设备树..ing
.dts==>.dtb ==>device_node ==> platform_device ==> led_dev.c ==>匹配 led_drv.c (设备树是对平台设备总线的一种改进)
1.使用设备树时平台设备总线源码分析
平台设备总线分析:https://www.cnblogs.com/zsy12138/p/10391933.html
struct bus_type platform_bus_type =
{
.name = "platform",
.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,
.match = platform_match,
/*
* platform_match --> platform_match(device,device_driver) --> of_driver_match_device(dev, drv)
* --> of_match_device(drv->of_match_table, dev)
* 最终用总线的 devices 和总线的 driver->of_match_table 相互比较
*
*/
.uevent = platform_uevent,
.dma_configure = platform_dma_configure,
.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
}; /*
* platform_driver 分配,设置,注册file_operations ,读取platform_device 硬件资源操作硬件
*/
struct platform_driver
{
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
bool prevent_deferred_probe;
}; /*
* platform_device 指定硬件资源
*/
struct platform_device
{
const char *name;
int id;
bool id_auto;
struct device dev;
u32 num_resources;
struct resource *resource; const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;
char *driver_override; /* Driver name to force a match */ /* MFD cell pointer */
struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell; /* arch specific additions */
struct pdev_archdata archdata;
}; .编写一个drv.c和.dts
通过比较 platform_device->device->device_node->property->name 属性名字
platform_driver->device_driver->of_device_id->compatible 是否相同来决定是否支持该设备 .编写一个drv.c和dev.c
通过比较 platform_driver->platform_device_id->name
platform_device->name 是否相同来决定是否支持该设备
匹配过程按优先顺序罗列如下:
a. 比较 platform_dev.driver_override 和 platform_driver.drv->name
b. 比较 platform_dev.dev.of_node的compatible属性 和 platform_driver.drv->of_match_table
c. 比较 platform_dev.name 和 platform_driver.id_table
d. 比较 platform_dev.name 和 platform_driver.drv->name
jz2440.dtb 的 led 节点:
#define S3C2410_GPF(_nr) ((5<<16) + (_nr))
led {
compatible = "jz2440_led";
reg = <S3C2410_GPF() >;
};
2.如何编译使用dts文件:
1. 将jz2440.dtbs文件传入 linux-4.19-rc3/arch/arm/boot/dts
2. 进入内核根目录,执行 make dtbs
3. 拷贝编译好的dtb文件到网络文件系统 cp linux-4.19-rc3/arch/arm/boot/dts/jz2440.dtb /work/nfs_root/
4. 重启开发板,进入u-boot 命令模式,从网络文件系统下载jz2440.dtb文件 nfs 32000000 192.168.1.123:/work/nfs_root/jz2440.dtb
5. 擦除 device_tree 分区,写入文件 nand erase device_tree & nand write.jiffs2 32000000 device_tree
6. 启动内核 boot
7. 启动后,进入 /sys/devices/platform/50005.led/of_node(open for node) ==> compatible , name , reg
cat compatible ==> jz2440_led/sys/fireware/devicetree/base/led
cat name ==> led/sys/fireware/devicetree/base/led
hexdump -C reg ==> 00 05 00 05 00 00 00 01 (大字节序) <==> S3C2410_GPF(5) 1
3.设备树规范
各个驱动的规范文档目录:linux-4.19\Documentation\devicetree\binding\
各个单板的设备树文件: linux-4.19\arch\arm\boot\dts
设备树官方语法: https://www.devicetree.org/specifications/
内核设备树语法: linux-4.19-rc3\Documentation\devicetree\usage-model.txt
3.1 .dts 格式
() 语法: Devicetree node格式:
[label:] node-name[@unit-address] {
[properties definitions]
[child nodes]
}; Property格式1:
[label:] property-name = value; Property格式2(没有值):
[label:] property-name; Property取值只有3种:
arrays of cells(1个或多个32位数据, 64位数据使用2个32位数据表示),
string(字符串),
bytestring(1个或多个字节) 示例:
a. Arrays of cells : cell就是一个32位的数据
interrupts = < 0xc>; b. 64bit数据使用2个cell来表示:
clock-frequency = <0x00000001 0x00000000>; c. A null-terminated string (有结束符的字符串):
compatible = "simple-bus"; d. A bytestring(字节序列) :
local-mac-address = [ ]; // 每个byte使用2个16进制数来表示
local-mac-address = []; // 每个byte使用2个16进制数来表示 e. 可以是各种值的组合, 用逗号隔开:
compatible = "ns16550", "ns8250";
example = <0xf00f0000 >, "a strange property format"; () DTS文件布局(layout): /dts-v1/; // 表示dts的版本
[memory reservations] // 表示保留的内存区域,格式为: /memreserve/ <address> <length>;
/ { // 根节点,设备树的起点
[property definitions] // 属性,用来描述硬件信息
[child nodes]
};
() 特殊的、默认的属性:
a. 根节点:
#address-cells // 在它的子节点的reg属性中, 使用多少个u32整数来描述地址(address)
#size-cells // 在它的子节点的reg属性中, 使用多少个u32整数来描述大小(size)
compatible // 定义一系列的字符串, 用来指定内核中哪个machine_desc可以支持本设备
// 即这个板子兼容哪些平台
// uImage : smdk2410 smdk2440 mini2440 ==> machine_desc model // 咱这个板子是什么
// 比如有2款板子配置基本一致, 它们的compatible是一样的
// 那么就通过model来分辨这2款板子 b. /memory
device_type = "memory";
reg // 用来指定内存的地址、大小 c. /chosen
bootargs // 内核command line参数, 跟u-boot中设置的bootargs作用一样 d. /cpus
/cpus节点下有1个或多个cpu子节点, cpu子节点中用reg属性用来标明自己是哪一个cpu
所以 /cpus 中有以下2个属性:
#address-cells // 在它的子节点的reg属性中, 使用多少个u32整数来描述地址(address) #size-cells // 在它的子节点的reg属性中, 使用多少个u32整数来描述大小(size) // 必须设置为0 e. /cpus/cpu*
device_type = "cpu";
reg // 表明自己是哪一个cpu () 引用其他节点:
a. phandle : // 节点中的phandle属性, 它的取值必须是唯一的(不要跟其他的phandle值一样) pic@ {
phandle = <>;
interrupt-controller;
}; another-device-node {
interrupt-parent = <>; // 使用phandle值为1来引用上述节点
}; b. label: PIC: pic@ {
interrupt-controller;
}; another-device-node {
interrupt-parent = <&PIC>; // 使用label来引用上述节点,
// 使用lable时实际上也是使用phandle来引用,
// 在编译dts文件为dtb文件时, 编译器dtc会在dtb中插入phandle属性
}; ()包含其他.dts文件:
#include"jz2440.dtsi"
&LED {
pin = <S3C2440_GPF()>;
}; () 语法:
3.2 .dtb 格式
使用dtc编译器把 .dts ==> .dtb
官方文档: https://www.devicetree.org/specifications/
内核文档:Documentation/devicetree/booting-without-of.txDTB文件布局:
base ---->
------------------------------
| ftd_header | ->头部用来表名各个部分偏移地址,整个文件的偏移大小
------------------------------
| (alignment gap) (*) | -> 填充00对齐
------------------------------
| memory | ->保留的内存起始地址和大小
------------------------------
| (alignment gap) |
------------------------------
| |
| block | ->存放节点的信息
| |
------------------------------
| (alignment gap) |
------------------------------
| |
| strings | ->dts文件中的属性的名字
| |
------------------------------
(base + totalsize)--> struct fdt_header
{
uint32_t magic; -> d00d feed
uint32_t totalsize; -> 整个文件的大小
uint32_t off_dt_struct; -> blockd 的偏移地址
uint32_t off_dt_strings; -> string 的偏移地址
uint32_t off_mem_rsvmap; -> memory 的偏移地址
uint32_t version; ->
uint32_t last_comp_version; ->
uint32_t boot_cpuid_phys; ->
uint32_t size_dt_strings; ->
uint32_t size_dt_struct; ->
}; memory reservation block ->
struct fdt_reserve_entry
{
uint64_t address; // 保留内存的起始地址
uint64_t size; // 保存内存的大小
}; strings block ->
struct // 代表属性 (属性的值放在这个结构体后面)
{
uint32_t len; // 属性值长度
uint32_t nameoff; // 属性名字在string的偏移地址
} <jz2440.dts>
#define S3C2410_GPF(_nr) ((5<<16) + (_nr)) /dts-v1/; / { -->0x00000001 表示根节点开始
led -->
{ -->0x00000001 表示节点开始 + 节点名字
compatible = "jz2440_led"; -->0x00000003 表示属性开始 +
struct{uint32_t len;属性值有多长 uint32_t nameoff;名字在string block的偏移值 }
+属性值(len个字节)
reg = <S3C2410_GPF() >; -->0x00000003 表示属性开始
}; -->0x00000002 表示节点结束
}; -->0x00000002 表示根节点结束
-->0x00000009 表示整个struct block 结束 fdt_begin_node 0x00000001
fdt_end_node 0x00000002
fdt_prop 0x00000003
fdt_nop 0x00000004
fdt_end 0x00000009
大端:低字节放在高地址
小端:低字节放在低地址
字符串,数组,结构体 没有大小端,都是先放低地址
.dtb为大端字节序
4. 内核对设备树的处理
4.1 u-boot ,head.S对设备树的处理(内核版本 linux-4.19):
uboot如何将设备树文件传递给内核
bootloader启动内核时,会设置r0,r1,r2三个寄存器,
thekernel=(void (*)(int,int ,unsigned int))0x30008000;
thekernel(,,0x30000100); //r0,r1,r2 r0一般设置为0;
r1一般设置为machine id (单板ID,在使用设备树时该参数没有被使用); // u-boot设置machine_id 和kernel设置machine_desc{init , num} ,
r2一般设置ATAGS或DTB的开始地址 // 当machine_id 和machine_desc->num 匹配则调用相应的machine_desc->init函数 bootloader给内核传递的参数时有2种方法:
ATAGS 或 DTB a. __lookup_processor_type : 使用汇编指令读取CPU ID, 根据该ID找到对应的proc_info_list结构体(里面含有这类CPU的初始化函数、信息)
b. __vet_atags : 判断是否存在可用的ATAGS或DTB
c. __create_page_tables : 创建页表, 即创建虚拟地址和物理地址的映射关系
d. __enable_mmu : 使能MMU, 以后就要使用虚拟地址了
e. __mmap_switched : 上述函数里将会调用__mmap_switched
f. 把bootloader传入的r2参数, 保存到变量__atags_pointer中
g. 调用C函数start_kernel head.S/head-common.S :
把bootloader传来的r0值, 赋给了C变量: processor_id
把bootloader传来的r1值, 赋给了C变量: __machine_arch_type
把bootloader传来的r2值, 赋给了C变量: __atags_pointer // dtb首地址
4.2 main.c 对设备树的处理:
寻找与jz2440.dts的根节点compatible适应度最高的machine_desc->dt_compat(model,compatible节点)
a. 设备树根节点的compatible属性列出了一系列的字符串,
表示它兼容的单板名,
从"最兼容"到次之 b. 内核中有多个machine_desc,
其中有dt_compat成员, 它指向一个字符串数组, 里面表示该machine_desc支持哪些单板 c. 使用compatile属性的值,
跟每一个machine_desc.dt_compat 比较,
成绩为"吻合的compatile属性值的位置",
成绩越低越匹配, 对应的machine_desc即被选中 d. 多个machine_desc 如何编译,存放,读取 static const char *const smdk2440_dt_compat[] __initconst= //一个 machine_desc->dt_compat[]有多个字符串
{ //表示一个machine_desc可以支持的单板
"samsung,smdk2440",
"samsung,smdk2410",
NULL
} MACHINE_START(S3C2440, "SMDK2440") // 使用MACHINE_START 与 MACHINE_END 定义一个machine desc 数据段
.atag_offset = 0x100,
.dt_compat = smdk2440_dt_compat, // 每个machine_desc->dt_compat 表明支持那些单板
.init_irq = s3c2440_init_irq,
.map_io = smdk2440_map_io,
.init_machine = smdk2440_machine_init,
.init_time = smdk2440_init_time,
MACHINE_END #define MACHINE_START(_type,_name) \ //通过GNU的attribute机制的指定段属性__section__,
static const struct machine_desc __mach_desc_##_type \ //将所有用MACHINE_START定义的machine_desc数据段存放在
__used \ //链接脚本变量__arch_info_begin ---- __arch_info_end中。
__attribute__((__section__(".arch.info.init"))) = { \ //
.nr = MACH_TYPE_##_type, \ //
.name = _name, // .init.arch.info : // \arch\arm\kernel\vmlinux.lds.S 内核链接脚本
{
__arch_info_begin = .;
*(.arch.info.init)
__arch_info_end = .;
} arch_get_next_mach()
machine_desc *mdesc = __arch_info_begin //通过直接把__arch_info_begin段地址当成指针赋给mdesc来读取machine_desc
*match = m->dt_compat // 返回 machine_desc->dt_compat 再与 .dts->compatible属性比较 e.dts想要什么样的machine_desc
/{
compatible = "samsung,smdk2440","samsung,smdk2410","samsung,smdk24xx"; // 优先第一个,依次下降
} 函数调用过程:
start_kernel // init/main.c
setup_arch(&command_line); // arch/arm/kernel/setup.c
mdesc = setup_machine_fdt(__atags_pointer); // arch/arm/kernel/devtree.c
early_init_dt_verify(phys_to_virt(dt_phys) // 判断是否是效的dtb(通过头部是否含有amgic), drivers/of/ftd.c
initial_boot_params = params;
mdesc = of_flat_dt_match_machine(mdesc_best, arch_get_next_mach); // 找到最匹配的machine_desc, drivers/of/ftd.c
while ((data = get_next_compat(&compat))) {
score = of_flat_dt_match(dt_root, compat);
if (score > && score < best_score) {
best_data = data;
best_score = score;
}
} machine_desc = mdesc;
4.3 内核对于设备树配置信息的处理
fdt.c如何将内核树信息提取出来(chosen,#address-cells,#size-cells ,memory节点)
函数调用过程:
start_kernel // init/main.c
setup_arch(&command_line); // arch/arm/kernel/setup.c
mdesc = setup_machine_fdt(__atags_pointer); // arch/arm/kernel/devtree.c
early_init_dt_scan_nodes(); // drivers/of/ftd.c
/* Retrieve various information from the /chosen node */
of_scan_flat_dt(early_init_dt_scan_chosen, boot_command_line); /* Initialize {size,address}-cells info */
of_scan_flat_dt(early_init_dt_scan_root, NULL); /* Setup memory, calling early_init_dt_add_memory_arch */
of_scan_flat_dt(early_init_dt_scan_memory, NULL); a. /chosen节点中bootargs属性的值, 存入全局变量: boot_command_line
b. 确定根节点的这2个属性的值: #address-cells, #size-cells 存入全局变量: dt_root_addr_cells, dt_root_size_cells
c. 解析/memory中的reg属性, 提取出"base, size", 最终调用memblock_add(base, size);添加一个内存块
4.4 dtb转换为device_node(unflatten)
unflatten_device_tree()如何将节点转化为树
函数调用过程:
start_kernel // init/main.c
setup_arch(&command_line); // arch/arm/kernel/setup.c
arm_memblock_init(mdesc);
early_init_fdt_reserve_self(); // 把DTB所占区域保留下来, 即调用: memblock_reserve
early_init_dt_reserve_memory_arch(__pa(initial_boot_params), fdt_totalsize(initial_boot_params),);
early_init_fdt_scan_reserved_mem(); // 根据dtb中的memreserve信息, 调用memblock_reserve
unflatten_device_tree(); // 把设备树转化为一棵树
__unflatten_device_tree(initial_boot_params, NULL,
&of_root,early_init_dt_alloc_memory_arch, false); // drivers/of/fdt.c
/* First pass, scan for size */
size = unflatten_dt_nodes(blob, NULL, dad, NULL);
/* Allocate memory for the expanded device tree */
mem = dt_alloc(size + , __alignof__(struct device_node));
/* Second pass, do actual unflattening */
unflatten_dt_nodes(blob, mem, dad, mynodes);
offset = fdt_next_node(blob, offset, &depth)) { // 将节点一个一个读取出来
populate_node() // 将读取出来的节点构造为设备树
np = unflatten_dt_alloc(mem, sizeof(struct device_node) +
allocl, __alignof__(struct device_node)); // 分配一个device_node空间 np->full_name = fn = ((char *)np) + sizeof(*np); // 把名字写到node最后 populate_properties // 设置device_node的属性
pp = unflatten_dt_alloc(mem, sizeof(struct property),__alignof__(struct property));
pp->name = (char *)pname;
pp->length = sz;
pp->value = (__be32 *)val; a. 在DTB文件中,
每一个节点都以TAG(FDT_BEGIN_NODE, 0x00000001)开始, 节点内部可以嵌套其他节点,
每一个属性都以TAG(FDT_PROP, 0x00000003)开始 b. 每一个节点都转换为一个device_node结构体:
struct device_node
{
const char *name; // 来自节点中的name属性, 如果没有该属性, 则设为"NULL"
const char *type; // 来自节点中的device_type属性, 如果没有该属性, 则设为"NULL"
phandle phandle;
const char *full_name; // 节点的名字, node-name[@unit-address]
struct fwnode_handle fwnode; struct property *properties; // 节点的属性
struct property *deadprops; /* removed properties */
struct device_node *parent; // 节点的父亲
struct device_node *child; // 节点的孩子(子节点)
struct device_node *sibling; // 节点的兄弟(同级节点)
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_KOBJ)
struct kobject kobj;
#endif
unsigned long _flags;
void *data;
#if defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
const char *path_component_name;
unsigned int unique_id;
struct of_irq_controller *irq_trans;
#endif
}; c. device_node结构体中有properties, 用来表示该节点的属性
每一个属性对应一个property结构体:
struct property
{
char *name; // 属性名字, 指向dtb文件中的字符串
int length; // 属性值的长度
void *value; // 属性值, 指向dtb文件中value所在位置, 数据仍以big endian存储
struct property *next;
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC) || defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
unsigned long _flags;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_PROMTREE)
unsigned int unique_id;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_KOBJ)
struct bin_attribute attr;
#endif
}; d. 这些device_node构成一棵树, 根节点为: of_root
4.5 设备树与device_node ,property关系图
jz2440.dts源码
#define S3C2410_GPF(_nr) ((5<<16) + (_nr))
/dts-v1/;
/ {
model = "SMDK24440";
compatible = "samsung,smdk2440";
#address-cells = <>;
#size-cells = <>;
memory@
{
device_type = "memory";
reg = <0x30000000 0x4000000>;
};
chosen
{
bootargs = "noinitrd root=/dev/mtdblock4 rw init=/linuxrc console=ttySAC0,115200";
};
led
{
compatible = "jz2440_led";
reg = <S3C2410_GPF() >;
};
};
关系图:
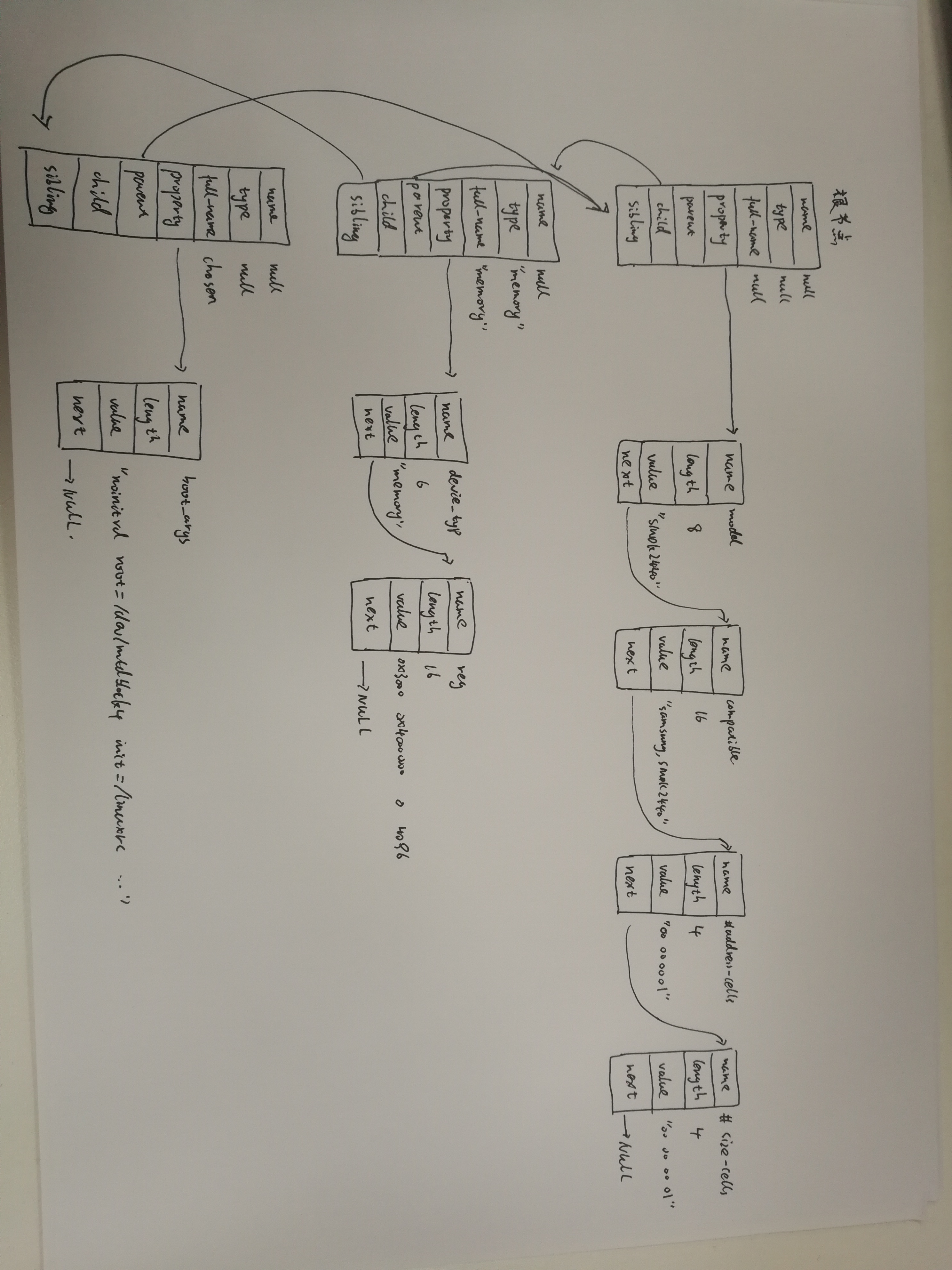
4.6 device_node转换为platform_device
platform_device->device->device_node
a. 哪些device_node可以转换为platform_device?
根节点下含有compatile属性的子节点
如果一个结点的compatile属性含有这些特殊的值("simple-bus","simple-mfd","isa","arm,amba-bus")之一, 那么它的子结点(需含compatile属性)也可以转换为platform_device
i2c, spi等总线节点下的子节点, 应该交给对应的总线驱动程序来处理, 它们不应该被转换为platform_device b. 怎么转换?
platform_device中含有resource数组, 它来自device_node的reg, interrupts属性,从device_node转换得到;
platform_device.dev.of_node指向device_node, 可以通过它获得其他属性 struct platform_device {
const char *name;
int id;
bool id_auto;
struct device dev; // device->of_node(device_node) 保存device_node其他属性
u32 num_resources; // 资源数组有多少项
struct resource *resource; // 资源数组(资源种类IO/MEM/INT)
}; b. 示例:
比如以下的节点,
/mytest会被转换为platform_device,
因为它兼容"simple-bus", 它的子节点/mytest/mytest@ 也会被转换为platform_device /i2c节点一般表示i2c控制器, 它会被转换为platform_device, 在内核中有对应的platform_driver;
/i2c/at24c02节点不会被转换为platform_device, 它被如何处理完全由父节点的platform_driver决定, 一般是被创建为一个i2c_client。 类似的也有/spi节点, 它一般也是用来表示SPI控制器, 它会被转换为platform_device, 在内核中有对应的platform_driver;
/spi/flash@0节点不会被转换为platform_device, 它被如何处理完全由父节点的platform_driver决定, 一般是被创建为一个spi_device。 / {
mytest {
compatile = "mytest", "simple-bus";
mytest@ {
compatile = "mytest_0";
};
}; i2c {
compatile = "samsung,i2c";
at24c02 {
compatile = "at24c02";
};
}; spi {
compatile = "samsung,spi";
flash@ {
compatible = "winbond,w25q32dw";
spi-max-frequency = <>;
reg = <>;
};
};
}; 函数调用过程:
a. of_platform_default_populate_init (drivers/of/platform.c) 被调用到过程:
start_kernel // init/main.c
rest_init();
pid = kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);
kernel_init
kernel_init_freeable();
do_basic_setup();
do_initcalls();
for (level = ; level < ARRAY_SIZE(initcall_levels) - ; level++)
do_initcall_level(level); // 比如 do_initcall_level(3)
for (fn = initcall_levels[]; fn < initcall_levels[+]; fn++)
do_one_initcall(initcall_from_entry(fn)); // 就是调用"arch_initcall_sync(fn)"中定义的fn函数
常见GNU的attribite指定section机制
arch_initcall_sync(of_platform_default_populate_init);
#define arch_initcall_sync(fn) __define_initcall(fn, 3s)
#define __define_initcall(fn, id) ___define_initcall(fn, id, .initcall##id)
#define ___define_initcall(fn, id, __sec) static initcall_t __initcall_##fn##id __used __attribute__((__section__(#__sec ".init"))) = fn; b. of_platform_default_populate_init (drivers/of/platform.c) 生成platform_device的过程:
of_platform_default_populate_init
of_platform_default_populate(NULL, NULL, NULL);
of_platform_populate(NULL, of_default_bus_match_table, NULL, NULL) // 如果节点中含有of_default_bus_match_table的值之一,就为子节点创建platform_device
for_each_child_of_node(root, child) { // 便利整个device_node树,为特定的节点生成platform_device
rc = of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, parent, true);// 创建总线
dev = of_device_alloc(np, bus_id, parent); // 根据device_node节点的属性设置platform_device的resource
of_address_to_resource(np, i, res); // address转资源
of_irq_to_resource_table(np, res, num_irq) // 中断转资源
if (rc) {
of_node_put(child);
break;
}
} c. of_platform_bus_create(bus, matches, ...)的调用过程(处理bus节点生成platform_devie, 并决定是否处理它的子节点):
dev = of_platform_device_create_pdata(bus, bus_id, platform_data, parent); // 生成bus节点的platform_device结构体
if (!dev || !of_match_node(matches, bus)) // 如果bus节点的compatile属性不吻合matches成表, 就不处理它的子节点
return ; for_each_child_of_node(bus, child) { // 取出每一个子节点
pr_debug(" create child: %pOF\n", child);
rc = of_platform_bus_create(child, matches, lookup, &dev->dev, strict); // 处理它的子节点, of_platform_bus_create是一个递归调用
if (rc) {
of_node_put(child);
break;
}
} d. I2C总线节点的处理过程:
/i2c节点一般表示i2c控制器, 它会被转换为platform_device, 在内核中有对应的platform_driver;
platform_driver的probe函数中会调用i2c_add_numbered_adapter: i2c_add_numbered_adapter // drivers/i2c/i2c-core-base.c
__i2c_add_numbered_adapter
i2c_register_adapter
of_i2c_register_devices(adap); // drivers/i2c/i2c-core-of.c
for_each_available_child_of_node(bus, node) {
client = of_i2c_register_device(adap, node);
client = i2c_new_device(adap, &info); // 设备树中的i2c子节点被转换为i2c_client
} e. SPI总线节点的处理过程:
/spi节点一般表示spi控制器, 它会被转换为platform_device, 在内核中有对应的platform_driver;
platform_driver的probe函数中会调用spi_register_master, 即spi_register_controller: spi_register_controller // drivers/spi/spi.c
of_register_spi_devices // drivers/spi/spi.c
for_each_available_child_of_node(ctlr->dev.of_node, nc) {
spi = of_register_spi_device(ctlr, nc); // 设备树中的spi子节点被转换为spi_device
spi = spi_alloc_device(ctlr);
rc = of_spi_parse_dt(ctlr, spi, nc);
rc = spi_add_device(spi);
}
5.1 内核中设备树的操作函数
dtb -> device_node -> platform_device
a. 处理DTB
of_fdt.h // dtb文件的相关操作函数, 我们一般用不到, 因为dtb文件在内核中已经被转换为device_node树(它更易于使用) b. 处理device_node
of.h // 提供设备树的一般处理函数, 比如 of_property_read_u32(读取某个属性的u32值), of_get_child_count(获取某个device_node的子节点数)
of_address.h // 地址相关的函数, 比如 of_get_address(获得reg属性中的addr, size值)
of_match_device(从matches数组中取出与当前设备最匹配的一项)
of_dma.h // 设备树中DMA相关属性的函数
of_gpio.h // GPIO相关的函数
of_graph.h // GPU相关驱动中用到的函数, 从设备树中获得GPU信息
of_iommu.h // 很少用到
of_irq.h // 中断相关的函数
of_mdio.h // MDIO (Ethernet PHY) API
of_net.h // OF helpers for network devices.
of_pci.h // PCI相关函数
of_pdt.h // 很少用到
of_reserved_mem.h // reserved_mem的相关函数 c. 处理 platform_device
of_platform.h // 把device_node转换为platform_device时用到的函数,
// 比如of_device_alloc(根据device_node分配设置platform_device),
// of_find_device_by_node (根据device_node查找到platform_device),
// of_platform_bus_probe (处理device_node及它的子节点)
of_device.h // 设备相关的函数, 比如 of_match_device
5.2 在根文件系统中查看设备树(有助于调试)
a. /sys/firmware/fdt // 原始dtb文件 hexdump -C /sys/firmware/fdt b. /sys/firmware/devicetree // 以目录结构程现的dtb文件, 根节点对应base目录, 每一个节点对应一个目录, 每一个属性对应一个文件 c. /sys/devices/platform // 系统中所有的platform_device, 有来自设备树的, 也有来有.c文件中注册的
对于来自设备树的platform_device,
可以进入 /sys/devices/platform/<设备名>/of_node 查看它的设备树属性 d. /proc/device-tree 是链接文件, 指向 /sys/firmware/devicetree/base
6 u-boot 可以对设备树做些什么
6.1 uboot如何传递设备树给内核
a. u-boot中内核启动命令:
bootm <uImage_addr> // 无设备树,bootm 0x30007FC0
bootm <uImage_addr> <initrd_addr> <dtb_addr> // 有设备树 比如 :
nand read.jffs2 0x30007FC0 kernel; // 读内核uImage到内存0x30007FC0
nand read.jffs2 device_tree; // 读dtb到内存32000000
bootm 0x30007FC0 - 0x32000000 // 启动, 没有initrd时对应参数写为"-" b. bootm命令怎么把dtb_addr写入r2寄存器传给内核?
ARM程序调用规则(ATPCS) c_function(p0, p1, p2) // p0 => r0, p1 => r1, p2 => r2 定义函数指针 the_kernel, 指向内核的启动地址,
然后执行: the_kernel(, machine_id, 0x32000000); c. dtb_addr 可以随便选吗?
c. 不要破坏u-boot本身
c. 不要挡内核的路: 内核本身的空间不能占用, 内核要用到的内存区域也不能占用
内核启动时一般会在它所处位置的下边放置页表, 这块空间(一般是0x4000即16K字节)不能被占用 JZ2440内存使用情况:
------------------------------
0x33f80000 ->| u-boot |
------------------------------
| u-boot所使用的内存(栈等)|
------------------------------
| |
| |
| 空闲区域 |
| |
| |
| |
| |
------------------------------
0x30008000 ->| zImage |
------------------------------ uImage = 64字节的头部+zImage
0x30007FC0 ->| uImage头部 |
------------------------------
0x30004000 ->| 内核创建的页表 | head.S
------------------------------
| |
| |
-----> ------------------------------
|
|
--- (内存基址 0x30000000) 命令示例:
a. 可以启动:
nand read.jffs2 device_tree
nand read.jffs2 0x30007FC0 kernel
bootm 0x30007FC0 - b. 不可以启动: 内核启动时会使用0x30004000的内存来存放页表,dtb会被破坏
nand read.jffs2 device_tree
nand read.jffs2 0x30007FC0 kernel
bootm 0x30007FC0 -
6.2 .dtb文件的修改原理
例子1. 修改属性的值,
假设 老值: len
新值: newlen (假设newlen > len) a. 把原属性val所占空间从len字节扩展为newlen字节:
把老值之后的所有内容向后移动(newlen - len)字节 b. 把新值写入val所占的newlen字节空间 c. 修改dtb头部信息中structure block的长度: size_dt_struct d. 修改dtb头部信息中string block的偏移值: off_dt_strings e. 修改dtb头部信息中的总长度: totalsize 例子2. 添加一个全新的属性
a. 如果在string block中没有这个属性的名字,
就在string block尾部添加一个新字符串: 属性的名
并且修改dtb头部信息中string block的长度: size_dt_strings
修改dtb头部信息中的总长度: totalsize b. 找到属性所在节点, 在节点尾部扩展一块空间, 内容及长度为:
TAG // 4字节, 对应0x00000003
len // 4字节, 表示属性的val的长度
nameoff // 4字节, 表示属性名的offset
val // len字节, 用来存放val c. 修改dtb头部信息中structure block的长度: size_dt_struct d. 修改dtb头部信息中string block的偏移值: off_dt_strings e. 修改dtb头部信息中的总长度: totalsize 可以从u-boot官网源码下载一个比较新的u-boot, 查看它的cmd/fdt.c
ftp://ftp.denx.de/pub/u-boot/
fdt命令集合:
"fdt move <fdt> <newaddr> <length> - Copy the fdt to <addr> and make it active\n"
"fdt resize [<extrasize>] - Resize fdt to size + padding to 4k addr + some optional <extrasize> if needed\n"
"fdt print <path> [<prop>] - Recursive print starting at <path>\n"
"fdt list <path> [<prop>] - Print one level starting at <path>\n"
"fdt get value <var> <path> <prop> - Get <property> and store in <var>\n"
"fdt get name <var> <path> <index> - Get name of node <index> and store in <var>\n"
"fdt get addr <var> <path> <prop> - Get start address of <property> and store in <var>\n"
"fdt get size <var> <path> [<prop>] - Get size of [<property>] or num nodes and store in <var>\n"
"fdt set <path> <prop> [<val>] - Set <property> [to <val>]\n"
"fdt mknode <path> <node> - Create a new node after <path>\n"
"fdt rm <path> [<prop>] - Delete the node or <property>\n"
"fdt header - Display header info\n"
"fdt bootcpu <id> - Set boot cpuid\n"
"fdt memory <addr> <size> - Add/Update memory node\n"
"fdt rsvmem print - Show current mem reserves\n"
"fdt rsvmem add <addr> <size> - Add a mem reserve\n"
"fdt rsvmem delete <index> - Delete a mem reserves\n"
"fdt chosen [<start> <end>] - Add/update the /chosen branch in the tree\n"
fdt命令调用过程:
fdt set <path> <prop> [<val>]
a. 根据path找到节点
b. 根据val确定新值长度newlen, 并把val转换为字节流
c. fdt_setprop
c. fdt_setprop_placeholder // 为新值在DTB中腾出位置
fdt_get_property_w // 得到老值的长度 oldlen
fdt_splice_struct_ // 腾空间
fdt_splice_ // 使用memmove移动DTB数据, 移动(newlen-oldlen)
fdt_set_size_dt_struct // 修改DTB头部, size_dt_struct
fdt_set_off_dt_strings // 修改DTB头部, off_dt_strings c. memcpy(prop_data, val, len); // 在DTB中存入新值
6.3 fdt命令的移植
我们仍然使用u-boot 1.1.,需要在里面添加fdc命令命令, 这个命令可以用来查看、修改dtb
从u-boot官网下载最新的源码, 把里面的 cmd/fdt.c移植过来. u-boot官网源码:
ftp://ftp.denx.de/pub/u-boot/ 最终的补丁存放在如下目录: doc_and_sources_for_device_tree\source_and_images\u-boot\u-boot-1.1.6_device_tree_for_jz2440_add_fdt_20181022.patch
补丁使用方法:
export PATH=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/work/system/gcc-linaro-4.9.-2017.01-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabi/bin
tar xjf u-boot-1.1..tar.bz2 // 解压
cd u-boot-1.1.
patch -p1 < ../u-boot-1.1.6_device_tree_for_jz2440_add_fdt_20181022.patch // 打补丁
make 100ask24x0_config // 配置
make // 编译, 可以得到u-boot.bin a. 移植fdt命令
a. 先把代码移过去, 修改Makefile来编译
u-boot-2018.11-rc2\lib\libfdt 主要用这个目录,
它里面的大部分文件是直接包含scripts\dtc\libfdt中的同名文件
只有2个文件是自己的版本
u-boot-2018.11-rc2\scripts\dtc\libfdt 把新u-boot中cmd/fdt.c重命名为cmd_fdt.c , 和 lib/libfdt // 一起复制到老u-boot的common/fdt目录
修改 老u-boot/Makefile, 添加一行: LIBS += common/fdt/libfdt.a
修改 老u-boot/common/fdt/Makefile, 仿照 drivers/nand/Makefile来修改 a. 根据编译的错误信息修改源码 移植时常见问题:
i. No such file or directory:
要注意,
#include "xxx.h" // 是在当前目录下查找xxx.h
#include <xxx.h> // 是在指定目录下查找xxx.h, 哪些指定目录呢?
// 编译文件时可以用"-I"选项指定头文件目录,
// 比如: arm-linux-gcc -I <dir> -c -o ....
// 对于u-boot来说, 一般就是源码的 include目录 解决方法:
确定头文件在哪, 把它移到include目录或是源码的当前目录 ii. xxx undeclared :
宏, 变量, 函数未声明/未定义 对于宏, 去定义它;
对于变量, 去定义它或是声明为外部变量;
对于函数, 去实现它或是声明为外部函数; iii. 上述2个错误是编译时出现的,
当一切都没问题时, 最后就是链接程序, 这时常出现: undefined reference to `xxx'
这表示代码里用到了xxx函数, 但是这个函数没有实现 解决方法: 去实现它, 或是找到它所在文件, 把这文件加入工程 b. fdt命令使用示例
nand read.jffs2 device_tree // 从flash读出dtb文件到内存(0x32000000)
fdt addr // 告诉fdt, dtb文件在哪
fdt print /led pin // 打印/led节点的pin属性
fdt get value XXX /led pin // 读取/led节点的pin属性, 并且赋给环境变量XXX
print XXX // 打印环境变量XXX的值
fdt set /led pin <0x00050005> // 设置/led节点的pin属性
fdt print /led pin // 打印/led节点的pin属性
nand erase device_tree // 擦除flash分区
nand write.jffs2 device_tree // 把修改后的dtb文件写入flash分区
7.1 Linux对中断处理的框架及代码流程简述
a. 异常向量入口: arch\arm\kernel\entry-armv.S
.section .vectors, "ax", %progbits
.L__vectors_start:
W(b) vector_rst
W(b) vector_und
W(ldr) pc, .L__vectors_start + 0x1000
W(b) vector_pabt
W(b) vector_dabt
W(b) vector_addrexcptn
W(b) vector_irq
W(b) vector_fiq
b. 中断向量: vector_irq
/*
* Interrupt dispatcher
*/
vector_stub irq, IRQ_MODE, // 相当于 vector_irq: ...,
// 它会根据SPSR寄存器的值,
// 判断被中断时CPU是处于USR状态还是SVC状态,
// 然后调用下面的__irq_usr或__irq_svc
.long __irq_usr @ (USR_26 / USR_32)
.long __irq_invalid @ (FIQ_26 / FIQ_32)
.long __irq_invalid @ (IRQ_26 / IRQ_32)
.long __irq_svc @ (SVC_26 / SVC_32)
.long __irq_invalid @
.long __irq_invalid @
.long __irq_invalid @
.long __irq_invalid @
.long __irq_invalid @
.long __irq_invalid @
.long __irq_invalid @ a
.long __irq_invalid @ b
.long __irq_invalid @ c
.long __irq_invalid @ d
.long __irq_invalid @ e
.long __irq_invalid @ f
c. __irq_usr/__irq_svc
__irq_usr:
usr_entry // 保存现场
kuser_cmpxchg_check
irq_handler // 调用 irq_handler
get_thread_info tsk
mov why, #
b ret_to_user_from_irq // 恢复现场
d. irq_handler: 将会调用C函数 handle_arch_irq
.macro irq_handler
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_MULTI_HANDLER
ldr r1, =handle_arch_irq
mov r0, sp
badr lr, 9997f
ldr pc, [r1]
#else
arch_irq_handler_default
#endif
:
.endm
e. handle.c
set_handle_irq( pointer_to_fun() )
handle_arch_irq = pointer_to_fun()
f. handle_arch_irq的处理过程: (读取中断控制器得到硬件中断号,然后再找到中断控制器对应的域,在域里面从硬件中断号得到虚拟中断号,找到irq_desc[virq])
读取寄存器获得中断信息: hwirq
把hwirq转换为virq // hwirq为硬件中断号,virq为虚拟中断号 (两者间有偏移值)
// #define S3C2410_CPUIRQ_OFFSET (16) #define S3C2410_IRQ(x) ((x) + S3C2410_CPUIRQ_OFFSET)
调用 1.irq_desc[virq].handle_irq //处理中断
2.irq_desc[virq].irq_data.irq_chip.fun() // 清中断
对于S3C2440,irq_s3c24xx.c是入口源文件, s3c24xx_handle_irq 是用于处理中断的C语言入口函数
set_handle_irq(s3c24xx_handle_irq);
注:
irq_desc[nr_irqs] // 包含有多个irq_desc结构体,每个对应不同的中断 struct irq_desc
{
struct irq_data irq_data; // 带有具体处理中断函数
irq_flow_handler_t handle_irq; // 1.调用action链表中的handler(也就是具体的处理函数) 2.再清中断(使用irq_data->chip的函数)
struct irqaction *action; // 指向irqaction链表
} struct irqaction
{
irq_handler_t handler; // 用户设置的中断的具体处理函数
void *dev_id; // request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, unsigned long flags,const char *name, void *dev)
struct irqaction *next;
}
struct irq_data
{
u32 mask;
unsigned int irq;
unsigned long hwirq;
struct irq_common_data *common;
struct irq_chip *chip; // 很多中断操作函数
struct irq_domain *domain;
void *chip_data;
};
struct irq_chip
{
void (*irq_enable)(struct irq_data *data); // 使能中断函数
void (*irq_disable)(struct irq_data *data); // 去使能中断函数
void (*irq_ack)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_mask)(struct irq_data *data); //屏蔽中断函数
void (*irq_unmask)(struct irq_data *data);
}
中断处理流程:
假设中断结构如下:
sub int controller ---> int controller ---> cpu
发生中断时,
cpu跳到"vector_irq", 保存现场, 调用C函数handle_arch_irq
handle_arch_irq:
a. 读 int controller, 得到hwirq
b. 根据hwirq得到virq
c. 调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq
如果该中断没有子中断, irq_desc[virq].handle_irq的操作:
a. 取出irq_desc[virq].action链表中的每一个handler, 执行它
b. 使用irq_desc[virq].irq_data.chip的函数清中断
如果该中断是由子中断产生, irq_desc[virq].handle_irq的操作:
a. 读 sub int controller, 得到hwirq'
b. 根据hwirq'得到virq
c. 调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq
调用过程:
s3c24xx_handle_intc
pnd = readl_relaxed(intc->reg_intpnd);
handle_domain_irq(intc->domain, intc_offset + offset, regs);
__handle_domain_irq(domain, hwirq, true, regs);
irq = irq_find_mapping(domain, hwirq);
generic_handle_irq(irq);
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(irq);
generic_handle_irq_desc(desc);
desc->handle_irq(desc);
7.2 中断号与domain域
不同的中断控制器对应不同的域,各个域的转换公式 不一样,防止不同硬件中断对应同一虚拟中断号(hwirq-->virq)
老中断体系,怎么使用中断
以前, 对于每一个硬件中断(hwirq)都预先确定它的中断号(virq),
这些中断号一般都写在一个头文件里, 比如arch\arm\mach-s3c24xx\include\mach\irqs.h
使用时,
a. 执行 request_irq(virq, my_handler) :
内核根据virq可以知道对应的硬件中断, 然后去设置、使能中断等
b. 发生硬件中断时,
内核读取硬件信息, 确定hwirq, 反算出virq,
然后调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq, 最终会用到my_handler 怎么根据hwirq计算出virq?
硬件上有多个intc(中断控制器),
对于同一个hwirq数值, 会对应不同的virq
所以在讲hwirq时,应该强调"是哪一个intc的hwirq",
在描述hwirq转换为virq时, 引入一个概念: irq_domain, 域, 在这个域里hwirq转换为某一个virq 当中断控制器越来越多、当中断越来越多,上述方法(virq和hwirq固定绑定)有缺陷:
a. 增加工作量, 你需要给每一个中断确定它的中断号, 写出对应的宏, 可能有成百上千个
b. 你要确保每一个硬件中断对应的中断号互不重复 有什么方法改进?
a. hwirq跟virq之间不再绑定
b. 要使用某个hwirq时,
先在irq_desc数组中找到一个空闲项, 它的位置就是virq
再在irq_desc[virq]中放置处理函数 新中断体系中, 怎么使用中断:
a.以前是request_irq发起,
现在是先在设备树文件中声明想使用哪一个中断(哪一个中断控制器下的哪一个中断) b. 内核解析设备树时,
会根据"中断控制器"确定irq_domain,
根据"哪一个中断"确定hwirq,
然后在irq_desc数组中找出一个空闲项, 它的位置就是virq
并且把virq和hwirq的关系保存在irq_domain中: irq_domain.linear_revmap[hwirq] = virq; c. 驱动程序 request_irq(virq, my_handler) d. 发生硬件中断时,
内核读取硬件信息, 确定hwirq, 确定中断控制器的域,确定 virq = irq_domain.linear_revmap[hwirq];
然后调用 irq_desc[virq].handle_irq, 最终会用到my_handler 假设要使用子中断控制器(subintc)的n号中断, 它发生时会导致父中断控制器(intc)的m号中断:
a. 设备树表明要使用<subintc n>
subintc表示要使用<intc m>
b. 解析设备树时,
会为<subintc n>找到空闲项 irq_desc[virq'], sub irq_domain.linear_revmap[n] = virq'; 会为<intc m> 找到空闲项 irq_desc[virq], irq_domain.linear_revmap[m] = virq;
并且设置它的handle_irq为某个分析函数demux_func c. 驱动程序 request_irq(virq', my_handler) d. 发生硬件中断时,
内核读取intc硬件信息, 确定hwirq = m, 确定 virq = irq_domain.linear_revmap[m];
然后调用 irq_desc[m].handle_irq, 即demux_func e. demux_func:
读取sub intc硬件信息, 确定hwirq = n, 确定 virq' = sub irq_domain.linear_revmap[n];
然后调用 irq_desc[n].handle_irq, 即my_handler 在设备树中设置中断控制器和硬件中断号,内核才会生成虚拟中断号。<intcxx,hwirqxx> --> virq
.xlate (解析设备树,得到hwirq,irq_type)
.map (hwirq <--> virq)建立联系
7.3 设备树如何描述中断
make uImage // 生成 arch/arm/boot/uImage
make dtbs // 生成 arch/arm/boot/dts/jz2440_irq.dtb 老内核:
/ # cat /proc/interrupts
CPU0
: s3c Edge samsung_time_irq
: s3c Edge ohci_hcd:usb1
: s3c Edge s3c2440-i2c.
: s3c-level Edge s3c2440-uart
: s3c-level Edge s3c2440-uart
: s3c-level Edge ts_pen
: s3c-level Edge adc
: s3c-level Edge s3c2410-wdt 新内核:
nfs 192.168.1.124:/work/nfs_root/uImage; nfs 192.168.1.124:/work/nfs_root/jz2440_irq.dtb; bootm - / # cat /proc/interrupts
CPU0
: s3c Edge s3c2410-rtc tick
: s3c Edge samsung_time_irq
: s3c Edge s3c2410-rtc alarm
: s3c-level Level .serial
: s3c-level Level .serial
: s3c-level Edge .watchdog a. 某个设备要使用中断, 需要在设备树中描述中断, 如何?
它要用哪一个中断? 这个中断连接到哪一个中断控制器去?
即: 使用哪一个中断控制器的哪一个中断? 至少有有2个属性:
interrupts // 表示要使用哪一个中断, 中断的触发类型等等
interrupt-parent // 这个中断要接到哪一个设备去? 即父中断控制器是谁 b. 上述的interrupts属性用多少个u32来表示?
这应该由它的父中断控制器来描述,
在父中断控制器中, 至少有2个属性:
interrupt-controller; // 表示自己是一个中断控制器
#interrupt-cells // 表示自己的子设备里应该有几个U32的数据来描述中断 c. 如何用设备树描述一个中断 --> (ethernet@)
.表明这个中断属于哪个中断控制器 --> interrupt_parent = intc
.表明这个中断属于中断控制器的哪个中断 --> interrupts = < intc_num [trigger_type] >
具体含义,用多少个U32描述,由中断控制器解释 d. 如何用设备树描述二级中断控制器 -->(gpg)(gpf)
.表明这是一个中断控制器 --> interrup_controller;
.表明控制器下一级中断要用多少U32描述下级中断 -->#interrupt-cells = <0x4>
.表明这个中断控制器的上一级中断控制器 --> phandle = <0x6> e. 根节点下如何描述中断 -->(/{)
interrupt-parent = <0x1> f. 如何用设备树描述一级中断控制器 -->(interrupt-controller@4a000000)
.表明控制器下一级中断要用多少U32描述下级中断 -->#interrupt-cells = <0x4>
.表明这是一个中断控制器 --> interrup_controller;
.表明他没有父节点 --> phandle = <0x1>
jz2440_irq_all.dts 源码
/dts-v1/;
/ {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440", "samsung,smdk2440";
interrupt-parent = <0x1>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
model = "JZ2440";
aliases {
pinctrl0 = "/pinctrl@56000000";
serial0 = "/serial@50000000";
serial1 = "/serial@50004000";
serial2 = "/serial@50008000";
i2c1 = "/i2c-gpio-1";
};
interrupt-controller@4a000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-irq";
reg = <0x4a000000 0x100>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <0x4>;
phandle = <0x1>;
};
pinctrl@ {
reg = <0x56000000 0x1000>;
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-pinctrl";
wakeup-interrupt-controller {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-wakeup-eint";
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x0 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x1 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x2 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x3 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x4 0x4 0x0 0x0 0x5 0x4>;
};
gpa {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
};
gpb {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
phandle = <0xd>;
};
gpc {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
};
gpd {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
};
gpe {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x7>;
};
gpf {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x6>;
};
gpg {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <0x2>;
};
gph {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
};
gpj {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
};
uart0-data {
samsung,pins = "gph-0", "gph-1";
samsung,pin-function = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x3>;
};
i2c0-bus {
samsung,pins = "gpe-14", "gpe-15";
samsung,pin-function = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x4>;
};
nand_pinctrl {
samsung,pins = "gpa-17", "gpa-18", "gpa-19", "gpa-20", "gpa-22";
samsung,pin-function = <0x1>;
phandle = <0x5>;
};
lcd_pinctrl {
samsung,pins = "gpc-8", "gpc-9", "gpc-10", "gpc-11", "gpc-12", "gpc-13", "gpc-14", "gpc-15", "gpd-0", "gpd-1", "gpd-2", "gpd-3", "gpd-4", "gpd-5", "gpd-6", "gpd-7", "gpd-8", "gpd-9", "gpd-10", "gpd-11", "gpd-12", "gpd-13", "gpd-14", "gpd-15", "gpc-1", "gpc-2", "gpc-3", "gpc-4";
samsung,pin-function = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x8>;
};
lcd_backlight {
samsung,pins = "gpg-4";
samsung,pin-function = <0x3>;
phandle = <0x9>;
};
uda1340_codec_pinctrl {
samsung,pins = "gpb-4", "gpb-3", "gpb-2";
samsung,pin-function = <0x1>;
phandle = <0xc>;
};
s3c2440_iis_pinctrl {
samsung,pins = "gpe-0", "gpe-1", "gpe-2", "gpe-3", "gpe-4";
samsung,pin-function = <0x2>;
phandle = <0xa>;
};
};
timer@ {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-pwm";
reg = <0x51000000 0x1000>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0xa 0x3 0x0 0x0 0xb 0x3 0x0 0x0 0xc 0x3 0x0 0x0 0xd 0x3 0x0 0x0 0xe 0x3>;
#pwm-cells = <0x4>;
clock-names = "timers";
clocks = <0x2 0x19>;
};
serial@ {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-uart";
reg = <0x50000000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <0x1 0x1c 0x0 0x4 0x1 0x1c 0x1 0x4>;
status = "okay";
clock-names = "uart";
clocks = <0x2 0x10>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl- = <0x3>;
};
serial@ {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-uart";
reg = <0x50004000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <0x1 0x17 0x3 0x4 0x1 0x17 0x4 0x4>;
status = "disabled";
};
serial@ {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-uart";
reg = <0x50008000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <0x1 0xf 0x6 0x4 0x1 0xf 0x7 0x4>;
status = "disabled";
};
watchdog@ {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-wdt";
reg = <0x53000000 0x100>;
interrupts = <0x1 0x9 0x1b 0x3>;
status = "okay";
clocks = <0x2 0x6>;
clock-names = "watchdog";
};
rtc@ {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-rtc";
reg = <0x57000000 0x100>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x1e 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x8 0x3>;
status = "okay";
clocks = <0x2 0x1a>;
clock-names = "rtc";
};
i2c@ {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-i2c";
reg = <0x54000000 0x100>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x1b 0x3>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
status = "disabled";
clocks = <0x2 0x13>;
clock-names = "i2c";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl- = <0x4>;
};
cpus {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
cpu {
compatible = "arm,arm920t";
};
};
xti_clock {
compatible = "fixed-clock";
clock-frequency = <0xb71b00>;
clock-output-names = "xti";
#clock-cells = <0x0>;
};
clock-controller@4c000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-clock";
reg = <0x4c000000 0x20>;
#clock-cells = <0x1>;
phandle = <0x2>;
};
nand@4e000000 {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-nand";
reg = <0x4e000000 0x40>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x18 0x3>;
clocks = <0x2 0x23>;
clock-names = "nand";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl- = <0x5>;
status = "okay";
nand,tacls = <0xa>;
nand,twrph0 = <0x19>;
nand,twrph1 = <0xa>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
partitions {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
nr-chips = <0x1>;
set-name = "jz2440-0";
partition@ {
label = "bootloader";
reg = <0x0 0x40000>;
read-only;
};
partition@ {
label = "device_tree";
reg = <0x40000 0x20000>;
read-only;
};
partition@ {
label = "params";
reg = <0x60000 0x20000>;
read-only;
};
partition@ {
label = "kernel";
reg = <0x80000 0x400000>;
read-only;
};
partition@ {
label = "rootfs";
reg = <0x480000 0x0>;
};
};
};
usb_ohci@ {
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-ohci";
reg = <0x49000000 0x60>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x1a 0x3>;
clocks = <0x2 0x21 0x2 0x7>;
clock-names = "usb-host", "usb-bus-host";
status = "okay";
};
memory {
device_type = "memory";
reg = <0x30000000 0x4000000>;
};
chosen {
bootargs = "noinitrd root=/dev/mtdblock4 rw init=/linuxrc console=ttySAC0,115200";
};
srom-cs4@ {
compatible = "simple-bus";
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
reg = <0x20000000 0x8000000>;
ranges;
ethernet@ {
compatible = "davicom,dm9000";
reg = <0x20000000 0x2 0x20000004 0x2>;
interrupt-parent = <0x6>;
interrupts = <0x7 0x1>;
local-mac-address = [ de ad be ef];
davicom,no-eeprom;
};
};
i2c-gpio- {
compatible = "i2c-gpio";
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
gpios = <0x7 0xf 0x0 0x7 0xe 0x0>;
i2c-gpio,delay-us = <0x5>;
status = "disabled";
eeprom@ {
compatible = "24c02";
reg = <0x50>;
pagesize = <0x20>;
status = "okay";
};
};
fb@4d000000 {
compatible = "jz2440,lcd";
reg = <0x4d000000 0x60>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x10 0x3>;
clocks = <0x2 0x20>;
clock-names = "lcd";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl- = <0x8 0x9>;
status = "okay";
lcdcon5 = <0xb09>;
type = <0x60>;
width = [ e0];
height = [ ];
pixclock = <0x186a0>;
xres = [ e0];
yres = [ ];
bpp = [ ];
left_margin = [ ];
right_margin = [ ];
hsync_len = [ ];
upper_margin = [ ];
lower_margin = [ ];
vsync_len = [ 0a];
};
jz2440ts@ {
compatible = "jz2440,ts";
reg = <0x58000000 0x100>;
reg-names = "adc_ts_physical";
interrupts = <0x1 0x1f 0x9 0x3 0x1 0x1f 0xa 0x3>;
interrupt-names = "int_ts", "int_adc_s";
clocks = <0x2 0x16>;
clock-names = "adc";
};
s3c2410-dma@4B000000 {
compatible = "s3c2440-dma";
reg = <0x4b000000 0x1000>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x0 0x11 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x12 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x13 0x3 0x0 0x0 0x14 0x3>;
#dma-cells = <0x1>;
phandle = <0xb>;
};
s3c2440_iis@ {
compatible = "s3c24xx-iis";
reg = <0x55000000 0x100>;
clocks = <0x2 0x18>;
clock-names = "iis";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl- = <0xa>;
dmas = <0xb 0x9 0xb 0xa>;
dma-names = "rx", "tx";
};
s3c24xx_uda134x {
compatible = "s3c24xx_uda134x";
clocks = <0x2 0x2 0x2 0x18>;
clock-names = "mpll", "iis";
};
uda134x-codec {
compatible = "uda134x-codec";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl- = <0xc>;
uda,clk_gpio = <0xd 0x4 0x1>;
uda,data_gpio = <0xd 0x3 0x1>;
uda,mode_gpio = <0xd 0x2 0x1>;
uda,use_gpios;
uda,data_hold;
uda,data_setup;
uda,clock_high;
uda,mode_hold;
uda,mode;
uda,mode_setup;
uda,model = <0x2>;
};
};
7.4 按键中断设备树节点:
buttons
{
compatible = "jz2440_button";
eint-pins = <&gpf >, <&gpf >, <&gpg >, <&gpg >;
interrupts-extended = <&intc >,<&intc >, <&gpg >, <&gpg >;
};
. interrupts-extended (扩展中断属性):
见:devicetree-specifications-v0. - 2.4.1节
interrupt-extend = <&intc > --> &intc表示中断控制器 表示描述的是哪个中断
3意义见:kernel/../samsung,s3c24xx-irq.txt:
<ctrl_num parent_irq ctrl_irq type>
val_1:ctrl_num contains the controller to use:(代表中断信号发给主还是子中断控制器)
- ... main controller
- ... sub controller
- ... second main controller on s3c2416 and s3c2450
val_2: parent_irq contains the parent bit in the main controller and
will be ignored in main controllers (代表子中断控制器是主中断控制器的中断)
val_3: ctrl_irq contains the interrupt bit of the controller(代表哪个中断)EINT0 EINT2
val_4: type contains the trigger type to use(中断的触发方式)
trigger type见kernel\..\samsung-pinctrl.txt
- = rising edge triggered
- = falling edge triggered
- = rising and falling edge triggered
- = high level triggered
- = low level triggered
<&gpg > 见:kernel\..\samsung-pinctrl.txt
- First Cell: represents the external gpio interrupt number local to the (代表哪个中断)EINT3 EINT11
external gpio interrupt space of the controller.
- Second Cell: flags to identify the type of the interrupt(代表中断触发方式)
- = rising edge triggered
- = falling edge triggered
- = rising and falling edge triggered
- = high level triggered
- = low level triggered
7.5内核对设备树中断信息的处理过程
从硬件结构上看, 处理过程分上下两个层面: 中断控制器, 使用中断的设备
从软件结构上看, 处理过程分左右两个部分: 在设备树中描述信息, 在驱动中处理设备树 中断分为三级
() 一级中断控制器 -->root_intc
这又分为root irq controller
a. root irq controller
a. 在设备树中的描述
a. 在内核中的驱动 ()二级中断控制器 -->pinctrl
b. gpf/gpg irq controller
b. 在设备树中的描述(在pinctrl节点里)
b. 在内核中的驱动 (在pinctrl驱动中) () 三级 设备的中断 -->按键中断
a. 在设备节点中描述(表明使用"哪一个中断控制器里的哪一个中断, 及中断触发方式")
a. 在内核中的驱动 (在platform_driver.probe中获得IRQ资源, 即中断号) irq_domain是核心:
{
.ops.map // 为硬件中断号 虚拟中断号创建联系
1.对于直达root_irq_control的中断,设置irq_desc[virq].handler_irq = handle_edeg_irq
2.对于先到达gpf_irq_control(virq_m),再到达root_irq_control(virq_n)的中断, 设置
先:irq_desc[virq_m].handler_irq = irq_demux(分发函数,需要读寄存器确定是哪个子中断产生,然后调用对应的handle_irq)
再:irq_desc[virq_n].handler_irq = handle_edeg_irq
.ops.xlate //解析设备树的中断信息,生成platform_device
.linear_revmap[hwirq]=virq // 将硬件中断号转化为虚拟中断号
}
a. 每一个中断控制器都有一个irq_domain
b. 对设备中断信息的解析,
b. 需要调用 irq_domain->ops->xlate (即从设备树中获得hwirq, type)
b. 获取未使用的virq, 保存: irq_domain->linear_revmap[hwirq] = virq;
b. 在hwirq和virq之间建立联系:
要调用 irq_domain->ops->map, 比如根据hwirq的属性设置virq的中断处理函数(是一个分发函数还是可以直接处理中断)
irq_desc[virq].handle_irq = 常规函数;
如果这个hwirq有上一级中断, 假设它的中断号为virq', 还要设置:
irq_desc[virq'].handle_irq = 中断分发函数; s3c2440设备树中断相关代码调用关系: () 上述处理过程如何触发?
a. 内核启动时初始化中断的入口:
start_kernel // init/main.c
init_IRQ();
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF) && !machine_desc->init_irq)
irqchip_init(); // 一般使用它
else
machine_desc->init_irq(); b. 设备树中的中断控制器的处理入口:
irqchip_init // drivers/irqchip/irqchip.c
of_irq_init(__irqchip_of_table); // 对设备树文件中每一个中断控制器节点, 调用对应的处理函数
为每一个符合的"interrupt-controller"节点,
分配一个of_intc_desc结构体, desc->irq_init_cb = match->data; // = IRQCHIP_DECLARE中传入的函数
并调用处理函数 (先调用root irq controller对应的函数, 再调用子控制器的函数, 再调用更下一级控制器的函数...) () root irq controller的中断控制器初始化过程: a. 为root irq controller定义处理函数:
IRQCHIP_DECLARE(s3c2410_irq, "samsung,s3c2410-irq", s3c2410_init_intc_of); //drivers/irqchip/irq-s3c24xx.c 其中:
#define IRQCHIP_DECLARE(name, compat, fn) OF_DECLARE_2(irqchip, name, compat, fn)
#define OF_DECLARE_2(table, name, compat, fn) \
_OF_DECLARE(table, name, compat, fn, of_init_fn_2)
#define _OF_DECLARE(table, name, compat, fn, fn_type) \
static const struct of_device_id __of_table_##name \
__used __section(__##table##_of_table) \
= { .compatible = compat, \
.data = (fn == (fn_type)NULL) ? fn : fn } 展开为:
static const struct of_device_id __of_table_s3c2410_irq \
__used __section("__irqchip_of_table") \
= { .compatible = "samsung,s3c2410-irq", \
.data = s3c2410_init_intc_of } 它定义了一个of_device_id结构体, 段属性为"__irqchip_of_table", 在编译内核时这些段被放在__irqchip_of_table地址处。
即__irqchip_of_table起始地址处,
放置了一个或多个 of_device_id, 它含有compatible成员;
设备树中的设备节点含有compatible属性,
如果双方的compatible相同, 并且设备节点含有"interrupt-controller"属性,
则调用of_device_id中的函数来处理该设备节点。 所以: IRQCHIP_DECLARE 是用来声明设备树中的中断控制器的处理函数。 b. root irq controller处理函数的执行过程:
s3c2410_init_intc_of // drivers/irqchip/irq-s3c24xx.c
// 初始化中断控制器: intc, subintc
s3c_init_intc_of(np, interrupt_parent, s3c2410_ctrl, ARRAY_SIZE(s3c2410_ctrl)); // 为中断控制器创建irq_domain
domain = irq_domain_add_linear(np, num_ctrl * ,
&s3c24xx_irq_ops_of, NULL); intc->domain = domain; // 设置handle_arch_irq, 即中断处理的C语言总入口函数
set_handle_irq(s3c24xx_handle_irq); () pinctrl系统中gpf/gpg irq controller的驱动调用过程: a. pinctrl系统的中断控制器初始化过程:
a. 源代码: drivers/pinctrl/samsung/pinctrl-samsung.c
static struct platform_driver samsung_pinctrl_driver = {
.probe = samsung_pinctrl_probe,
.driver = {
.name = "samsung-pinctrl",
.of_match_table = samsung_pinctrl_dt_match, // 含有 { .compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-pinctrl", .data = &s3c2440_of_data },
.suppress_bind_attrs = true,
.pm = &samsung_pinctrl_pm_ops,
},
}; a. 设备树中:
pinctrl@ {
reg = <0x56000000 0x1000>;
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-pinctrl"; // 据此找到驱动 a. 驱动中的操作:
samsung_pinctrl_probe // drivers/pinctrl/samsung/pinctrl-samsung.c
最终会调用到 s3c24xx_eint_init // drivers/pinctrl/samsung/pinctrl-s3c24xx.c // eint0,1,2,3的处理函数在处理root irq controller时已经设置;
// 设置eint4_7, eint8_23的处理函数(它们是分发函数)
for (i = ; i < NUM_EINT_IRQ; ++i) {
unsigned int irq; if (handlers[i]) /* add by weidongshan@qq.com, 不再设置eint0,1,2,3的处理函数 */
{
irq = irq_of_parse_and_map(eint_np, i);
if (!irq) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to get wakeup EINT IRQ %d\n", i);
return -ENXIO;
} eint_data->parents[i] = irq;
irq_set_chained_handler_and_data(irq, handlers[i], eint_data);
}
} // 为GPF、GPG设置irq_domain
for (i = ; i < d->nr_banks; ++i, ++bank) { ops = (bank->eint_offset == ) ? &s3c24xx_gpf_irq_ops
: &s3c24xx_gpg_irq_ops; bank->irq_domain = irq_domain_add_linear(bank->of_node, bank->nr_pins, ops, ddata);
} () 使用中断的驱动初始化过程:
a. 在设备节点中描述(表明使用"哪一个中断控制器里的哪一个中断, 及中断触发方式")
比如:
buttons {
compatible = "jz2440_button";
eint-pins = <&gpf >, <&gpf >, <&gpg >, <&gpg >;
interrupts-extended = <&intc >,
<&intc >,
<&gpg >,
<&gpg >;
}; b. 设备节点会被转换为 platform_device,
"中断的硬件信息" 会转换为"中断号",
保存在platform_device的"中断资源"里 第3课第05节_device_node转换为platform_device, 讲解了设备树中设备节点转换为 platform_device 的过程;
我们只关心里面对中断信息的处理: of_device_alloc (drivers/of/platform.c)
dev = platform_device_alloc("", PLATFORM_DEVID_NONE); // 分配 platform_device num_irq = of_irq_count(np); // 计算中断数 of_irq_to_resource_table(np, res, num_irq) // drivers/of/irq.c, 根据设备节点中的中断信息, 构造中断资源
of_irq_to_resource
int irq = of_irq_get(dev, index); // 获得virq, 中断号
rc = of_irq_parse_one(dev, index, &oirq); // drivers/of/irq.c, 解析设备树中的中断信息, 保存在of_phandle_args结构体中 domain = irq_find_host(oirq.np); // 查找irq_domain, 每一个中断控制器都对应一个irq_domain irq_create_of_mapping(&oirq); // kernel/irq/irqdomain.c, 创建virq和中断信息的映射
irq_create_fwspec_mapping(&fwspec);
irq_create_fwspec_mapping(&fwspec);
irq_domain_translate(domain, fwspec, &hwirq, &type) // 调用irq_domain->ops->xlate, 把设备节点里的中断信息解析为hwirq, type virq = irq_find_mapping(domain, hwirq); // 看看这个hwirq是否已经映射, 如果virq非0就直接返回 virq = irq_create_mapping(domain, hwirq); // 否则创建映射
virq = irq_domain_alloc_descs(-, , hwirq, of_node_to_nid(of_node), NULL); // 返回未占用的virq irq_domain_associate(domain, virq, hwirq) // 调用irq_domain->ops->map(domain, virq, hwirq), 做必要的硬件设置 c. 驱动程序从platform_device的"中断资源"取出中断号, 就可以request_irq()
8.3设备树的clock
文档:
内核 Documentation/devicetree/bindings/clock/clock-bindings.txt
内核 Documentation/devicetree/bindings/clock/samsung,s3c2410-clock.txt s3c2440时钟:
FCLK (cpu内核时钟)
INPUT_CLOCK->MPLL->CLOCK_DIVN->CLOCK_CON->CLOCK_SLOW-> HCLK (AHB总线时钟) DMA NAND SDRAM
PCKL (PHB总线时钟) PWM ADC GPIO UART a. 设备树中一级时钟(MPLL),在文档中称之为"Clock providers", 比如:
xti_clock
{
compatible = "fixed-clock"; //根据compatible,找到对应函数设置时钟为0xb71b00
clock-frequency = <0xb71b00>;
clock-output-names = "xti";
#clock-cells = <0x0>;
}; b. 设备树中二级时钟(FCLK,HCLK,PCLK), 在文档中称之为"Clock providers", 比如:
clocks: clock-controller@4c000000
{
compatible = "samsung,s3c2440-clock"; //根据ccompatible,找到函数,通过reg寄存器设置时钟,并为每个子设备分配一个ID
reg = <0x4c000000 0x20>;
#clock-cells = <>; // 想使用这个clocks时要表明设备是这个时钟的哪个子设备(ID)用32位来表示, 比如这个clocks中发出的LCD时钟、PWM时钟,NAND时钟
}; c. 设备树中三级时钟(AHB/PHB总线上的设备),它是"Clock consumers", 它描述了使用哪一个"Clock providers"中的哪一个时钟(id), 比如:
fb0: fb@4d000000
{
compatible = "jz2440,lcd";
reg = <0x4D000000 0x60>;
interrupts = < >;
clocks = <&clocks HCLK_LCD>; // 使用clocks即时钟提供者,HCLK_LCD为时钟提供者的哪个子设备(ID)
}; d. 驱动中获得/使能时钟: // 确定时钟个数
int nr_pclks = of_count_phandle_with_args(dev->of_node, "clocks",
"#clock-cells");
// 获得时钟
for (i = ; i < nr_pclks; i++) {
struct clk *clk = of_clk_get(dev->of_node, i);
} // 使能时钟
clk_prepare_enable(clk); // 禁止时钟
clk_disable_unprepare(clk);
8.2设备树中的pinctrl
文档:
内核 Documentation/devicetree/bindings/pinctrl/samsung-pinctrl.txt 几个概念: Bank: 以引脚名为依据, 这些引脚分为若干组, 每组称为一个Bank
比如s3c2440里有GPA、GPB、GPC等Bank,
每个Bank中有若干个引脚, 比如GPA0,GPA1, ..., GPC0, GPC1,...等引脚 Group: 以功能为依据, 具有相同功能的引脚称为一个Group
比如s3c2440中串口0的TxD、RxD引脚使用 GPH2,GPH3, 那这2个引脚可以列为一组
比如s3c2440中串口0的流量控制引脚使用 GPH0,GPH1, 那这2个引脚也可以列为一组 State: 设备的某种状态, 比如内核自己定义的"default","init","idel","sleep"状态;
也可以是其他自己定义的状态, 比如串口的"flow_ctrl"状态(使用流量控制) 设备处于某种状态时, 它可以使用若干个Group引脚 a. 设备树中pinctrl节点:
a. 它定义了各种 pin bank, 比如s3c2440有GPA,GPB,GPC,...,GPB各种BANK, 每个BANK中有若干引脚:
pinctrl_0: pinctrl@ {
reg = <0x56000000 0x1000>; gpa: gpa {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <>; /* 以后想使用gpa bank中的引脚时, 需要2个u32来指定引脚 */
}; gpb: gpb {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <>;
}; gpc: gpc {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <>;
}; gpd: gpd {
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <>;
};
}; a. 它还定义了各种group(组合), 某种功能所涉及的引脚称为group,
比如串口0要用到2个引脚: gph0, gph1: uart0_data: uart0-data {
samsung,pins = "gph-0", "gph-0";
samsung,pin-function = <>; /* 在GPHCON寄存器中gph0,gph1可以设置以下值:
0 --- 输入功能
1 --- 输出功能
2 --- 串口功能
我们要使用串口功能,
samsung,pin-function 设置为2
*/
}; uart0_sleep: uart0_sleep {
samsung,pins = "gph-0", "gph-1";
samsung,pin-function = <>; /* 在GPHCON寄存器中gph0,gph1可以设置以下值:
0 --- 输入功能
1 --- 输出功能
2 --- 串口功能
我们要使用输入功能,
samsung,pin-function 设置为0
*/
}; b. 设备节点中要使用某一个 pin group:
serial@ {
......
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep"; /* 既是名字, 也称为state(状态) */
pinctrl- = <&uart0_data>;
pinctrl- = <&uart0_sleep>;
}; pinctrl-names中定义了2种state: default 和 sleep,
default 对应的引脚是: pinctrl-, 它指定了使用哪些pin group: uart0_data
sleep 对应的引脚是: pinctrl-, 它指定了使用哪些pin group: uart0_sleep c. platform_device, platform_driver匹配时: "第3课第06节_platform_device跟platform_driver的匹配" 中讲解了platform_device和platform_driver的匹配过程,
最终都会调用到 really_probe (drivers/base/dd.c) really_probe:
/* If using pinctrl, bind pins now before probing */
ret = pinctrl_bind_pins(dev);
dev->pins->default_state = pinctrl_lookup_state(dev->pins->p,
PINCTRL_STATE_DEFAULT); /* 获得"default"状态的pinctrl */
dev->pins->init_state = pinctrl_lookup_state(dev->pins->p,
PINCTRL_STATE_INIT); /* 获得"init"状态的pinctrl */ ret = pinctrl_select_state(dev->pins->p, dev->pins->init_state); /* 优先设置"init"状态的引脚 */
ret = pinctrl_select_state(dev->pins->p, dev->pins->default_state); /* 如果没有init状态, 则设置"default"状态的引脚 */ ......
ret = drv->probe(dev); 所以: 如果设备节点中指定了pinctrl, 在对应的probe函数被调用之前, 先"bind pins", 即先绑定、设置引脚 d. 驱动中想选择、设置某个状态的引脚:
devm_pinctrl_get_select_default(struct device *dev); // 使用"default"状态的引脚
pinctrl_get_select(struct device *dev, const char *name); // 根据name选择某种状态的引脚 pinctrl_put(struct pinctrl *p); // 不再使用, 退出时调用
设备树..ing的更多相关文章
- Linux设备树语法详解
概念 Linux内核从3.x开始引入设备树的概念,用于实现驱动代码与设备信息相分离.在设备树出现以前,所有关于设备的具体信息都要写在驱动里,一旦外围设备变化,驱动代码就要重写.引入了设备树之后,驱动代 ...
- 扁平设备树(FDT)
组成 扁平设备树主要由4大部分组成:头部(header),预留内存块(memory reservation block),结构块(struct block)和字符串块(strings block).这 ...
- Linux 获取设备树源文件(DTS)里描述的资源
Linux 获取设备树源文件(DTS)里的资源 韩大卫@吉林师范大学 在linux使用platform_driver_register() 注册 platform_driver 时, 需要在 plat ...
- 基于tiny4412的Linux内核移植 -- 设备树的展开
作者信息 作者: 彭东林 邮箱:pengdonglin137@163.com QQ:405728433 平台简介 开发板:tiny4412ADK + S700 + 4GB Flash 要移植的内核版本 ...
- linux设备树笔记__dts基本概念及语法【转】
转自:http://www.360doc.com/content/15/1113/11/15700426_512794532.shtml 设备树手册(Device Tree Usage)原文地址:ht ...
- 设备树的interrupt
http://www.cnblogs.com/targethero/p/5080499.html https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaojiang1025/p/6131381.htm ...
- Linux设备树语法详解【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaojiang1025/p/6131381.html 概念 Linux内核从3.x开始引入设备树的概念,用于实现驱动代码与设备信息相分离.在设备 ...
- 我眼中的Linux设备树(六 memory&chosen节点)
六 memory&chosen节点根节点那一节我们说过,最简单的设备树也必须包含cpus节点和memory节点.memory节点用来描述硬件内存布局的.如果有多块内存,既可以通过多个memor ...
- 我眼中的Linux设备树(五 根节点)
五 根节点一个最简单的设备树必须包含根节点,cpus节点,memory节点.根节点的名字及全路径都是"/",至少需要包含model和compatible两个属性.model属性我们 ...
随机推荐
- H+ 关闭menuTab页面
//注:在contabs.js文件中 $(function () { }); 方法外 加入//注: data-name="' + menuName + '" 这句是加入的自定义属性 ...
- Introducing DataFrames in Apache Spark for Large Scale Data Science(中英双语)
文章标题 Introducing DataFrames in Apache Spark for Large Scale Data Science 一个用于大规模数据科学的API——DataFrame ...
- puppeteer新手遇到的坑
puppeteer安装以及遇到的坑 1. 环境和安装 Puppeteer 至少需要 Node v6.4.0,如要使用 async / await,只有 Node v7.6.0 或更高版本才支持. no ...
- easyui的datagrid和treegrid的使用
$('#listTree').treegrid({ idField: 'id', treeField: 'menuName', columns: [[ { title: 'Task Name', fi ...
- vim常用技巧
# vim常用技巧 ## 行操作------------------------------ 行首 0- 行尾 $- 第一个非空字符 ^ ## 列编辑模式----------------------- ...
- 【GMT43智能液晶模块】基于HAL库的SDRAM和LCD驱动例程(MDK工程&CubeMX工程)
说明: 1.该工程基于HAL库实现动态存储器SDRAM驱动以及液晶控制器LCD驱动. 2.工程通过STM32CubeMX(Version 4.22.0)配置生成,可直接打开进行配置. 3.KEIL M ...
- Java编程的逻辑 (91) - Lambda表达式
本系列文章经补充和完善,已修订整理成书<Java编程的逻辑>,由机械工业出版社华章分社出版,于2018年1月上市热销,读者好评如潮!各大网店和书店有售,欢迎购买,京东自营链接:http: ...
- C#编程高并发的几种处理方法
并发(英文Concurrency),其实是一个很泛的概念,字面意思就是“同时做多件事”,不过方式有所不同.在.NET的世界里面,处理高并发大致有以下几种方法: 1,异步编程 异步编程就是使用futur ...
- windows 端口被占用,并杀死进程的方法
netstat -ano | findstr 8081 查询端口 被什么进程占用 tasklist | findstr 2184 根据进程号 查询任务名称 taskkill /f /t /im jav ...
- nginx 内置变量
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/articlelist_1834459124_1_1.html nginx内置变量杂谈 http://nginx.org/en/docs/http ...
