机器学习中,使用NMS对框取优
一、NMS实现代码
# http://www.pyimagesearch.com/2015/02/16/faster-non-maximum-suppression-python/ import numpy as np class NMSuppression(object):
def __init__(self, bbs, overlapThreshold = 0.45):
self.bbs = bbs
self.overlapThreshold = overlapThreshold def _check_empty(self):
# return an empty list, if there are no boxes
if len(self.bbs) == 0:
return []
else:
return self.bbs def _check_dtype(self):
# if the bounding boxes integers, convert them to floats (divisions)
if self.bbs.dtype.kind == "i":
self.bbs = self.bbs.astype("float")
return self.bbs def bb_coordinates(self):
# get the coordinates of the bounding boxes
x1 = self.bbs[:, 0]
y1 = self.bbs[:, 1]
x2 = self.bbs[:, 2]
y2 = self.bbs[:, 3]
return x1, y1, x2, y2 def bb_area(self):
# compute the area of the bounding boxes
x1, y1, x2, y2 = self.bb_coordinates()
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
return area def calc_ovarlap(self, x1, y1, x2, y2, idxs, last, i, area):
# find the largest (x, y) coordinates for the start of
# the bounding box and the smallest (x, y) coordinates
# for the end of the bounding box
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idxs[:last]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idxs[:last]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idxs[:last]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idxs[:last]]) # compute the width and height of the bounding box
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1) # compute the ratio of overlap
overlap = (w * h) / area[idxs[:last]] return overlap def slow_suppress(self):
self._check_empty()
self._check_dtype() # initialize the list of picked indexes
picked = [] x1, y1, x2, y2 = self.bb_coordinates() # compute the area of the bounding boxes
area = self.bb_area() # sort the bounding boxes by the bottom-right y-coordinate of the bounding box
idxs = np.argsort(y2) # keep looping while some indexes still remain in the indexes list
while len(idxs) > 0:
# grab the last index in the indexes list, add the index
# value to the list of picked indexes, then initialize
# the suppression list (i.e. indexes that will be deleted)
# using the last index
last = len(idxs) - 1
i = idxs[last]
picked.append(i)
suppress = [last] # loop over all indexes in the indexes list
for pos in xrange(0, last):
# grab the current index
j = idxs[pos] # find the largest (x, y) coordinates for the start of
# the bounding box and the smallest (x, y) coordinates
# for the end of the bounding box
xx1 = max(x1[i], x1[j])
yy1 = max(y1[i], y1[j])
xx2 = min(x2[i], x2[j])
yy2 = min(y2[i], y2[j]) # compute the width and height of the bounding box
w = max(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = max(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1) # compute the ratio of overlap between the computed
# bounding box and the bounding box in the area list
overlap = float(w * h) / area[j] # if there is sufficient overlap, suppress the
# current bounding box
if overlap > self.overlapThreshold:
suppress.append(pos) # delete all indexes from the index list that are in the
# suppression list
idxs = np.delete(idxs, suppress) # return only the bounding boxes that were picked
return self.bbs[picked] def fast_suppress(self):
self._check_empty()
self._check_dtype() # initialize the list of picked indexes
picked = [] x1, y1, x2, y2 = self.bb_coordinates() # compute the area of the bounding boxes
area = self.bb_area() # sort the bounding boxes by the bottom-right y-coordinate of the bounding box
idxs = np.argsort(y2) # keep looping while some indexes still remain in the indexes list
while len(idxs) > 0:
# take the last index in the indexes list and add the
# index value to the list of picked indexes
last = len(idxs) - 1
i = idxs[last]
picked.append(i) overlap = self.calc_ovarlap(x1, y1, x2, y2, idxs, last, i, area) # delete all indexes from the index list that have
idxs = np.delete(idxs, np.concatenate(([last], np.where(overlap > self.overlapThreshold)[0]))) # return only the bounding boxes that were picked using the
# integer data type return self.bbs[picked].astype("int")
二、调用测试
#taken from: http://www.pyimagesearch.com/2014/11/17/non-maximum-suppression-object-detection-python
"""
Project parts (taken from the tutorial above):
1. Sampling positive images
2. Sampling negative images
3. Training a Linear SVM
4. Performing hard-negative mining
5. Re-training your Linear SVM using the hard-negative samples
6. Evaluating your classifier on your test dataset, utilizing non-maximum
suppression to ignore redundant, overlapping bounding boxes The sample images in this project are taken from the web (labeled as: no licensing needed for non-comertial use).
""" from nm_suppression import NMSuppression
import numpy as np
import cv2 # construct a list containing the images that will be examined
# along with their respective bounding boxes
images = [
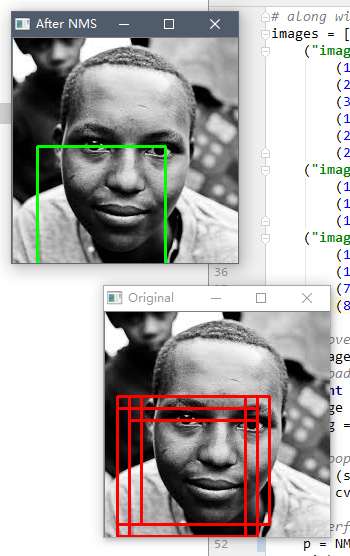
("images/africa.jpeg", np.array([
(12, 84, 140, 212),
(24, 84, 152, 212),
(36, 84, 164, 212),
(12, 96, 140, 224),
(24, 96, 152, 224),
(24, 108, 152, 236)])),
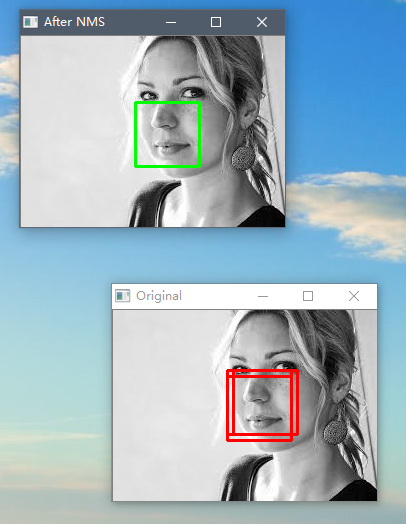
("images/girl.jpeg", np.array([
(114, 60, 178, 124),
(120, 60, 184, 124),
(114, 66, 178, 130)])),
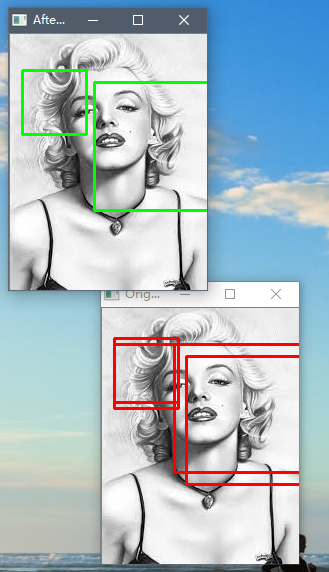
("images/monroe.jpeg", np.array([
(12, 30, 76, 94),
(12, 36, 76, 100),
(72, 36, 200, 164),
(84, 48, 212, 176)]))] # loop over the images
for (imagePath, boundingBoxes) in images:
# load the image and clone it
print "[x] %d initial bounding boxes" % (len(boundingBoxes))
image = cv2.imread(imagePath)
orig = image.copy() # loop over the bounding boxes for each image and draw them
for (startX, startY, endX, endY) in boundingBoxes:
cv2.rectangle(orig, (startX, startY), (endX, endY), (0, 0, 255), 2) # perform non-maximum suppression on the bounding boxes
p = NMSuppression(bbs=boundingBoxes, overlapThreshold=0.5)
pick = p.fast_suppress()
print "[x] after applying non-maximum, %d bounding boxes" % (len(pick)) # loop over the picked bounding boxes and draw them
for (startX, startY, endX, endY) in pick:
cv2.rectangle(image, (startX, startY), (endX, endY), (0, 255, 0), 2) # display the images
cv2.imshow("Original", orig)
cv2.imshow("After NMS", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
三、效果
机器学习中,使用NMS对框取优的更多相关文章
- paper 126:[转载] 机器学习中的范数规则化之(一)L0、L1与L2范数
机器学习中的范数规则化之(一)L0.L1与L2范数 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 今天我们聊聊机器学习中出现的非常频繁的问题:过拟合与规则化. ...
- 机器学习中的范数规则化之(一)L0、L1与L2范数(转)
http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/24971995 机器学习中的范数规则化之(一)L0.L1与L2范数 zouxy09@qq.com http: ...
- 机器学习中的范数规则化之(一)L0、L1与L2范数 非常好,必看
机器学习中的范数规则化之(一)L0.L1与L2范数 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 今天我们聊聊机器学习中出现的非常频繁的问题:过拟合与规则化. ...
- 机器学习中的范数规则化-L0,L1和L2范式(转载)
机器学习中的范数规则化之(一)L0.L1与L2范数 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 今天我们聊聊机器学习中出现的非常频繁的问题:过拟合与规则化. ...
- 机器学习中模型泛化能力和过拟合现象(overfitting)的矛盾、以及其主要缓解方法正则化技术原理初探
1. 偏差与方差 - 机器学习算法泛化性能分析 在一个项目中,我们通过设计和训练得到了一个model,该model的泛化可能很好,也可能不尽如人意,其背后的决定因素是什么呢?或者说我们可以从哪些方面去 ...
- 机器学习中的算法(2)-支持向量机(SVM)基础
版权声明:本文由LeftNotEasy发布于http://leftnoteasy.cnblogs.com, 本文可以被全部的转载或者部分使用,但请注明出处,如果有问题,请联系wheeleast@gma ...
- 机器学习中的规则化范数(L0, L1, L2, 核范数)
目录: 一.L0,L1范数 二.L2范数 三.核范数 今天我们聊聊机器学习中出现的非常频繁的问题:过拟合与规则化.我们先简单的来理解下常用的L0.L1.L2和核范数规则化.最后聊下规则化项参数的选择问 ...
- 机器学习中的损失函数 (着重比较:hinge loss vs softmax loss)
https://blog.csdn.net/u010976453/article/details/78488279 1. 损失函数 损失函数(Loss function)是用来估量你模型的预测值 f( ...
- 机器学习中的范数规则化 L0、L1与L2范数 核范数与规则项参数选择
http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/24971995 机器学习中的范数规则化之(一)L0.L1与L2范数 zouxy09@qq.com http: ...
随机推荐
- 查看webservice服务下的所有方法和参数类型
方法:直接在IE浏览器中输入webservice的地址,查看返回的XML数据即可. 效果如下:
- spring源码之—Assert.notNull
org.springframework.util.Assert Assert翻译为中文为"断言".用过JUNIT的应该都知道这个概念了. 就是断定某一个实际的值就为自己预期想得到的 ...
- Oracle 备份、恢复单表或多表数据步骤
Oracle 备份.恢复单表或多表数据步骤,适用于 Oracle 8.9.10. *备份单表或多表数据: exp user/password@server file=filefullpa ...
- ntp测试
cmd下 w32tm /stripchart /computer:time1.aliyun.com linux ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com
- JDK(Java SE Development Kit)的安装与环境变量的配置
本文参考于:http://jingyan.baidu.com/article/6dad5075d1dc40a123e36ea3.html 感谢作者的贡献~ 首先,进入网址下载JDK:http://ww ...
- [转]InnoDB和MyISAM区别
From : http://blog.csdn.net/ghosc/article/details/5391544 MySQL作为当前最为流行的免费数据库服务引擎,已经风靡了很长一段时间,不过也许也有 ...
- C/C++ signal 信号处理函数
软中断信号(signal,又简称为信号)用来通知进程发生了异步事件.进程之间可以互相通过系统调用kill发送软中断信号. 内核也可以因为内部事件而给进程发送信号,通知进程发生了某个事件. 注意,信号只 ...
- Linux下线程同步的几种方法
Linux下提供了多种方式来处理线程同步,最常用的是互斥锁.条件变量和信号量. 一.互斥锁(mutex) 锁机制是同一时刻只允许一个线程执行一个关键部分的代码. 1. 初始化锁 int pthrea ...
- Neo4j 2.0 生产环境集群搭建
一.在windows上搭建Neo4j ha cluster的配置方法: 例如:建立集群的三台机器的ip分别为:10.230.9.91,10.230.9.92,10.230.9.93. 10.230.9 ...
- ES6 主要的新特性
本文基于lukehoban/es6features ,同时参考了大量博客资料,具体见文末引用. ES6(ECMAScript 6)是即将到来的新版本JavaScript语言的标准,代号harmony( ...
