第七十七课 最小生成树(Kruskal)
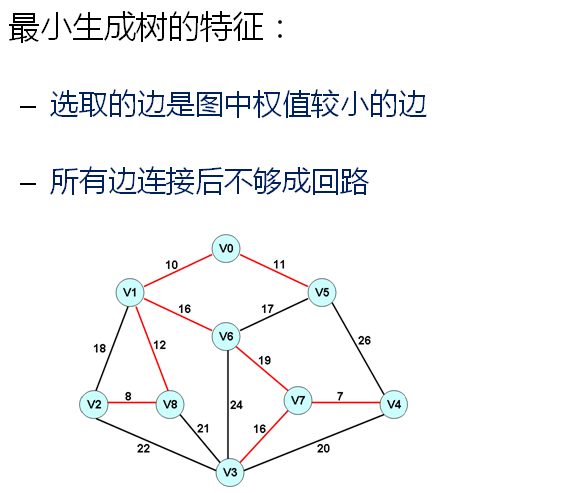


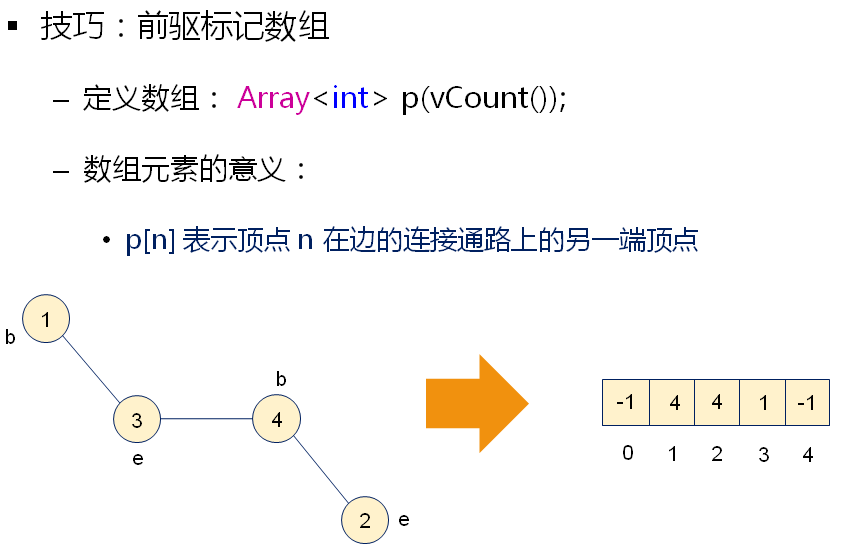
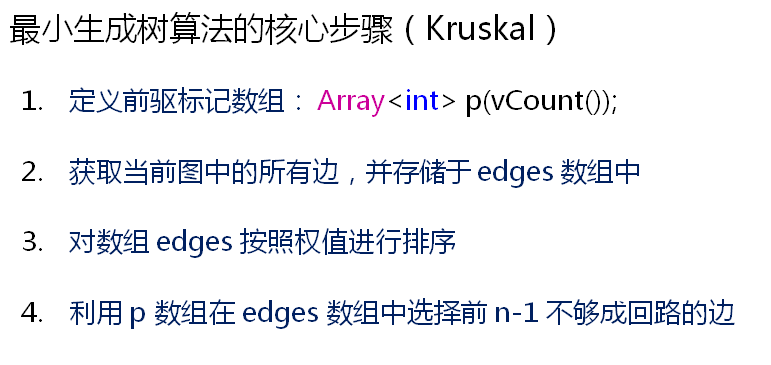

添加kruskal算法:
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H #include "Object.h"
#include "SharedPointer.h"
#include "Array.h"
#include "DynamicArray.h"
#include "LinkQueue.h"
#include "LinkStack.h"
#include "Sort.h" namespace DTLib
{ template < typename E >
struct Edge : public Object
{
int b;
int e;
E data; Edge(int i=-, int j=-)
{
b = i;
e = j;
} Edge(int i, int j, const E& value)
{
b = i;
e = j;
data = value;
} bool operator == (const Edge<E>& obj)
{
return (b == obj.b) && (e == obj.e); //在这里不关注权值大小
} bool operator != (const Edge<E>& obj)
{
return !(*this == obj);
} bool operator < (const Edge<E>& obj)
{
return (data < obj.data);
} bool operator > (const Edge<E>& obj)
{
return (data > obj.data);
}
}; template < typename V, typename E >
class Graph : public Object
{
protected:
template < typename T >
DynamicArray<T>* toArray(LinkQueue<T>& queue)
{
DynamicArray<T>* ret = new DynamicArray<T>(queue.length()); if( ret != NULL )
{
for(int i=; i<ret->length(); i++, queue.remove())
{
ret->set(i, queue.front());
}
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to create ret object...");
} return ret;
} SharedPointer< Array<Edge<E> > > getUndirectedEdges()
{
DynamicArray<Edge<E>>* ret = NULL; if( asUndirected() )
{
LinkQueue<Edge<E>> queue; for(int i=; i<vCount(); i++)
{
for(int j=i; j<vCount(); j++)
{
if( isAdjacent(i, j) )
{
queue.add(Edge<E>(i, j, getEdge(i, j)));
}
}
} ret = toArray(queue);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "This function is for undirected graph only...");
} return ret;
} int find(Array<int>& p, int v)
{
while( p[v] != -)
{
v = p[v];
} return v;
}
public:
virtual V getVertex(int i) = ;
virtual bool getVertex(int i, V& value) = ;
virtual bool setVertex(int i, const V& value) = ;
virtual SharedPointer< Array<int> > getAdjacent(int i) = ;
virtual bool isAdjacent(int i, int j) = ;
virtual E getEdge(int i, int j) = ;
virtual bool getEdge(int i, int j, E& value) = ;
virtual bool setEdge(int i, int j, const E& value) = ;
virtual bool removeEdge(int i, int j) = ;
virtual int vCount() = ;
virtual int eCount() = ;
virtual int OD(int i) = ;
virtual int ID(int i) = ; virtual int TD(int i)
{
return ID(i) + OD(i);
} bool asUndirected()
{
bool ret = true; for(int i=; i<vCount(); i++)
{
for(int j=; j<vCount(); j++)
{
if( isAdjacent(i, j) )
{
ret = ret && isAdjacent(j, i) && (getEdge(i, j) == getEdge(j, i));
}
}
} return ret;
} SharedPointer< Array< Edge<E > > > prim(const E& LIMIT, const bool MINIUM = true) //参数为理论上的最大权值
{
LinkQueue< Edge<E> > ret; if( asUndirected() )
{
DynamicArray<int> adjVex(vCount());
DynamicArray<bool> mark(vCount());
DynamicArray<E> cost(vCount());
SharedPointer< Array<int> > aj = NULL;
bool end = false;
int v = ; for(int i=; i<vCount(); i++)
{
adjVex[i] = -;
mark[i] = false;
cost[i] = LIMIT;
} mark[v] = true; aj = getAdjacent(v); for(int j=; j<aj->length(); j++)
{
cost[(*aj)[j]] = getEdge(v, (*aj)[j]);
adjVex[(*aj)[j]] = v;
} for(int i=; (i<vCount()) && !end; i++)
{
E m = LIMIT;
int k = -; for(int j=; j<vCount(); j++)
{
if( !mark[j] && (MINIUM ? (cost[j] < m) : (cost[j] > m)))
{
m = cost[j];
k = j;
}
} end = (k == -); if( !end )
{
ret.add(Edge<E>(adjVex[k], k, getEdge(adjVex[k], k))); mark[k] = true; aj = getAdjacent(k); for(int j=; j<aj->length(); j++)
{
if( !mark[(*aj)[j]] && (MINIUM ? (getEdge(k, (*aj)[j]) < cost[(*aj)[j]]) : (getEdge(k, (*aj)[j]) > cost[(*aj)[j]])) )
{
cost[(*aj)[j]] = getEdge(k, (*aj)[j]);
adjVex[(*aj)[j]] = k;
}
}
}
}
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "Prim operator is for undirected graph only...");
} if( ret.length() != (vCount() - ) )
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No enough edge for prim operation...");
} return toArray(ret);
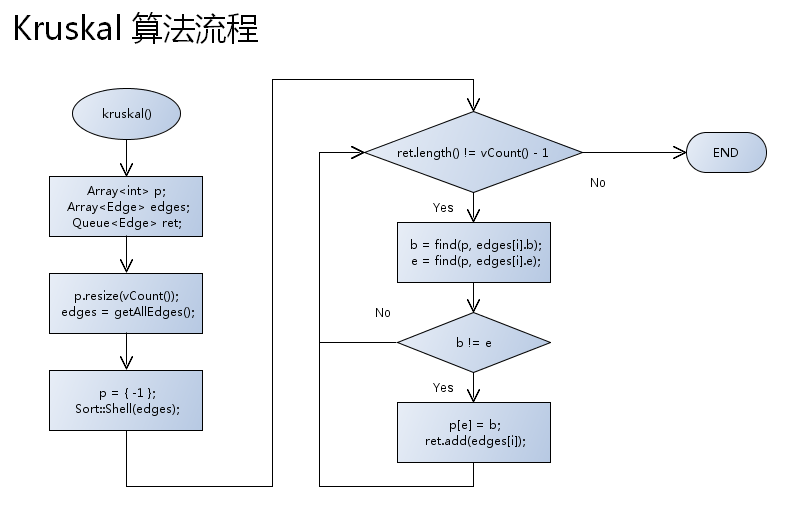
} SharedPointer< Array<Edge<E> > > kruskal(const bool MINMUM = true)
{
LinkQueue< Edge<E> > ret; SharedPointer< Array< Edge<E> > > edges = getUndirectedEdges(); DynamicArray<int> p(vCount()); //前驱标记数组 for(int i=; i<p.length(); i++)
{
p[i] = -;
} Sort::Shell(*edges, MINMUM); for(int i=; (i<edges->length()) && (ret.length() < (vCount() - )); i++)
{
int b = find(p, (*edges)[i].b);
int e = find(p, (*edges)[i].e); if( b != e )
{
p[e] = b; ret.add((*edges)[i]);
}
} if( ret.length() != (vCount() - ) )
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No enough edges for Kruskal operation...");
} return toArray(ret);
} SharedPointer< Array<int> > BFS(int i)
{
DynamicArray<int>* ret = NULL; if( ( <= i) && (i < vCount()) )
{
LinkQueue<int> q;
LinkQueue<int> r;
DynamicArray<bool> visited(vCount()); for(int i=; i<visited.length(); i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
} q.add(i); while( q.length() > )
{
int v = q.front(); q.remove(); if( !visited[v] )
{
SharedPointer< Array<int> > aj = getAdjacent(v); for(int j=; j<aj->length(); j++)
{
q.add((*aj)[j]);
} r.add(v); visited[v] = true;
}
} ret = toArray(r);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidParameterException, "Index i is invalid...");
} return ret;
} SharedPointer< Array<int> > DFS(int i)
{
DynamicArray<int>* ret = NULL; if( ( <= i) && (i < vCount()) )
{
LinkStack<int> s;
LinkQueue<int> r;
DynamicArray<bool> visited(vCount()); for(int j=; j<visited.length(); j++)
{
visited[j] = false;
} s.push(i); while( s.size() > )
{
int v = s.top(); s.pop(); if( !visited[v] )
{
SharedPointer< Array<int> > aj = getAdjacent(v); for(int j=aj->length() - ; j>=; j--)
{
s.push((*aj)[j]);
} r.add(v); visited[v] = true;
}
} ret = toArray(r);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidParameterException, "Index i is invalid...");
} return ret;
} }; } #endif // GRAPH_H
测试程序如下:
#include <iostream>
#include "MatrixGraph.h"
#include "ListGraph.h" using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib; template< typename V, typename E >
Graph<V, E>& GraphEasy()
{
static MatrixGraph<, V, E> g; g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); return g;
} template< typename V, typename E >
Graph<V, E>& GraphComplex()
{
static ListGraph<V, E> g(); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); g.setEdge(, , );
g.setEdge(, , ); return g;
} int main()
{
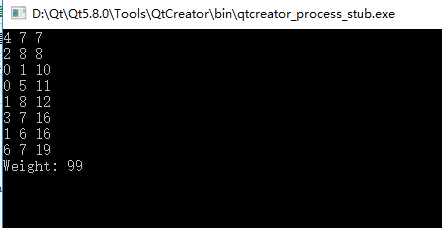
Graph<int, int>& g = GraphComplex<int, int>(); SharedPointer< Array< Edge<int> > > sa = g.kruskal(); int w = ; for(int i=; i<sa->length(); i++)
{
w += (*sa)[i].data;
cout << (*sa)[i].b << " " << (*sa)[i].e << " " << (*sa)[i].data << endl;
} cout << "Weight: " << w << endl; return ;
}
结果如下:
小结:

第七十七课 最小生成树(Kruskal)的更多相关文章
- python六十七课——网络编程(基础知识了解)
网络编程: 什么是网络编程? 网络:它是一种隐形的媒介:可以将多台计算机使用(将它们连接到一起) 网络编程:将多台计算机之间可以相互通信了(做数据交互) 一旦涉及到网络编程,划分为两个方向存在,一方我 ...
- NeHe OpenGL教程 第四十七课:CG顶点脚本
转自[翻译]NeHe OpenGL 教程 前言 声明,此 NeHe OpenGL教程系列文章由51博客yarin翻译(2010-08-19),本博客为转载并稍加整理与修改.对NeHe的OpenGL管线 ...
- NeHe OpenGL教程 第三十七课:卡通映射
转自[翻译]NeHe OpenGL 教程 前言 声明,此 NeHe OpenGL教程系列文章由51博客yarin翻译(2010-08-19),本博客为转载并稍加整理与修改.对NeHe的OpenGL管线 ...
- NeHe OpenGL教程 第二十七课:影子
转自[翻译]NeHe OpenGL 教程 前言 声明,此 NeHe OpenGL教程系列文章由51博客yarin翻译(2010-08-19),本博客为转载并稍加整理与修改.对NeHe的OpenGL管线 ...
- NeHe OpenGL教程 第十七课:2D图像文字
转自[翻译]NeHe OpenGL 教程 前言 声明,此 NeHe OpenGL教程系列文章由51博客yarin翻译(2010-08-19),本博客为转载并稍加整理与修改.对NeHe的OpenGL管线 ...
- 第三百七十七节,Django+Xadmin打造上线标准的在线教育平台—apps目录建立,以及数据表生成
第三百七十七节,Django+Xadmin打造上线标准的在线教育平台—apps目录建立,以及数据表生成 apps目录建立 我们创建一个apps目录,将所有的app放到apps目录里去,这样方便管理,也 ...
- centos Linux下磁盘管理 parted,df ,du,fdisk,partprobe,mkfs.ext4,mount,/etc/fstab,fsck,e2fsck,mk2efs,tmpfs ,nr_inodes, LVM,传统方式扩容文件系统 第七节课
centos Linux下磁盘管理 parted,df ,du,fdisk,partprobe,mkfs.ext4,mount,/etc/fstab,fsck,e2fsck,mk2efs,tmpf ...
- “全栈2019”Java第七十七章:抽象内部类与抽象静态内部类详解
难度 初级 学习时间 10分钟 适合人群 零基础 开发语言 Java 开发环境 JDK v11 IntelliJ IDEA v2018.3 文章原文链接 "全栈2019"Java第 ...
- 模板——最小生成树kruskal算法+并查集数据结构
并查集:找祖先并更新,注意路径压缩,不然会时间复杂度巨大导致出错/超时 合并:(我的祖先是的你的祖先的父亲) 找父亲:(初始化祖先是自己的,自己就是祖先) 查询:(我们是不是同一祖先) 路径压缩:(每 ...
随机推荐
- C# 3.0 / C# 3.5 自动属性
自动属性的好处 自动属性简化了我们在做 C# 开发的时候手写一堆私有成员 + 属性的编程方式,我们只需要使用如下方式声明一个属性,编译器就会自动生成所需的成员变量. 传统属性概念 属性的目的一是封装字 ...
- Lexicography
An anagram of a string is any string that can be formed using the same letters as the original. (We ...
- PE文件结构解析
说明:本文件中各种文件头格式截图基本都来自看雪的<加密与解密>:本文相当<加密与解密>的阅读笔记. 1.PE文件总体结构 PE文件框架结构,就是exe文件的排版结构.也就是说我 ...
- asp企业网站源码部分
ASP的网页文件的格式是.asp,现在常用于各种动态网站中.PHP是一种 HTML 内嵌式的语言,PHP与微软的ASP颇有几分相似,都是一种在服务器端执行的嵌入HTML文档的脚本语言,语言的风格有类似 ...
- matlab画图变粗脚本
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_708637950100uag0.html figure_FontSize=18;set(get(gca,'XLabel'),'FontS ...
- Ubuntu下如何访问Windows磁盘?
有些同学的电脑原来是Windows系统的,但为了需要,又下载了一个Ubuntu系统,变成双系统的电脑. 但是,在Ubuntu下,Windows的磁盘是打不开的,用网盘或者U盘又是很不方便,所以ljn教 ...
- Java压缩文件
压缩文件 package com.iss.cpf.windmanger.userprivilegeexport.bizlogic; import java.io.BufferedInputStream ...
- Java反射《三》获取属性
package com.study.reflect; import java.lang.reflect.Field; /** * 反射,获取属性 * @ClassName: FieldDemo * @ ...
- day4-python基础-运算符
本章节主要说明Python的运算符.举个简单的例子 4 +5 = 9 . 例子中,4 和 5 被称为操作数,"+" 称为运算符. Python语言支持以下类型的运算符: 算术运算符 ...
- nexus下载远程maven中央仓库的解决方案
参考:http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-03/98708.htm https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/.index/ 下载这两 ...
