intermediate-python-for-data-science
当前的学习也是调参的过程
matplotlib
plot
# Print the last item of gdp_cap and life_exp
print(gdp_cap)
print(life_exp)
# Make a line plot, gdp_cap on the x-axis, life_exp on the y-axis
plt.plot(gdp_cap,life_exp)
# Display the plot
plt.show()
Scatter Plot
# Change the line plot below to a scatter plot
plt.plot(gdp_cap, life_exp)
# Put the x-axis on a logarithmic scale
plt.scatter(gdp_cap, life_exp)
plt.xscale('log')
# Show plot
plt.show()
histogram
# Create histogram of life_exp data
plt.hist(life_exp)
# Display histogram
plt.show()
# Build histogram with 5 bins
plt.hist(life_exp,bins=5)
# Show and clean up plot
plt.show()
plt.clf()
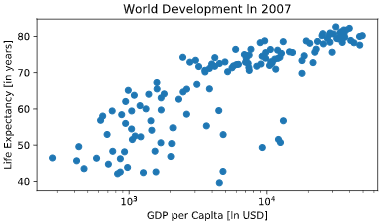
Customization
自定义绘图
# Basic scatter plot, log scale
plt.scatter(gdp_cap, life_exp)
plt.xscale('log')
# Strings
xlab = 'GDP per Capita [in USD]'
ylab = 'Life Expectancy [in years]'
title = 'World Development in 2007'
# Add axis labels
plt.xlabel(xlab )
plt.ylabel(ylab)
# Add title
plt.title(title)
# After customizing, display the plot
plt.show()
plt.xticks
# Scatter plot
plt.scatter(gdp_cap, life_exp)
# Previous customizations
plt.xscale('log')
plt.xlabel('GDP per Capita [in USD]')
plt.ylabel('Life Expectancy [in years]')
plt.title('World Development in 2007')
# Definition of tick_val and tick_lab
tick_val = [1000, 10000, 100000]
tick_lab = ['1k', '10k', '100k']
# Adapt the ticks on the x-axis
plt.xticks(tick_val, tick_lab)
# After customizing, display the plot
plt.show()
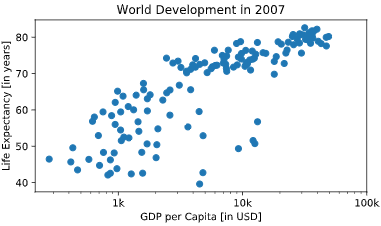
# Specify c and alpha inside plt.scatter()
plt.scatter(x = gdp_cap, y = life_exp, s = np.array(pop) * 2,c=col,alpha=0.8)
# Previous customizations
plt.xscale('log')
plt.xlabel('GDP per Capita [in USD]')
plt.ylabel('Life Expectancy [in years]')
plt.title('World Development in 2007')
plt.xticks([1000,10000,100000], ['1k','10k','100k'])
# Show the plot
plt.show()
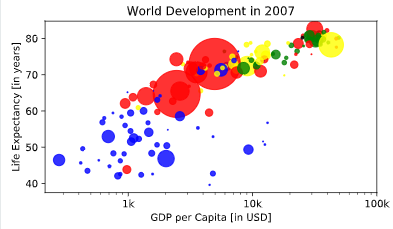
plt.test
# Scatter plot
plt.scatter(x = gdp_cap, y = life_exp, s = np.array(pop) * 2, c = col, alpha = 0.8)
# Previous customizations
plt.xscale('log')
plt.xlabel('GDP per Capita [in USD]')
plt.ylabel('Life Expectancy [in years]')
plt.title('World Development in 2007')
plt.xticks([1000,10000,100000], ['1k','10k','100k'])
# Additional customizations
plt.text(1550, 71, 'India')
plt.text(5700, 80, 'China')
# Add grid() call
plt.grid(True)
# Show the plot
plt.show()
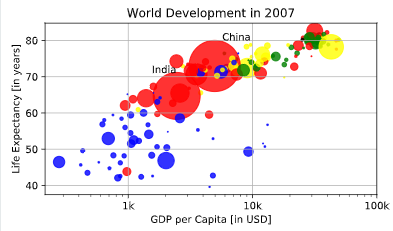
Dictionaries, Part 1
# Definition of countries and capital
countries = ['spain', 'france', 'germany', 'norway']
capitals = ['madrid', 'paris', 'berlin', 'oslo']
# Get index of 'germany': ind_ger
ind_ger=countries.index('germany')
# Use ind_ger to print out capital of Germany
print(capitals[ind_ger])
Create dictionary
# Definition of countries and capital
countries = ['spain', 'france', 'germany', 'norway']
capitals = ['madrid', 'paris', 'berlin', 'oslo']
# From string in countries and capitals, create dictionary europe
europe = { 'spain':'madrid','france':'paris', 'germany':'berlin', 'norway':'oslo' }
# Print europe
print(europe)
dictionary keys
可以直接用[]来取出key所对应的值
# Definition of dictionary
europe = {'spain':'madrid', 'france':'paris', 'germany':'berlin', 'norway':'oslo' }
# Print out the keys in europe
#直接调用keys方法
print(europe.keys())
# Print out value that belongs to key 'norway'
print(europe['norway'])
给已经存在的字典中继续增加元素
# Definition of dictionary
europe = {'spain':'madrid', 'france':'paris', 'germany':'berlin', 'norway':'oslo' }
# Add italy to europe
europe['italy']='rome'
# Print out italy in europe
print('italy' in europe)
# Add poland to europe
europe['poland']='warsaw'
# Print europe
print(europe)
添加删除键值对
使用del删除
# Definition of dictionary
europe = {'spain':'madrid', 'france':'paris', 'germany':'bonn',
'norway':'oslo', 'italy':'rome', 'poland':'warsaw',
'australia':'vienna' }
# Update capital of germany
europe['germany']='berlin'
# Remove australia
#使用del函数直接删
del(europe['australia'])
# Print europe
print(europe)
筛选字典中的值
# Dictionary of dictionaries
europe = { 'spain': { 'capital':'madrid', 'population':46.77 },
'france': { 'capital':'paris', 'population':66.03 },
'germany': { 'capital':'berlin', 'population':80.62 },
'norway': { 'capital':'oslo', 'population':5.084 } }
# Print out the capital of France
print(europe['france']['capital'])
# Create sub-dictionary data
data = { 'capital':'rome', 'population':59.83 }
# Add data to europe under key 'italy'
europe['italy'] = data
# Print europe
print(europe)
pandas学习
dataframe
# Pre-defined lists
names = ['United States', 'Australia', 'Japan', 'India', 'Russia', 'Morocco', 'Egypt']
dr = [True, False, False, False, True, True, True]
cpc = [809, 731, 588, 18, 200, 70, 45]
# Import pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Create dictionary my_dict with three key:value pairs: my_dict
my_dict = { 'country':names, 'drives_right':dr, 'cars_per_cap':cpc }
# Build a DataFrame cars from my_dict: cars
cars = pd.DataFrame(my_dict)
# Print cars
print(cars)
<script.py> output:
cars_per_cap country drives_right
0 809 United States True
1 731 Australia False
2 588 Japan False
3 18 India False
4 200 Russia True
5 70 Morocco True
6 45 Egypt True
index
在python中index是指数据框的行名
import pandas as pd
# Build cars DataFrame
names = ['United States', 'Australia', 'Japan', 'India', 'Russia', 'Morocco', 'Egypt']
dr = [True, False, False, False, True, True, True]
cpc = [809, 731, 588, 18, 200, 70, 45]
cars_dict = { 'country':names, 'drives_right':dr, 'cars_per_cap':cpc }
cars = pd.DataFrame(cars_dict)
print(cars)
# Definition of row_labels
row_labels = ['US', 'AUS', 'JPN', 'IN', 'RU', 'MOR', 'EG']
# Specify row labels of cars
cars.index=row_labels
# Print cars again
print(cars)
pd.read_csv
# Import pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Import the cars.csv data: cars
cars=pd.read_csv("cars.csv")
# Fix import by including index_col
cars = pd.read_csv('cars.csv',index_col=0)
# Print out cars
print(cars)
loc
根据行名取行值
iloc
根据行的索引值
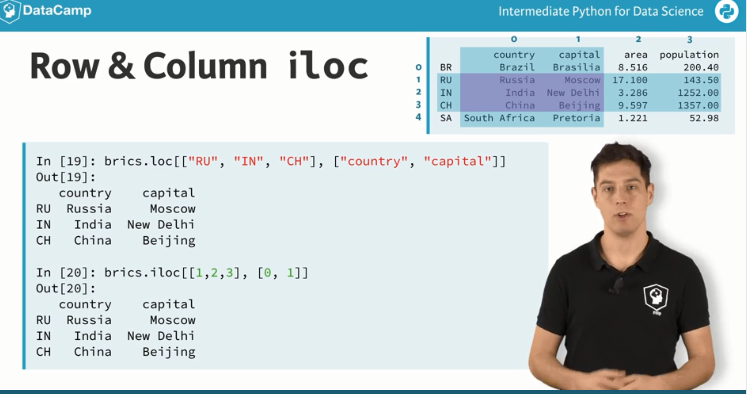
# Import cars data
import pandas as pd
cars = pd.read_csv('cars.csv', index_col = 0)
# Print out observation for Japan
print(cars.iloc[2])
#两种表示方法
# Print out observations for Australia and Egypt
print(cars.loc[['AUS', 'EG']])
# Import cars data
import pandas as pd
cars = pd.read_csv('cars.csv', index_col = 0)
# Print out drives_right value of Morocco
print(cars.iloc[5,2])
# Print sub-DataFrame
print(cars.iloc[[4,5],[1,2]])
[]&[[]]
# Import cars data
import pandas as pd
cars = pd.read_csv('cars.csv', index_col = 0)
# Print out country column as Pandas Series
print(cars["country"])
# Print out country column as Pandas DataFrame
print(cars[['country']])
# Print out DataFrame with country and drives_right columns
print(cars[['country','drives_right']])
# Import cars data
import pandas as pd
cars = pd.read_csv('cars.csv', index_col = 0)
# Print out first 3 observations
print(cars[0:3])
# Print out fourth, fifth and sixth observation
print(cars[3:6])
<script.py> output:
cars_per_cap country drives_right
US 809 United States True
AUS 731 Australia False
JPN 588 Japan False
cars_per_cap country drives_right
IN 18 India False
RU 200 Russia True
MOR 70 Morocco True
提取数据框中的某一列
# Import cars data
import pandas as pd
cars = pd.read_csv('cars.csv', index_col = 0)
# Print out drives_right column as Series
print(cars.iloc[:, 2])
# Print out drives_right column as DataFrame
print(cars.iloc[:, [2]])
# Print out cars_per_cap and drives_right as DataFrame
print(cars.loc[:, ['cars_per_cap', 'drives_right']])
<script.py> output:
US True
AUS False
JPN False
IN False
RU True
MOR True
EG True
Name: drives_right, dtype: bool
drives_right
US True
AUS False
JPN False
IN False
RU True
MOR True
EG True
cars_per_cap drives_right
US 809 True
AUS 731 False
JPN 588 False
IN 18 False
RU 200 True
MOR 70 True
EG 45 True
Comparison Operators
NUMPY中的逻辑运算符
# Create arrays
import numpy as np
my_house = np.array([18.0, 20.0, 10.75, 9.50])
your_house = np.array([14.0, 24.0, 14.25, 9.0])
# my_house greater than 18.5 or smaller than 10
print(np.logical_or(my_house > 18.5, my_house < 10))
# Both my_house and your_house smaller than 11
print(np.logical_and(my_house < 11, your_house < 11))
Filtering Pandas DataFrame
while循环语句
# Initialize offset
offset = -6
# Code the while loop
while offset != 0 :
print("correcting...")
if offset > 0 :
offset=offset-1
else :
offset=offset+1
print(offset)
for loop
# areas list
areas = [11.25, 18.0, 20.0, 10.75, 9.50]
# Change for loop to use enumerate() and update print()
for index, area in enumerate(areas) :
print("room " + str(index) + ": " + str(area))
<script.py> output:
room 0: 11.25
room 1: 18.0
room 2: 20.0
room 3: 10.75
room 4: 9.5
遍历list
# house list of lists
house = [["hallway", 11.25],
["kitchen", 18.0],
["living room", 20.0],
["bedroom", 10.75],
["bathroom", 9.50]]
# Build a for loop from scratch
for x in house:
print("the " + x[0] + " is " + str(x[1]) + " sqm")
遍历数据框的每一行
Iterating over a Pandas DataFrame is typically done with the iterrows() method. Used in a for loop, every observation is iterated over and on every iteration the row label and actual row contents are available:
# Import cars data
import pandas as pd
cars = pd.read_csv('cars.csv', index_col = 0)
# Iterate over rows of cars
for lab, row in cars.iterrows() :
print(lab)
print(row)
<script.py> output:
US
cars_per_cap 809
country United States
drives_right True
Name: US, dtype: object
AUS
cars_per_cap 731
country Australia
drives_right False
Name: AUS, dtype: object
JPN
cars_per_cap 588
country Japan
drives_right False
Name: JPN, dtype: object
IN
cars_per_cap 18
country India
drives_right False
Name: IN, dtype: object
RU
cars_per_cap 200
country Russia
drives_right True
Name: RU, dtype: object
MOR
cars_per_cap 70
country Morocco
drives_right True
Name: MOR, dtype: object
EG
cars_per_cap 45
country Egypt
drives_right True
Name: EG, dtype: object
增加列
可以直接增加,也可以使用apply函数
# Import cars data
import pandas as pd
cars = pd.read_csv('cars.csv', index_col = 0)
# Use .apply(str.upper)
cars["COUNTRY"] = cars["country"].apply(str.upper)
# Import cars data
import pandas as pd
cars = pd.read_csv('cars.csv', index_col = 0)
# Use .apply(str.upper)
for lab, row in cars.iterrows() :
cars.loc[lab, "COUNTRY"] = row["country"].upper()
Random float
随机数问题
Randomness has many uses in science, art, statistics, cryptography, gaming, gambling, and other fields. You're going to use randomness to simulate a game.
All the functionality you need is contained in the random package, a sub-package of numpy. In this exercise, you'll be using two functions from this package:
- seed(): sets the random seed, so that your results are reproducible between simulations. As an argument, it takes an integer of your choosing. If you call the function, no output will be generated.
- rand(): if you don't specify any arguments, it generates a random float between zero and one.
# Import numpy as np
import numpy as np
# Set the seed
np.random.seed(123)
# Generate and print random float
print(np.random.rand())
random_walk
# Numpy is imported, seed is set
# Initialize random_walk
random_walk = [0]
# Complete the ___
for x in range(100) :
# Set step: last element in random_walk
step = random_walk[-1]
# Roll the dice
dice = np.random.randint(1,7)
# Determine next step
if dice <= 2:
step = step - 1
elif dice <= 5:
step = step + 1
else:
step = step + np.random.randint(1,7)
# append next_step to random_walk
random_walk.append(step)
# Print random_walk
print(random_walk)
<script.py> output:
[0, 3, 4, 5, 4, 5, 6, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, 0, 5, 4, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 7, 8, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 10, 14, 15, 14, 15, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 24, 25, 26, 27, 32, 33, 37, 38, 37, 38, 39, 38, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44, 43, 42, 43, 44, 43, 42, 43, 44, 46, 45, 44, 45, 44, 45, 46, 47, 49, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 52, 51, 52, 51, 52, 53, 52, 55, 56, 57, 58, 57, 58, 59]
distrubition
transpose()
转置函数
np.random.randint()
可以指定生成随机数组的维度
参考
看一个小的demo
# numpy and matplotlib imported, seed set
# Simulate random walk 250 times
all_walks = []
for i in range(250) :
random_walk = [0]
for x in range(100) :
step = random_walk[-1]
dice = np.random.randint(1,7)
if dice <= 2:
step = max(0, step - 1)
elif dice <= 5:
step = step + 1
else:
step = step + np.random.randint(1,7)
# Implement clumsiness
if np.random.rand() <= 0.001 :
step = 0
random_walk.append(step)
all_walks.append(random_walk)
# Create and plot np_aw_t
np_aw_t = np.transpose(np.array(all_walks))
plt.plot(np_aw_t)
plt.show()
intermediate-python-for-data-science的更多相关文章
- 学习笔记之Intermediate Python for Data Science | DataCamp
Intermediate Python for Data Science | DataCamp https://www.datacamp.com/courses/intermediate-python ...
- Intermediate Python for Data Science learning 2 - Histograms
Histograms from:https://campus.datacamp.com/courses/intermediate-python-for-data-science/matplotlib? ...
- Intermediate Python for Data Science learning 1 - Basic plots with matplotlib
Basic plots with matplotlib from:https://campus.datacamp.com/courses/intermediate-python-for-data-sc ...
- Intermediate Python for Data Science learning 3 - Customization
Customization from:https://campus.datacamp.com/courses/intermediate-python-for-data-science/matplotl ...
- 40 Questions to test your skill in Python for Data Science
Comes from: https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2017/05/questions-python-for-data-science/ Python i ...
- Intro to Python for Data Science Learning 8 - NumPy: Basic Statistics
NumPy: Basic Statistics from:https://campus.datacamp.com/courses/intro-to-python-for-data-science/ch ...
- Intro to Python for Data Science Learning 7 - 2D NumPy Arrays
2D NumPy Arrays from:https://campus.datacamp.com/courses/intro-to-python-for-data-science/chapter-4- ...
- Intro to Python for Data Science Learning 5 - Packages
Packages From:https://campus.datacamp.com/courses/intro-to-python-for-data-science/chapter-3-functio ...
- Intro to Python for Data Science Learning 2 - List
List from:https://campus.datacamp.com/courses/intro-to-python-for-data-science/chapter-2-python-list ...
- Intro to Python for Data Science Learning 6 - NumPy
NumPy From:https://campus.datacamp.com/courses/intro-to-python-for-data-science/chapter-4-numpy?ex=1 ...
随机推荐
- 简单说说常用的css选择器
这里先来一段HTML代码 <div id="div" class="div"> <p class="div_P1"> ...
- <packaging>pom</packaging>是什么意思
<packaging>pom</packaging>是什么意思? 答: 以下配置<packaging>pom</packaging>的意思是使用mave ...
- Spring的BeanFactory和FactoryBean
官方定义 BeanFactory:Spring Bean容器的根接口 FactoryBean:各个对象的工厂接口,如果bean实现了这个接口,它将被用作对象的工厂,而不是直接作为bean实例. 源码解 ...
- 00 - PXE | 环境准备
00 - PXE | 环境准备 TFTP PXE 1. TFTP服务搭建 安装环境Centos7.3 1.1 安装 # yum install xinetd # yum install tftp # ...
- BZOJ #2989. 数列 [树套树]
考虑转化问题模型,这个没必要可持久化,直接加点就可以了,还不用删点 每次的问题是求 曼哈顿距离,变成切比雪夫距离然后求解 然后我们考虑将这玩意旋转 45度, 然后原坐标的 \((x,y)\) 会变成 ...
- adworld python-trade | python反编译
附件是.pyc格式的文件. Python程序中,原始程序代码存储在.py文件里,而Python会在执行.py文件的时候,会将.py形式的程序编译成中间式文件(byte-compiled)的.pyc文件 ...
- Java使用POI读取Word中的表格
个人博客 地址:https://www.wenhaofan.com/a/20190627135921 代码 package live.autu.word; import java.io.FileInp ...
- Tensor--tensorflow的数据类型
在tensorflow2.0版本之前,1.x版本的tensorflow的基本数据类型有计算图(Computation Graph)和张量(Tensor)两种,但tensorflow2.0之后的版本取消 ...
- JavaDay10(下)
生产者消费者问题 问题描述 有两个进程:一组生产者进程和一组消费者进程共享一个初始为空.固定大小为n的缓存(缓冲区).生产者的工作是制造一段数据,只有缓冲区没满时,生产者才能把消息放入到缓冲区,否则必 ...
- 安装Ansible到CentOS(YUM)
运行环境 系统版本:CentOS Linux release 7.3.1611 (Core) 软件版本:ansible 硬件要求:无 安装过程 1.安装YUM-EPEL源 HTTP-Tools软件包由 ...
