HBase读写的几种方式(三)flink篇
1. HBase连接的方式概况
主要分为:
- 纯Java API读写HBase的方式;
- Spark读写HBase的方式;
- Flink读写HBase的方式;
- HBase通过Phoenix读写的方式;
第一种方式是HBase自身提供的比较原始的高效操作方式,而第二、第三则分别是Spark、Flink集成HBase的方式,最后一种是第三方插件Phoenix集成的JDBC方式,Phoenix集成的JDBC操作方式也能在Spark、Flink中调用。
注意:
这里我们使用HBase2.1.2版本,flink1.7.2版本,scala-2.12版本。
2. Flink Streaming和Flink DataSet读写HBase
Flink上读取HBase数据有两种方式:
- 继承RichSourceFunction重写父类方法(flink streaming)
- 实现自定义TableInputFormat接口(flink streaming和flink dataSet)
Flink上将数据写入HBase也有两种方式:
- 继承RichSinkFunction重写父类方法(flink streaming)
- 实现OutputFormat接口(flink streaming和flink dataSet)
注意:
① Flink Streaming流式处理有上述两种方式;但是Flink DataSet批处理,读只有“实现TableInputFormat接口”一种方式,写只有”实现OutputFormat接口“一种方式。
②TableInputFormat接口是在flink-hbase-2.12-1.7.2里面的,而该jar包对应的hbase版本是1.4.3,而项目中我们使用HBase2.1.2版本,故需要对TableInputFormat重写。
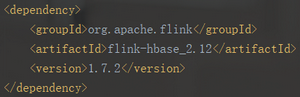
2.1 Flink读取HBase的两种方式
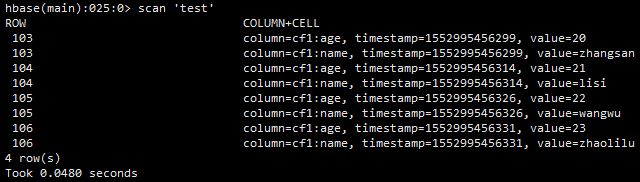
注意:读取HBase之前可以先执行节点2.2.2实现OutputFormat接口:Flink dataSet 批处理写入HBase的方法,确保HBase test表里面有数据,数据如下:
2.1.1 继承RichSourceFunction重写父类方法:
package cn.swordfall.hbaseOnFlink import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.RichSourceFunction
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.SourceFunction.SourceContext
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.{Cell, HBaseConfiguration, HConstants, TableName}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.{Connection, ConnectionFactory, Scan, Table}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes
import scala.collection.JavaConverters._
/**
* @Author: Yang JianQiu
* @Date: 2019/2/28 18:05
*
* 以HBase为数据源
* 从HBase中获取数据,然后以流的形式发射
*
* 从HBase读取数据
* 第一种:继承RichSourceFunction重写父类方法
*/
class HBaseReader extends RichSourceFunction[(String, String)]{ private var conn: Connection = null
private var table: Table = null
private var scan: Scan = null /**
* 在open方法使用HBase的客户端连接
* @param parameters
*/
override def open(parameters: Configuration): Unit = {
val config: org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create() config.set(HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_QUORUM, "192.168.187.201")
config.set(HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT, "2181")
config.setInt(HConstants.HBASE_CLIENT_OPERATION_TIMEOUT, 30000)
config.setInt(HConstants.HBASE_CLIENT_SCANNER_TIMEOUT_PERIOD, 30000) val tableName: TableName = TableName.valueOf("test")
val cf1: String = "cf1"
conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config)
table = conn.getTable(tableName)
scan = new Scan()
scan.withStartRow(Bytes.toBytes("100"))
scan.withStopRow(Bytes.toBytes("107"))
scan.addFamily(Bytes.toBytes(cf1))
} /**
* run方法来自java的接口文件SourceFunction,使用IDEA工具Ctrl + o 无法便捷获取到该方法,直接override会提示
* @param sourceContext
*/
override def run(sourceContext: SourceContext[(String, String)]): Unit = {
val rs = table.getScanner(scan)
val iterator = rs.iterator()
while (iterator.hasNext){
val result = iterator.next()
val rowKey = Bytes.toString(result.getRow)
val sb: StringBuffer = new StringBuffer()
for (cell:Cell <- result.listCells().asScala){
val value = Bytes.toString(cell.getValueArray, cell.getValueOffset, cell.getValueLength)
sb.append(value).append("_")
}
val valueString = sb.replace(sb.length() - 1, sb.length(), "").toString
sourceContext.collect((rowKey, valueString))
}
} /**
* 必须添加
*/
override def cancel(): Unit = { } /**
* 关闭hbase的连接,关闭table表
*/
override def close(): Unit = {
try {
if (table != null) {
table.close()
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close()
}
} catch {
case e:Exception => println(e.getMessage)
}
}
}
调用继承RichSourceFunction的HBaseReader类,Flink Streaming流式处理的方式:
/**
* 从HBase读取数据
* 第一种:继承RichSourceFunction重写父类方法
*/
def readFromHBaseWithRichSourceFunction(): Unit ={
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.enableCheckpointing(5000)
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
env.getCheckpointConfig.setCheckpointingMode(CheckpointingMode.EXACTLY_ONCE)
val dataStream: DataStream[(String, String)] = env.addSource(new HBaseReader)
dataStream.map(x => println(x._1 + " " + x._2))
env.execute()
}
2.1.2 实现自定义的TableInputFormat接口:
由于版本不匹配,这里我们需要对flink-hbase-2.12-1.7.2里面的三个文件进行重写,分别是TableInputSplit、AbstractTableInputFormat、TableInputFormat
TableInputSplit重写为CustomTableInputSplit:
package cn.swordfall.hbaseOnFlink.flink172_hbase212; import org.apache.flink.core.io.LocatableInputSplit; /**
* @Author: Yang JianQiu
* @Date: 2019/3/19 11:50
*/
public class CustomTableInputSplit extends LocatableInputSplit {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** The name of the table to retrieve data from. */
private final byte[] tableName; /** The start row of the split. */
private final byte[] startRow; /** The end row of the split. */
private final byte[] endRow; /**
* Creates a new table input split.
*
* @param splitNumber
* the number of the input split
* @param hostnames
* the names of the hosts storing the data the input split refers to
* @param tableName
* the name of the table to retrieve data from
* @param startRow
* the start row of the split
* @param endRow
* the end row of the split
*/
CustomTableInputSplit(final int splitNumber, final String[] hostnames, final byte[] tableName, final byte[] startRow,
final byte[] endRow) {
super(splitNumber, hostnames); this.tableName = tableName;
this.startRow = startRow;
this.endRow = endRow;
} /**
* Returns the table name.
*
* @return The table name.
*/
public byte[] getTableName() {
return this.tableName;
} /**
* Returns the start row.
*
* @return The start row.
*/
public byte[] getStartRow() {
return this.startRow;
} /**
* Returns the end row.
*
* @return The end row.
*/
public byte[] getEndRow() {
return this.endRow;
}
}
AbstractTableInputFormat重写为CustomeAbstractTableInputFormat:
package cn.swordfall.hbaseOnFlink.flink172_hbase212; import org.apache.flink.addons.hbase.AbstractTableInputFormat;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.io.LocatableInputSplitAssigner;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.io.RichInputFormat;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.io.statistics.BaseStatistics;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.flink.core.io.InputSplitAssigner;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Result;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ResultScanner;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Scan;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Pair;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; /**
* @Author: Yang JianQiu
* @Date: 2019/3/19 11:16
*
* 由于flink-hbase_2.12_1.7.2 jar包所引用的是hbase1.4.3版本,而现在用到的是hbase2.1.2,版本不匹配
* 故需要重写flink-hbase_2.12_1.7.2里面的AbstractTableInputFormat,主要原因是AbstractTableInputFormat里面调用的是hbase1.4.3版本的api,
* 而新版本hbase2.1.2已经去掉某些api
*/
public abstract class CustomAbstractTableInputFormat<T> extends RichInputFormat<T, CustomTableInputSplit> {
protected static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbstractTableInputFormat.class); // helper variable to decide whether the input is exhausted or not
protected boolean endReached = false; protected transient HTable table = null;
protected transient Scan scan = null; /** HBase iterator wrapper. */
protected ResultScanner resultScanner = null; protected byte[] currentRow;
protected long scannedRows; /**
* Returns an instance of Scan that retrieves the required subset of records from the HBase table.
*
* @return The appropriate instance of Scan for this use case.
*/
protected abstract Scan getScanner(); /**
* What table is to be read.
*
* <p>Per instance of a TableInputFormat derivative only a single table name is possible.
*
* @return The name of the table
*/
protected abstract String getTableName(); /**
* HBase returns an instance of {@link Result}.
*
* <p>This method maps the returned {@link Result} instance into the output type {@link T}.
*
* @param r The Result instance from HBase that needs to be converted
* @return The appropriate instance of {@link T} that contains the data of Result.
*/
protected abstract T mapResultToOutType(Result r); /**
* Creates a {@link Scan} object and opens the {@link HTable} connection.
*
* <p>These are opened here because they are needed in the createInputSplits
* which is called before the openInputFormat method.
*
* <p>The connection is opened in this method and closed in {@link #closeInputFormat()}.
*
* @param parameters The configuration that is to be used
* @see Configuration
*/
@Override
public abstract void configure(Configuration parameters); @Override
public void open(CustomTableInputSplit split) throws IOException {
if (table == null) {
throw new IOException("The HBase table has not been opened! " +
"This needs to be done in configure().");
}
if (scan == null) {
throw new IOException("Scan has not been initialized! " +
"This needs to be done in configure().");
}
if (split == null) {
throw new IOException("Input split is null!");
} logSplitInfo("opening", split); // set scan range
currentRow = split.getStartRow();
/* scan.setStartRow(currentRow);
scan.setStopRow(split.getEndRow());*/
scan.withStartRow(currentRow);
scan.withStopRow(split.getEndRow()); resultScanner = table.getScanner(scan);
endReached = false;
scannedRows = 0;
} @Override
public T nextRecord(T reuse) throws IOException {
if (resultScanner == null) {
throw new IOException("No table result scanner provided!");
}
try {
Result res = resultScanner.next();
if (res != null) {
scannedRows++;
currentRow = res.getRow();
return mapResultToOutType(res);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
resultScanner.close();
//workaround for timeout on scan
LOG.warn("Error after scan of " + scannedRows + " rows. Retry with a new scanner...", e);
/*scan.setStartRow(currentRow);*/
scan.withStartRow(currentRow);
resultScanner = table.getScanner(scan);
Result res = resultScanner.next();
if (res != null) {
scannedRows++;
currentRow = res.getRow();
return mapResultToOutType(res);
}
} endReached = true;
return null;
} private void logSplitInfo(String action, CustomTableInputSplit split) {
int splitId = split.getSplitNumber();
String splitStart = Bytes.toString(split.getStartRow());
String splitEnd = Bytes.toString(split.getEndRow());
String splitStartKey = splitStart.isEmpty() ? "-" : splitStart;
String splitStopKey = splitEnd.isEmpty() ? "-" : splitEnd;
String[] hostnames = split.getHostnames();
LOG.info("{} split (this={})[{}|{}|{}|{}]", action, this, splitId, hostnames, splitStartKey, splitStopKey);
} @Override
public boolean reachedEnd() throws IOException {
return endReached;
} @Override
public void close() throws IOException {
LOG.info("Closing split (scanned {} rows)", scannedRows);
currentRow = null;
try {
if (resultScanner != null) {
resultScanner.close();
}
} finally {
resultScanner = null;
}
} @Override
public void closeInputFormat() throws IOException {
try {
if (table != null) {
table.close();
}
} finally {
table = null;
}
} @Override
public CustomTableInputSplit[] createInputSplits(final int minNumSplits) throws IOException {
if (table == null) {
throw new IOException("The HBase table has not been opened! " +
"This needs to be done in configure().");
}
if (scan == null) {
throw new IOException("Scan has not been initialized! " +
"This needs to be done in configure().");
} // Get the starting and ending row keys for every region in the currently open table
final Pair<byte[][], byte[][]> keys = table.getRegionLocator().getStartEndKeys();
if (keys == null || keys.getFirst() == null || keys.getFirst().length == 0) {
throw new IOException("Expecting at least one region.");
}
final byte[] startRow = scan.getStartRow();
final byte[] stopRow = scan.getStopRow();
final boolean scanWithNoLowerBound = startRow.length == 0;
final boolean scanWithNoUpperBound = stopRow.length == 0; final List<CustomTableInputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<CustomTableInputSplit>(minNumSplits);
for (int i = 0; i < keys.getFirst().length; i++) {
final byte[] startKey = keys.getFirst()[i];
final byte[] endKey = keys.getSecond()[i];
final String regionLocation = table.getRegionLocator().getRegionLocation(startKey, false).getHostnamePort();
// Test if the given region is to be included in the InputSplit while splitting the regions of a table
if (!includeRegionInScan(startKey, endKey)) {
continue;
}
// Find the region on which the given row is being served
final String[] hosts = new String[]{regionLocation}; // Determine if regions contains keys used by the scan
boolean isLastRegion = endKey.length == 0;
if ((scanWithNoLowerBound || isLastRegion || Bytes.compareTo(startRow, endKey) < 0) &&
(scanWithNoUpperBound || Bytes.compareTo(stopRow, startKey) > 0)) { final byte[] splitStart = scanWithNoLowerBound || Bytes.compareTo(startKey, startRow) >= 0 ? startKey : startRow;
final byte[] splitStop = (scanWithNoUpperBound || Bytes.compareTo(endKey, stopRow) <= 0)
&& !isLastRegion ? endKey : stopRow;
int id = splits.size();
final CustomTableInputSplit split = new CustomTableInputSplit(id, hosts, table.getName().getName(), splitStart, splitStop);
splits.add(split);
}
}
LOG.info("Created " + splits.size() + " splits");
for (CustomTableInputSplit split : splits) {
logSplitInfo("created", split);
}
return splits.toArray(new CustomTableInputSplit[splits.size()]);
} /**
* Test if the given region is to be included in the scan while splitting the regions of a table.
*
* @param startKey Start key of the region
* @param endKey End key of the region
* @return true, if this region needs to be included as part of the input (default).
*/
protected boolean includeRegionInScan(final byte[] startKey, final byte[] endKey) {
return true;
} @Override
public InputSplitAssigner getInputSplitAssigner(CustomTableInputSplit[] inputSplits) {
return new LocatableInputSplitAssigner(inputSplits);
} @Override
public BaseStatistics getStatistics(BaseStatistics cachedStatistics) {
return null;
}
}
TableInputFormat重写为CustomTableInputFormat:
package cn.swordfall.hbaseOnFlink.flink172_hbase212; import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Result;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Scan; /**
* @Author: Yang JianQiu
* @Date: 2019/3/19 11:15
* 由于flink-hbase_2.12_1.7.2 jar包所引用的是hbase1.4.3版本,而现在用到的是hbase2.1.2,版本不匹配
* 故需要重写flink-hbase_2.12_1.7.2里面的TableInputFormat
*/
public abstract class CustomTableInputFormat<T extends Tuple> extends CustomAbstractTableInputFormat<T> { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /**
* Returns an instance of Scan that retrieves the required subset of records from the HBase table.
* @return The appropriate instance of Scan for this usecase.
*/
@Override
protected abstract Scan getScanner(); /**
* What table is to be read.
* Per instance of a TableInputFormat derivative only a single tablename is possible.
* @return The name of the table
*/
@Override
protected abstract String getTableName(); /**
* The output from HBase is always an instance of {@link Result}.
* This method is to copy the data in the Result instance into the required {@link Tuple}
* @param r The Result instance from HBase that needs to be converted
* @return The appropriate instance of {@link Tuple} that contains the needed information.
*/
protected abstract T mapResultToTuple(Result r); /**
* Creates a {@link Scan} object and opens the {@link HTable} connection.
* These are opened here because they are needed in the createInputSplits
* which is called before the openInputFormat method.
* So the connection is opened in {@link #configure(Configuration)} and closed in {@link #closeInputFormat()}.
*
* @param parameters The configuration that is to be used
* @see Configuration
*/
@Override
public void configure(Configuration parameters) {
table = createTable();
if (table != null) {
scan = getScanner();
}
} /**
* Create an {@link HTable} instance and set it into this format.
*/
private HTable createTable() {
LOG.info("Initializing HBaseConfiguration");
//use files found in the classpath
org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration hConf = HBaseConfiguration.create(); try {
return null;
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("Error instantiating a new HTable instance", e);
}
return null;
} @Override
protected T mapResultToOutType(Result r) {
return mapResultToTuple(r);
}
}
继承自定义的CustomTableInputFormat,进行hbase连接、读取操作:
package cn.swordfall.hbaseOnFlink import java.io.IOException import cn.swordfall.hbaseOnFlink.flink172_hbase212.CustomTableInputFormat
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2
import org.apache.flink.addons.hbase.TableInputFormat
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.{Cell, HBaseConfiguration, HConstants, TableName}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client._
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes import scala.collection.JavaConverters._
/**
* @Author: Yang JianQiu
* @Date: 2019/3/1 1:14
*
* 从HBase读取数据
* 第二种:实现TableInputFormat接口
*/
class HBaseInputFormat extends CustomTableInputFormat[Tuple2[String, String]]{ // 结果Tuple
val tuple2 = new Tuple2[String, String] /**
* 建立HBase连接
* @param parameters
*/
override def configure(parameters: Configuration): Unit = {
val tableName: TableName = TableName.valueOf("test")
val cf1 = "cf1"
var conn: Connection = null
val config: org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create config.set(HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_QUORUM, "192.168.187.201")
config.set(HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT, "2181")
config.setInt(HConstants.HBASE_CLIENT_OPERATION_TIMEOUT, 30000)
config.setInt(HConstants.HBASE_CLIENT_SCANNER_TIMEOUT_PERIOD, 30000) try {
conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config)
table = conn.getTable(tableName).asInstanceOf[HTable]
scan = new Scan()
scan.withStartRow(Bytes.toBytes("001"))
scan.withStopRow(Bytes.toBytes("201"))
scan.addFamily(Bytes.toBytes(cf1))
} catch {
case e: IOException =>
e.printStackTrace()
}
} /**
* 对获取的数据进行加工处理
* @param result
* @return
*/
override def mapResultToTuple(result: Result): Tuple2[String, String] = {
val rowKey = Bytes.toString(result.getRow)
val sb = new StringBuffer()
for (cell: Cell <- result.listCells().asScala){
val value = Bytes.toString(cell.getValueArray, cell.getValueOffset, cell.getValueLength)
sb.append(value).append("_")
}
val value = sb.replace(sb.length() - 1, sb.length(), "").toString
tuple2.setField(rowKey, 0)
tuple2.setField(value, 1)
tuple2
} /**
* tableName
* @return
*/
override def getTableName: String = "test" /**
* 获取Scan
* @return
*/
override def getScanner: Scan = {
scan
} }
调用实现CustomTableInputFormat接口的类HBaseInputFormat,Flink Streaming流式处理的方式:
/**
* 从HBase读取数据
* 第二种:实现TableInputFormat接口
*/
def readFromHBaseWithTableInputFormat(): Unit ={
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.enableCheckpointing(5000)
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
env.getCheckpointConfig.setCheckpointingMode(CheckpointingMode.EXACTLY_ONCE) val dataStream = env.createInput(new HBaseInputFormat)
dataStream.filter(_.f0.startsWith("10")).print()
env.execute()
}
而Flink DataSet批处理的方式为:
/**
* 读取HBase数据方式:实现TableInputFormat接口
*/
def readFromHBaseWithTableInputFormat(): Unit ={
val env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment val dataStream = env.createInput(new HBaseInputFormat)
dataStream.filter(_.f1.startsWith("20")).print()
}
2.2 Flink写入HBase的两种方式
这里Flink Streaming写入HBase,需要从Kafka接收数据,可以开启kafka单机版,利用kafka-console-producer.sh往topic "test"写入如下数据:
100,hello,20
101,nice,24
102,beautiful,26
2.2.1 继承RichSinkFunction重写父类方法:
package cn.swordfall.hbaseOnFlink import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.{RichSinkFunction, SinkFunction}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.{HBaseConfiguration, HConstants, TableName}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client._
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes /**
* @Author: Yang JianQiu
* @Date: 2019/3/1 1:34
*
* 写入HBase
* 第一种:继承RichSinkFunction重写父类方法
*
* 注意:由于flink是一条一条的处理数据,所以我们在插入hbase的时候不能来一条flush下,
* 不然会给hbase造成很大的压力,而且会产生很多线程导致集群崩溃,所以线上任务必须控制flush的频率。
*
* 解决方案:我们可以在open方法中定义一个变量,然后在写入hbase时比如500条flush一次,或者加入一个list,判断list的大小满足某个阀值flush一下
*/
class HBaseWriter extends RichSinkFunction[String]{ var conn: Connection = null
val scan: Scan = null
var mutator: BufferedMutator = null
var count = 0 /**
* 建立HBase连接
* @param parameters
*/
override def open(parameters: Configuration): Unit = {
val config:org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create
config.set(HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_QUORUM, "192.168.187.201")
config.set(HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT, "2181")
config.setInt(HConstants.HBASE_CLIENT_OPERATION_TIMEOUT, 30000)
config.setInt(HConstants.HBASE_CLIENT_SCANNER_TIMEOUT_PERIOD, 30000)
conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config) val tableName: TableName = TableName.valueOf("test")
val params: BufferedMutatorParams = new BufferedMutatorParams(tableName)
//设置缓存1m,当达到1m时数据会自动刷到hbase
params.writeBufferSize(1024 * 1024) //设置缓存的大小
mutator = conn.getBufferedMutator(params)
count = 0
} /**
* 处理获取的hbase数据
* @param value
* @param context
*/
override def invoke(value: String, context: SinkFunction.Context[_]): Unit = {
val cf1 = "cf1"
val array: Array[String] = value.split(",")
val put: Put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(array(0)))
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(cf1), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes(array(1)))
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(cf1), Bytes.toBytes("age"), Bytes.toBytes(array(2)))
mutator.mutate(put)
//每满2000条刷新一下数据
if (count >= 2000){
mutator.flush()
count = 0
}
count = count + 1
} /**
* 关闭
*/
override def close(): Unit = {
if (conn != null) conn.close()
}
}
调用继承RichSinkFunction的HBaseWriter类,Flink Streaming流式处理的方式:
/**
* 写入HBase
* 第一种:继承RichSinkFunction重写父类方法
*/
def write2HBaseWithRichSinkFunction(): Unit = {
val topic = "test"
val props = new Properties
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "192.168.187.201:9092")
props.put("group.id", "kv_flink")
props.put("enable.auto.commit", "true")
props.put("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000")
props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer")
props.put("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer")
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.enableCheckpointing(5000)
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
env.getCheckpointConfig.setCheckpointingMode(CheckpointingMode.EXACTLY_ONCE)
val myConsumer = new FlinkKafkaConsumer[String](topic, new SimpleStringSchema, props)
val dataStream: DataStream[String] = env.addSource(myConsumer)
//写入HBase
dataStream.addSink(new HBaseWriter)
env.execute()
}
2.2.2 实现OutputFormat接口:
package cn.swordfall.hbaseOnFlink import org.apache.flink.api.common.io.OutputFormat
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.{HBaseConfiguration, HConstants, TableName}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client._
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes /**
* @Author: Yang JianQiu
* @Date: 2019/3/1 1:40
*
* 写入HBase提供两种方式
* 第二种:实现OutputFormat接口
*/
class HBaseOutputFormat extends OutputFormat[String]{ val zkServer = "192.168.187.201"
val port = "2181"
var conn: Connection = null
var mutator: BufferedMutator = null
var count = 0 /**
* 配置输出格式。此方法总是在实例化输出格式上首先调用的
*
* @param configuration
*/
override def configure(configuration: Configuration): Unit = { } /**
* 用于打开输出格式的并行实例,所以在open方法中我们会进行hbase的连接,配置,建表等操作。
*
* @param i
* @param i1
*/
override def open(i: Int, i1: Int): Unit = {
val config: org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create
config.set(HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_QUORUM, zkServer)
config.set(HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT, port)
config.setInt(HConstants.HBASE_CLIENT_OPERATION_TIMEOUT, 30000)
config.setInt(HConstants.HBASE_CLIENT_SCANNER_TIMEOUT_PERIOD, 30000)
conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config) val tableName: TableName = TableName.valueOf("test") val params: BufferedMutatorParams = new BufferedMutatorParams(tableName)
//设置缓存1m,当达到1m时数据会自动刷到hbase
params.writeBufferSize(1024 * 1024) //设置缓存的大小
mutator = conn.getBufferedMutator(params)
count = 0
} /**
* 用于将数据写入数据源,所以我们会在这个方法中调用写入hbase的API
*
* @param it
*/
override def writeRecord(it: String): Unit = { val cf1 = "cf1"
val array: Array[String] = it.split(",")
val put: Put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(array(0)))
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(cf1), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes(array(1)))
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(cf1), Bytes.toBytes("age"), Bytes.toBytes(array(2)))
mutator.mutate(put)
//每4条刷新一下数据,如果是批处理调用outputFormat,这里填写的4必须不能大于批处理的记录总数量,否则数据不会更新到hbase里面
if (count >= 4){
mutator.flush()
count = 0
}
count = count + 1
} /**
* 关闭
*/
override def close(): Unit = {
try {
if (conn != null) conn.close()
} catch {
case e: Exception => println(e.getMessage)
}
}
}
调用实现OutputFormat的HBaseOutputFormat类,Flink Streaming流式处理的方式:
/**
* 写入HBase
* 第二种:实现OutputFormat接口
*/
def write2HBaseWithOutputFormat(): Unit = {
val topic = "test"
val props = new Properties
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "192.168.187.201:9092")
props.put("group.id", "kv_flink")
props.put("enable.auto.commit", "true")
props.put("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000")
props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer")
props.put("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer")
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.enableCheckpointing(5000)
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
env.getCheckpointConfig.setCheckpointingMode(CheckpointingMode.EXACTLY_ONCE)
val myConsumer = new FlinkKafkaConsumer[String](topic, new SimpleStringSchema, props)
val dataStream: DataStream[String] = env.addSource(myConsumer)
dataStream.writeUsingOutputFormat(new HBaseOutputFormat)
env.execute()
}
而Flink DataSet批处理的方式为:
/**
* 写入HBase方式:实现OutputFormat接口
*/
def write2HBaseWithOutputFormat(): Unit = {
val env: ExecutionEnvironment = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment //2.定义数据
val dataSet: DataSet[String] = env.fromElements("103,zhangsan,20", "104,lisi,21", "105,wangwu,22", "106,zhaolilu,23")
dataSet.output(new HBaseOutputFormat)
//运行下面这句话,程序才会真正执行,这句代码针对的是data sinks写入数据的
env.execute()
}
注意:
如果是批处理调用的,应该要注意HBaseOutputFormat类的writeRecord方法每次批量刷新的数据量不能大于批处理的总记录数据量,否则数据更新不到hbase里面。
3. 总结
【其他相关文章】
HBase连接的几种方式(一)java篇 查看纯Java API读写HBase
HBase连接的几种方式(二)spark篇 查看Spark上读写HBase
github地址:
https://github.com/SwordfallYeung/HBaseDemo(flink读写hbase包括java和scala两个版本的代码)
【参考资料】
https://blog.csdn.net/liguohuabigdata/article/details/78588861
https://blog.csdn.net/aA518189/article/details/86544844
HBase读写的几种方式(三)flink篇的更多相关文章
- HBase读写的几种方式(二)spark篇
1. HBase读写的方式概况 主要分为: 纯Java API读写HBase的方式: Spark读写HBase的方式: Flink读写HBase的方式: HBase通过Phoenix读写的方式: 第一 ...
- HBase读写的几种方式(一)java篇
1.HBase读写的方式概况 主要分为: 纯Java API读写HBase的方式: Spark读写HBase的方式: Flink读写HBase的方式: HBase通过Phoenix读写的方式: 第一种 ...
- 【转帖】HBase读写的几种方式(二)spark篇
HBase读写的几种方式(二)spark篇 https://www.cnblogs.com/swordfall/p/10517177.html 分类: HBase undefined 1. HBase ...
- java文件读写的两种方式
今天搞了下java文件的读写,自己也总结了一下,但是不全,只有两种方式,先直接看代码: public static void main(String[] args) throws IOExceptio ...
- Hive映射HBase表的几种方式
1.Hive内部表,语句如下 CREATE TABLE ods.s01_buyer_calllogs_info_ts( key string comment "hbase rowkey&qu ...
- vba txt读写的几种方式
四种方式写txt 1.这种写出来的是ANSI格式的txt Dim TextExportFile As String TextExportFile = ThisWorkbook.Path & & ...
- .net学习笔记--文件读写的几种方式
在.net中有很多有用的类库来读写硬盘上的文件 一般比较常用的有: File:1.什么时候使用:当读写件大小不大,同时可以一次性进行读写操作的时候使用 2.不同的方式可以读写文件类型不 ...
- python对csv文件读写的两种方式 和 读写文件编码问题处理
''' 如果文件读取数据出错,可以考虑加一个encoding属性,取值可以是:utf-8,gbk,gb18030 或者加一个属性error,取值为ignore,例如 open(path, encodi ...
- python 发送邮件的两种方式【终极篇】
一,利用python自带的库 smtplib简单高效 from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart from email.mime.text impor ...
随机推荐
- 升级Mac OS X上的git
今天一打开visual studio code就提示我git版本low,需要升级,然后提供了一个下载链接(git官方下载地址:https://git-scm.com/),然后我就根据链接去下载了mac ...
- 使用 prismjs 在网页中高亮显示代码
最近在总结这一年来制作的网页模块,网站风格统一的情况下,网站页面结构不会改变,因此想记录一部分网站中统一的结构,方便日后维护. 用到的相关技术: vue, element-ui, prismjs, v ...
- 从0开始的Python学习014面向对象编程
简介 到目前为止,我们的编程都是根据数据的函数和语句块来设计的,面向过程的编程.还有一种我们将数据和功能结合起来使用对象的形式,使用它里面的数据和方法这种方法叫做面向对象的编程. 类和对象是面向对象 ...
- LeetCode算法题-Largest Number At Least Twice of Others(Java实现)
这是悦乐书的第308次更新,第328篇原创 01 看题和准备 今天介绍的是LeetCode算法题中Easy级别的第177题(顺位题号是747).在给定的整数数组中,总有一个最大的元素.查找数组中的最大 ...
- pyhton从开始到光棍的day11
纪念我这个开始学python的光棍天,光棍天依旧是函数,这次的函数有个小高级,比昨天的low函数稍微高级点,就是在使用函数中是可以赋值的,比如索引一个值什么的.函数还可以当做参数进行传递,把这个函数名 ...
- ztree 为节点添加点击触发事件
<SCRIPT type="text/javascript"> var setting = { data : { key : { title : "code& ...
- 这可能是最简单的Page Object库
做过web自动化测试的同学,对Page object设计模式应该不陌生. Page object库应该根据以下目标开发: Page object应该易于使用 清晰的结构 PageObjects 对于页 ...
- [Alpha阶段]发布说明
[Alplha阶段]发布说明 小小易校园小程序发布说明 版本功能 [Alpha版本]功能说明 1.注册及登录功能 2.修改密码功能 3.自动登录.退出登录功能 4.个人资料修改及简历模板功能 5.查看 ...
- Docker部署脚本
实现 1.检查内核版本 2.检查docker是否已安装 3.安装docker,如因网络等原因失败循环安装至安装完成 #!/bin/bash #file:docker_install.sh #From: ...
- AngularJS路由变化 监听方法
#使用AngularJS时,当路由发生改变时,我们需要做某些处理,此时可以监听路由事件,常用的是$routeStartChange, $routeChangeSuccess ##使用场景:在路由配置文 ...
