codeforce 378 div 2 F —— Drivers Dissatisfaction (最小生成树,LCA,倍增)
官方题解:
If you choose any n - 1 roads then price of reducing overall dissatisfaction is equal to min(c1, c2, ..cn - 1) where сi is price of reducing by 1 dissatisfaction of i-th edge. So the best solution is to choose one edge and reduce dissatisfaction of it until running out of budget.
Let's construct minimal spanning tree using Prim or Kruskal algorithm using edges of weights equal to dissatisfaction and calculate minimal price of reducing dissatisfaction. Time complexity —  .
.
Now we can iterate over edges implying that current is the one to be reduced to minimum. For example, for every edge we can build new MST and recalculate answer. It's 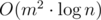 . Therefore we should use this fact: it's poinless to reduce dissatisfaction of edges which weren't selected to be main.
. Therefore we should use this fact: it's poinless to reduce dissatisfaction of edges which weren't selected to be main.
Then we can transform original MST instead of constructing m new ones. Add next edge to MST, now it contains a cycle from which edge with maximal dissatisfaction is about to be deleted. This can be achieved in such a way: find LCA of vertices of new edge in 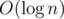 and using binary lifting with precalc in
and using binary lifting with precalc in 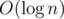 find the edge to delete.
find the edge to delete.
Time complexity — 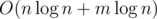 .
.
大意是:
经分析所有的预算用在一条干道上最合算(这条干道的修路花费是所挑选的n-1条干道中最小的),首先建立一棵最小生成树MST,然后枚举M条边,假设当前枚举到的边编号是i,将所有预算用到边 i 上然后添加到MST中形成一个环,找到环中权值最大的边删除。设边i的两端点为 a, b, 找到结点u = LCA(MST,a, b),那么这个环就是由 a~u,b~u 以及边 i 围成。
如何找到权值最大的边呢?可以通过倍增法,具体做法如下:
设mw[a][j]表示结点 a 到它的第 2^j 倍祖先的路径上权值最大的边编号,类似LCA倍增法的做法预处理出所有结点的mw[a][j]值
for(int j = ; (<<j) < n; j++) //倍增
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) if(pa[i][j-] != -){
pa[i][j] = pa[pa[i][j-]][j-]; //计算节点i的第2^j倍祖先
int e1 = mw[i][j-];
int e2 = mw[pa[i][j-]][j-];
mw[i][j] = weight[e1] < weight[e2] ? e2 : e1;
}
然后计算更换边之后新树的权值,找到使总干道权值最低的更新方法,最后跑一边最小生成树算法即可。
代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <queue> using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5 + ; #define rep(i, x, n) for(int i = x; i <= n; i++)
struct edge{
int u, v;
int w, c;
edge(int uu, int vv, int ww, int cc): u(uu), v(vv), w(ww), c(cc){}
bool operator<(const edge& b) const {
return w < b.w;
}
}; typedef long long LL;
vector<edge> E;
int r[maxn];
vector<int> G[maxn]; void add_edge(int a, int b, int w, int c) {
E.push_back(edge(a, b, w, c));
int id = E.size() - ;
G[a].push_back(id);
G[b].push_back(id);
} int n, m, S;
int w[maxn];
int c[maxn];
int fa[maxn];
LL w_mst;
int findfa(int x) {return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = findfa(fa[x]);} //并查集
vector<int> G2[maxn];
bool cmp(int a, int b) {
return E[a] < E[b];
}
vector<int> A;
LL kurskal() { //计算MST
LL ans = ;
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) fa[i] = i;
for(int i = ; i < m; i++) r[i] = i;
sort(r, r+m, cmp);
for(int i = ; i < m; i++) {
edge e = E[r[i]];
int x = findfa(e.u);
int y = findfa(e.v);
if(x != y) {
fa[x] = y;
ans += e.w;
A.push_back(r[i]); //将添加的边同时保存在A中
G2[e.u].push_back(r[i]);
G2[e.v].push_back(r[i]);
}
}
return ans;
}
int dep[maxn];
int pa[maxn][]; //表示结点a的第 2^j 倍祖先
int mw[maxn][]; //表示结点 a 到它的第 2^j 倍祖先的路径上权值最大的边编号
void dfs(int u, int f, int d) { //dfs计算MST中所有结点的深度,初始化pa数组和mw数组
dep[u] = d;
pa[u][] = f;
for(int i = ; i < G2[u].size(); i++) {
edge& e = E[G2[u][i]];
int v = e.u == u ? e.v : e.u;
if(v != f) {
mw[v][] = G2[u][i];
dfs(v, u, d+);
}
}
}
void pre() { //预处理出所有结点的mw,pa
for(int j = ; (<<j) < n; j++)
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) if(pa[i][j-] != -){
pa[i][j] = pa[pa[i][j-]][j-];
int e1 = mw[i][j-];
int e2 = mw[pa[i][j-]][j-];
mw[i][j] = E[e1] < E[e2] ? e2 : e1;
}
} int lca(int a, int b, int &me) { //计算最近公共祖先的同时算出a,b路径中权值最大的边保存到me中
me = -;
if(dep[a] < dep[b]) swap(a, b);
int i, j;
for(i = ; (<<i) <= dep[a]; i++);
i--;
for(j = i; j >= ; j--)
if(dep[a] - (<<j) >= dep[b]) {
int e_id = mw[a][j];
a = pa[a][j];
if(me == -) me = e_id;
me = E[me] < E[e_id] ? e_id : me;
}
if(a == b) return a;
for(j = i; j >= ; j--)
if(pa[a][j] != - && pa[a][j] != pa[b][j]) {
int e1 = mw[a][j];
int e2 = mw[b][j];
a = pa[a][j];
b = pa[b][j];
if(me == -) me = e1;
me = E[me] < E[e1] ? e1 : me;
me = E[me] < E[e2] ? e2 : me;
}
int e1 = mw[a][];
int e2 = mw[b][];
if(me == -) me = e1;
me = E[me] < E[e1] ? e1 : me;
me = E[me] < E[e2] ? e2 : me;
return pa[a][];
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = ; i <= m; i++) scanf("%d", &w[i]);
for(int i = ; i <= m; i++) scanf("%d", &c[i]);
for(int i = ; i <= m; i++) {
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
add_edge(a, b, w[i], c[i]);
}
scanf("%d", &S);
w_mst = kurskal();
memset(pa, -, sizeof pa);
memset(mw, , sizeof mw);
dfs(, -, );
pre();
LL ans_w = w_mst;
int ans_e = -;
for(int i = ; i <= m; i++) {
int e = i-;
int me;
lca(E[e].u, E[e].v, me);
LL temp = w_mst - E[me].w + E[e].w - S/c[i];
//cout << i <<" : me : "<< me <<endl;
if(temp < ans_w) {
ans_w = temp;
ans_e = e;
//cout << "ans_w : " << ans_w<< "ans_e : " << ans_e+1 <<endl;
}
}
if(ans_e != -) E[ans_e].w -= S/c[ans_e+];
A.clear();
w_mst = kurskal();
cout << ans_w << endl;
for(int i = ; i < A.size(); i++)
cout << A[i] + << " " << E[A[i]].w << endl;
return ;
}
codeforce 378 div 2 F —— Drivers Dissatisfaction (最小生成树,LCA,倍增)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #378 (Div. 2) F - Drivers Dissatisfaction
F - Drivers Dissatisfaction 题目大意:给你n个点,m条边,每个边都有一个权重w,每条边也有一个c表示,消耗c元可以把这条边的权重减1,求最多消耗s元的最小生成树. 思路:因 ...
- Codeforces Round #378 (Div. 2)F - Drivers Dissatisfaction GNU
http://codeforces.com/contest/733/problem/F 题意:给你一些城市和一些路,每条路有不满意程度和每减少一点不满意程度的花费,给出最大花费,要求找出花费小于s的最 ...
- Drivers Dissatisfaction 最小生成树+LCA
题意:给一张n个点m条边的连通图,每条边(ai,bi)有一个权值wi和费用ci, 表示这条边每降低1的权值需要ci的花费.现在一共有S费用可以用来降低某些边的权值 (可以降到负数),求图中的一棵权值和 ...
- Codeforces Round #378 (Div. 2)F
题目:一个带权连通无向图,给第i条边权值减1需要花费ci元,你一共有S元,求最小生成树. 容易得出钱全部花在一条边上是最优的. 我们先做一遍最小生成树. 然后我们枚举减哪一条边. 如果这条边是树上的, ...
- CF733F Drivers Dissatisfaction【链剖】【最小生成树应用】
F. Drivers Dissatisfaction time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input s ...
- Drivers Dissatisfaction
Drivers Dissatisfaction time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stan ...
- Codeforces Round #378 (Div. 2)
A: 思路: 水题,没啥意思; B: 思路: 暴力,也没啥意思; C: 思路: 思维,可以发现从前往后和为b[i]的分成一块,然后这一块里面如果都相同就没法开始吃,然后再暴力找到那个最大的且能一开始就 ...
- Codeforces Educational Codeforces Round 44 (Rated for Div. 2) F. Isomorphic Strings
Codeforces Educational Codeforces Round 44 (Rated for Div. 2) F. Isomorphic Strings 题目连接: http://cod ...
- Codeforces Round #485 (Div. 2) F. AND Graph
Codeforces Round #485 (Div. 2) F. AND Graph 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/987/problem/F Descri ...
随机推荐
- SpringBoot启动报错Failed to determine a suitable driver class
SpringBoot启动报错如下 Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your app ...
- 【机器学习PAI实战】—— 玩转人工智能之商品价格预测
摘要: 我们经常思考机器学习,深度学习,以至于人工智能给我们带来什么?在数据相对充足,足够真实的情况下,好的学习模型可以发现事件本身的内在规则,内在联系.我们去除冗余的信息,可以通过最少的特征构建最简 ...
- Unicode, UTF-8, GBK, ASCII的区别
看完知乎的两篇文章大概就明白了 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25435644 https://www.zhihu.com/question/23374078 看完总结一下 ...
- SQLServer —— 数据类型的转换
一.使用convert函数实现强制转换 例如我们现在有如下一张学员成绩表: 现在想查询学号等于100003的学员总成绩,并按照要求打印出来,我们可以这样实现: 结果报错,因为最后一句字符串不能和数值相 ...
- 学习iOS设计--iOS8的颜色、文字和布局学习
在去年,Apple针对新时代用户彻底更新了其设计语言.现在的设计语言相对之前大为简化,能够让设计师将精力集中到动画和功能上,而不是繁复的视觉细节上. 很多人都曾问过我:设计应当如何入门?成为一名优秀设 ...
- 2019-8-30-C#-从零开始写-SharpDx-应用-笔刷
title author date CreateTime categories C# 从零开始写 SharpDx 应用 笔刷 lindexi 2019-8-30 8:50:0 +0800 2019-6 ...
- Excel中IP地址排序
思路 将IP地址按"."分隔,提取"."之间的每个数,然后根据提取出的列从左至右进行主要字段及次要字段排序 公式说明 返回一个字符串在另一个字符串中出现的起始位 ...
- 2019-5-25-win10-uwp-win2d-入门-看这一篇就够了
title author date CreateTime categories win10 uwp win2d 入门 看这一篇就够了 lindexi 2019-5-25 20:0:52 +0800 2 ...
- Libevent:11使用Libevent的DNS上层和底层功能
Libevent提供了一些API用来进行DNS域名解析,并且提供了实现简单DNS服务器的能力. 本章首先描述域名解析的上层功能,然后介绍底层功能及服务器功能. 注意:Libevent的当前DNS客户端 ...
- 从Kubernetes 1.14 发布,看技术社区演进方向
Kubernetes 1.14 正式发布已经过去了一段时间,相信你已经从不同渠道看过了各种版本的解读. 不过,相比于代码 Release,马上就要迎来5周岁生日的Kubernetes 项目接下来如何演 ...
