javaIO流(四)--输入与输出支持
一.打印流
如果现在要想通过程序实现内容的输出,核心的本质一定要依靠OutputStream类来支持但是OutputStream类有一个最大的缺点,这个类的数据输出操作功能有限,所有的数据一定要转为字节数组后才可以进行才操作:public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException,假设说项目中可能输出的是long,double,date,在这样的情况下就必须将这些数据转变为字节的形式来进行处理,这样的处理一定是非常麻烦的.所以在开发之中最初的时候为了解决此类的重复操作,往往会由开发者自行定义一些功能类来简化输出操作:
class PrintUtil { //实现一些常用数据的山输出
private OutputStream output; //不管如何进行输出操作,核心就是OutputStream
public void print(String str) throws IOException { //输出字符串
this.output.write(str.getBytes());
}
}
--在我们的输出过中,我们的输出操作不可能只会向文件,内存,管道中单一的进行输出,所针对的输出环境可能是非常多的,因此我们无法限定输出环境,因此如果我们在PrintUtil类中直接定义了OutputStream类的实例化对象,那么这个类所完成的代码就将造成严重的耦合(这个类只能对指定的类进行输出使用),既然OutputStream类有很多的子类可以被我们使用,最好的解决办法就是通过构造方法,外部传入OutputStream的对象,我们可以模仿java打印流的实现思路来完善我们的代码:
class PrintUtil implements AutoCloseable { //实现一些常用数据的山输出
private OutputStream output; //不管如何进行输出操作,核心就是OutputStream
public PrintUtil(OutputStream output) {
this.output = output;
}
public void print(long num) throws IOException {
this.print(String.valueOf(num));
}
public void print(String str) throws IOException { //输出字符串
this.output.write(str.getBytes());
}
public void println(long num) throws IOException {
this.println(String.valueOf(num));
}
public void println(String str) throws IOException {
this.print(str + "\r\n");
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
output.close();
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "java_test" + File.separator + "demo01.txt");
PrintUtil printUtil = new PrintUtil(new FileOutputStream(file));
printUtil.println("第一次输出: 你好");
printUtil.println("第二此输出: 你也好");
printUtil.print(",你喜欢写代码吗?");
printUtil.print(123456);
printUtil.close();
}
}
--打开文件查看输出结果
第一次输出: 你好
第二此输出: 你也好
,你喜欢写代码吗?123456
--在整个的操作过程中,打印流的设计思想的本质在于提高已有类的功能,OutputStream类是唯一可以提供输出的操作标标准类,所以应该以其为核心根本,但是这个类输出的操作功能有限,所以不方便进行输出各个数据类型,那么就为他作出了一层包装.上述的代码设计思想那么我们就可以称其为"装饰设计模式".
--既然我们已经发现了原始的OutputStream功能的不足,java的设计者也一定可以发现这个问题,所以在java,io包中为我们提供了打印流:
PrintStream(JDK1.0): 字节打印流

--可以发现在PrintStream的构造方法中又传递了OutputStream,这样的结构形式和代理模式是非常相似的,但是其主要的区别是:代理是围绕接口展开的,代理的时候调用的方法一定是接口中的方法而装饰设计模式中所使用的方法一定不是OutputStream中的方法,
PrintWriter(JDK1.1): 字符打印流
--可以发现PrintWriter的构造方法中,除了可以接收OutputStream以外,还可以接收Writer等参数.
--范例:使用PrintWriter来实现数据的输出操作:
public class PrintWriterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "java_test" + File.separator + "demo01.txt");
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream(file));
printWriter.println("第一次输出: 你好");
printWriter.println("第二此输出: 你也好");
printWriter.print(",你喜欢写代码吗?");
printWriter.print(123456);
printWriter.close();
}
}
--PrintWriter在JDK1.5之后追加了格式化输出操作的支持:public PrintWriter printf(String format, Object ... args)
--范例:格式化输出
public class PrintWriterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "java_test" + File.separator + "demo01.txt");
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream(file));
String name = "张三";
int age = 75;
double money = 45612.5236856;
printWriter.printf("姓名:%s,年龄:%d,收入:%9.2f", name, age, money);
printWriter.close();
}
}
--打开文件查看输出结果
姓名:张三,年龄:75,收入: 45612.52
--相比直接使用OutputStream类,那么使用PrintWriter,PrintStream类的处理操作会更加的简单,因此只要是程序进行内容输出的时候应全部使用打印流.
二.System类的IO的支持
System类是一个系统类,而且是一直都在被使用的系统类,而且在这个类中定义有三个常量:
--System类中的静态常量:
标准输出(显示器):public final static PrintStream out
错误输出:public final static PrintStream err
标准输入(键盘):public final static InputStream in
--范例:查看标准输出与错误输出
public class OutAndErrorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Integer.valueOf("a");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
System.err.println(e);
}
}
}
--运行结果
java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "a"
java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "a" Process finished with exit code 0
---我们所使用的编译器可以为我们进行一些细微的差别优化(颜色),如果使用命令行去编译执行我们的java代码,那么我们将无法区别两者输出显示的差别
--System.out以及System.err是同一种类型的,最早设置两个输出的操作是有目的的:System.out是输出那些希望用户可以看见的信息,而System.err是输出那些不希望用户看见的信息.如果有需要,现在也可以修改输出的位置:
--修改out的输出位置:
public class OutAndErrorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "java_test" + File.separator + "demo02.txt");
System.setErr(new PrintStream(
new FileOutputStream(file)));
try {
Integer.valueOf("a");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
System.err.println(e);
}
}
}
--在System类中还提供有一个in的常量,而这个常量对应的是标准输入设备键盘的输出处理,可以实现键盘的数据输入:
public class SystemInDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream input = System.in; //此时的输入流为键盘输入
System.out.println("请输入信息:");
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
int len = input.read(data);
System.out.println("输入内容为: " + new String(data,0,len));
}
}
--执行结果
请输入信息:
你好
输入内容为: 你好 Process finished with exit code 0
--这样的键盘输入处理,本身是有缺陷的,如果我们接受的数组长度不足,那么只能接受部分数据,所以输入有可能需要进行重复的输入流数据接受,而且在接收的时候,还有可能会牵扯到输入中文的情况,如果我们对中文的处理不当,则有可能造成乱码问题.
三.BufferedReader缓冲流
BufferedReader类提供的是一个缓冲字符输入流的概念,也就是说利用BufferedReader类可以很好的解决输入流数据的读取问题,实际上java.io所提供的Buffer类还有BufferedOutputStream,BufferedInputStream,BufferedWriter等类,但是BufferedReader这个类是在最初的时候提供的最完善的数据输入的处理(JDK1.5),在之后则出了一个功能更为强大的类.之所以我们使用BufferedReader类来处理,因为该方法中有一个重要的方法:public String readLine() throws IOExpection;以换行符为分割点读取一行数据
--BufferedReader类继承结构分析:
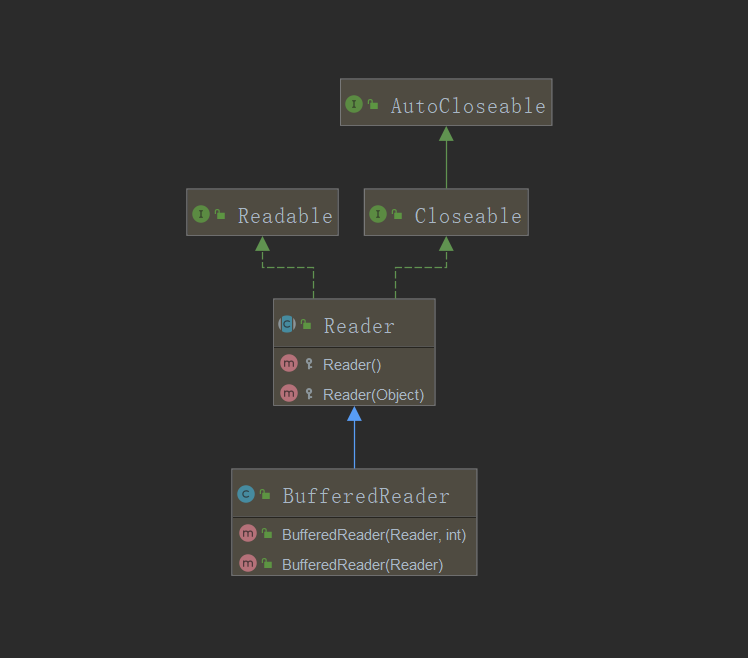
--要先使用此类完成一个键盘输入事件的处理,我们需要知道对于键盘输入事件,java所提供的方法就是System.in(InputStream),而BufferedReader的构造器所接受的是Reader类,因此我们需要使用到转换流:InputStreamReader:
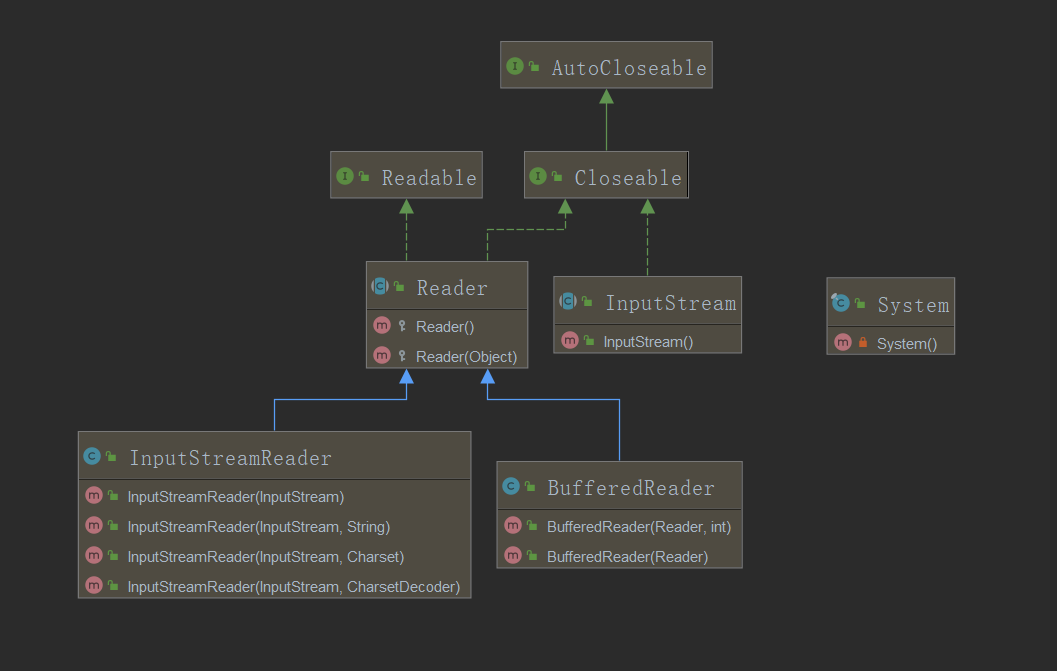
--范例:实现键盘数据输入
public class BufferedReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("请输入信息:");
String msg = input.readLine(); //接收输入信息
System.out.println("输入内容为: " + msg);
}
}
--运行结果
请输入信息:
hello你好
输入内容为: hello你好 Process finished with exit code 0
--在实际的开发之中,经常会遇见输入数据的情况,而所有输入数据的类型,都是通过String描述的,那么这样就方便了接收者进行各种处理
--范例:接收整型数据并验证
public class BufferedReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("请输入您的年龄:");
String msg = ""; //接收输入信息
while (!(msg = input.readLine()).matches("\\d+")) {
System.out.println("您输入的数据有误,请重新输入: ");
}
System.out.println("输入的年龄为: " + msg);
}
}
--运行结果
请输入您的年龄:
sad
您输入的数据有误,请重新输入:
ss
您输入的数据有误,请重新输入:
56
输入的年龄为: 56 Process finished with exit code 0
--对于现代的java开发,由键盘输入数据的情况并不多,但是作为一些基础的逻辑训练,还是可以使用键盘输入数据的,而最早的键盘输入数据的实现做法就是如上的操作
四.Scanner类
Scanner类是在java.util下在JDK1.5之后追加的程序类,其主要的目的是为了解决输入流的访问问题的,可以理解为BufferedReader的替代产品类,此类存在如下构造方法:Scanner(InputStream source)
--常用方法:
判断是否有数据: public boolean hasNext();
取出数据: public String next();
设置分隔符:public Scanner useDelimiter(String pattern)
--范例:使用Scanner实现键盘数据输入:
public class ScannerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入年龄:");
if(scanner.hasNextInt()){ //是否有整数输入
int age = scanner.nextInt(); //直接接收数据
System.out.println("您的年龄: " + age);
}else {
System.out.println("您输入的不对啊");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
--运行结果
请输入年龄:
55
您的年龄: 55 Process finished with exit code 0
--我们可以发现Scanner的处理会更加的简单,使用Scanner输入数据,最大的特点是直接可以结合正则使用进行自定义输入验证:
public class ScannerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您的生日:");
if (!scanner.hasNext("\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}")) {
System.out.println("您的输入有误");
}else {
String birthday = scanner.next();
System.out.println("您的生日为: " + new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").parse(birthday));
}
scanner.close();
}
}
--运行结果
请输入您的生日:
1888-08-05
您的生日为: Sun Aug 05 00:00:00 CST 1888 Process finished with exit code 0
--可以发现Scanner的整体设计要好于BufferReader,而且要比直接使用InputStream类要强大的,读取更加方便.例如现在要读取一个文本文件中的所有内容信息,如果采用的
是InputStream,那么必须采用内存输出流进行临时数据的保存,随后还需要判断读取的内容是否是换行,再进行输出,如果使用Scanner读取则结果如下:
public class ScannerReadFileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "java_test" + File.separator + "demo01.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file);
scanner.useDelimiter("\n"); //设置读取分割符
while (scanner.hasNext()){
System.out.println(scanner.next());
}
scanner.close();
}
}
--运行结果
姓名:张三,年龄:75,收入: 45612.52
姓名:张三,年龄:75,收入: 45612.52
大叔关于不压缩大本营
1561441852
水水水水水水水水水水水水水水 Process finished with exit code 0
--在此我们可以进行如下总结:如果程序需要输出数据一定使用打印流,输入数据使用Scanner(BufferReader)
javaIO流(四)--输入与输出支持的更多相关文章
- Java-IO流之输入输出流基础示例
一.理论: 1.什么是输入输出? 输入输出的对象是数据,数据的存储区域是磁盘或者光盘等设备,我们知道还有一个存储数据的空间----内存,其中磁盘的速度比较慢,内存的速度比较快,把数据读入内存的动作称作 ...
- mybatis学习记录四——输入、输出映射
6 输入映射 通过parameterType指定输入参数的类型,类型可以是简单类型.hashmap.pojo的包装类型. 6.1.1 需求 完成用户信息的综合查询,需要传入查询条件很 ...
- Java:文件字符流和字节流的输入和输出
最近在学习Java,所以就总结一篇文件字节流和字符流的输入和输出. 总的来说,IO流分类如下: 输入输出方向: 输入流(从外设读取到内存)和输出流(从内存输出到外设) 数据的操作方式: 字节流 ...
- 输入和输出--IO流
JavaIO流 首先要理解这个"流"(stream)字:Java把不同的输入,输出源抽象成为流,通过流的方式允许Java程序使用相同的方式来访问不同的输入,输出源.把这里的&quo ...
- 1.java.io包中定义了多个流类型来实现输入和输出功能,
1.java.io包中定义了多个流类型来实现输入和输出功能,可以从不同的角度对其进行分 类,按功能分为:(C),如果为读取的内容进行处理后再输出,需要使用下列哪种流?(G) A.输入流和输出流 B ...
- (19)IO流之字符流FileReader和FileWriter,缓冲字符流---缓冲输入字符流BufferedReader和缓冲输出字符流BufferedWriter
字符流,读取的文件是字符的时候,有两个基类一个是Reader,一个是Writer这有点拟人的感觉,人直接看懂的是文字 字符流 字节流:读取的是文件中的二进制字节流并不会帮你转换成看的懂得字符 字符流: ...
- USB限流IC,输入5V,输出5V,最大3A限流
USB限流芯片,5V输入,输出5V电压,限流值可以通过外围电阻进行调节,PWCHIP产品中可在限流范围0.4A-4.8A,并具有过压关闭保护功能. 过压关闭保护: 如芯片:PW1555,USB我们一半 ...
- (转)MyBatis框架的学习(四)——Mapper.xml文件中的输入和输出映射以及动态sql
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/71893689 前面对MyBatis框架的学习中,我们对Mapper.xml映射文件多少有些了解 ...
- c语言学习笔记第四章——字符串和格式化输入、输出
B站有视频演示 本章学习printf函数的输入输出,字符串的定义与实用. 字符串 字符串(character string)是一个或多个字符的序列,如下所示: "Zing went the ...
随机推荐
- hdu3664 Permutation Counting(dp)
hdu3664 Permutation Counting 题目传送门 题意: 在一个序列中,如果有k个数满足a[i]>i:那么这个序列的E值为k,问你 在n的全排列中,有多少个排列是恰好是E值为 ...
- python学习第三十六天命名空间的概念
python命名空间也叫名字空间,也叫名称空间,任何编程语言都有命名空间,大体意思都一样,定义文件所在的目录,下面详细讲述命名空间几种情况 1,locals: 是函数内的名称空间,包括局部变量和形参 ...
- 如何为自己的网站添加HTTPS服务
如何为自己的网站添加HTTPS服务,针对单个域名而言的,下面介绍网站添加https方法,拿阿里云方法 1.准备证书文件 进入阿里云管理控制台-安全-证书服务点击购买证书服务,进入证书购买页面(放心,我 ...
- 有关css的兼容问题
兼容性 1 页面在不同浏览器中可能显示不同 在IE6下 子级的宽度会撑开父级设置好的宽度 温馨提示:和模型的计算一定要精确,IE浏览器可能显示不同 兼容性 2 在IE6中,元素浮 ...
- 《TED演讲的秘密》:TED组织者总结的演讲技巧集锦。三星推荐。
对演讲感兴趣的可以看看.对TED内容感兴趣的也可以翻翻,书中有不少作者认为演讲技巧比较经典(一般来说内容上也有特色)的TED演讲的二维码.三星推荐.http://t.cn/RvFStu7
- excel条件格式 满足包含xx的整行高亮
条件格式-->新建规则-->使用公式确定要设置格式的单元格 =COUNTIF($D4,"*_S_*") =COUNTIF($D4,"*_M_*&quo ...
- [BZOJ3625][Codeforces Round #250]小朋友和二叉树 多项式开根+求逆
https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3625 愉快地列式子.设\(F[i]\)表示权值为\(i\) 的子树的方案数,\(A[i]\)为\( ...
- 自建云存储:Nextcloud vs. ownCloud vs. Seafile
Self-hosted Cloud Storage: Nextcloud vs. ownCloud vs. Seafile By Ashutosh KS in Hosting. Updated on ...
- springMVC使用map接收入参 + mybatis使用map 传入查询参数
测试例子: controllel层 ,使用map接收请求参数,通过Debug可以看到,请求中的参数的值都是字符串形式,如果将这个接收参数的map直接传入service,mybatis接收参数时会报错, ...
- 线性规划(Simplex单纯形)与对偶问题
线性规划 首先一般所有的线性规划问题我们都可以转换成如下标准型: 但是我们可以发现上面都是不等式,而我们计算中更希望是等式,所以我们引入这个新的概念:松弛型: 很显然我们最后要求是所有的约束左边的变量 ...
