Android7.0 Phone应用源码分析(三) phone拒接流程分析
接上篇博文:Android7.0 Phone应用源码分析(二) phone来电流程分析
今天我们再来分析下Android7.0 的phone的拒接流程

下面先来看一下拒接电话流程时序图
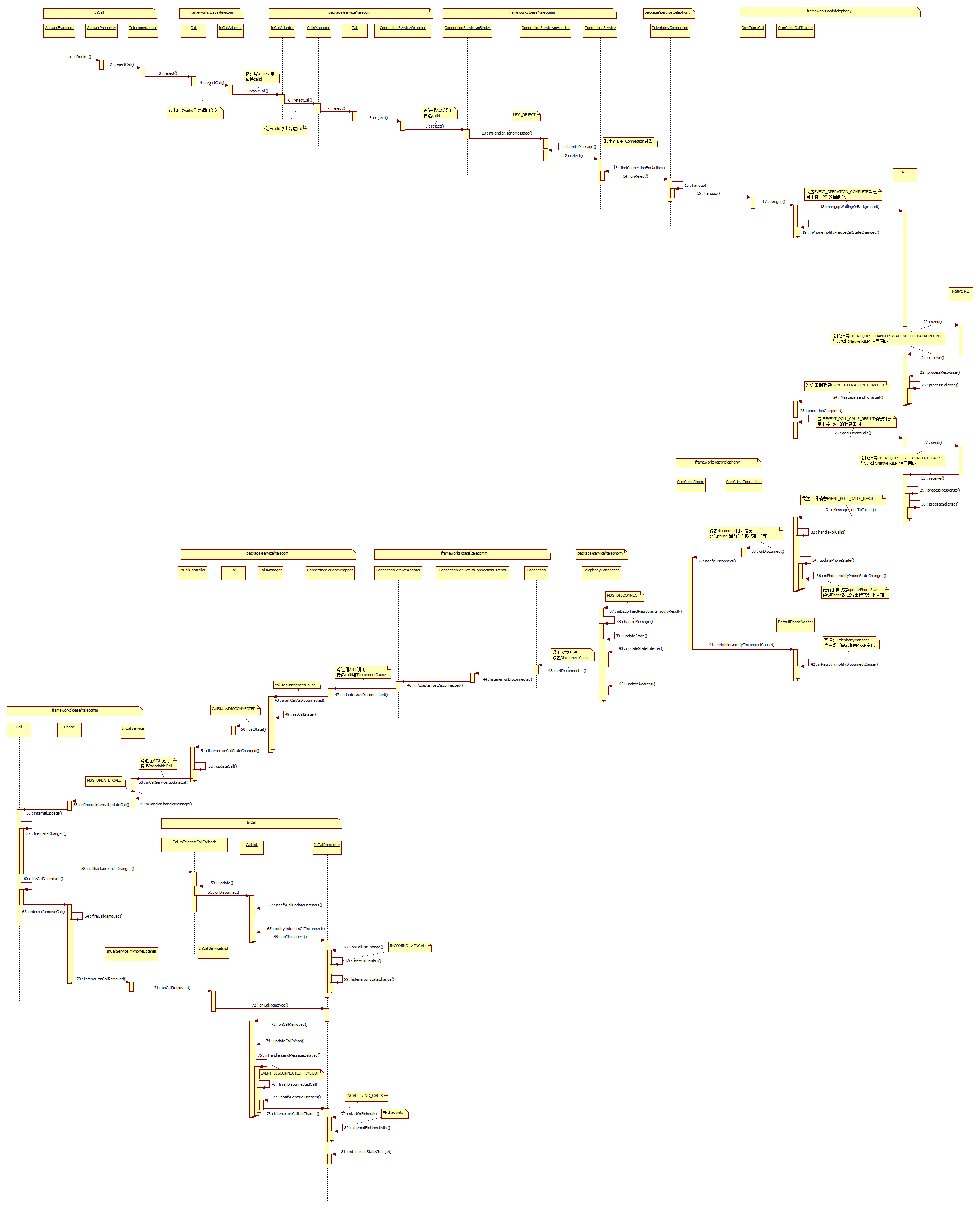
步骤1:滑动按钮到拒接图标,会调用到AnswerFragment的onDecline方法
com.android.incallui.AnswerFragment
public void onDecline(Context context) {
getPresenter().onDecline(context);
}
最后是调用到AnswerPresenteronDecline方法
com.android.incallui.AnswerPresenter
public void onDecline(Context context) {
Log.d(this, "onDecline " + mCallId);
if (mCall.getSessionModificationState()
== Call.SessionModificationState.RECEIVED_UPGRADE_TO_VIDEO_REQUEST) {
InCallPresenter.getInstance().declineUpgradeRequest(context);
} else {
TelecomAdapter.getInstance().rejectCall(mCall.getId(), false, null);
}
}
步骤2:进入TelecomAdapter的rejectCall方法
com.android.incallui.TelecomAdapter
void rejectCall(String callId, boolean rejectWithMessage, String message) {
android.telecom.Call call = getTelecomCallById(callId);
if (call != null) {
call.reject(rejectWithMessage, message);
} else {
Log.e(this, "error rejectCall, call not in call list: " + callId);
}
}
TelecomAdapter是incallui与telecom通信的代理类,这里通过callid取出对应的Call对象(android.telecom.Call)
步骤3:调用到framework里Call的reject方法
android.telecom.Call
public void reject(boolean rejectWithMessage, String textMessage) {
mInCallAdapter.rejectCall(mTelecomCallId, rejectWithMessage, textMessage);
}
这里mInCallAdapter是android.telecom.InCallAdapter类,是在Call对象创建的时候由外部传入的参数
在telecom绑定InCallService服务的时候,会传递一个AIDL接口对象,InCallService会生成InCallAdapter对象来保存这个接口对象
步骤4:InCallAdapter的rejectCall方法
android.telecom.InCallAdapter
public void rejectCall(String callId, boolean rejectWithMessage, String textMessage) {
try {
mAdapter.rejectCall(callId, rejectWithMessage, textMessage);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
mAdapter就是incallui与telecom通信的AIDL接口
步骤5:跨进程调用进入telecom进程,该AIDL接口具体实现类是InCallAdapter,虽然类名一样但是不同的包名,这里需要注意一下
com.android.server.telecom.InCallAdapter
public void rejectCall(String callId, boolean rejectWithMessage, String textMessage) {
try {
Log.startSession("ICA.rC", mOwnerComponentName);
long token = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
synchronized (mLock) {
Log.d(this, "rejectCall(%s,%b,%s)", callId, rejectWithMessage, textMessage);
Call call = mCallIdMapper.getCall(callId);
if (call != null) {
mCallsManager.rejectCall(call, rejectWithMessage, textMessage);
} else {
Log.w(this, "setRingback, unknown call id: %s", callId);
}
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(token);
}
} finally {
Log.endSession();
}
}
这里同样是根据callid取出对应Call(com.android.server.telecom.Call),最后调用CallsManager的rejectCall方法传入call
步骤6:CallsManager的rejectCall方法
com.android.server.telecom.CallsManager
public void rejectCall(Call call, boolean rejectWithMessage, String textMessage) {
if (!mCalls.contains(call)) {
Log.i(this, "Request to reject a non-existent call %s", call);
} else {
for (CallsManagerListener listener : mListeners) {
listener.onIncomingCallRejected(call, rejectWithMessage, textMessage);
}
call.reject(rejectWithMessage, textMessage);
}
}
这里先通知观察者来电拒接事件,比如CallAudioManager对该事件感兴趣,它的处理是停止播放来电铃声和来电等待声
com.android.server.telecom.CallAudioManager
public void onIncomingCallRejected(Call call, boolean rejectWithMessage, String message) {
maybeStopRingingAndCallWaitingForAnsweredOrRejectedCall(call);
}
private void maybeStopRingingAndCallWaitingForAnsweredOrRejectedCall(Call call) {
// Check to see if the call being answered/rejected is the only ringing call, since this
// will be called before the connection service acknowledges the state change.
if (mRingingCalls.size() == 0 ||
(mRingingCalls.size() == 1 && call == mRingingCalls.iterator().next())) {
mRinger.stopRinging();
mRinger.stopCallWaiting();
}
}
最后再调用前面传进来的call对象的reject方法
步骤7:Call的reject方法
com.android.server.telecom.Call
public void reject(boolean rejectWithMessage, String textMessage) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(mConnectionService); // Check to verify that the call is still in the ringing state. A call can change states
// between the time the user hits 'reject' and Telecomm receives the command.
if (isRinging("reject")) {
// Ensure video state history tracks video state at time of rejection.
mVideoStateHistory |= mVideoState; mConnectionService.reject(this, rejectWithMessage, textMessage);
Log.event(this, Log.Events.REQUEST_REJECT);
}
}
这里的mConnectionService是ConnectionServiceWrapper类,是telecom与telephony通信的代理类
步骤8:ConnectionServiceWrapper的reject方法
com.android.server.telecom.ConnectionServiceWrapper
void reject(Call call, boolean rejectWithMessage, String message) {
final String callId = mCallIdMapper.getCallId(call);
if (callId != null && isServiceValid("reject")) {
try {
logOutgoing("reject %s", callId); if (rejectWithMessage && call.can(
Connection.CAPABILITY_CAN_SEND_RESPONSE_VIA_CONNECTION)) {
mServiceInterface.rejectWithMessage(callId, message);
} else {
mServiceInterface.reject(callId);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
}
这里mServiceInterface就是telephony提供给telecom调用的AIDL接口
步骤9:跨进程调用进入telephony进程,telephony进程实际服务类是TelephonyConnectionService继承于ConnectionService类在manifest声明如下:
<service
android:singleUser="true"
android:name="com.android.services.telephony.TelephonyConnectionService"
android:label="@string/pstn_connection_service_label"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_TELECOM_CONNECTION_SERVICE" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.telecom.ConnectionService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
而AIDL接口具体实现是其父类ConnectionService的mBinder成员变量
android.telecom.ConnectionService
private final IBinder mBinder = new IConnectionService.Stub() { @Override
public void reject(String callId) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_REJECT, callId).sendToTarget();
}
}
步骤10~13:发送MSG_REJECT消息到队列里处理
private void reject(String callId) {
Log.d(this, "reject %s", callId);
findConnectionForAction(callId, "reject").onReject();
}
private Connection findConnectionForAction(String callId, String action) {
if (mConnectionById.containsKey(callId)) {
return mConnectionById.get(callId);
}
Log.w(this, "%s - Cannot find Connection %s", action, callId);
return getNullConnection();
}
根据callid找到对应的connection对象(android.telecom.Connection),调用onReject方法
步骤14:TelephonyConnection继承于connection
com.android.services.telephony.TelephonyConnection
public void onReject() {
Log.v(this, "onReject");
if (isValidRingingCall()) {
hangup(android.telephony.DisconnectCause.INCOMING_REJECTED);
}
super.onReject();
}
protected void hangup(int telephonyDisconnectCode) {
if (mOriginalConnection != null) {
try {
// Hanging up a ringing call requires that we invoke call.hangup() as opposed to
// connection.hangup(). Without this change, the party originating the call will not
// get sent to voicemail if the user opts to reject the call.
if (isValidRingingCall()) {
Call call = getCall();
if (call != null) {
call.hangup();
} else {
Log.w(this, "Attempting to hangup a connection without backing call.");
}
} else {
// We still prefer to call connection.hangup() for non-ringing calls in order
// to support hanging-up specific calls within a conference call. If we invoked
// call.hangup() while in a conference, we would end up hanging up the entire
// conference call instead of the specific connection.
mOriginalConnection.hangup();
}
} catch (CallStateException e) {
Log.e(this, e, "Call to Connection.hangup failed with exception");
}
}
}
步骤15,16:这获取mOriginalConnection的call(com.android.internal.telephony.Call)对象,并调用hangup方法
protected Call getCall() {
if (mOriginalConnection != null) {
return mOriginalConnection.getCall();
}
return null;
}
Call是抽象类,具体子类是GsmCdmaCall
com.android.internal.telephony.GsmCdmaCall
public void hangup() throws CallStateException {
mOwner.hangup(this);
}
mOwner是GsmCdmaCallTracker对象
步骤17:GsmCdmaCallTracker的hangup方法
com.android.internal.telephony.GsmCdmaCallTracker
public void hangup(GsmCdmaCall call) throws CallStateException {
if (call.getConnections().size() == 0) {
throw new CallStateException("no connections in call");
} if (call == mRingingCall) {
if (Phone.DEBUG_PHONE) log("(ringing) hangup waiting or background");
mCi.hangupWaitingOrBackground(obtainCompleteMessage());
} else if (call == mForegroundCall) {
if (call.isDialingOrAlerting()) {
if (Phone.DEBUG_PHONE) {
log("(foregnd) hangup dialing or alerting...");
}
hangup((GsmCdmaConnection)(call.getConnections().get(0)));
} else if (isPhoneTypeGsm()
&& mRingingCall.isRinging()) {
// Do not auto-answer ringing on CHUP, instead just end active calls
log("hangup all conns in active/background call, without affecting ringing call");
hangupAllConnections(call);
} else {
hangupForegroundResumeBackground();
}
} else if (call == mBackgroundCall) {
if (mRingingCall.isRinging()) {
if (Phone.DEBUG_PHONE) {
log("hangup all conns in background call");
}
hangupAllConnections(call);
} else {
hangupWaitingOrBackground();
}
} else {
throw new RuntimeException ("GsmCdmaCall " + call +
"does not belong to GsmCdmaCallTracker " + this);
} call.onHangupLocal();
mPhone.notifyPreciseCallStateChanged();
}
由于是ringcall,这里调用mCi.hangupWaitingOrBackground(obtainCompleteMessage());
mCi是CommandsInterface即RILJ接口,包装了一个EVENT_OPERATION_COMPLETE回调消息,发送给RIL
步骤18:RIL的hangupWaitingOrBackground方法
com.android.internal.telephony.RIL
hangupWaitingOrBackground (Message result) {
RILRequest rr = RILRequest.obtain(RIL_REQUEST_HANGUP_WAITING_OR_BACKGROUND,
result);
if (RILJ_LOGD) riljLog(rr.serialString() + "> " + requestToString(rr.mRequest));
mEventLog.writeRilHangup(rr.mSerial, RIL_REQUEST_HANGUP_WAITING_OR_BACKGROUND, -1);
send(rr);
}
给RIL层发送RIL_REQUEST_HANGUP_WAITING_OR_BACKGROUND消息
步骤19:mPhone.notifyPreciseCallStateChanged通知Phone状态监听事件
步骤20~24:收到RIL层的回应消息并处理,最后发送回调消息EVENT_OPERATION_COMPLETE给GsmCdmaCallTracker
步骤25:GsmCdmaCallTracker处理回调消息EVENT_OPERATION_COMPLETE
com.android.internal.telephony.GsmCdmaCallTracker
private void operationComplete() {
mPendingOperations--; if (DBG_POLL) log("operationComplete: pendingOperations=" +
mPendingOperations + ", needsPoll=" + mNeedsPoll); if (mPendingOperations == 0 && mNeedsPoll) {
mLastRelevantPoll = obtainMessage(EVENT_POLL_CALLS_RESULT);
mCi.getCurrentCalls(mLastRelevantPoll);
} else if (mPendingOperations < 0) {
// this should never happen
Rlog.e(LOG_TAG,"GsmCdmaCallTracker.pendingOperations < 0");
mPendingOperations = 0;
}
}
这里再次向RIL发送消息主动获取当前Call状态,包装的回调消息为EVENT_POLL_CALLS_RESULT
步骤26~32:RIL返回消息,GsmCdmaCallTracker接收EVENT_POLL_CALLS_RESULT消息并处理
protected synchronized void handlePollCalls(AsyncResult ar) {
...................
for (int i = mDroppedDuringPoll.size() - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
GsmCdmaConnection conn = mDroppedDuringPoll.get(i);
//CDMA
boolean wasDisconnected = false;
if (conn.isIncoming() && conn.getConnectTime() == 0) {
// Missed or rejected call
int cause;
if (conn.mCause == DisconnectCause.LOCAL) {
cause = DisconnectCause.INCOMING_REJECTED;
} else {
cause = DisconnectCause.INCOMING_MISSED;
}
if (Phone.DEBUG_PHONE) {
log("missed/rejected call, conn.cause=" + conn.mCause);
log("setting cause to " + cause);
}
mDroppedDuringPoll.remove(i);
hasAnyCallDisconnected |= conn.onDisconnect(cause);
wasDisconnected = true;
} else if (conn.mCause == DisconnectCause.LOCAL
|| conn.mCause == DisconnectCause.INVALID_NUMBER) {
mDroppedDuringPoll.remove(i);
hasAnyCallDisconnected |= conn.onDisconnect(conn.mCause);
wasDisconnected = true;
}
if (!isPhoneTypeGsm() && wasDisconnected && unknownConnectionAppeared
&& conn == newUnknownConnectionCdma) {
unknownConnectionAppeared = false;
newUnknownConnectionCdma = null;
}
...................
...................
updatePhoneState();
if (unknownConnectionAppeared) {
if (isPhoneTypeGsm()) {
for (Connection c : newUnknownConnectionsGsm) {
log("Notify unknown for " + c);
mPhone.notifyUnknownConnection(c);
}
} else {
mPhone.notifyUnknownConnection(newUnknownConnectionCdma);
}
}
if (hasNonHangupStateChanged || newRinging != null || hasAnyCallDisconnected) {
mPhone.notifyPreciseCallStateChanged();
}
}
这里设置DisconnectCause.INCOMING_REJECTED为连接断开的cause并调用GsmCdmaConnection的onDisconnect方法
步骤33:GsmCdmaConnection的onDisconnect方法
com.android.internal.telephony.GsmCdmaConnection
public boolean onDisconnect(int cause) {
boolean changed = false; mCause = cause; if (!mDisconnected) {
doDisconnect(); if (DBG) Rlog.d(LOG_TAG, "onDisconnect: cause=" + cause); mOwner.getPhone().notifyDisconnect(this); if (mParent != null) {
changed = mParent.connectionDisconnected(this);
} mOrigConnection = null;
}
clearPostDialListeners();
releaseWakeLock();
return changed;
}
doDisconnect方法设置断开时间以及通话时长
private void doDisconnect() {
mIndex = -1;
mDisconnectTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
mDuration = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - mConnectTimeReal;
mDisconnected = true;
clearPostDialListeners();
}
最后通知注册者断开事件mOwner.getPhone().notifyDisconnect(this);
步骤34,36:通知phone状态变化事件给相关监听者
步骤35:GsmCdmaPhone通知通话断开事件
com.android.internal.telephony.GsmCdmaPhone
public void notifyDisconnect(Connection cn) {
mDisconnectRegistrants.notifyResult(cn); mNotifier.notifyDisconnectCause(cn.getDisconnectCause(), cn.getPreciseDisconnectCause());
}
步骤37~40:TelephonyConnection注册了断开事件监听,接收并处理断开消息
com.android.services.telephony.TelephonyConnection
void setOriginalConnection(com.android.internal.telephony.Connection originalConnection) {
Log.v(this, "new TelephonyConnection, originalConnection: " + originalConnection);
......
getPhone().registerForDisconnect(mHandler, MSG_DISCONNECT, null);
......
}
void updateState() {
if (mOriginalConnection == null) {
return;
}
updateStateInternal();
updateStatusHints();
updateConnectionCapabilities();
updateConnectionProperties();
updateAddress();
updateMultiparty();
}
void updateStateInternal() {
if (mOriginalConnection == null) {
return;
}
Call.State newState;
// If the state is overridden and the state of the original connection hasn't changed since,
// then we continue in the overridden state, else we go to the original connection's state.
if (mIsStateOverridden && mOriginalConnectionState == mOriginalConnection.getState()) {
newState = mConnectionOverriddenState;
} else {
newState = mOriginalConnection.getState();
}
Log.v(this, "Update state from %s to %s for %s", mConnectionState, newState, this);
if (mConnectionState != newState) {
mConnectionState = newState;
switch (newState) {
case IDLE:
break;
case ACTIVE:
setActiveInternal();
break;
case HOLDING:
setOnHold();
break;
case DIALING:
case ALERTING:
setDialing();
break;
case INCOMING:
case WAITING:
setRinging();
break;
case DISCONNECTED:
setDisconnected(DisconnectCauseUtil.toTelecomDisconnectCause(
mOriginalConnection.getDisconnectCause(),
mOriginalConnection.getVendorDisconnectCause()));
close();
break;
case DISCONNECTING:
break;
}
}
}
通过DisconnectCauseUtil的toTelecomDisconnectCause方法生成DisconnectCause(android.telecom.DisconnectCause)对象
包含code, label, description, reason,toneToPlay信息
步骤41,42:通知外部监听者断开事件mNotifier.notifyDisconnectCause
步骤43:调用父类Connection的setDisconnected方法
public final void setDisconnected(DisconnectCause disconnectCause) {
checkImmutable();
mDisconnectCause = disconnectCause;
setState(STATE_DISCONNECTED);
Log.d(this, "Disconnected with cause %s", disconnectCause);
for (Listener l : mListeners) {
l.onDisconnected(this, disconnectCause);
}
}
回调通知观察者ConnectionService注册了该事件,mConnectionListener接收处理
步骤44:mConnectionListener处理onDisconnected事件
android.telecom.ConnectionService
private final Connection.Listener mConnectionListener = new Connection.Listener() {
......
@Override
public void onDisconnected(Connection c, DisconnectCause disconnectCause) {
String id = mIdByConnection.get(c);
Log.d(this, "Adapter set disconnected %s", disconnectCause);
mAdapter.setDisconnected(id, disconnectCause);
} }
根据connection对象取出对应的callid
步骤45:TelephonyConnection的updateAddress方法更新connection信息
步骤46:ConnectionServiceAdapter的setDisconnected方法
android.telecom.ConnectionServiceAdapter
void setDisconnected(String callId, DisconnectCause disconnectCause) {
for (IConnectionServiceAdapter adapter : mAdapters) {
try {
adapter.setDisconnected(callId, disconnectCause);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
}
telecom在绑定TelephonyConnectionService的时候,会设置AIDL回调接口对象给telephony即ConnectionServiceWrapper的Adapter成员变量
步骤47:跨进程调用到telecom进程,ConnectionServiceWrapper的Adapter处理setDisconnected
com.android.server.telecom.ConnectionServiceWrapper
private final class Adapter extends IConnectionServiceAdapter.Stub {
......
@Override
public void setDisconnected(String callId, DisconnectCause disconnectCause) {
Log.startSession("CSW.sD");
long token = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
synchronized (mLock) {
logIncoming("setDisconnected %s %s", callId, disconnectCause);
Call call = mCallIdMapper.getCall(callId);
Log.d(this, "disconnect call %s %s", disconnectCause, call);
if (call != null) {
mCallsManager.markCallAsDisconnected(call, disconnectCause);
} else {
// Log.w(this, "setDisconnected, unknown call id: %s", args.arg1);
}
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(token);
Log.endSession();
}
}
......
}
根据callid取出Call(com.android.server.telecom.Call)对象,给CallsManager传递Call和disconnectCause
步骤48,49,50:CallsManager的markCallAsDisconnected方法
com.android.server.telecom.CallsManager
void markCallAsDisconnected(Call call, DisconnectCause disconnectCause) {
call.setDisconnectCause(disconnectCause);
setCallState(call, CallState.DISCONNECTED, "disconnected set explicitly");
}
给Call设置disconnectCause,同时设置callstate
private void setCallState(Call call, int newState, String tag) {
if (call == null) {
return;
}
int oldState = call.getState();
Log.i(this, "setCallState %s -> %s, call: %s", CallState.toString(oldState),
CallState.toString(newState), call);
if (newState != oldState) {
// Unfortunately, in the telephony world the radio is king. So if the call notifies
// us that the call is in a particular state, we allow it even if it doesn't make
// sense (e.g., STATE_ACTIVE -> STATE_RINGING).
// TODO: Consider putting a stop to the above and turning CallState
// into a well-defined state machine.
// TODO: Define expected state transitions here, and log when an
// unexpected transition occurs.
call.setState(newState, tag);
maybeShowErrorDialogOnDisconnect(call);
Trace.beginSection("onCallStateChanged");
// Only broadcast state change for calls that are being tracked.
if (mCalls.contains(call)) {
updateCallsManagerState();
for (CallsManagerListener listener : mListeners) {
if (Log.SYSTRACE_DEBUG) {
Trace.beginSection(listener.getClass().toString() + " onCallStateChanged");
}
listener.onCallStateChanged(call, oldState, newState);
if (Log.SYSTRACE_DEBUG) {
Trace.endSection();
}
}
}
Trace.endSection();
}
}
最后回调onCallStateChanged方法通知监听者,这里监听call状态变化的对象有很多,我们看下InCallController的处理
步骤51,52:InCallController的onCallStateChanged方法
com.android.server.telecom.InCallController
@Override
public void onCallStateChanged(Call call, int oldState, int newState) {
updateCall(call);
}
private void updateCall(Call call, boolean videoProviderChanged) {
if (!mInCallServices.isEmpty()) {
ParcelableCall parcelableCall = ParcelableCallUtils.toParcelableCall(
call,
videoProviderChanged /* includeVideoProvider */,
mCallsManager.getPhoneAccountRegistrar());
Log.i(this, "Sending updateCall %s ==> %s", call, parcelableCall);
List<ComponentName> componentsUpdated = new ArrayList<>();
for (Map.Entry<ComponentName, IInCallService> entry : mInCallServices.entrySet()) {
ComponentName componentName = entry.getKey();
IInCallService inCallService = entry.getValue();
componentsUpdated.add(componentName);
try {
inCallService.updateCall(parcelableCall);
} catch (RemoteException ignored) {
}
}
Log.i(this, "Components updated: %s", componentsUpdated);
}
}
}
根据call信息生成ParcelableCall对象,给incallservice传递ParcelableCall
步骤53,54:InCallService的updateCall方法
android.telecom.InCallService
@Override
public void updateCall(ParcelableCall call) {
mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_UPDATE_CALL, call).sendToTarget();
}
private final Handler mHandler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
......
case MSG_UPDATE_CALL:
mPhone.internalUpdateCall((ParcelableCall) msg.obj);
break;
}
步骤55:Phone的internalUpdateCall方法
android.telecom.Phone
final void internalUpdateCall(ParcelableCall parcelableCall) {
Call call = mCallByTelecomCallId.get(parcelableCall.getId());
if (call != null) {
checkCallTree(parcelableCall);
call.internalUpdate(parcelableCall, mCallByTelecomCallId);
}
}
这里的Phone对象只是一个管理类,保存call列表信息和与telecom通信的AIDL接口对象,通过callid取出Call(android.telecom.Call)对象
步骤56:Call的internalUpdate方法
android.telecom.Call
final void internalUpdate(ParcelableCall parcelableCall, Map<String, Call> callIdMap) { Details details = Details.createFromParcelableCall(parcelableCall); ......
...... // Now we fire updates, ensuring that any client who listens to any of these notifications
// gets the most up-to-date state. if (stateChanged) {
fireStateChanged(mState);
}
if (detailsChanged) {
fireDetailsChanged(mDetails);
}
if (cannedTextResponsesChanged) {
fireCannedTextResponsesLoaded(mCannedTextResponses);
}
if (videoCallChanged) {
fireVideoCallChanged(mVideoCallImpl);
}
if (parentChanged) {
fireParentChanged(getParent());
}
if (childrenChanged) {
fireChildrenChanged(getChildren());
} // If we have transitioned to DISCONNECTED, that means we need to notify clients and
// remove ourselves from the Phone. Note that we do this after completing all state updates
// so a client can cleanly transition all their UI to the state appropriate for a
// DISCONNECTED Call while still relying on the existence of that Call in the Phone's list.
if (mState == STATE_DISCONNECTED) {
fireCallDestroyed();
} }
步骤57:转化ParcelableCall 信息为Detail信息,判断call状态是否有变化,有则进入fireStateChanged
private void fireStateChanged(final int newState) {
for (CallbackRecord<Callback> record : mCallbackRecords) {
final Call call = this;
final Callback callback = record.getCallback();
record.getHandler().post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callback.onStateChanged(call, newState);
}
});
}
}
步骤58:这里遍历Call(android.telecom.Call)对象里的回调监听者
private final List<CallbackRecord<Callback>> mCallbackRecords = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
也就是每次InCallPresenter添加Call(android.telecom.Call)时添加的注册回调事件
com.android.incallui.InCallPresenter
public void onCallAdded(final android.telecom.Call call) {
if (shouldAttemptBlocking(call)) {
maybeBlockCall(call);
} else {
mCallList.onCallAdded(call);
} // Since a call has been added we are no longer waiting for Telecom to send us a call.
setBoundAndWaitingForOutgoingCall(false, null);
call.registerCallback(mCallCallback);
}
这里有两个地方注册了事件回调,一个是在CallList的onCallAdd方法里转化Call(android.telecom.Call)创建了Call(com.android.incallui.Call)对象时注册的
com.android.incallui.CallList
public void onCallAdded(final android.telecom.Call telecomCall) {
Trace.beginSection("onCallAdded");
final Call call = new Call(telecomCall);
Log.d(this, "onCallAdded: callState=" + call.getState()); if (call.getState() == Call.State.INCOMING ||
call.getState() == Call.State.CALL_WAITING) {
onIncoming(call, call.getCannedSmsResponses());
} else {
onUpdate(call);
} call.logCallInitiationType();
Trace.endSection();
}
com.android.incallui.Call
public Call(android.telecom.Call telecomCall) {
mTelecomCall = telecomCall;
mId = ID_PREFIX + Integer.toString(sIdCounter++); updateFromTelecomCall(); mTelecomCall.registerCallback(mTelecomCallCallback); mTimeAddedMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
还有就是InCallPresenter的成员变量mCallCallback的注册
这里onStateChange只有Call(com.android.incallui.Call)的成员变量mTelecomCallCallback有处理
com.android.incallui.Call
private final android.telecom.Call.Callback mTelecomCallCallback =
new android.telecom.Call.Callback() {
......
......
@Override
public void onStateChanged(android.telecom.Call call, int newState) {
Log.d(this, "TelecomCallCallback onStateChanged call=" + call + " newState="
+ newState);
update();
} @Override
public void onCallDestroyed(android.telecom.Call call) {
Log.d(this, "TelecomCallCallback onStateChanged call=" + call);
call.unregisterCallback(this);
} };
步骤59:进入Call(com.android.incallui.Call)的update方法
private void update() {
Trace.beginSection("Update");
int oldState = getState();
updateFromTelecomCall();
if (oldState != getState() && getState() == Call.State.DISCONNECTED) {
CallList.getInstance().onDisconnect(this);
} else {
CallList.getInstance().onUpdate(this);
}
Trace.endSection();
}
步骤61~69:由于是DISCONNECTED状态,进入CallList的onDisconnect,最后回调到InCallPresenter的onDisconnect方法
com.android.incallui.InCallPresenter
@Override
public void onDisconnect(Call call) {
maybeShowErrorDialogOnDisconnect(call); // We need to do the run the same code as onCallListChange.
onCallListChange(mCallList); if (isActivityStarted()) {
mInCallActivity.dismissKeyguard(false);
} if (call.isEmergencyCall()) {
FilteredNumbersUtil.recordLastEmergencyCallTime(mContext);
}
}
InCallPresenter内部更新call状态事件并触发回调通知,细节再次就不一一罗列了
回调步骤57在执行完fireStateChanged方法后,后续还有fireDetailsChanged等事件(如果有变化的话),这里我们关注下fireCallDestroyed
android.telecom.Call
private void fireCallDestroyed() { final Call call = this;
if (mCallbackRecords.isEmpty()) {
// No callbacks registered, remove the call from Phone's record.
mPhone.internalRemoveCall(call);
}
for (final CallbackRecord<Callback> record : mCallbackRecords) {
final Callback callback = record.getCallback();
record.getHandler().post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
boolean isFinalRemoval = false;
RuntimeException toThrow = null;
try {
callback.onCallDestroyed(call);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
toThrow = e;
}
synchronized(Call.this) {
mCallbackRecords.remove(record);
if (mCallbackRecords.isEmpty()) {
isFinalRemoval = true;
}
}
if (isFinalRemoval) {
mPhone.internalRemoveCall(call);
}
if (toThrow != null) {
throw toThrow;
}
}
});
}
}
这里 callback.onCallDestroyed(call);通知call销毁事件
步骤60:反注册Call(android.telecom.Call )的监听事件
com.android.incallui.Call
@Override
public void onCallDestroyed(android.telecom.Call call) {
Log.d(this, "TelecomCallCallback onStateChanged call=" + call);
call.unregisterCallback(this);
}
步骤63,64:mPhone.internalRemoveCall(call); 把Call(android.telecom.Call)对象从列表中移除,通知onCallRemoved事件
android.telecom.Phone
final void internalRemoveCall(Call call) {
mCallByTelecomCallId.remove(call.internalGetCallId());
mCalls.remove(call); InCallService.VideoCall videoCall = call.getVideoCall();
if (videoCall != null) {
videoCall.destroy();
}
fireCallRemoved(call);
}
private void fireCallRemoved(Call call) {
for (Listener listener : mListeners) {
listener.onCallRemoved(this, call);
}
}
步骤70,71:InCallService处理onCallRemoved事件
com.android.incallui.InCallServiceImpl @Override
public void onCallAdded(Call call) {
InCallPresenter.getInstance().onCallAdded(call);
}
步骤72:进入InCallPresenter的onCallRemoved方法
com.android.incallui.InCallPresenter
public void onCallRemoved(android.telecom.Call call) {
mCallList.onCallRemoved(call);
call.unregisterCallback(mCallCallback);
}
步骤73~78:CallList的onCallRemoved方法:
com.android.incallui.CallList
public void onCallRemoved(android.telecom.Call telecomCall) {
if (mCallByTelecomCall.containsKey(telecomCall)) {
Call call = mCallByTelecomCall.get(telecomCall);
Logger.logCall(call);
if (updateCallInMap(call)) {
Log.w(this, "Removing call not previously disconnected " + call.getId());
}
updateCallTextMap(call, null);
}
}
CallList内部更新状态最终回调InCallPresenter的onCallListChange方法
com.android.incallui.InCallPresenter
public void onCallListChange(CallList callList) {
if (mInCallActivity != null && mInCallActivity.getCallCardFragment() != null &&
mInCallActivity.getCallCardFragment().isAnimating()) {
mAwaitingCallListUpdate = true;
return;
}
if (callList == null) {
return;
} mAwaitingCallListUpdate = false; InCallState newState = getPotentialStateFromCallList(callList);
InCallState oldState = mInCallState;
Log.d(this, "onCallListChange oldState= " + oldState + " newState=" + newState);
newState = startOrFinishUi(newState);
Log.d(this, "onCallListChange newState changed to " + newState); // Set the new state before announcing it to the world
Log.i(this, "Phone switching state: " + oldState + " -> " + newState);
mInCallState = newState; // notify listeners of new state
for (InCallStateListener listener : mListeners) {
Log.d(this, "Notify " + listener + " of state " + mInCallState.toString());
listener.onStateChange(oldState, mInCallState, callList);
} if (isActivityStarted()) {
final boolean hasCall = callList.getActiveOrBackgroundCall() != null ||
callList.getOutgoingCall() != null;
mInCallActivity.dismissKeyguard(hasCall);
}
}
步骤79,80,81:InCallPresenter处理disconnected事件并触发相关回调更新界面等
至此,一个来电的整体流程都分析完了,大致流程如下:
InCallUI →TeleComService→TeleponyService→TelephonyFramework →RIL→
RIL→TelephonyFramework →TeleponyService→TeleComFramework→TeleComService→TeleComFramework-->InCallUI
下一章节:Android7.0 Phone应用源码分析(四) phone挂断流程分析
Android7.0 Phone应用源码分析(三) phone拒接流程分析的更多相关文章
- Android7.0 Phone应用源码分析(二) phone来电流程分析
接上篇博文:Android7.0 Phone应用源码分析(一) phone拨号流程分析 今天我们再来分析下Android7.0 的phone的来电流程 1.1TelephonyFramework 当有 ...
- Android7.0 Phone应用源码分析(一) phone拨号流程分析
1.1 dialer拨号 拨号盘点击拨号DialpadFragment的onClick方法会被调用 public void onClick(View view) { int resId = view. ...
- Android7.0 Phone应用源码分析(四) phone挂断流程分析
电话挂断分为本地挂断和远程挂断,下面我们就针对这两种情况各做分析 先来看下本地挂断电话的时序图: 步骤1:点击通话界面的挂断按钮,会调用到CallCardPresenter的endCallClicke ...
- Android7.0 拨号盘应用源码分析(一) 界面浅析
前言 android拨号盘的源码目录在package/app/Dialer 自7.0以后Incallui的源码直接放到了Dialer目录下,虽然在7.0以前incallui有自己独立的目录,但实际编译 ...
- spring-boot-2.0.3启动源码篇三 - run方法(二)之prepareEnvironment
前言 此系列是针对springboot的启动,旨在于和大家一起来看看springboot启动的过程中到底做了一些什么事.如果大家对springboot的源码有所研究,可以挑些自己感兴趣或者对自己有帮助 ...
- spring-boot-2.0.3启动源码篇 - 阶段总结
前言 开心一刻 朋友喜欢去按摩,第一次推门进来的是一个学生美眉,感觉还不错:后来经常去,有时是护士,有时是空姐,有时候是教师.昨天晚上推门进去的是一个女警察,长得贼好看,身材也很好,朋友嗷的一声就扑上 ...
- 助力SpringBoot自动配置的条件注解ConditionalOnXXX分析--SpringBoot源码(三)
注:该源码分析对应SpringBoot版本为2.1.0.RELEASE 1 前言 本篇接 如何分析SpringBoot源码模块及结构?--SpringBoot源码(二) 上一篇分析了SpringBoo ...
- jdk源码剖析三:锁Synchronized
一.Synchronized作用 (1)确保线程互斥的访问同步代码 (2)保证共享变量的修改能够及时可见 (3)有效解决重排序问题.(Synchronized同步中的代码JVM不会轻易优化重排序) 二 ...
- HashMap源码深度剖析,手把手带你分析每一行代码,包会!!!
HashMap源码深度剖析,手把手带你分析每一行代码! 在前面的两篇文章哈希表的原理和200行代码带你写自己的HashMap(如果你阅读这篇文章感觉有点困难,可以先阅读这两篇文章)当中我们仔细谈到了哈 ...
随机推荐
- Linux 软件包安装管理
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/Quains/archive/2012/01/03/2311049.html 本文主要是记录下RedHat系列的软件包管理. 内容分为以下三个部分: ...
- android gridview画分割线
dongyangzhang android gridview画分割线,如图: 1.先上图: 2.具体实现代码: public class LineGridView extends GridView { ...
- Leetcode题1
Given an array of integers, find two numbers such that they add up to a specific target number. The ...
- angular中的$http配置和参数
依赖:$httpBackend $cacheFactory $rootScope $q $injector 使用:$http(config); 参数: method:字符串,请求方法. url:字符串 ...
- STM32标准IIC驱动
IIC(Inter-Integrated Circuit)总线是一种由 PHILIPS 公司开发的两线式串行总线,用于连接 微控制器及其外围设备.也是目前很流行的通讯总线,使用IIC总线做产品能够很大 ...
- UIButton常用属性小结(编辑中。。。)
Button的功能很黄很暴力,即能显示文字,又能显示图片,还能随时调整内部图片和文字的位置,用的地方很多. (1)按钮常用的四种状态: normal(普通状态) 默认情况(Default) 对应的枚举 ...
- 分页。php 引用代码
<?php /** file: page.class.php 完美分页类 Page */ class Page { private $total; //数据表中总记录数 private $lis ...
- IOS开发中UITableView(表视图)的滚动优化及自定义Cell
IOS开发中UITableView(表视图)的滚动优化及自定义Cell IOS 开发中UITableView是非常常用的一个控件,我们平时在手机上看到的联系人列表,微信好友列表等都是通过UITable ...
- iOS bug 之 H5 页面没有弹出提示框
描述:在安卓上有提示框,但是在iOS上没有提示框. step 1: 失误,是我没有在正确的位置设置网址. step 2: 修改之后,测试页能弹出提示框,但是正式的页面没有提示框. step 3: 我输 ...
- POST请求中参数以form data和request payload形式+清空数组方式
测试与服务端ajax时用的dva封装的request方法,而后端怎么也拿不到参数.结果返现参数在request payload里. HTTP POST表单请求提交时:Content-Typeappli ...
