Winform同步调用异步函数死锁原因分析、为什么要用异步
1、前言
几年前,一个开发同学遇到同步调用异步函数出现死锁问题,导致UI界面假死。我解释了一堆,关于状态机、线程池、WindowsFormsSynchronizationContext.Post、control.BeginInvoke、APC、IOCP,结果我也没讲明白、他也没听明白。后来路过他座位时看到他在各种摸索、尝试,使用Task、await、async各种组合,当时的场景是这样的:
 。问题有点复杂,随着那个开发同学离职转做产品后,就不了了之了。工作中许多同事对于同步、异步也不是特别了解,我会以执行流程图表加源码的形式表述,希望通过这篇文章最少能让大家了解.NET的async await出现deadlock的原因,最好能粗略了解async状态机机制、.NET在不同平台网络调用实现机制。如果文章中表述存在问题,欢迎指正。
。问题有点复杂,随着那个开发同学离职转做产品后,就不了了之了。工作中许多同事对于同步、异步也不是特别了解,我会以执行流程图表加源码的形式表述,希望通过这篇文章最少能让大家了解.NET的async await出现deadlock的原因,最好能粗略了解async状态机机制、.NET在不同平台网络调用实现机制。如果文章中表述存在问题,欢迎指正。
2、场景再现、执行过程解析
Winform死锁场景
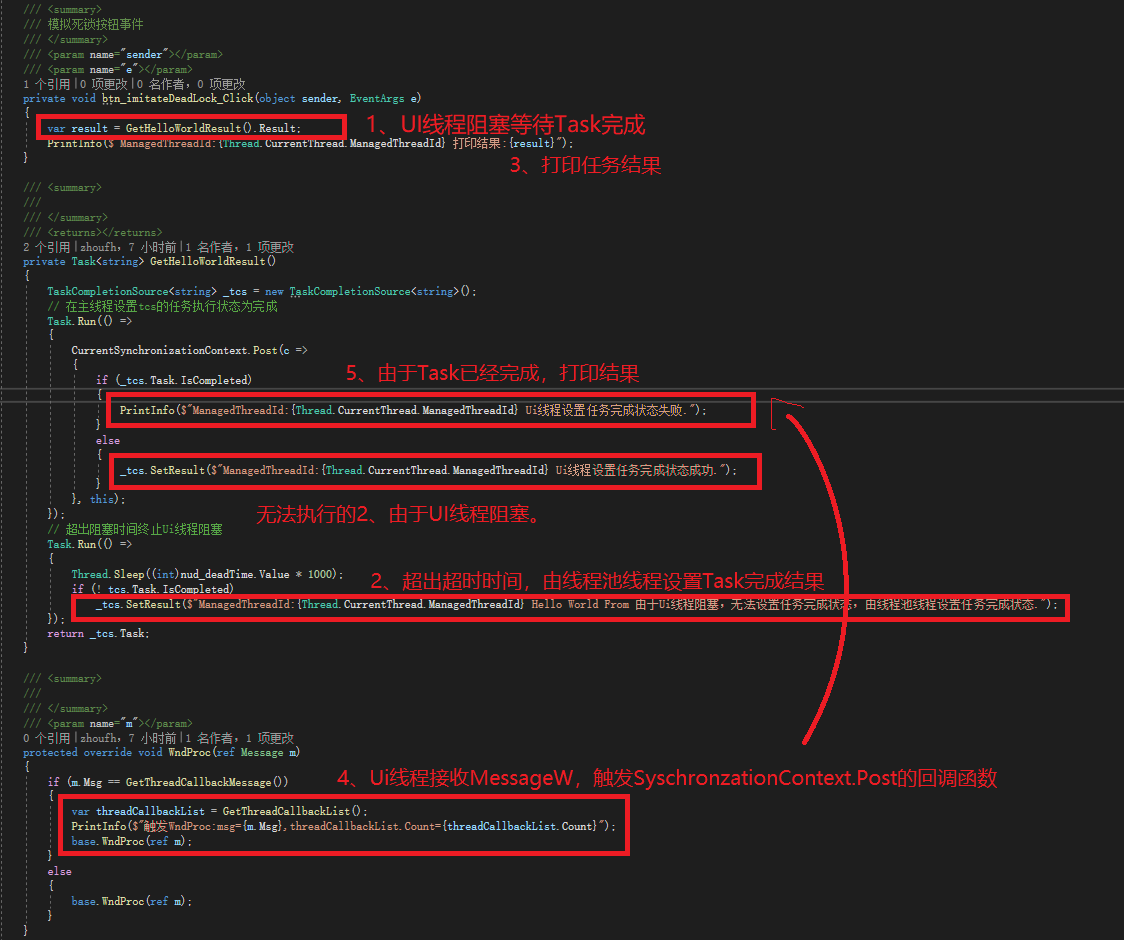
如下代码,如果点击按钮触发btn_realDead_Click事件,Ui线程将挂起在DeadTask().Result陷入死锁。
死锁产生的原因: Ui线程阻塞等待Task完成,Task需要通过Ui线程设置完成结果。
private void btn_realDead_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var result = DeadTask().Result; // UI线程挂起位置
PrintInfo(result);
}
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private async Task<string> DeadTask()
{
await Task.Delay(500);
return await Task.FromResult("Hello world");
}
场景模拟,解析WindowsFormsSynchronizationContext.Post执行过程
Demo代码地址 : https://gitee.com/RiverBied/async-demo
死锁模拟代码
使用async关键字将会由编译器生成状态机代码,反编译的代码也不太直观,所以我先使用非async代码进行简化模拟,async代码下文在解析。
死锁产生的原因: Ui线程阻塞等待Task完成,Task需要通过Ui线程设置完成结果。
解除死锁: 通过其他线程设置Task完成结果,Ui线程等到Task完成信号继续执行,死锁得到解除。
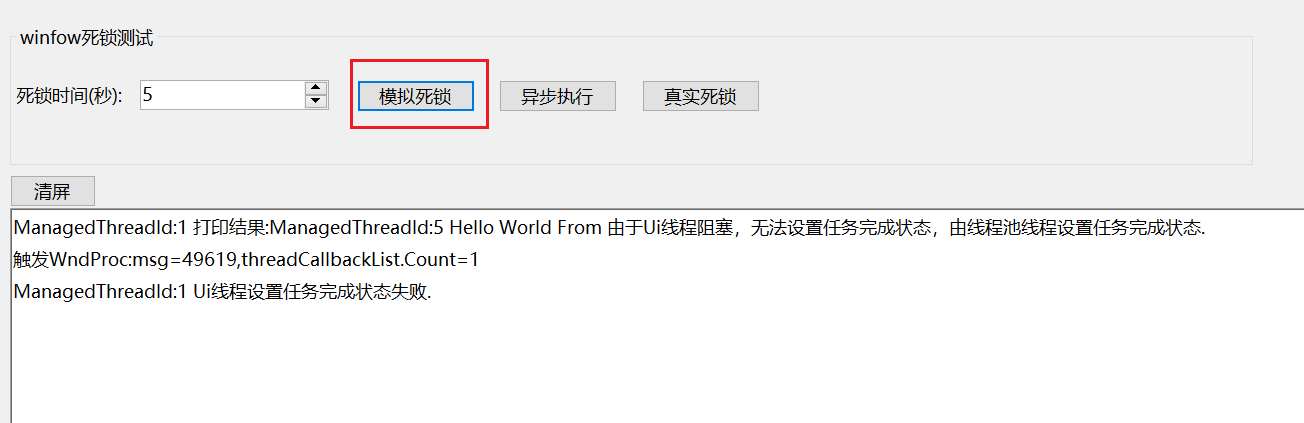
点击模拟死锁后,输出信息:
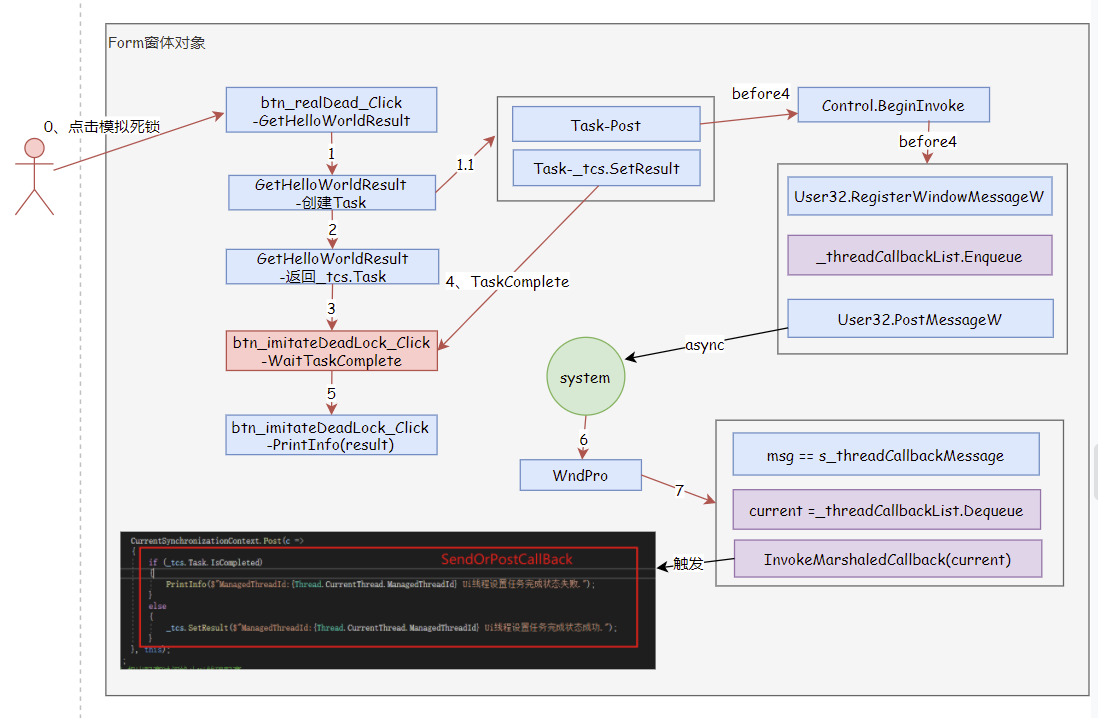
执行过程
相信大家看完下面这个图,会有更直观认识。可以看到CurrentSynchronizationContext.Post的SendOrPostCallback内容被包装为ThreadMethodEntry写入到窗体的队列对象的_threadCallbackList。但是 _threadCallbackList什么触发的,采用的是User32 MessageW异步消息接口,最后在UI线程空闲时系统触发窗体回调函数WndProc。
CurrentSynchronizationContext=WindowsFormsSynchronizationContext
WindowsFormsSynchronizationContext设置代码:
// 示例代码
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
CurrentSynchronizationContext = SynchronizationContext.Current;
var controlToSendToField = typeof(WindowsFormsSynchronizationContext).GetField("controlToSendTo", BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
// controlToSendTo设置为当前窗口对象,让重写的WndProc执行接收到消息
controlToSendToField.SetValue(CurrentSynchronizationContext, this);
}
WindowsFormsSynchronizationContext.Post源码:
SynchronizationContext.Post功能为发送一个异步委托消息,不阻塞当前线程,委托消息需要在SynchronizationContext绑定线程进行执行。在死锁模拟场景中SynchronizationContext绑定的为Ui线程,所以委托消息需要在Ui线程进行执行。
//源码地址: //https://github.com/dotnet/winforms/blob/release/5.0/src/System.Windows.Forms/src/System/Windows/Forms/WindowsFormsSynchronizationContext.cs#L90
public override void Post(SendOrPostCallback d, object state)
{
// 调用form1窗口对象的BeginInvoke
controlToSendTo?.BeginInvoke(d, new object[] { state });
}
Control.BeginInvoke
BeginInvoke关键源码:
// 定义保证在整个系统中唯一的窗口消息,消息值可用于发送或发布消息,返回窗口消息标识(int)。
s_threadCallbackMessage = User32.RegisterWindowMessageW(Application.WindowMessagesVersion + "_ThreadCallbackMessage");
// 将回调函数执行信息添加到回调函数队列,回调函数即为WindowsFormsSynchronizationContext.Post的SendOrPostCallback参数,_threadCallbackList为Control字段
_threadCallbackList.Enqueue(tme);
// 在与创建指定窗口的线程关联的消息队列中放置(发布)一条消息,并在不等待线程处理消息的情况下返回
User32.PostMessageW(this, s_threadCallbackMessage);
BeginInvoke源码:
//源码地址:
//https://github.com/dotnet/winforms/blob/release/5.0/src/System.Windows.Forms/src/System/Windows/Forms/Control.cs#L4678
private object MarshaledInvoke(Control caller, Delegate method, object[] args, bool synchronous)
{
if (!IsHandleCreated)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.ErrorNoMarshalingThread);
}
ActiveXImpl activeXImpl = (ActiveXImpl)Properties.GetObject(s_activeXImplProperty);
// We don't want to wait if we're on the same thread, or else we'll deadlock.
// It is important that syncSameThread always be false for asynchronous calls.
bool syncSameThread = false;
if (User32.GetWindowThreadProcessId(this, out _) == Kernel32.GetCurrentThreadId())
{
if (synchronous)
{
syncSameThread = true;
}
}
ExecutionContext executionContext = null;
if (!syncSameThread)
{
executionContext = ExecutionContext.Capture();
}
ThreadMethodEntry tme = new ThreadMethodEntry(caller, this, method, args, synchronous, executionContext);
lock (this)
{
if (_threadCallbackList is null)
{
_threadCallbackList = new Queue();
}
}
lock (_threadCallbackList)
{
if (s_threadCallbackMessage == User32.WM.NULL)
{
// 注册消息返回消息标识(int)
s_threadCallbackMessage = User32.RegisterWindowMessageW(Application.WindowMessagesVersion + "_ThreadCallbackMessage");
}
// 将回调函数执行信息添加到回调函数队列
_threadCallbackList.Enqueue(tme);
}
// 同一个线程则直接执行
if (syncSameThread)
{
InvokeMarshaledCallbacks();
}
else
{
// 将一个消息放入(寄送)到与指定窗口创建的线程相联系消息队列里
User32.PostMessageW(this, s_threadCallbackMessage);
}
if (synchronous)
{
if (!tme.IsCompleted)
{
WaitForWaitHandle(tme.AsyncWaitHandle);
}
if (tme._exception != null)
{
throw tme._exception;
}
return tme._retVal;
}
else
{
return tme;
}
}
WndProc
应用程序中定义的回调函数,用于处理发送到窗口的消息。
示例中的代码:
/// <summary>
/// 重写接收窗口的消息的回调函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="m"></param>
protected override void WndProc(ref Message m)
{
if (m.Msg == GetThreadCallbackMessage())
{
var threadCallbackList = GetThreadCallbackList();
PrintInfo($"触发WndProc:msg={m.Msg},threadCallbackList.Count={threadCallbackList.Count}");
base.WndProc(ref m);
}
else
{
base.WndProc(ref m);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取需要在Ui线程执行的回调委托队列
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private System.Collections.Queue GetThreadCallbackList()
{
var threadCallbackListFiled = typeof(Control).GetField("_threadCallbackList", BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance);
return (System.Collections.Queue)threadCallbackListFiled.GetValue(this);
}
private static int _threadCallbackMessage = 0;
/// <summary>
/// 获取触发回调委托的窗口消息标识
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private int GetThreadCallbackMessage()
{
if (_threadCallbackMessage == 0)
{
var threadCallbackMessageFiled = typeof(Control).GetField("s_threadCallbackMessage", BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Static);
_threadCallbackMessage = Convert.ToInt32(threadCallbackMessageFiled.GetValue(null));
}
return _threadCallbackMessage;
}
WndProc源码:
WndProc接收到s_threadCallbackMessage消息触发执行队列_threadCallbackList的消息。
//源码地址:
//https://github.com/dotnet/winforms/blob/release/5.0/src/System.Windows.Forms/src/System/Windows/Forms/Control.cs#L12681
/// <summary>
/// Base wndProc. All messages are sent to wndProc after getting filtered
/// through the preProcessMessage function. Inheriting controls should
/// call base.wndProc for any messages that they don't handle.
/// </summary>
protected virtual void WndProc(ref Message m)
{
// 此处省略代码未知行
// If you add any new messages below (or change the message handling code for any messages)
// please make sure that you also modify AxHost.WndProc to do the right thing and intercept
// messages which the Ocx would own before passing them onto Control.WndProc.
switch ((User32.WM)m.Msg)
{
// 此处省略代码未知行
default:
// If we received a thread execute message, then execute it.
if (m.Msg == (int)s_threadCallbackMessage && m.Msg != 0)
{
InvokeMarshaledCallbacks();
return;
}
break;
// 此处省略代码未知行
}
// 此处省略代码未知行
}
/// <summary>
/// Called on the control's owning thread to perform the actual callback.
/// This empties this control's callback queue, propagating any exceptions
/// back as needed.
/// </summary>
private void InvokeMarshaledCallbacks()
{
ThreadMethodEntry current = null;
lock (_threadCallbackList)
{
if (_threadCallbackList.Count > 0)
{
current = (ThreadMethodEntry)_threadCallbackList.Dequeue();
}
}
// Now invoke on all the queued items.
while (current != null)
{
if (current._method != null)
{
try
{
// If we are running under the debugger, don't wrap asynchronous
// calls in a try catch. It is much better to throw here than pop up
// a thread exception dialog below.
if (NativeWindow.WndProcShouldBeDebuggable && !current._synchronous)
{
InvokeMarshaledCallback(current);
}
else
{
try
{
InvokeMarshaledCallback(current);
}
catch (Exception t)
{
current._exception = t.GetBaseException();
}
}
}
finally
{
current.Complete();
if (!NativeWindow.WndProcShouldBeDebuggable &&
current._exception != null && !current._synchronous)
{
Application.OnThreadException(current._exception);
}
}
}
lock (_threadCallbackList)
{
if (_threadCallbackList.Count > 0)
{
current = (ThreadMethodEntry)_threadCallbackList.Dequeue();
}
else
{
current = null;
}
}
}
}
3、async deadlock代码解析
死锁代码示例、反编译代码查看
https://sharplab.io/很不错的一个网站,可在线查看C#编译后代码、中间语言代码。
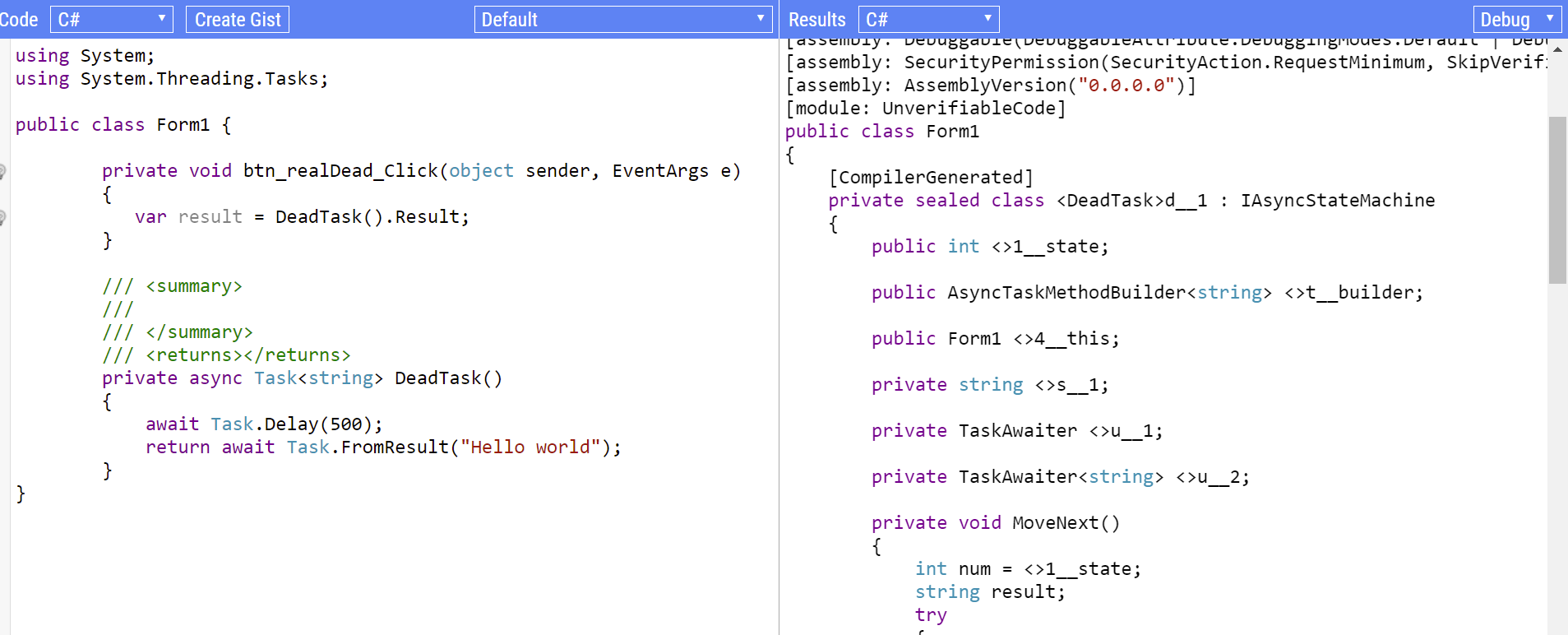
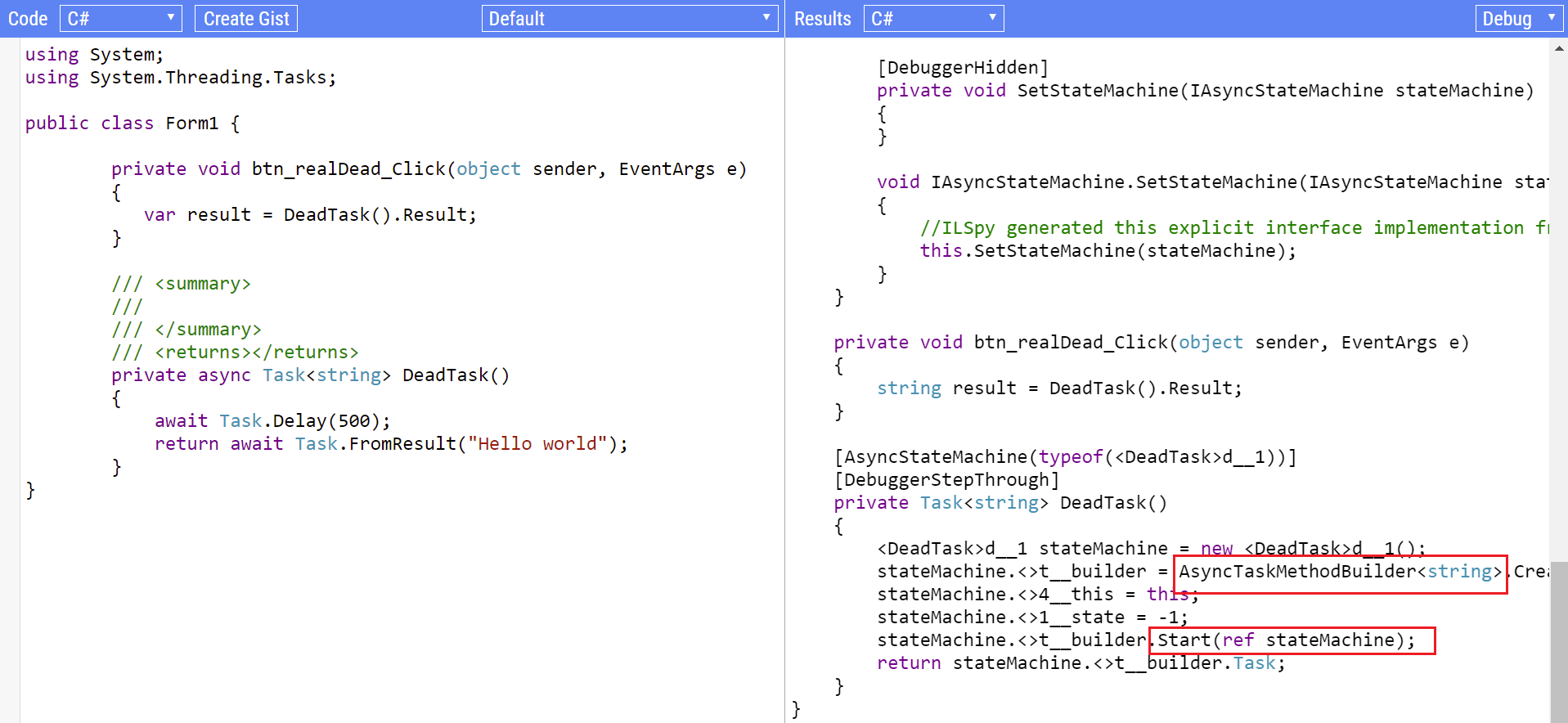
执行过程:
可以看到9和10都在UI线程执行,但是UI线程已经被10的执行流程占用,导致9无法将任务设置为完成状态,陷入死锁。
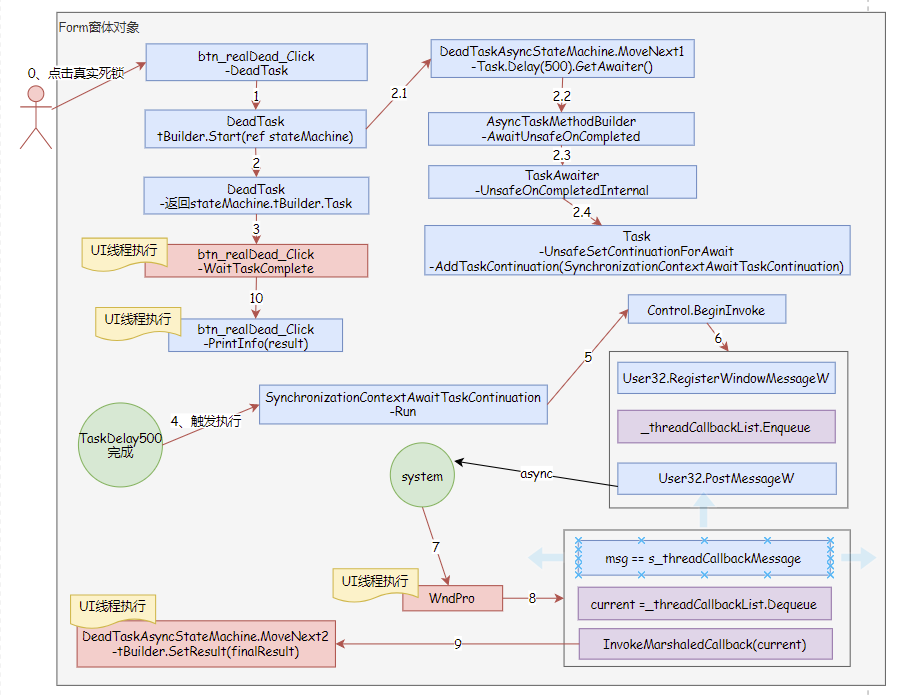
编译后的DeadTask函数
由于编译的代码不清晰,我进行重命名和代码精简。
可以看到DeadTask返回DeadTaskAsyncStateMachine.Task,看来要整明白AsyncTaskMethodBuilder执行过程,才能清楚来龙去脉了。
private Task<string> DeadTask()
{
DeadTaskAsyncStateMachine stateMachine = new DeadTaskAsyncStateMachine();
stateMachine.tBuilder = AsyncTaskMethodBuilder<string>.Create();
stateMachine.form1 = this;
stateMachine.state1 = -1;
stateMachine.tBuilder.Start(ref stateMachine);
return stateMachine.tBuilder.Task;
}
编译生成的DeadTaskAsyncStateMachine类
由于编译的代码不清晰,我进行重命名。
private sealed class DeadTaskAsyncStateMachine : IAsyncStateMachine
{
public int state1;
public AsyncTaskMethodBuilder<string> tBuilder;
public Form1 form1;
private string taskResult;
private TaskAwaiter delay500Awaiter;
private TaskAwaiter<string> helloWorldAwaiter;
private void MoveNext()
{
int num = state1;
string finalResult;
try
{
TaskAwaiter<string> awaiter;
TaskAwaiter awaiter2;
if (num != 0)
{
if (num == 1)
{
awaiter = helloWorldAwaiter;
helloWorldAwaiter = default(TaskAwaiter<string>);
num = (state1 = -1);
goto finalTag;
}
awaiter2 = Task.Delay(500).GetAwaiter();
if (!awaiter2.IsCompleted)
{
num = (state1 = 0);
delay500Awaiter = awaiter2;
DeadTaskAsyncStateMachine stateMachine = this;
tBuilder.AwaitUnsafeOnCompleted(ref awaiter2, ref stateMachine);
return;
}
}
else
{
awaiter2 = delay500Awaiter;
delay500Awaiter = default(TaskAwaiter);
num = (state1 = -1);
}
awaiter2.GetResult();
awaiter = Task.FromResult("Hello world").GetAwaiter();
// 因为awaiter.IsCompleted == true,部分代码进行移除
goto finalTag;
finalTag:
finalResult = awaiter.GetResult();
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
state1 = -2;
tBuilder.SetException(exception);
return;
}
state1 = -2;
tBuilder.SetResult(finalResult); // 设置结果,同时设置任务为完成状态
}
void IAsyncStateMachine.MoveNext()
{
//ILSpy generated this explicit interface implementation from .override directive in MoveNext
this.MoveNext(); // 执行状态机当前任务,初始状态state1 = -1
}
private void SetStateMachine(IAsyncStateMachine stateMachine)
{
}
void IAsyncStateMachine.SetStateMachine(IAsyncStateMachine stateMachine)
{
//ILSpy generated this explicit interface implementation from .override directive in SetStateMachine
this.SetStateMachine(stateMachine);
}
}
关键代码:
MoveNext源码
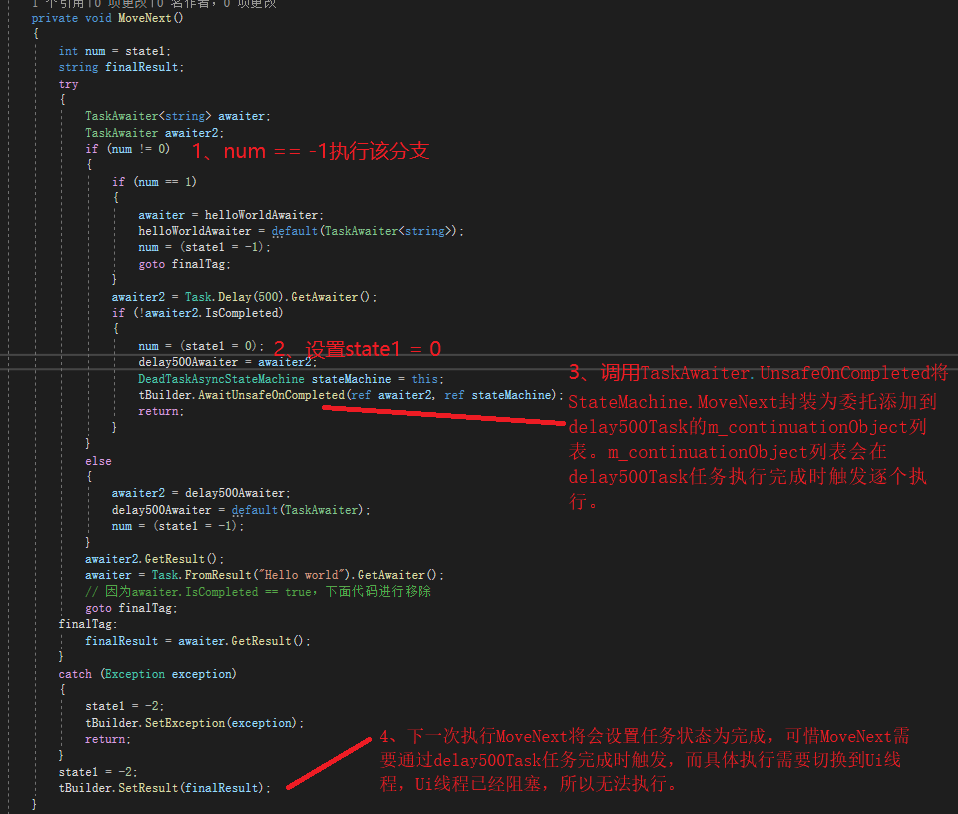
AsyncTaskMethodBuilder.AwaitUnsafeOnCompleted源码:
可以看到将会调用函数TaskAwaiter.UnsafeOnCompletedInternal(ta.m_task, box, continueOnCapturedContext: true)。
public void Start<TStateMachine>(ref TStateMachine stateMachine) where TStateMachine : IAsyncStateMachine =>
AsyncMethodBuilderCore.Start(ref stateMachine);
//源码地址:
//https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/blob/release/5.0/src/libraries/System.Private.CoreLib/src/System/Runtime/CompilerServices/AsyncTaskMethodBuilderT.cs#L101
internal static void AwaitUnsafeOnCompleted<TAwaiter>(
ref TAwaiter awaiter, IAsyncStateMachineBox box)
where TAwaiter : ICriticalNotifyCompletion
{
// 执行位置,默认continueOnCapturedContext = true即为继续在上下文执行
// 最终SynchronizationContext.Current.Post触发执行stateMachine.MoveNext
if ((null != (object?)default(TAwaiter)) && (awaiter is ITaskAwaiter))
{
ref TaskAwaiter ta = ref Unsafe.As<TAwaiter, TaskAwaiter>(ref awaiter); // relies on TaskAwaiter/TaskAwaiter<T> having the same layout
TaskAwaiter.UnsafeOnCompletedInternal(ta.m_task, box, continueOnCapturedContext: true);
}
// ConfigureAwait(false).GetAwaiter()返回类型为IConfiguredTaskAwaiter,可以避免死锁
else if ((null != (object?)default(TAwaiter)) && (awaiter is IConfiguredTaskAwaiter))
{
ref ConfiguredTaskAwaitable.ConfiguredTaskAwaiter ta = ref Unsafe.As<TAwaiter, ConfiguredTaskAwaitable.ConfiguredTaskAwaiter>(ref awaiter);
TaskAwaiter.UnsafeOnCompletedInternal(ta.m_task, box, ta.m_continueOnCapturedContext);
}
// 省略代码未知行
}
AsyncMethodBuilderCore.Start源码:
//源码地址
//https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/blob/release/5.0/src/libraries/System.Private.CoreLib/src/System/Runtime/CompilerServices/AsyncMethodBuilderCore.cs#L21
public static void Start<TStateMachine>(ref TStateMachine stateMachine) where TStateMachine : IAsyncStateMachine
{
if (stateMachine == null) // TStateMachines are generally non-nullable value types, so this check will be elided
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.stateMachine);
}
// enregistrer variables with 0 post-fix so they can be used in registers without EH forcing them to stack
// Capture references to Thread Contexts
Thread currentThread0 = Thread.CurrentThread;
Thread currentThread = currentThread0;
ExecutionContext? previousExecutionCtx0 = currentThread0._executionContext;
ExecutionContext? previousExecutionCtx = previousExecutionCtx0;
SynchronizationContext? previousSyncCtx = currentThread0._synchronizationContext;
try
{
// 执行DeadTaskAsyncStateMachine.MoveNext()
stateMachine.MoveNext();
}
finally
{
// Re-enregistrer variables post EH with 1 post-fix so they can be used in registers rather than from stack
SynchronizationContext? previousSyncCtx1 = previousSyncCtx;
Thread currentThread1 = currentThread;
// The common case is that these have not changed, so avoid the cost of a write barrier if not needed.
if (previousSyncCtx1 != currentThread1._synchronizationContext)
{
// Restore changed SynchronizationContext back to previous
currentThread1._synchronizationContext = previousSyncCtx1;
}
ExecutionContext? previousExecutionCtx1 = previousExecutionCtx;
ExecutionContext? currentExecutionCtx1 = currentThread1._executionContext;
if (previousExecutionCtx1 != currentExecutionCtx1)
{
ExecutionContext.RestoreChangedContextToThread(currentThread1, previousExecutionCtx1, currentExecutionCtx1);
}
}
}
TaskAwaiter.UnsafeOnCompletedInternal源码:
// 源码地址
//https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/blob/release/5.0/src/libraries/System.Private.CoreLib/src/System/Runtime/CompilerServices/TaskAwaiter.cs#L220
internal static void UnsafeOnCompletedInternal(Task task, IAsyncStateMachineBox stateMachineBox, bool continueOnCapturedContext)
{
task.UnsafeSetContinuationForAwait(stateMachineBox, continueOnCapturedContext);
}
Task.UnsafeSetContinuationForAwait源码:
// 源码地址
//https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/blob/release/5.0/src/libraries/System.Private.CoreLib/src/System/Threading/Tasks/Task.cs#L2513
internal void UnsafeSetContinuationForAwait(IAsyncStateMachineBox stateMachineBox, bool continueOnCapturedContext)
{
// continueOnCapturedContext == true,走这个分支
if (continueOnCapturedContext)
{
SynchronizationContext? syncCtx = SynchronizationContext.Current;
if (syncCtx != null && syncCtx.GetType() != typeof(SynchronizationContext))
{
var tc = new SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation(syncCtx, stateMachineBox.MoveNextAction, flowExecutionContext: false);
// 添加到m_continuationObject,如果添加失败则代表任务已经完成,tc直接执行
if (!AddTaskContinuation(tc, addBeforeOthers: false))
{
tc.Run(this, canInlineContinuationTask: false);
}
return;
}
else
{
TaskScheduler? scheduler = TaskScheduler.InternalCurrent;
if (scheduler != null && scheduler != TaskScheduler.Default)
{
var tc = new TaskSchedulerAwaitTaskContinuation(scheduler, stateMachineBox.MoveNextAction, flowExecutionContext: false);
if (!AddTaskContinuation(tc, addBeforeOthers: false))
{
tc.Run(this, canInlineContinuationTask: false);
}
return;
}
}
}
// Otherwise, add the state machine box directly as the continuation.
// If we're unable to because the task has already completed, queue it.
if (!AddTaskContinuation(stateMachineBox, addBeforeOthers: false))
{
ThreadPool.UnsafeQueueUserWorkItemInternal(stateMachineBox, preferLocal: true);
}
}
SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation源码:
// 源码地址
//https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/blob/release/5.0/src/libraries/System.Private.CoreLib/src/System/Threading/Tasks/TaskContinuation.cs#L364
/// <summary>Task continuation for awaiting with a current synchronization context.</summary>
internal sealed class SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation : AwaitTaskContinuation
{
/// <summary>SendOrPostCallback delegate to invoke the action.</summary>
private static readonly SendOrPostCallback s_postCallback = static state =>
{
Debug.Assert(state is Action);
((Action)state)();
};
/// <summary>Cached delegate for PostAction</summary>
private static ContextCallback? s_postActionCallback;
/// <summary>The context with which to run the action.</summary>
private readonly SynchronizationContext m_syncContext;
internal SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation(
SynchronizationContext context, Action action, bool flowExecutionContext) :
base(action, flowExecutionContext)
{
Debug.Assert(context != null);
m_syncContext = context;
}
internal sealed override void Run(Task task, bool canInlineContinuationTask)
{
// If we're allowed to inline, run the action on this thread.
if (canInlineContinuationTask &&
m_syncContext == SynchronizationContext.Current)
{
RunCallback(GetInvokeActionCallback(), m_action, ref Task.t_currentTask);
}
// Otherwise, Post the action back to the SynchronizationContext.
else
{
TplEventSource log = TplEventSource.Log;
if (log.IsEnabled())
{
m_continuationId = Task.NewId();
log.AwaitTaskContinuationScheduled((task.ExecutingTaskScheduler ?? TaskScheduler.Default).Id, task.Id, m_continuationId);
}
// 执行PostAction
RunCallback(GetPostActionCallback(), this, ref Task.t_currentTask);
}
// Any exceptions will be handled by RunCallback.
}
private static void PostAction(object? state)
{
Debug.Assert(state is SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation);
var c = (SynchronizationContextAwaitTaskContinuation)state;
TplEventSource log = TplEventSource.Log;
if (log.IsEnabled() && log.TasksSetActivityIds && c.m_continuationId != 0)
{
// 调用Control.BeginInvoke
c.m_syncContext.Post(s_postCallback, GetActionLogDelegate(c.m_continuationId, c.m_action));
}
else
{
c.m_syncContext.Post(s_postCallback, c.m_action); // s_postCallback is manually cached, as the compiler won't in a SecurityCritical method
}
}
private static Action GetActionLogDelegate(int continuationId, Action action)
{
return () =>
{
Guid activityId = TplEventSource.CreateGuidForTaskID(continuationId);
System.Diagnostics.Tracing.EventSource.SetCurrentThreadActivityId(activityId, out Guid savedActivityId);
try { action(); }
finally { System.Diagnostics.Tracing.EventSource.SetCurrentThreadActivityId(savedActivityId); }
};
}
[MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.AggressiveInlining)]
private static ContextCallback GetPostActionCallback() => s_postActionCallback ??= PostAction;
}
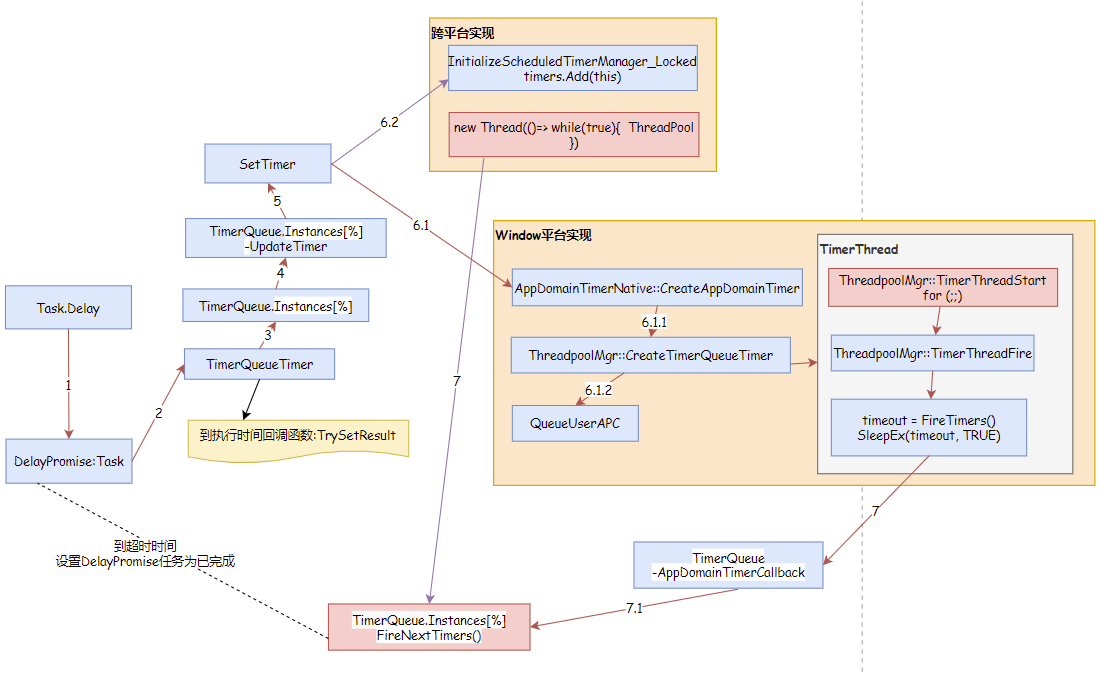
Task.Delay实现过程
Task.Delay有多种实现,我精简后画了大致实现流程,感兴趣的同学可以阅读一下源码,部分在coreclr实现。
QueueUseAPC: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/processthreadsapi/nf-processthreadsapi-queueuserapc
SleepEx: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/synchapi/nf-synchapi-sleepex
为什么IO型、延时任务要采用async
原因: 线程池默认的最小工作线程数量为CPU核心数,如果不采用async会导致线程同步阻塞,需要线程池创建更多的工作线程来应对的并发。当线程池工作线程的数量大于最小工作线程数量时,工作线程的创建速度受限于最小工作线程数量,每秒不超过2个,这时候程序会出现假死的情况。线程池默认设置最小工作线程数量为CPU核心数,主要是希望使用async通过多路复用来提升程序的并发性能。如果旧程序不好改造,快速解决的方法就是通过ThreadPool.SetMinThreads设置最小工作线程数量,放开工作线程创建速度限制,以多线程模型应对更多的并发,虽然系统性能差一些,至少不会假死。
小实验:
Demo源码地址: https://gitee.com/RiverBied/async-demo
启动Web.Api站点,运行WinForms.App进行测试,不过不要在调试状态运行。
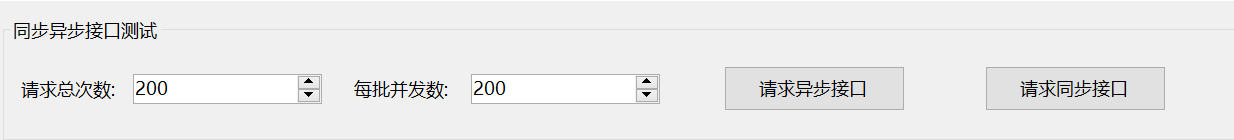
HttpClient.GetStringAsync执行过程
可以看到在Windows平台是通过IOCP触发回调事件。在Unix平台是在SocketAsyncEngine类创建while(true)循环的执行线程,再通过Wait epoll或kqueue获取IO事件,最后触发回调事件。IOPC为异步非阻塞IO、epoll为同步非阻塞IO,IOCP、epoll会涉及IO模型、IO多路复用等知识,网上介绍较多,可以自行查阅。同时需要注意AwaitableSocketAsyncEventArgs既继承SocketAsyncEventArgs类也实现IValueTaskSource接口。
HttpClient.GetStringAsync请求:
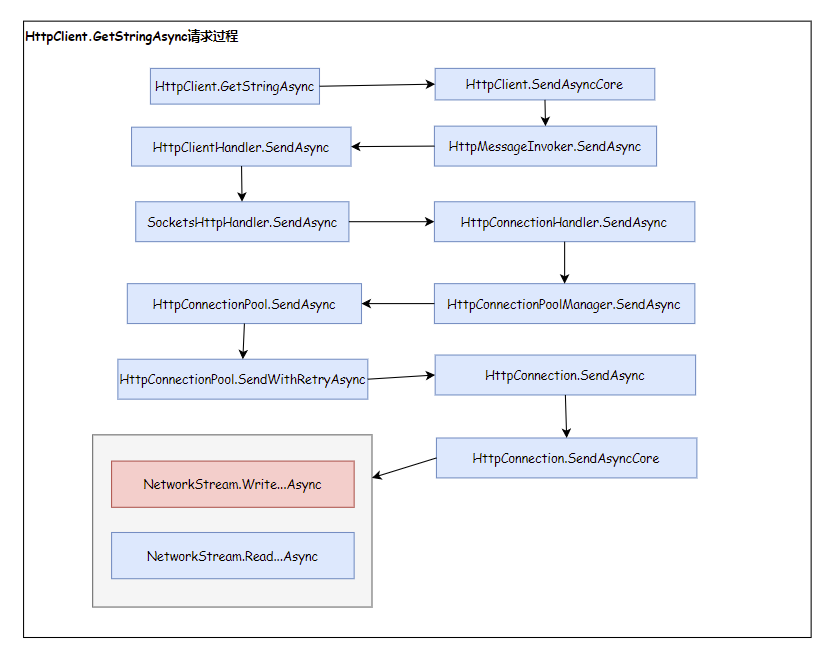
NetworkStream.WriteAsync在Windows平台实现:
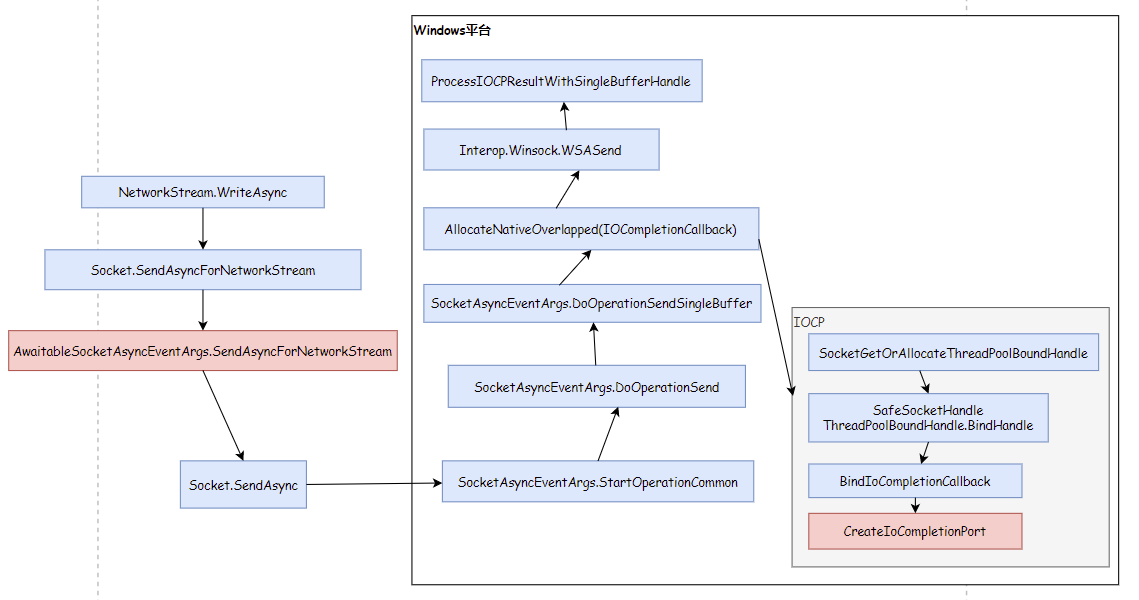
NetworkStream.WriteAsync在Unix平台实现:
async await推荐实践方法
async/await适用于IO型(文件读取、网络通信)、延时型任务。对于计算型任务可以使用Task.Factory创建LongRunning任务,该任务会独立新建一个后台线程进行处理。
关于MySql驱动组件: 建议采用MySqlConnector组件。因为MySqlConnector组件支持异步IO,MySql.Data组件不支持真实的异步IO。
如果条件允许、尽量使用ConfigureAwait(false)。如果不设置在Winform场景下会调用SynchronizationContext.Post通过UI线程执行回调函数,同步方法调用异步方式时会出现死锁。
Task方法替代清单:
| 同步方法 | 异步方式 | 描述信息 |
|---|---|---|
| task.Wait | await task | 等待一个任务执行完成 |
| task.Result | await task | 获取任务返回结果 |
| Task.WaitAny | await Task.WhenAny | 等待其中一个任务执行完成,继续执行 |
| Task.WaitAll | await Task.WhenAll | 等待所有任务执行完成,继续执行 |
| Thread.Sleep | await Task.Delay | 延时几秒继续执行 |
附
Demo代码地址 : https://gitee.com/RiverBied/async-demo
Winform同步调用异步函数死锁原因分析、为什么要用异步的更多相关文章
- Mysql update后insert造成死锁原因分析及解决
系统中出现死锁的日志如下: ) TRANSACTION: , ACTIVE sec inserting mysql tables , locked LOCK WAIT lock struct(s), ...
- MySQL死锁原因分析
行级锁有三种模式: innodb 行级锁 record-level lock大致有三种:record lock, gap lock and Next-KeyLocks. record lock 锁住 ...
- Winform中调用js函数
var wb = new WebBrowser(); wb.AllowNavigation = true; wb.ScriptErrorsSuppressed = false; wb.Navigate ...
- 10-Node.js学习笔记-异步函数
异步函数 异步函数是异步编程语法的终极解决方案,它可以让我们将异步代码写成同步的形式,让代码不再有回调函数嵌套,是代码变得清晰明了 const fn = async()=>{} async fu ...
- 【校招面试 之 C/C++】第10题 C++不在构造函数和析构函数中调用虚函数
1.不要在构造函数中调用虚函数的原因 在概念上,构造函数的工作是为对象进行初始化.在构造函数完成之前,被构造的对象被认为“未完全生成”.当创建某个派生类的对象时,如果在它的基类的构造函数中调用虚函数, ...
- Python并发编程06 /阻塞、异步调用/同步调用、异步回调函数、线程queue、事件event、协程
Python并发编程06 /阻塞.异步调用/同步调用.异步回调函数.线程queue.事件event.协程 目录 Python并发编程06 /阻塞.异步调用/同步调用.异步回调函数.线程queue.事件 ...
- dubbo同步调用、异步调用和是否返回结果源码分析和实例
0. dubbo同步调用.异步调用和是否返回结果配置 (1)dubbo默认为同步调用,并且有返回结果. (2)dubbo异步调用配置,设置 async="true",异步调用可以提 ...
- python 并发编程 同步调用和异步调用 回调函数
提交任务的两张方式: 1.同步调用 2.异步调用 同步调用:提交完任务后,就在原地等待任务执行完后,拿到结果,再执行下一行代码 同步调用,导致程序串行执行 from concurrent.future ...
- 『审慎』.Net4.6 Task 异步函数 比 同步函数 慢5倍 踩坑经历
异步Task简单介绍 本标题有点 哗众取宠,各位都别介意(不排除个人技术能力问题) —— 接下来:我将会用一个小Demo 把 本文思想阐述清楚. .Net 4.0 就有了 Task 函数 —— 异步编 ...
随机推荐
- html调用swf的语句
<div style="width: 1000px; height: 202px; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto"> &l ...
- Android Jetpack基本架构之ViewModel+LiveData+DataBinding入门
前提:导入所有依赖,开启DataBinding app的build.gradle android { defaultConfig { ... dataBinding { enabled true } ...
- MySQL存储结构及SQL分类
MySQL目录结构 bin -- mysql执行程序 docs -- 文档 share - 各国编码信息 data -- 存放mysql 数据文件 * 每个数据库 创建一个同名文件夹,.frm 存放t ...
- 安全强化机制——SELinux
1.基本 SELINUX 安全性概念 SELINUX(Security Enhanced Linux),意思是安全增强型Linux, 是可保护你系统安全性的额外机制 在某种程度上 , 它可以被看作是与 ...
- python variable scope 变量作用域
python 中变量的作用域经常让我感到很迷 In Python, on the other hand, variables declared in if-statements, for-loop b ...
- Spring事物入门简介及AOP陷阱分析
转载请注明出处: https://www.cnblogs.com/qnlcy/p/15237377.html 一.事务的定义 事务(Transaction),是指访问并可能更新数据库中各种数据项的一个 ...
- noip模拟18
\(\color{white}{\mathbb{曲径通幽,星汉隐约,缥缈灯影,朦胧缺月,名之以:薄雾}}\) 放眼望去前十被我弃掉的 \(t2\) 基本都上85了-- 开考就以为 \(t2\) 是个大 ...
- pluto中监听各个网口的500端口处理逻辑
1. pluto中监听各个网口的500端口处理逻辑 whack_handle() find_ifaces() find_raw_ifaces4() socket.setsockopt.bind.ioc ...
- CodeForce-810B Summer sell-off (结构体排序)
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/810/B 已知n天里,已知第i天的供货量和需求量,给定一个f,可以在n天之中选f天促销使得供货量翻倍. 问选择其中f ...
- JavaScript进行表单提交
表单结构,设置form表单的id属性,method="post/get","action"要跳转的页面(jsp或servlet) <form name=& ...
