[转]Python in Visual Studio Code
本文转自:https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/languages/python
Working with Python in Visual Studio Code, using the Microsoft Python extension, is simple, fun, and productive. The extension makes VS Code an excellent IDE, and works on any operating system with a variety of Python interpreters. It leverages all of VS Code's power to provide auto complete and IntelliSense, linting, debugging, and unit testing, along with the ability to easily switch between Python environments, including virtual and conda environments.
This article provides only an overview of the different capabilities of the Python extension for VS Code. For a walkthrough of editing, running, and debugging code, use the button below.
Install Python and the Python extension
The tutorial guides you through installing Python and using the extension. You must install a Python interpreter yourself separately from the extension. For a quick install, use Python 3.6 from python.org and install the extension from the VS Code marketplace.
Once you have a version of Python installed, activate it using the Python: Select Interpreter command. If VS Code doesn't automatically locate the interpreter you're looking for, refer to Environments - Manually specify an interpreter.
You configure the Python extension through settings. See the Settings reference.
Run Python code
To experience Python, create a file (using the File Explorer) named hello.py and paste in the following code (assuming Python 3):
print("Hello World")
The Python extension then provides shortcuts to run Python code in the currently selected interpreter (Python: Select Interpreter in the Command Palette):
- In the text editor: right-click anywhere in the editor and select Run Python File in Terminal. If invoked on a selection, only that selection is run.
- In Explorer: right-click a Python file and select Run Python File in Terminal.
You can also use the Terminal: Create New Integrated Terminal command to create a terminal in which VS Code automatically activates the currently selected interpreter. See Environments below. The Python: Start REPL activates a terminal with the currently selected interpreter and then runs the Python REPL.
For a more specific walkthrough on running code, see the tutorial.
Autocomplete and IntelliSense
The Python extension supports code completion and IntelliSense using the currently selected interpreter. IntelliSense is a general term for a number of features, including intelligent code completion (in-context method and variable suggestions) across all your files and for built-in and third-party modules.
IntelliSense quickly shows methods, class members, and documentation as you type, and you can trigger completions at any time with Ctrl+Space. You can also hover over identifiers for more information about them.
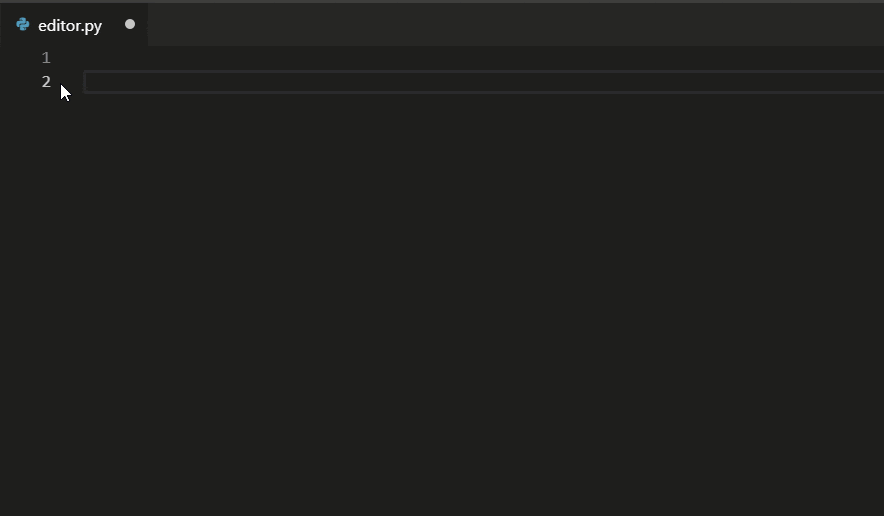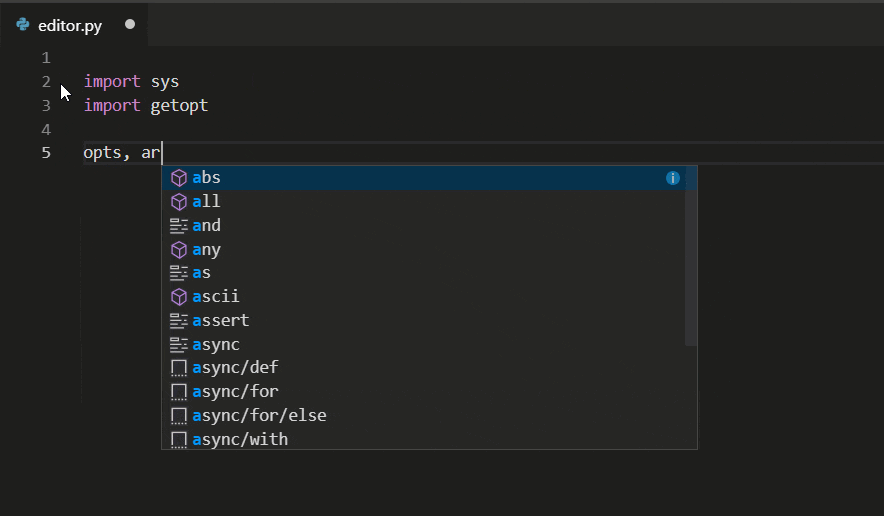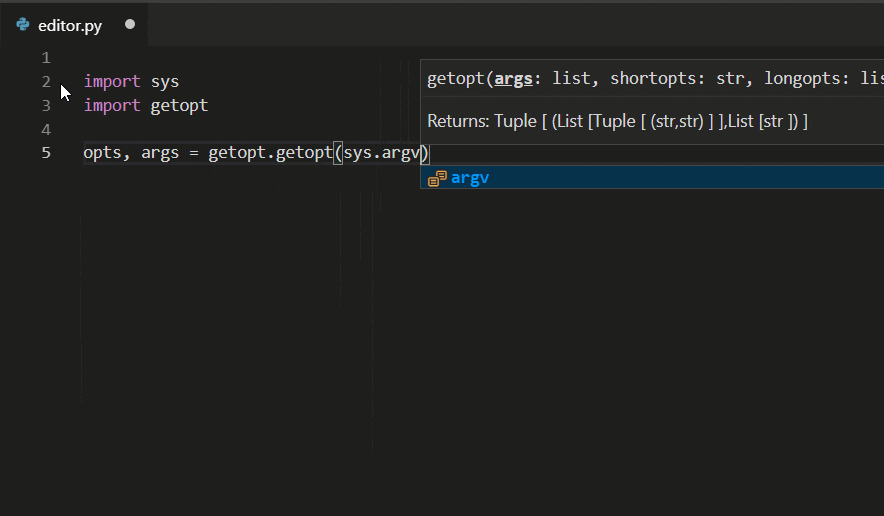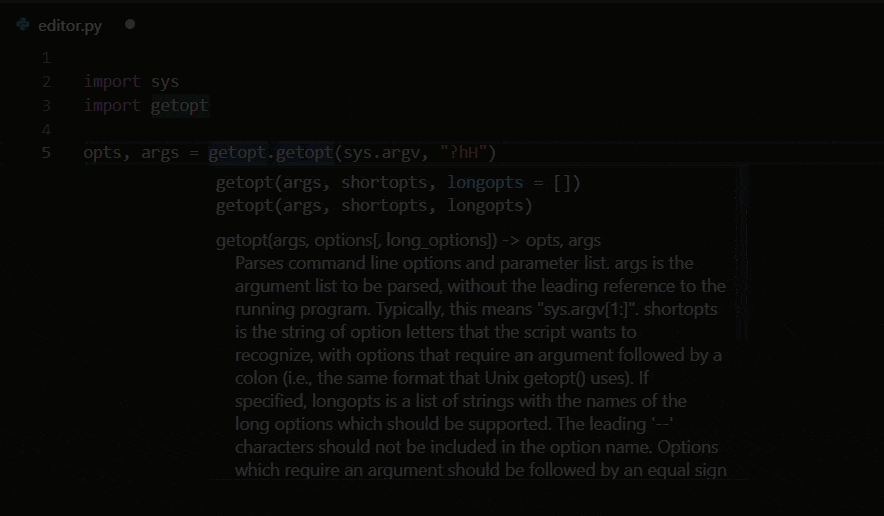
Tip: Check out the IntelliCode extension for VS Code (preview). IntelliCode provides a set of AI-assisted capabilities for IntelliSense in Python, such as inferring the most relevant auto-completions based on the current code context.
Linting
Linting analyzes your Python code for potential errors, making it easy to navigate to and correct different problems.
The Python extension can apply a number of different linters including Pylint, Pep8, Flake8, mypy, pydocstyle, prospector, and pylama. See Linting.
Debugging
No more print statement debugging! Set breakpoints, inspect data, and use the debug console as you run your program step by step. Debug a number of different types of Python applications, including multi-threaded, web, and remote applications.
For Python-specific details, including setting up your launch.json configuration and remote debugging, see Debugging. General VS Code debugging information is found in the debugging document. The Django and Flask tutorials also demonstrate debugging in the context of those web apps, including debugging Django page templates.
Snippets
Snippets take productivity to the next level. You can configure your own snippets and use snippets provided by an extension. Snippets appear in the same way as code completion Ctrl+Space. For specific examples with Python, see the Django and Flask tutorials.
Environments
The Python extension automatically detects Python interpreters that are installed in standard locations. It also detects conda environments as well as virtual environments in the workspace folder. See Configuring Python environments. You can also use the python.pythonPath setting to point to an interpreter anywhere on your computer.
The current environment is shown on the left side of the VS Code Status Bar:

The Status Bar also indicates if no interpreter is selected:
The selected environment is used for IntelliSense, auto-completions, linting, formatting, and any other language-related feature other than debugging. It is also activated when you use run Python in a terminal.
To change the current interpreter, which includes switching to conda or virtual environments, select the interpreter name on the Status Bar or use the Python: Select Interpreter command.
VS Code prompts you with a list of detected environments as well as any you've added manually to your user settings (see Configuring Python environments).
Installing packages
Packages are installed using the Terminal panel and commands like pip install <package_name>(Windows) and pip3 install <package_name> (macOS/Linux). VS Code installs that package into your project along with its dependencies. Examples are given in the Python tutorial as well as the Django and Flask tutorials.
Jupyter notebooks
If you open a Jupyter notebook file (.ipynb) in VS Code, the Python extension prompts you to import the notebook as a Python code file. The notebook's cells are delimited in the Python file with #%% comments, and the Python extension shows Run Cell or Run All Cells CodeLens. Selecting either CodeLens starts the Jupyter server and runs the cell(s) in the Python interactive window:
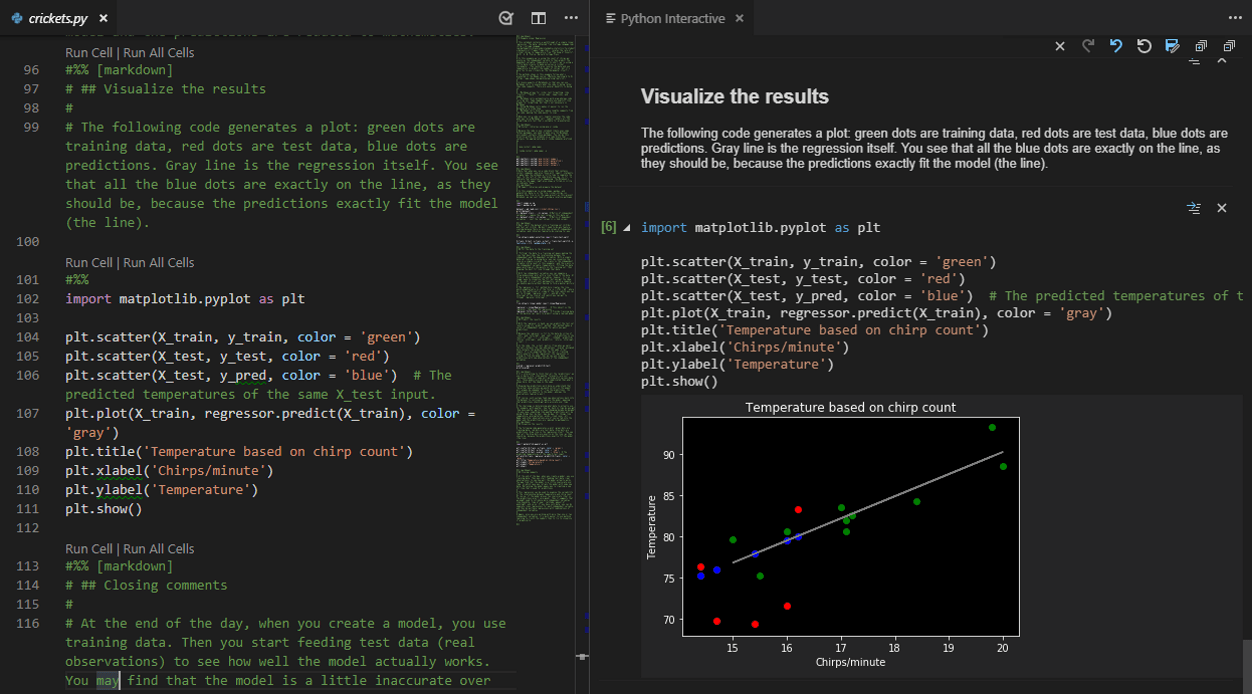
You can also connect to a remote Jupyter server for running the code.
Furthermore, importing a notebook into VS Code allows you to use all of VS Code's debugging capabilities. You can then save the notebook file and open it again as a notebook in Jupyter or upload to a service like Azure Notebooks.
For more information, see Jupyter support.
Unit testing
The Python extension supports unit testing with the unittest, pytest, and nose test frameworks.
To run unit tests, you enable one of the frameworks in settings. Each framework also has specific settings, such as arguments that identify paths and patterns for test discovery.
Once discovered, VS Code provides a variety of commands (on the Status Bar, the Command Palette, and elsewhere) to run and debug tests, including ability to run individual test files and individual methods.
Configuration
The Python extension provides a wide variety of settings for its various features. These are described on their relevant topics, such as Editing code, Linting, Debugging, and Unit Testing. The complete list is found in the Settings reference.
Other popular Python extensions
The Microsoft Python extension provides all of the features described previously in this article. Additional Python language support can be added to VS Code by installing other popular Python extensions. For Jupyter support, we recommend the "Jupyter" extension from Don Jayamanne.
- Open the Extensions view (Ctrl+Shift+X).
- Filter the extension list by typing 'python'.
The extensions shown above are dynamically queried. Click on an extension tile above to read the description and reviews to decide which extension is best for you. See more in the Marketplace.
Next steps
- Python Hello World tutorial - Get started with Python in VS Code.
- Editing Python - Learn about auto-completion, formatting, and refactoring for Python.
- Basic Editing - Learn about the powerful VS Code editor.
- Code Navigation - Move quickly through your source code.
- Django tutorial
- Flask tutorial
Was this documentation helpful?
[转]Python in Visual Studio Code的更多相关文章
- Python + Djang+ Visual Studio Code(VSCode)
使用 Visual Studio Code(VSCode)搭建简单的 Python + Django 开发环境 https://www.cnblogs.com/Dy1an/p/10130518.htm ...
- 【Python】Visual Studio Code 安装&&使用 hello python~~~~
1.安装Python 官网下载: https://www.python.org/downloads/ 选择版本下载 2.下载完毕后,点击安装. 3.看到页面,直接下一步,全部默认选项. 4.安装即 ...
- visual studio code——运行python
How to run Python in Visual Studio Code Getting Started with Python in VS Code python教程 vs code 安装py ...
- 如何用visual studio code更好的编写python
目录 1.先决条件 2.Visual Studio Code扩展安装Python 3.Visual Studio Code扩展安装Python for VSCode 4.Visual Studio C ...
- Visual Studio Code 安装美化合集
这是一个关于VSCode编辑器的各种配置. 你可以在这里找到VSCode 的各种操作,如果这里找不到,请移步官方文档C++ programming with Visual Studio Code以及各 ...
- visual studio code 里调试运行 Python代码
最近对微软的visual studio code 挺感兴趣的,微软的跨平台开发工具.轻量简洁. 版本迭代的也挺快的,截止16年8月2日已经1.3.1版本了,功能也愈加完善.(16年12月18日 已经, ...
- visual studio code 安装python扩展
Ctrl+P 调出控制台,在控制台里输入ext install python,点击第一个安装 如果出现: visual studio code connect ETIMEDOUT 191.238.17 ...
- Visual Studio Code 搭建Python开发环境
1.下载Python https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/ 选择一个版本,目前2.0的源码比较多,我下载的2.7.12 2.配置环境变量 3.Visual ...
- Visual Studio Code 写Python 代码
最近在博客园新闻里面看到微软发布的Visual Studio Code 挺好用的,现在在学习Python,查看官网发布的VSCode 是支持Python代码,自己试着安装用一下,下面是我的安装以及配置 ...
随机推荐
- Java IO--字符流--InputStreamReader 和 OutputStreamWriter
今天继续学习字符流的子类!!!! 先来熟悉一下适配器设计模式:(手写的,,嘿嘿) 因为据说InputStreamReader 和OutputStreamWriter采用了适配器模式(现在我还没能理解, ...
- 谈谈.NET架构师面试及如何设计面试题
上星期:应老东家的要求,帮其面试.NET架构师. 于是:老东家进行了一星期的简历收集: 终于:在一堆简历里,精挑细选了四个: 约了:周末上午下午各两个. 面试者年龄:在30-35岁左右,差不多10年. ...
- Bootstrap优秀模板-Unify.2.6.2
这是一个非常老牌的Bootstrap商业模板,全面性和稳定性俱佳,有LandingPage.BussinessPage.AdminPage多种模式,非常推荐用来构建官网.响应式应用Web.管理端Web ...
- STM32学习笔记(一):跑马灯
本实验所采用的开发板为正点原子的MiniSTM32f103rc开发板,主函数程序如下,注释如下:main.c #include "stm32f10x.h" void Delay(u ...
- Vue 进阶之路(四)
之前的文章我们已经对 vue 有了初步认识,这篇文章我们通过一个例子说一下 vue 的样式绑定. 现在我们想要是想这样一个需求,页面上有个单词,当我们点击它的时候颜色变为红色,再点击一次变为原来的颜色 ...
- WebSocket协议详解与c++&c#实现
摘要: 随着手机游戏.H5游戏以及微信小游戏的普及,越来越多的客户端-服务器端的通讯采用websocket协议.Websocket协议是全双工的.基于数据帧的.建立在tcp之上的长连接协议.Webso ...
- Asp.NetCore轻松学-部署到 Linux 进行托管
前言 上一篇文章介绍了如何将开发好的 Asp.Net Core 应用程序部署到 IIS,且学习了进程内托管和进程外托管的区别:接下来就要说说应用 Asp.Net Core 的特性(跨平台),将 .Ne ...
- Spring Boot入门(一):使用IDEA创建Spring Boot项目并使用yaml配置文件
由于公司最近在做技术转型(从.Net转Java),因此自己也开启了学习Java之路.学习Java怎么能不学习这几年这么火的Spring Boot框架,由于自己有总结的习惯,因此会把学习的过程以博客的形 ...
- Python库的安装
window下python2.python3安装包的方法 一.在线安装 安装好python.设置好环境变量后,在python安装目录下Script文件夹内会存在pip.exe和easy_install ...
- Linux记录~持续更新~
ls -ildha /etc -i 显示对应id号 唯一标识 -l 显示详情 -d 显示当前文件夹 不包括子目录 -h 单位为KB 而不是B -a 显示所有 包括隐藏文件 mkdir mkdir -p ...
