[考试记录] 2024.7.15 csp-s模拟赛4
2024.7.15 csp-s模拟赛4
T1 传送带
题面翻译
有一个长度为 \(n\) 的一维网格。网格的第 \(i\) 个单元格包含字符 \(s_i\) ,是“<”或“>”。当弹球放在其中一个格子上时,它会按照以下规则移动:
如果弹球位于第 \(i\) 个格子上且 \(s_i\) 为 '<',则弹球在下一秒会向左移动一个单元格;如果 \(s_i\) 为 '>',则向右移动一个单元格。弹球移动后,字符 \(s_i\) 会反转(即,如果 \(s_i\) 原来是 '<',则变为 '>',反之亦然)。无论是离开左边界还是从右边界,当弹球离开网格时,它都会停止移动。
您需要回答 \(t(1\le t \le 10^5)\) 个独立的查询。每一组查询中有一个长度 \(n(1\le n\le 5\times10^5)\),及一个只包含 “<” 和 “>”的字符串。弹球可以放在任意一个位置上。对于每个查询,在同一行输出 \(n\) 个数,第 \(i\) 个数表示弹球放置在第 \(i\) 格时离开网格的时长,用空格隔开。
题目描述
There is a one-dimensional grid of length $ n $ . The $ i $ -th cell of the grid contains a character $ s_i $ , which is either '<' or '>'.
When a pinball is placed on one of the cells, it moves according to the following rules:
- If the pinball is on the $ i $ -th cell and $ s_i $ is '<', the pinball moves one cell to the left in the next second. If $ s_i $ is '>', it moves one cell to the right.
- After the pinball has moved, the character $ s_i $ is inverted (i. e. if $ s_i $ used to be '<', it becomes '>', and vice versa).
- The pinball stops moving when it leaves the grid: either from the left border or from the right one.
You need to answer $ n $ independent queries. In the $ i $ -th query, a pinball will be placed on the $ i $ -th cell. Note that we always place a pinball on the initial grid.
For each query, calculate how many seconds it takes the pinball to leave the grid. It can be shown that the pinball will always leave the grid within a finite number of steps.
输入格式
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases $ t $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 10^5 $ ). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains an integer $ n $ ( $ 1 \le n \le 5 \cdot 10^5 $ ).
The second line of each test case contains a string $ s_1s_2 \ldots s_{n} $ of length $ n $ consisting of characters '<' and '>'.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $ n $ over all test cases does not exceed $ 5 \cdot 10^5 $ .
输出格式
For each test case, for each $ i $ ( $ 1 \le i \le n $ ) output the answer if a pinball is initially placed on the $ i $ -th cell.
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
3
3
><<
4
<<<<
6
<><<<>
样例输出 #1
3 6 5
1 2 3 4
1 4 7 10 8 1
提示
In the first test case, the movement of the pinball for $ i=1 $ is shown in the following pictures. It takes the pinball $ 3 $ seconds to leave the grid.
 The movement of the pinball for $ i=2 $ is shown in the following pictures. It takes the pinball $ 6 $ seconds to leave the grid.
The movement of the pinball for $ i=2 $ is shown in the following pictures. It takes the pinball $ 6 $ seconds to leave the grid.

解析
部分分
60pts
可以发现对于每个 \(i\) 开始移动的下标,他会沿着 \(i\) 开始的方向来回弹跳直到走出去,且幅度越来越大。所以很容易想到,对每个点跑双指针模拟这个过程,扩展的过程就是暴力跳下标,理论时间复杂度 \(\mathcal{O}(N^2)\),但实际复杂度可能到 \(\mathcal{O}(N^3)\) 甚至到 \(\mathcal{O}(N^4)\),比如大于小于号交替的极限数据。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n; string s;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>s;
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
string k = s;
int ans = 0, it = i;
while(it && it <= n){
if(k[it-1] == '<') k[--it] = '>';
else k[it-1] = '<', ++it;
++ans;
}
cout<<ans<<' ';
} return 0;
}
80pts
60pts 的优化版。我们不去一个一个跳下标,而是预处理出下一个和上一个大于小于号的位置,直接转移。由此对每个点用双指针模拟这个过程即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
constexpr int N = 5e5 + 5;
int n, nxt[N], lst[N], dayu, xiaoyu;
string s;
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>s;
xiaoyu = n+1, dayu = n+1;
for(int i=n; i>=1; --i){
if(s[i-1] == '>'){
nxt[i] = xiaoyu;
dayu = i;
}
else{
nxt[i] = xiaoyu;
xiaoyu = i;
}
}
dayu = 0, xiaoyu = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
if(s[i-1] == '<'){
lst[i] = dayu;
xiaoyu = i;
} else{
lst[i] = dayu;
dayu = i;
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
int l = i, r = i, ans = 0;
if(s[i-1] == '<'){
while(l && r <= n){
l = lst[l], ans += r - l;
if(!l) break;
r = nxt[r], ans += r - l;
}
}
else{
while(l && r <= n){
r = nxt[r], ans += r - l;
if(r > n) break;
l = lst[l], ans += r - l;
}
}
cout<<ans<<' ';
}
return 0;
}
正解
两个方法复杂度都为 \(\mathcal{O}(N)\),法二常数小。
法一
观察来回弹跳时对答案产生的贡献,比如 \(i\) 在 < 开始,向左跳到第一个 >,然后变向,向右跳到 \(i\) 右边第一个 <,以此类推。所以最后的答案就是:
ans_i&=(i-l_1)+(r_1-l_1)+(r_1-l_2)+\cdots +(r_{k-1}-l_{k-1})+r_k\\
&=i+2*\sum r_k-l_k
\end{split}
\]
维护 \(l\) 和 \(r\) 的前缀和,讨论起始方向计算即可。
法二
考虑相邻答案的转移。考虑串 ><>><,第一个 > 走到右边第一个 < 时变向,所以第一个 > 对答案产生的贡献为 \(2\times (r-i)-1\)。\(r\) 为第一个 < 的坐标。接着看下一个字符 <,可以看作第一个字符 > 向右走到 < 然后回到 >,由于贡献是累加起来的,所以 \(sum+=2\times (r-i)-1\)。然后把 \(sum\) 贡献到答案里去。
由于当前只考虑了向右跳过去跳回来的贡献,所以还要跑一遍向左跳过去跳回来的情况。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
constexpr int N = 5e5 + 5;
string s; int n, ans[N];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>s;
for(int i=1, j=1, sum=0; i<=n; ++i){
while(j <= n && s[j-1] == '>') ++j;
if(j > n) break;
sum += 2 * (j++ - i) + 1;
ans[i] += sum;
}
for(int i=n, j=n, sum=0; i>=1; --i){
while(j >= 1 && s[j-1] == '<') --j;
if(j < 1) break;
sum += 2 * (i - j--) + 1;
ans[i] += sum;
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cout<<ans[i]<<' ';
return 0;
}
T2 math
Description
沉迷于数学的小G最近口胡出一种数据生成方法: 开始,小G有一个长度为 \(n\) 的正整数序列,序列中的第 \(i\) 个数为 \(a_i\in [1,10^9]\)。 然后,小G会通过某种方式生成一个长度为 \(n\) 的非负整数序列,序列中的第 \(i\) 个数为 \(b_i\in[0,+\infty]\)。 最终,小G会得到一个整数 \(x=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}a_ib_i\bmod k\)。
小G想知道这种数据生成方法可以生成哪些不同的非负整数。
Sample
样例输入
2 8
4 12
样例输出
2
0 4
解析
很好的数论题,但考场上并没有推出这一结论,而是找归路分类讨论,wa了几个点,78pts。
很好的数论题。考虑 \(n=1\) 的情况,有 \(a*b \equiv x \pmod{k}\),可化为 \(ab+ky=x\)。若该狮子有整数解,那么当且仅当 \(\gcd(a,k)\mid x\)。因此答案 \(x\) 只能是 \(gcd\) 的整数倍,并且小于 \(k\)。所以计算出所有 \(a\) 与 \(k\) 的 \(gcd\),枚举输出答案即可。复杂度 \(\mathcal{O}((n+v)\log n)\)。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, k, gcd, a, ans;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>k; gcd = k;
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin>>a, gcd = __gcd(a, gcd);
ans = k / gcd; cout<<ans<<'\n';
for(int i=0; i*gcd < k; ++i) cout<<i*gcd<<' ';
return 0;
}
T3
letax 懒得打了。

解析
很好的DP题。暴力40pts。
首先对每个 \(a!=0\) 的点进行排序,这是显然的。然后我就在思考怎么单调队列 \(\mathcal{O}(n)\) 转移,然后发现这个绝对值把 i 和 j 绑在一起了,然后就想怎么把绝对值去掉,然后就考虑平方一下,然后成功地又把 i 和 j 绑一起了。于是打BL。其实单调队列也可以维护,只不过要把坐标转为切比雪夫距离,最后记录路径计算答案即可。
不会切比雪夫):?考虑简单DP。设当前需要转移的点为 \(i\) ,那么 \(j\) 可以在 \(i\) 的左上、左下、右上和右下四种情况。需要在转移时判断点在那个方位吗?不需要,因为取绝对值的原因,所以 xy 坐标给的贡献必须大于 0,所以只要在这四种转移里取 max 即可。这是本题极为关键的一点。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
constexpr int N = 2e3 + 2;
int n, m, x[N*N], y[N*N], a[N*N], b[N*N], cnt, dp[N*N], p1[N*N], num2[N*N], tot;
int rnk[N][N], srt[N*N], p[N*N], num[N*N], tail, way[N*N], ans, nxt[4], lst[4];
bool cmp(int q, int w){ return a[q] < a[w]; }
int dx[4] = {1, 1, -1, -1}, dy[4] = {1, -1, 1, -1};
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) for(int j=1; j<=m; ++j){
cin>>a[++cnt];
x[cnt] = i, y[cnt] = j;
rnk[i][j] = cnt;
srt[cnt] = cnt;
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) for(int j=1; j<=m; ++j)
cin>>b[rnk[i][j]];
sort(srt+1, srt+1+cnt, cmp);
int bg = 1; while(!a[srt[bg]]) ++bg;
for(int i=bg; i<=cnt; ++i){
if(a[srt[i]] != a[srt[i-1]] && a[srt[i-1]]){ bg = i; break; }
dp[srt[i]] = b[srt[i]];
for(int j=0; j<4; ++j)
nxt[j] = max(nxt[j], dp[srt[i]] + x[srt[i]]*dx[j] + y[srt[i]]*dy[j]);
ans = max(ans, dp[srt[i]]);
}
for(int i=bg; i<=cnt; ++i){
if(a[srt[i]] != a[srt[i-1]]) for(int j=0; j<4; ++j)
lst[j] = nxt[j], nxt[j] = 0;
for(int j=0; j<4; ++j)
dp[srt[i]] = max(dp[srt[i]], b[srt[i]] - x[srt[i]]*dx[j] - y[srt[i]]*dy[j] + lst[j]);
for(int j=0; j<4; ++j)
nxt[j] = max(nxt[j], dp[srt[i]] + x[srt[i]]*dx[j] + y[srt[i]]*dy[j]);
ans = max(ans, dp[srt[i]]);
}
return cout<<ans, 0;
}
T4

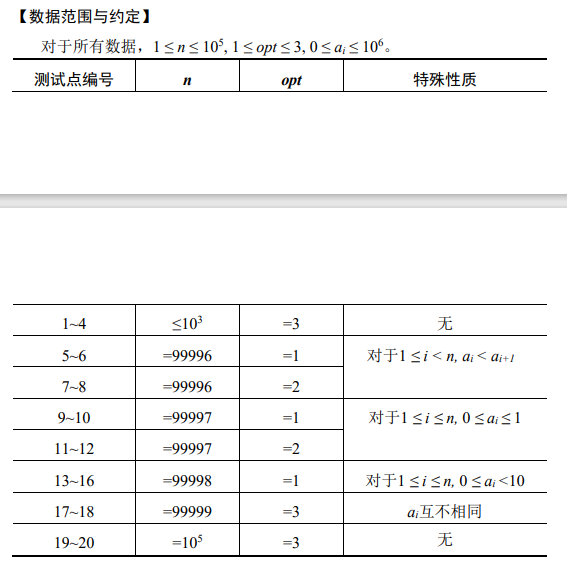
个人能力有限,暂时该不出来,所以先咕~。
[考试记录] 2024.7.15 csp-s模拟赛4的更多相关文章
- 【2018.10.15】noip模拟赛Day1
题面 wzj的题解 T1 随便搜 #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long using namespace std; inline int ...
- 6.15 省选模拟赛 老魔杖 博弈论 SG函数
这道题确实没有一个很好的解决办法 唯一的正解可能就是打表找规律 或者 直接猜结论了吧. 尽管如此 在此也给最终结论一个完整的证明. 对于70分 容易发现状态数量不大 可以进行暴力dp求SG函数. 原本 ...
- 5.15 省选模拟赛 容斥 生成函数 dp
LINK:5.15 T2 个人感觉生成函数更无脑 容斥也好推的样子. 容易想到每次放数和数字的集合无关 所以得到一个dp f[i][j]表示前i个数字 逆序对为j的方案数. 容易得到转移 使用前缀和优 ...
- 5.15 省选模拟赛 T1 点分治 FFT
LINK:5.15 T1 对于60分的暴力 都很水 就不一一赘述了. 由于是询问所有点的这种信息 确实不太会. 想了一下 如果只是询问子树内的话 dsu on tree还是可以做的. 可以自己思考一下 ...
- 4.15 省选模拟赛 编码 trie树 前缀和优化建图 2-sat
好题 np. 对于20分 显然可以爆搜. 对于50分 可以发现每个字符串上的问号要么是0,要么是1.考虑枚举一个字符串当前是0还是1 这会和其他字符串产生矛盾. 所以容易 发现这是一个2-sat问题. ...
- 10.17 NOIP模拟赛
目录 2018.10.17 NOIP模拟赛 A 咒语curse B 神光light(二分 DP) C 迷宫maze(次短路) 考试代码 B 2018.10.17 NOIP模拟赛 时间:1h15min( ...
- 10.16 NOIP模拟赛
目录 2018.10.16 NOIP模拟赛 A 购物shop B 期望exp(DP 期望 按位计算) C 魔法迷宫maze(状压 暴力) 考试代码 C 2018.10.16 NOIP模拟赛 时间:2h ...
- [总结] NOIP 前的考试记录
sb博主又犯sb错误了! 他觉得以往模拟赛因为犯sb错误扔的分足足有1k分了! 于是他想记录一下自己犯的sb错误看看自己到底有多sb! 嗯就从今天开始吧 2018.9.28 1. 二分边界写错.骚什么 ...
- NOIP2017提高组 模拟赛15(总结)
NOIP2017提高组 模拟赛15(总结) 第一题 讨厌整除的小明 [题目描述] 小明作为一个数学迷,总会出于数字的一些性质喜欢上某个数字,然而当他喜欢数字k的时候,却十分讨厌那些能够整除k而比k小的 ...
- CSP模拟赛游记
时间:2019.10.5 考试时间:100分钟(连正式考试时间的一半还没有到)题目:由于某些原因不能公开. 由于第一次接触NOIinux系统所以连怎么建文件夹,调字体,如何编译都不知道,考试的前半小时 ...
随机推荐
- Oh-My-Zsh 提示符只显示当前路径,不需要修改主题文件
我真是服了.就这么一个简单的小问题我在网上找了一个多小时,一大堆 CSDN 文章都是抄 同一篇博客 的教程,所有的博客都要我去把 ~/.oh-my-zsh/themes/*.zsh-theme 文件里 ...
- 使用iperf3调试网络
介绍 Iperf是一款基于TCP/IP和UDP/IP的网络性能测试工具,它可以用来测量网络带宽和网络质量,还可以提供网络延迟抖动.数据包丢失率.最大传输单元等统计信息.网络管理员可以根据这些信息了解并 ...
- mysqldump备份时保持数据一致性分析--master-data=2 --single-transaction
对MySQL数据进行备份,常见的方式如以下三种,可能有很多人对备份时数据一致性并不清楚 1.直接拷贝整个数据目录下的所有文件到新的机器.优点是简单.快速,只需要拷贝:缺点也很明显,在整个备份过程中新机 ...
- 3.8折钜惠,瑞芯微RK3568J国产工业评估板“限时折扣”!
- 从 Dict 转到 Dataclass
从 dataclass 转到 dict 可以用 asdict 函数 , 反向转换的时候 就比较困难. 不用外部的包的情况下, 提供一种思路. def mask(v, d): #v 是 dict 数据, ...
- windows10 iis 环境下部署 asp.net core 应用程序的步骤
1.运行powershell,在运行窗口中输入:powershell,点回车,如下图: 2.安装choco,在打开的powershell窗口中输入:Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass ...
- Ubuntu 查看用户历史记录
Ubuntu 查看用户历史记录 1. 查看用户命令行历史记录 1. 查看当前登录账号所属用户的历史命令行记录 打开命令行,输入 history 就会看到当前登录账号所属用户的历史记录 2. 查看系统所 ...
- EasyBPM进销存之物料管理
本文是EasyBPM平台实现进销存系列中的一篇,主要讲述物料的相关的管理. 在ERP系统中,"物料"一词有着广泛的含义,它是所有产品.半成品.在制品.原材料.配套件.协作件.易耗品 ...
- [oeasy]python019_ 如何在github仓库中进入目录_找到程序代码_找到代码
继续运行 回忆上次内容 上上次 真写了万行代码 这 万行代码 都是写在明面上的 这次 使用git命令 下载了 github上面的仓库 添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选) 下载仓库 ...
- [oeasy]python0127_中文系统_gbk_BIG5_南极星_内码转化
中文系统bgk 回忆上次内容 汉字字形通过 点阵式打字机 像素级寻址的屏幕 进入了计算机的世界 添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选) 在海峡对岸的台湾同胞 也进入了汉字时代 他 ...
