Music in Car
1 second
256 megabytes
Sasha reaches the work by car. It takes exactly k minutes. On his way he listens to music. All songs in his playlist go one by one, after listening to the i-th song Sasha gets a pleasure which equals ai. The i-th song lasts for ti minutes.
Before the beginning of his way Sasha turns on some song x and then he listens to the songs one by one: at first, the song x, then the song (x + 1), then the song number (x + 2), and so on. He listens to songs until he reaches the work or until he listens to the last song in his playlist.
Sasha can listen to each song to the end or partly.
In the second case he listens to the song for integer number of minutes, at least half of the song's length. Formally, if the length of the song equals d minutes, Sasha listens to it for no less than 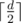 minutes, then he immediately switches it to the next song (if there is such). For example, if the length of the song which Sasha wants to partly listen to, equals 5 minutes, then he should listen to it for at least 3 minutes, if the length of the song equals 8 minutes, then he should listen to it for at least 4 minutes.
minutes, then he immediately switches it to the next song (if there is such). For example, if the length of the song which Sasha wants to partly listen to, equals 5 minutes, then he should listen to it for at least 3 minutes, if the length of the song equals 8 minutes, then he should listen to it for at least 4 minutes.
It takes no time to switch a song.
Sasha wants to listen partly no more than w songs. If the last listened song plays for less than half of its length, then Sasha doesn't get pleasure from it and that song is not included to the list of partly listened songs. It is not allowed to skip songs. A pleasure from a song does not depend on the listening mode, for the i-th song this value equals ai.
Help Sasha to choose such x and no more than w songs for partial listening to get the maximum pleasure. Write a program to find the maximum pleasure Sasha can get from the listening to the songs on his way to the work.
The first line contains three integers n, w and k (1 ≤ w ≤ n ≤ 2·105, 1 ≤ k ≤ 2·109) — the number of songs in the playlist, the number of songs Sasha can listen to partly and time in minutes which Sasha needs to reach work.
The second line contains n positive integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 104), where ai equals the pleasure Sasha gets after listening to thei-th song.
The third line contains n positive integers t1, t2, ..., tn (2 ≤ ti ≤ 104), where ti equals the length of the i-th song in minutes.
Print the maximum pleasure Sasha can get after listening to the songs on the way to work.
7 2 11
3 4 3 5 1 4 6
7 7 3 6 5 3 9
12
8 4 20
5 6 4 3 7 5 4 1
10 12 5 12 14 8 5 8
19
1 1 5
6
9
6
1 1 3
4
7
0
In the first example Sasha needs to start listening from the song number 2. He should listen to it partly (for 4 minutes), then listen to the song number 3 to the end (for 3 minutes) and then partly listen to the song number 4 (for 3 minutes). After listening to these songs Sasha will get pleasure which equals 4 + 3 + 5 = 12. Sasha will not have time to listen to the song number 5 because he will spend4 + 3 + 3 = 10 minutes listening to songs number 2, 3 and 4 and only 1 minute is left after that.
分析:two pointer+ two sets;
一个set维护听part的歌曲,一个维护full;
右指针向右时,优先考虑能否part,若不能,考虑full或将part里替换出一个来;
左指针向右delete后,考虑能否将full的加到part里;
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#define rep(i,m,n) for(i=m;i<=n;i++)
#define mod 1000000007
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define vi vector<int>
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define ll long long
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define Lson L, mid, ls[rt]
#define Rson mid+1, R, rs[rt]
#define sys system("pause")
const int maxn=2e5+;
using namespace std;
ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==?p:gcd(q,p%q);}
ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=;while(q){if(q&)f=f*p%mod;p=p*p%mod;q>>=;}return f;}
inline void umax(int &p,int q){if(p<q)p=q;}
inline void umin(int &p,int q){if(p>q)p=q;}
inline ll read()
{
ll x=;int f=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<''||ch>''){if(ch=='-')f=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){x=x*+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
int n,m,k,w,a[maxn],t[maxn],ma,now;
set<pii>full,half;
int main()
{
int i,j;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&k,&w);
rep(i,,n)a[i]=read();
rep(i,,n)t[i]=read();
int l,r;
l=r=;
while(r<=n)
{
//right pointer;
while(r<=n)
{
if(k)
{
if(w>=(t[r]+)/)
{
w-=(t[r]+)/;
umax(ma,now+=a[r]);
half.insert(mp(t[r],r));
r++;
k--;
}
else break;
}
else
{
int tmp=half.begin()->fi;
if(tmp<=t[r]&&w>=(t[r]+)/-(tmp+)/+tmp)
{
w-=(t[r]+)/-(tmp+)/+tmp;
umax(ma,now+=a[r]);
auto p=half.begin();
full.insert(*p);
half.erase(p);
half.insert(mp(t[r],r));
r++;
}
else if(tmp>t[r]&&w>=t[r])
{
w-=t[r];
umax(ma,now+=a[r]);
full.insert(mp(t[r],r));
r++;
}
else break;
}
}
//left pointer;
if(l<r)
{
if(full.find(mp(t[l],l))!=full.end())
{
w+=t[l];
now-=a[l];
full.erase(mp(t[l],l));
}
else
{
w+=(t[l]+)/;
now-=a[l];
half.erase(mp(t[l],l));
k++;
if(!full.empty())
{
auto p=--full.end();
w+=p->fi-(p->fi+)/;
half.insert(*p);
k--;
full.erase(p);
}
}
l++;
}
else l++,r++;
}
printf("%d\n",ma);
return ;
}
随机推荐
- luogu1345 奶牛的电信
拆点.最小割的模板题. 我只想说一点.拆点时不可以下意识地初始化!起点和终点不能直接写编号!写拆点后的Id! #include <cstdio> #include <cstring& ...
- C++ Web 编程(菜鸟教程)
C++ Web 编程(菜鸟教程) C++ Web 编程 什么是 CGI? 公共网关接口(CGI),是一套标准,定义了信息是如何在 Web 服务器和客户端脚本之间进行交换的. CGI 规范目前是由 NC ...
- .NET页面事件执行顺序
摘自:http://www.cnblogs.com/kenkofox/archive/2011/03/18/1987998.html和http://blog.csdn.net/yiruoyun/art ...
- A Round Peg in a Ground Hole(圆与凸包)
http://poj.org/problem?id=1584 题意:判断所给的点能不能形成凸包,并判断所给的圆是否在凸包内. 改了好几天的一个题,今天才发现是输入顺序弄错了,办过的最脑残的事情..sa ...
- codevs2800送外卖(floyd+状压dp)
2800 送外卖 时间限制: 2 s 空间限制: 256000 KB 题目等级 : 钻石 Diamond 题目描述 Description 有一个送外卖的,他手上有n份订单,他要把n份东 ...
- c#,Java aes加密
1.c#版本 /// <summary> /// Aes加密解密.c#版 /// </summary> public class BjfxEncryptHelper { /// ...
- BZOJ 1037 生日聚会 DP
[ZJOI2008]生日聚会Party Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MB Description 今天是hidadz小朋友的生日,她邀请了许多朋友来参加她 ...
- 安卓手机USB无法共享、上网或卡顿的解决方法
安卓手机通过USB为电脑(Windows10)提供网络接入点时,系统程序会异常卡顿. 1)设备管理器2)点击“网络适配器”,在弹出的下拉列表中选择”Remote NDIS based Internet ...
- EnforceLearning-被动强化学习
前言: 画图挺好:深度学习进阶之路-从迁移学习到强化学习 专家系统给出了知识节点和规则,使用粒度描述准确性,依靠分解粒度解决矛盾,并反馈知识和推理规则更新.专家系统与机器学习有本质区别,但从机器学习的 ...
- OpenCV中IplImage/CvMat/Mat转化关系
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/summerRQ/articles/2406109.html 如对内容和版权有何疑问,请拜访原作者或者通知本人. opencv中常见的与图像操作 ...
