Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)
我的代码应该不会被hack,立个flag
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
It is winter now, and Max decided it's about time he watered the garden.
The garden can be represented as n consecutive garden beds, numbered from 1 to n. k beds contain water taps (i-th tap is located in the bed xi), which, if turned on, start delivering water to neighbouring beds. If the tap on the bed xi is turned on, then after one second has passed, the bed xi will be watered; after two seconds have passed, the beds from the segment [xi - 1, xi + 1] will be watered (if they exist); after j seconds have passed (j is an integer number), the beds from the segment [xi - (j - 1), xi + (j - 1)] will be watered (if they exist). Nothing changes during the seconds, so, for example, we can't say that the segment [xi - 2.5, xi + 2.5] will be watered after 2.5seconds have passed; only the segment [xi - 2, xi + 2] will be watered at that moment.
 The garden from test 1. White colour denotes a garden bed without a tap, red colour — a garden bed with a tap.
The garden from test 1. White colour denotes a garden bed without a tap, red colour — a garden bed with a tap. The garden from test 1 after 2 seconds have passed after turning on the tap. White colour denotes an unwatered garden bed, blue colour — a watered bed.
The garden from test 1 after 2 seconds have passed after turning on the tap. White colour denotes an unwatered garden bed, blue colour — a watered bed.
Max wants to turn on all the water taps at the same moment, and now he wonders, what is the minimum number of seconds that have to pass after he turns on some taps until the whole garden is watered. Help him to find the answer!
The first line contains one integer t — the number of test cases to solve (1 ≤ t ≤ 200).
Then t test cases follow. The first line of each test case contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 200, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) — the number of garden beds and water taps, respectively.
Next line contains k integers xi (1 ≤ xi ≤ n) — the location of i-th water tap. It is guaranteed that for each 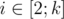 condition xi - 1 < xiholds.
condition xi - 1 < xiholds.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all test cases doesn't exceed 200.
Note that in hacks you have to set t = 1.
For each test case print one integer — the minimum number of seconds that have to pass after Max turns on some of the water taps, until the whole garden is watered.
3
5 1
3
3 3
1 2 3
4 1
1
3
1
4
The first example consists of 3 tests:
- There are 5 garden beds, and a water tap in the bed 3. If we turn it on, then after 1 second passes, only bed 3 will be watered; after 2seconds pass, beds [1, 3] will be watered, and after 3 seconds pass, everything will be watered.
- There are 3 garden beds, and there is a water tap in each one. If we turn all of them on, then everything will be watered after 1 second passes.
- There are 4 garden beds, and only one tap in the bed 1. It will take 4 seconds to water, for example, bed 4.
A题意很长是个模拟,自己也迷了好久,枚举每个点就可以了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[],b[];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
memset(b,,sizeof(b));
int n,k,ma=;
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i=; i<k; i++)
cin>>a[i],b[a[i]]=;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
int sum=,tl=i,tr=i;
while(b[tl]!=&&b[tr]!=)
{
if(tl->)tl--;
if(tr+<=n)tr++;
sum++;
}
ma=max(ma,sum);
}
cout<<ma<<endl;
}
return ;
}
qls的代码超级优秀的,妈耶,长知识
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=;
int x[MAXN];
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
int n,k;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(int i=;i<=k;i++)
scanf("%d",&x[i]);
int res=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int mi=n;
for(int j=;j<=k;j++)
mi=min(mi,abs(i-x[j]));
res=max(res,mi);
}
printf("%d\n",res+);
}
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Recently n students from city S moved to city P to attend a programming camp.
They moved there by train. In the evening, all students in the train decided that they want to drink some tea. Of course, no two people can use the same teapot simultaneously, so the students had to form a queue to get their tea.
i-th student comes to the end of the queue at the beginning of li-th second. If there are multiple students coming to the queue in the same moment, then the student with greater index comes after the student with lesser index. Students in the queue behave as follows: if there is nobody in the queue before the student, then he uses the teapot for exactly one second and leaves the queue with his tea; otherwise the student waits for the people before him to get their tea. If at the beginning of ri-th second student i still cannot get his tea (there is someone before him in the queue), then he leaves the queue without getting any tea.
For each student determine the second he will use the teapot and get his tea (if he actually gets it).
The first line contains one integer t — the number of test cases to solve (1 ≤ t ≤ 1000).
Then t test cases follow. The first line of each test case contains one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000) — the number of students.
Then n lines follow. Each line contains two integer li, ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ 5000) — the second i-th student comes to the end of the queue, and the second he leaves the queue if he still cannot get his tea.
It is guaranteed that for every 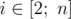 condition li - 1 ≤ li holds.
condition li - 1 ≤ li holds.
The sum of n over all test cases doesn't exceed 1000.
Note that in hacks you have to set t = 1.
For each test case print n integers. i-th of them must be equal to the second when i-th student gets his tea, or 0 if he leaves without tea.
2
2
1 3
1 4
3
1 5
1 1
2 3
1 2
1 0 2
The example contains 2 tests:
- During 1-st second, students 1 and 2 come to the queue, and student 1 gets his tea. Student 2 gets his tea during 2-nd second.
- During 1-st second, students 1 and 2 come to the queue, student 1 gets his tea, and student 2 leaves without tea. During 2-nd second, student 3 comes and gets his tea.
n个人排队,有进队时间和出队时间,进队时间相同的话,编号小的优先
队列或者数组模拟吧
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int l[],r[],M[];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int n;
cin>>n;
memset(M,,sizeof M);
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
cin>>l[i]>>r[i];
int tot=;
queue<int> q;
for(int i=; i<=; i++)
{
while(tot<=n&&l[tot]==i)
q.push(tot++);
while(q.size()&&r[q.front()]<i)
q.pop();
if(q.size())
{
int tmp=q.front();
q.pop();
M[tmp]=i;
}
}
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
cout<<M[i]<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
}
return ;
}
vector的
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<pair<int,pair<int,int> > >V;
int M[];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
V.clear();
int n;
cin>>n;
memset(M,,sizeof M);
for(int i=,l,r; i<=n; i++)
cin>>l>>r,V.push_back(make_pair(l,make_pair(i,r)));
sort(V.begin(),V.end());
int j=,l=n;
for(int i=; i<= &&j<n; i++)
{
while((V[j].second).second<i&&j<n)j++;
if(V[j].first<=i)
M[(V[j].second).first]=i,j++;
}
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
cout<<M[i]<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
}
return ;
}
qls很优秀的代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int now=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int l,r;
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
if(now>r)printf("");
else
{
now=max(now,l);
printf("%d",now++);
}
printf("%c"," \n"[i==n]);
}
}
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You have an array a consisting of n integers. Each integer from 1 to n appears exactly once in this array.
For some indices i (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) it is possible to swap i-th element with (i + 1)-th, for other indices it is not possible. You may perform any number of swapping operations any order. There is no limit on the number of times you swap i-th element with (i + 1)-th (if the position is not forbidden).
Can you make this array sorted in ascending order performing some sequence of swapping operations?
The first line contains one integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 200000) — the number of elements in the array.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 200000) — the elements of the array. Each integer from 1 to n appears exactly once.
The third line contains a string of n - 1 characters, each character is either 0 or 1. If i-th character is 1, then you can swap i-th element with (i + 1)-th any number of times, otherwise it is forbidden to swap i-th element with (i + 1)-th.
If it is possible to sort the array in ascending order using any sequence of swaps you are allowed to make, print YES. Otherwise, print NO.
6
1 2 5 3 4 6
01110
YES
6
1 2 5 3 4 6
01010
NO
In the first example you may swap a3 and a4, and then swap a4 and a5.
交换相邻的其实就是在排序啊,所以出现连续的1就去sort好了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[];
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin>>n)
{
int f=;
string s;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
cin>>a[i];
cin>>s;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int l=,r=;
for(int i=;s[i];i++)
{
if(s[i]=='')continue;
l=i;
for(;s[i];i++)
{
if(s[i]=='')break;
r=i;
}
sort(a+l+,a+r+);
}
for(int i=;i<=n&&f;i++)
if(a[i]!=i)f=;
if(f)cout<<"YES\n";
else cout<<"NO\n";
}
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given an undirected graph consisting of n vertices and 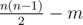 edges. Instead of giving you the edges that exist in the graph, we give you m unordered pairs (x, y) such that there is no edge between x and y, and if some pair of vertices is not listed in the input, then there is an edge between these vertices.
edges. Instead of giving you the edges that exist in the graph, we give you m unordered pairs (x, y) such that there is no edge between x and y, and if some pair of vertices is not listed in the input, then there is an edge between these vertices.
You have to find the number of connected components in the graph and the size of each component. A connected component is a set of vertices X such that for every two vertices from this set there exists at least one path in the graph connecting these vertices, but adding any other vertex to X violates this rule.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 200000, 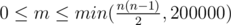 ).
).
Then m lines follow, each containing a pair of integers x and y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n, x ≠ y) denoting that there is no edge between x and y. Each pair is listed at most once; (x, y) and (y, x) are considered the same (so they are never listed in the same test). If some pair of vertices is not listed in the input, then there exists an edge between those vertices.
Firstly print k — the number of connected components in this graph.
Then print k integers — the sizes of components. You should output these integers in non-descending order.
5 5
1 2
3 4
3 2
4 2
2 5
2
1 4
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+;
set<int>M[N+N];
queue<int>Q;
int q[N],yy[N],n,m,k;
void bfs()
{
while(!Q.empty())
{
int tot=,u=Q.front();
Q.pop();
q[]=u;
for(int i=; i<tot; i++)
{
int now=n-tot;
while(now>&&!Q.empty())
{
int v=Q.front();
Q.pop();
if(!M[q[i]].count(v)) q[tot++]=v;
else Q.push(v);
--now;
}
}
yy[k++]=tot;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=,u,v; i<m; i++)
cin>>u>>v,M[u].insert(v),M[v].insert(u);
for(int i=; i<=n; i++) Q.push(i);
bfs();
sort(yy,yy+k);
printf("%d\n",k);
for(int i=; i<k; i++)printf("%d ",yy[i]);
return ;
}
Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)的更多相关文章
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)C. Swap Adjacent Elements (思维,前缀和)
Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)C. Swap Adjacent Elements time limit per test 1 se ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2) 920E E. Connected Components?
题 OvO http://codeforces.com/contest/920/problem/E 解 模拟一遍…… 1.首先把所有数放到一个集合 s 中,并创建一个队列 que 2.然后每次随便取一 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2) G
G. List Of Integers time limit per test 5 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- [Codeforces]Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)
Water The Garden #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000") #include<stdio.h ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Connected Components? 图论
E. Connected Components? You are given an undirected graph consisting of n vertices and edges. Inste ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 72 (Rated for Div. 2)-D. Coloring Edges-拓扑排序
Educational Codeforces Round 72 (Rated for Div. 2)-D. Coloring Edges-拓扑排序 [Problem Description] 给你 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 60 (Rated for Div. 2) - C. Magic Ship
Problem Educational Codeforces Round 60 (Rated for Div. 2) - C. Magic Ship Time Limit: 2000 mSec P ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 60 (Rated for Div. 2) - D. Magic Gems(动态规划+矩阵快速幂)
Problem Educational Codeforces Round 60 (Rated for Div. 2) - D. Magic Gems Time Limit: 3000 mSec P ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 43 (Rated for Div. 2)
Educational Codeforces Round 43 (Rated for Div. 2) https://codeforces.com/contest/976 A #include< ...
随机推荐
- Jenkins系列——使用Dashboard View分类展示作业
1.目标 创建的作业多了,在一个视图中展示多有不便.因此需要使用 Dashboard View 将作业按照后缀进行分类展示. 如下图,可以按照后缀添加CODE,TEST和OTHER视图. 2.环境说明 ...
- ftp和sftp
一.ftp ftp是文件传输协议,ftp协议包括两部分,一个是ftp客户端,另一个是ftp服务器. 原理:一般情况下,当使用FTP服务的时候,我们都知道默认是21号端口,其实还有一个20号端口.FTP ...
- BZOJ 2851: 极限满月 虚树 or 树链的并
2851: 极限满月 Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MBSubmit: 170 Solved: 82[Submit][Status][Discuss] ...
- BZOJ 2725: [Violet 6]故乡的梦 最短路+线段树
2725: [Violet 6]故乡的梦 Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 678 Solved: 204[Submit][Status ...
- CF Gym 100463A (树状数组求逆序数)
题意:给你一个序列,和标准序列连线,求交点数. 题解:就是求逆序对个数,用树状数组优化就行了.具体过程就是按照顺序往树状数组了插点(根据点的大小),因为第i大的点应该排在第i位,插进去的时候他前面本该 ...
- iOS 微信和支付宝关于回调处理
在支付这一块,发现讲支付集成的比较多,但是关于支付后回调处理的不多见,(当时因为这个问题懵逼了好久)就自己总结一下, 1.支付宝回调 支付宝的回调想对来说比较简单一些,因为支付宝的回调就在调起支付宝的 ...
- SQLSTATE=42000 #42000
在使用PowerDesigner生成数据库表的时候遇到了这个问题. 原来是在填写属性的类型的时候, 少了两个括号, 造成了mysql数据类型错误 本来应该是varchar(50)的,写成了varcha ...
- java基础—流
一.JAVA流式输入/输出原理
- Linux下Jenkins与GitHub自动构建Node项目(Vue)
根据上篇文章<Linux下Jenkins与GitHub自动构建NetCore与部署>,我们知道了Jenkins的强大功能,自动构建,部署了一个NetCore的Web,让开发人员专注于开发, ...
- maven,gradle本地缓存位置
gradle: 配置系统环境变量GRADLE_USER_HOME即可,值为缓存位置. maven: 修改settings文件:maven的home路径下的conf文件夹下的settings.xml 对 ...
