total cost
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
sess.run(train_step)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Compute the generated image by running the session on the current model['input']
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
generated_image = sess.run(model["input"])
### END CODE HERE ###
# Print every 20 iteration.
if i%20 == 0:
Jt, Jc, Js = sess.run([J, J_content, J_style])
print("Iteration " + str(i) + " :")
print("total cost = " + str(Jt))
print("content cost = " + str(Jc))
print("style cost = " + str(Js))
# save current generated image in the "/output" directory
save_image("output/" + str(i) + ".png", generated_image)
# save last generated image
save_image('output/generated_image.jpg', generated_image)
return generated_image
model_nn(sess, generated_image)
Result:
Iteration 0 :
total cost = 5.04752e+09
content cost = 7865.72
style cost = 1.26186e+08
Iteration 20 :
total cost = 9.44841e+08
content cost = 15236.9
style cost = 2.36172e+07
Iteration 40 :
total cost = 4.80354e+08
content cost = 16712.4
style cost = 1.20047e+07
Iteration 60 :
total cost = 3.10203e+08
content cost = 17443.6
style cost = 7.75072e+06
(略)
Result:




7 - Summary
- Neural Style Transfer is an algorithm that given a content image C and a style image S can generate an artistic image
- It uses representations (hidden layer activations) based on a pretrained ConvNet.
- The content cost function is computed using one hidden layer's activations.
- The style cost function for one layer is computed using the Gram matrix of that layer's activations. The overall style cost function is obtained using several hidden layers.
- Optimizing the total cost function results in synthesizing new images.
8 - References
https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs230/
DeepLearning.ai-Week4-Deep Learning & Art: Neural Style Transfer的更多相关文章
- Art: Neural Style Transfer
Andrew Ng deeplearning courese-4:Convolutional Neural Network Convolutional Neural Networks: Step by ...
- 课程四(Convolutional Neural Networks),第四 周(Special applications: Face recognition & Neural style transfer) —— 2.Programming assignments:Art generation with Neural Style Transfer
Deep Learning & Art: Neural Style Transfer Welcome to the second assignment of this week. In thi ...
- Spark MLlib Deep Learning Convolution Neural Network (深度学习-卷积神经网络)3.1
3.Spark MLlib Deep Learning Convolution Neural Network (深度学习-卷积神经网络)3.1 http://blog.csdn.net/sunbow0 ...
- Spark MLlib Deep Learning Convolution Neural Network (深度学习-卷积神经网络)3.2
3.Spark MLlib Deep Learning Convolution Neural Network(深度学习-卷积神经网络)3.2 http://blog.csdn.net/sunbow0 ...
- Spark MLlib Deep Learning Convolution Neural Network (深度学习-卷积神经网络)3.3
3.Spark MLlib Deep Learning Convolution Neural Network(深度学习-卷积神经网络)3.3 http://blog.csdn.net/sunbow0 ...
- 项目总结四:神经风格迁移项目(Art generation with Neural Style Transfer)
1.项目介绍 神经风格转换 (NST) 是深部学习中最有趣的技术之一.它合并两个图像, 即 内容图像 C(content image) 和 样式图像S(style image), 以生成图像 G(ge ...
- [C4W4] Convolutional Neural Networks - Special applications: Face recognition & Neural style transfer
第四周:Special applications: Face recognition & Neural style transfer 什么是人脸识别?(What is face recogni ...
- fast neural style transfer图像风格迁移基于tensorflow实现
引自:深度学习实践:使用Tensorflow实现快速风格迁移 一.风格迁移简介 风格迁移(Style Transfer)是深度学习众多应用中非常有趣的一种,如图,我们可以使用这种方法把一张图片的风格“ ...
- 神经风格转换Neural Style Transfer a review
原文:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/t_jknoYuyAM9fu6CI8OdNw 作者:Yongcheng Jing 等 机器之心编译 风格迁移是近来人工智能领域内的一个热门研究 ...
随机推荐
- JS学习笔记Day6
一.数组 1.数组就是个容器,里面可以存放任意类型的数 2.定义数组:1)var arr = []: 2)var arr = new Array():构造函数定义方式,如果括号中有一个整数,该正数代表 ...
- windows远程桌面无法粘贴复制的问题解决方法
这两天遇到一个困扰我很久的问题,每次通过winodws远程桌面,本地的数据无法通过复制粘贴到远程服务器上.现把我找到的解决方案记录下来分享给大家 一般出现问题可能性比较大的原因就是rdpclip.ex ...
- node.js(小案例)_实现学生信息增删改
一.前言 本节内容主要对小案例做一个总结: 1.如何开始搭建小项目 2.路由设计 3.模块应用 4.项目源码以及实现过程github地址: 项目演示如下: 二.主要内容 1.项目的关键性js源码: 项 ...
- libmysqlclient.so.18: cannot open shared object file
libmysqlclient.so.18: cannot open shared object file 解决libmysqlclient.so.18: cannot open shared obje ...
- golang 热升级
需求场景 干净利落地升级正在运行的agent程序.适用于Devops团队. 目标: 不关闭现有连接:例如我们不希望关掉已部署的运行中的程序.但又想不受限制地随时升级服务. 新的进程要能够启动并替换掉旧 ...
- 建立Heapster Influxdb Grafana集群性能监控平台
依赖于kubenets dns服务 图形化展示度量指标的实现需要集成k8s的另外一个Addons组件: Heapster .Heapster原生支持K8s(v1.0.6及以后版本)和 CoreOS , ...
- Tensorflow搞一个聊天机器人
catalogue . 前言 . 训练语料库 . 数据预处理 . 词汇转向量 . 训练 . 聊天机器人 - 验证效果 0. 前言 不是搞机器学习算法专业的,3个月前开始补了一些神经网络,卷积,神经网络 ...
- ranger部署文档(记)
目录 概览... 2 1. ranger-admin. 2 2. ranger-user-sync. 2 3. ranger-*-plugins. 2 安装... 3 1 ...
- java io系列03之 ByteArrayOutputStream的简介,源码分析和示例(包括OutputStream)
前面学习ByteArrayInputStream,了解了“输入流”.接下来,我们学习与ByteArrayInputStream相对应的输出流,即ByteArrayOutputStream.本章,我们会 ...
- Java NIO系列教程(七) selector原理 Epoll版的Selector
目录: Reactor(反应堆)和Proactor(前摄器) <I/O模型之三:两种高性能 I/O 设计模式 Reactor 和 Proactor> <[转]第8章 前摄器(Proa ...
