[WPF 基础知识系列] —— 绑定中的数据校验Vaildation
前言:
只要是有表单存在,那么就有可能有对数据的校验需求。如:判断是否为整数、判断电子邮件格式等等。
WPF采用一种全新的方式 - Binding,来实现前台显示与后台数据进行交互,当然数据校验方式也不一样了。
本专题全面介绍一下WPF中4种Validate方法,帮助你了解如何在WPF中对binding的数据进行校验,并处理错误显示。
一、简介
正常情况下,只要是绑定过程中出现异常或者在converter中出现异常,都会造成绑定失败。
但是WPF不会出现任何异常,只会显示一片空白(当然有些Converter中的异常会造成程序崩溃)。
这是因为默认情况下,Binding.ValidatesOnException为false,所以WPF忽视了这些绑定错误。
但是如果我们把Binding.ValidatesOnException为true,那么WPF会对错误做出以下反应:
- 设置绑定元素的附加属性 Validation.HasError为true(如TextBox,如果Text被绑定,并出现错误)。
- 创建一个包含错误详细信息(如抛出的Exception对象)的ValidationError对象。
- 将上面产生的对象添加到绑定对象的Validation.Errors附加属性当中。
- 如果Binding.NotifyOnValidationError是true,那么绑定元素的附加属性中的Validation.Error附加事件将被触发。(这是一个冒泡事件)
我们的Binding对象,维护着一个ValidationRule的集合,当设置ValidatesOnException为true时,
默认会添加一个ExceptionValidationRule到这个集合当中。
PS:对于绑定的校验只在Binding.Mode 为TwoWay和OneWayToSource才有效,
即当需要从target控件将值传到source属性时,很容易理解,当你的值不需要被别人使用时,就很可能校验也没必要。
二、四种实现方法
1、在Setter方法中进行判断
直接在Setter方法中,对value进行校验,如果不符合规则,那么就抛出异常。然后修改XAML不忽视异常。
public class PersonValidateInSetter : ObservableObject
{
private string name;
private int age;
public string Name
{
get { return this.name; }
set
{
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value))
{
throw new ArgumentException("Name cannot be empty!");
} if (value.Length < )
{
throw new ArgumentException("Name must have more than 4 char!");
}
this.name = value;
this.OnPropertyChanged(() => this.Name);
}
}
public int Age
{
get
{ return this.age; }
set
{
if (value < )
{
throw new ArgumentException("You must be an adult!");
}
this.age = value;
this.OnPropertyChanged(() => this.Age);
}
}
}
<Grid DataContext="{Binding PersonValidateInSetter}">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" />
<ColumnDefinition />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<TextBlock Text="Name:" />
<TextBox Grid.Column="1"
Margin="1"
Text="{Binding Name,
ValidatesOnExceptions=True,
UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" />
<TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Text="Age:" />
<TextBox Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="1"
Margin="1"
Text="{Binding Age,
ValidatesOnExceptions=True,
UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" />
</Grid>
当输入的值,在setter方法中校验时出现错误,就会出现一个红色的错误框。
关键代码:ValidatesOnExceptions=True, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged。
PS:这种方式有一个BUG,首次加载时不会对默认数据进行检验。
2、继承IDataErrorInfo接口
使Model对象继承IDataErrorInfo接口,并实现一个索引进行校验。如果索引返回空表示没有错误,如果返回不为空,
表示有错误。另外一个Erro属性,但是在WPF中没有被用到。
public class PersonDerivedFromIDataErrorInfo : ObservableObject, IDataErrorInfo
{
private string name;
private int age;
public string Name
{
get
{
return this.name;
}
set
{
this.name = value;
this.OnPropertyChanged(() => this.Name);
}
}
public int Age
{
get
{
return this.age;
}
set
{
this.age = value;
this.OnPropertyChanged(() => this.Age);
}
}
// never called by WPF
public string Error
{
get
{
return null;
}
}
public string this[string propertyName]
{
get
{
switch (propertyName)
{
case "Name":
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(this.Name))
{
return "Name cannot be empty!";
}
if (this.Name.Length < )
{
return "Name must have more than 4 char!";
}
break;
case "Age":
if (this.Age < )
{
return "You must be an adult!";
}
break;
}
return null;
}
}
}
<Grid DataContext="{Binding PersonDerivedFromIDataErrorInfo}">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" />
<ColumnDefinition />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<TextBlock Text="Name:" />
<TextBox Grid.Column="1"
Margin="1"
Text="{Binding Name,
NotifyOnValidationError=True,
ValidatesOnDataErrors=True,
UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" />
<TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Text="Age:" />
<TextBox Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="1"
Margin="1"
Text="{Binding Age,
NotifyOnValidationError=True,
ValidatesOnDataErrors=True,
UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" />
PS:这种方式,没有了第一种方法的BUG,但是相对很麻烦,既需要继承接口,又需要添加一个索引,如果遗留代码,那么这种方式就不太好。
3、自定义校验规则
一个数据对象或许不能包含一个应用要求的所有不同验证规则,但是通过自定义验证规则就可以解决这个问题。
在需要的地方,添加我们创建的规则,并进行检测。
通过继承ValidationRule抽象类,并实现Validate方法,并添加到绑定元素的Binding.ValidationRules中。
public class MinAgeValidation : ValidationRule
{
public int MinAge { get; set; } public override ValidationResult Validate(object value, CultureInfo cultureInfo)
{
ValidationResult result = null; if (value != null)
{
int age; if (int.TryParse(value.ToString(), out age))
{
if (age < this.MinAge)
{
result = new ValidationResult(false, "Age must large than " + this.MinAge.ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
}
}
else
{
result = new ValidationResult(false, "Age must be a number!");
}
}
else
{
result = new ValidationResult(false, "Age must not be null!");
} return new ValidationResult(true, null);
}
}
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" />
<ColumnDefinition />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<TextBlock Text="Name:" />
<TextBox Grid.Column="1" Margin="1" Text="{Binding Name}">
</TextBox>
<TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Text="Age:" />
<TextBox Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="1"
Margin="1">
<TextBox.Text>
<Binding Path="Age"
UpdateSourceTrigger="PropertyChanged"
ValidatesOnDataErrors="True">
<Binding.ValidationRules>
<validations:MinAgeValidation MinAge="18" />
</Binding.ValidationRules>
</Binding>
</TextBox.Text>
</TextBox>
</Grid>
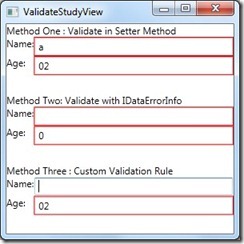
这种方式,也会有第一种方法的BUG,暂时还不知道如何解决,但是这个能够灵活的实现校验,并且能传参数。
效果图:
4、使用数据注解(特性方式)
在System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotaions命名空间中定义了很多特性,
它们可以被放置在属性前面,显示验证的具体需要。放置了这些特性之后,
属性中的Setter方法就可以使用Validator静态类了,来用于验证数据。
public class PersonUseDataAnnotation : ObservableObject
{
private int age;
private string name;
[Range(, , ErrorMessage = "Age must be a positive integer")]
public int Age
{
get
{
return this.age;
}
set
{
this.ValidateProperty(value, "Age");
this.SetProperty(ref this.age, value, () => this.Age);
}
}
[Required(ErrorMessage = "A name is required")]
[StringLength(, MinimumLength = , ErrorMessage = "Name must have at least 3 characters")]
public string Name
{
get
{
return this.name;
}
set
{
this.ValidateProperty(value, "Name");
this.SetProperty(ref this.name, value, () => this.Name);
}
}
protected void ValidateProperty<T>(T value, string propertyName)
{
Validator.ValidateProperty(value,
new ValidationContext(this, null, null) { MemberName = propertyName });
}
}
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" />
<ColumnDefinition />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<TextBlock Text="Name:" />
<TextBox Grid.Column="1"
Margin="1"
Text="{Binding Name,
ValidatesOnExceptions=True,
UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" />
<TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Text="Age:" />
<TextBox Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="1"
Margin="1"
Text="{Binding Age,
ValidatesOnExceptions=True,
UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" />
</Grid>
使用特性的方式,能够很自由的使用自定义的规则,而且在.Net4.5中新增了很多特性,可以很方便的对数据进行校验。
例如:EmailAddress, Phone, and Url等。
三、自定义错误显示模板
在上面的例子中,我们可以看到当出现验证不正确时,绑定控件会被一圈红色错误线包裹住。
这种方式一般不能够正确的展示出,错误的原因等信息,所以有可能需要自己的错误显示方式。
前面,我们已经讲过了。当在检测过程中,出现错误时,WPF会把错误信息封装为一个ValidationError对象,
并添加到Validation.Errors中,所以我们可以取出错误详细信息,并显示出来。
1、为控件创建ErrorTemplate
下面就是一个简单的例子,每次都把错误信息以红色展示在空间上面。这里的AdornedElementPlaceholder相当于
控件的占位符,表示控件的真实位置。这个例子是在书上直接拿过来的,只能做基本展示用。
<ControlTemplate x:Key="ErrorTemplate">
<Border BorderBrush="Red" BorderThickness="2">
<Grid>
<AdornedElementPlaceholder x:Name="_el" />
<TextBlock Margin="0,0,6,0"
HorizontalAlignment="Right"
VerticalAlignment="Center"
Foreground="Red"
Text="{Binding [0].ErrorContent}" />
</Grid>
</Border>
</ControlTemplate>
<TextBox x:Name="AgeTextBox"
Grid.Row="1"
Grid.Column="1"
Margin="1" Validation.ErrorTemplate="{StaticResource ErrorTemplate}" >
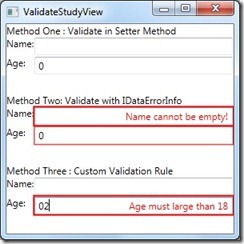
使用方式非常简单,将上面的模板作为逻辑资源加入项目中,然后像上面一样引用即可。
效果图:
对知识梳理总结,希望对大家有帮助!
[WPF 基础知识系列] —— 绑定中的数据校验Vaildation的更多相关文章
- 基础知识系列☞C#中→属性和字段的区别
"好吧...准备写个'基础知识系列',算是记录下吧,时时看看,更加加深记忆···" 其实本来准备叫"面试系列"... 字段.属性.你先知道的哪个概念? ***我 ...
- 基础知识系列☞C#中数组Array、ArrayList和List三者的区别
数组() #region 数组 //初始化方式_0:先声明再赋值 ]; weekDays_0[] = "Sun"; weekDays_0[] = "Mon"; ...
- [C# 基础知识系列]C#中易混淆的知识点
一.引言 今天在论坛中看到一位朋友提出这样的一个问题,问题大致(问题的链接为:http://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/zh-CN/52e6c11f-ad28-4 ...
- 基础知识系列☞C#中→委托
有些.NET中的高级特性,比如:委托! 有一种怎么也搞不懂的赶脚... 博客读了好几篇,代码也动手写了,书中的一些介绍也看了, 各种搜索关于委托的,至今还处于"会用"的阶段. 该怎 ...
- C# 基础知识系列- 3 集合数组
简单的介绍一下集合,通俗来讲就是用来保管多个数据的方案.比如说我们是一个公司的仓库管理,公司有一堆货物需要管理,有同类的,有不同类的,总而言之就是很多.很乱.我们对照集合的概念对仓库进行管理的话,那么 ...
- C# 基础知识系列- 9 字符串的更多用法(一)
0. 前言 在前面的文章里简单介绍了一下字符串的相关内容,并没有涉及到更多的相关内容,这一篇将尝试讲解一下在实际开发工作中会遇到的字符串的很多操作. 1. 创建一个字符串 这部分介绍一下如何创建一个字 ...
- C# 基础知识系列-13 常见类库(三)
0. 前言 在<C# 基础知识系列- 13 常见类库(二)>中,我们介绍了一下DateTime和TimeSpan这两个结构体的内容,也就是C#中日期时间的简单操作.本篇将介绍Guid和Nu ...
- C# 基础知识系列- 14 IO篇 文件的操作 (3)
本篇继续前两篇内容,跟大家介绍一下Path类以及FileSystemInfo这个类的主要方法和属性. 上文提到,在<C# 基础知识系列-IO篇>之文件相关的内容完结之后,会带领大家开发一个 ...
- C# 基础知识系列- 14 IO篇 流的使用
0. 前言 继续之前的C# IO流,在前几篇小短片中我们大概看了下C# 的基础IO也对文件.目录和路径的操作有了一定的了解.这一篇开始,给大家演示一下流的各种操作.以文件流为例,一起来看看如何操作吧. ...
随机推荐
- (转) 面向对象设计原则(二):开放-封闭原则(OCP)
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/tjiyu/article/details/57079927 面向对象设计原则(二):开放-封闭原则(OCP) 开放-封闭原则(Open-closed ...
- SQL Server性能优化(6)查询语句建议
1. 如果对数据不是工业级的访问(允许脏读),在select里添加 with(nolock) ID FROM Measure_heat WITH (nolock) 2. 限制结果集的数据量,如使用TO ...
- Nginx 配置 Location 规则优先级问题
nginx 的 location与配置中 location 顺序没有关系,与 location 表达式的类型有关.相同类型的表达式,字符串长的会优先匹配. 以下是按优先级排列说明: 等号类型(=)的优 ...
- 一对一Socket简单聊天的实现
今天终于调试通了Socket一对一的聊天,每次发送连接请求后,将用户名发送到Socket中去,然后将用户名和新建的socket存到map中,然后根据用户名来确定接收方是谁,以实现一对一的聊天功能. 上 ...
- top 动态查看进程
top 统计信息前五行是系统整体的统计信息 1.第一行是任务队列信息 同uptime质性命令结果一样. 06:47:11 up 6:39, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0 ...
- Linux添加防火墙、iptables的安装和配置(亲测)
iptables基础 规则(rules)其实就是网络管理员预定义的条件,规则一般的定义为“如果数据包头符合这样的条件,就这样处理这个数据包”.规则存储在内核空间的信息 包过滤表中,这些规则分别指定了源 ...
- mysql命令行查看建表语句
命令如下: SHOW CREATE TABLE tbl_name 例子: mysql> SHOW CREATE TABLE t\G . row ************************* ...
- 你真的理解编码吗?unicode,utf8,utf16详解
背景 前两天在网上看到一篇关于编码的讨论,仔细学习了一下unicode,utf8,utf16的定义.这篇博客旨在让读者真正理解他们是什么. 什么是编码 在阅读本文之前建议读者先去阅读这篇文章:http ...
- java web 答辩总结
今天我们组答辩.在昨天前三个组答辩之后,整理了一些试题. 在这个项目的答辩准备:首先把这个java web这本书大概的看了一遍:对整理的那些试题也把答案整理出来了:针对老师提问频率较高的试题:针对自己 ...
- k8s使用nfs动态存储
1.Kubernetes集群管理员通过提供不同的存储类,可以满足用户不同的服务质量级别.备份策略和任意策略要求的存储需求.动态存储卷供应使用StorageClass进行实现,其允许存储卷按需被创建.如 ...
